1. Introduction
At the beginning of the last century, the response for outbreaks and epidemics of infectious diseases was linked to the mythical, magical, and religious conception of them [
1]. By the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th, the discoveries of microorganisms that cause specific diseases (tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, tetanus, pneumonia, meningitis, syphilis, and others) and the identification of vectors capable of transmitting diseases (the Anopheles mosquito for malaria) [
2] consolidated a new paradigm for the study of infectious diseases, their control and prevention [
3]. In addition, with the development of vaccines and the emergence of antimicrobial therapy during the first half of the 20th century, we were excited about the disappearance of infectious diseases [
4]. At least, that was the perception that high-income countries had during the 1960s and 1970s, especially inspired by the eradication of smallpox [
5] and which, in some way, motivated the theory of epidemiological transition [
6].
The experience of the eradication of smallpox related to the mobilization of resources in public health, the learning curve in decision-making and the international alignment around common health objectives, launched a new stage of discussion around setting goals for the eradication/elimination of infectious diseases. This new stage was mainly inspired on the goal of "Health for all by the year 2000" of the WHO [
7]. Thus, in 1993 the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published a list describing the potentially eradicable diseases, based on the recommendations resulting from the International Task Force for the Eradication of Diseases (ITFDE) [
8]. The aim of the ITFDE was to establish criteria to systematically assess the potential of eradication of other diseases after the Smallpox Eradication Program. The ITFDE defined eradication as “the reduction to zero of the incidence of a disease worldwide, as a result of deliberate efforts, obviating the need for additional control measures” [
8].
Based on the existence of highly effective control measures (vaccine against HBV and treatment against HCV), WHO, in 2016, outlined ambitious targets to achieve its global elimination by 2030, defined as a 90% reduction in new infections and a 65% reduction in mortality [
9]. "However, it is a silent epidemic because infected people do not present symptoms until the liver has already been damaged. That is why it is important for the countries to step up efforts to reach the goal of eliminating hepatitis as a public health problem in the Region by 2030," said Massimo Ghidinelli, chief of the HIV, Hepatitis, Tuberculosis, and Sexually Transmitted Infections unit at PAHO/WHO [
10].
Although the definition of eradication and elimination of an infectious disease is clear, the parameters to achieve it are associated with the estimation of the existing disease burden, its current dynamics, and probable future scenarios, given the effectiveness of the respective intervention controls. The Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) gathers disability and mortality data on the HBV and HCV infections, from 1990 to 2019 [
11]. GBD is the single largest and most detailed scientific effort ever conducted to quantify levels and trends in health. The GBD produces regular estimates of all-cause mortality, deaths by cause, years of life lost due to premature mortality (YLLs), years lived with disability (YLDs), and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) [
12].
In the present study, we assessed the trends of the global burden of viral hepatitis (B and C) disease for both sexes, ages, and countries grouped by Sociodemographic-Index (SDI), to evaluate the feasibility of achieving elimination targets by 2030.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design
We conducted an ecological study to describe trends in prevalence, incidence and mortality from HBV and HCV infections worldwide for 1990-2019. The Sociodemographic Index (SDI) regions (High, Medium-high, Medium, Medium, Medium-low and Low) measuring 195 countries and territories grouped according to the total fertility rate of those under 25, the years of education of those over 15 and the lag in the distribution of per capita income were also considered [
11].
2.2. Data
Data were taken from the GBD 2019, a publicly available resource online “
https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results/” by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington [
11]. The IHME estimated prevalence, incidence, and death (number, percent and rate) by cause, location, age, sex, year and annual rate of change, from 1990 to 2019. The rate are Age-standardized Prevalence Rates (ASPR), Age-standardized Incidence Rates (ASIR) and Age-standardized Mortality Rates (ASMR) for the analyzed period [
11].
For this study, the cause selected were identified as “Total burden related to hepatitis B” and “Total burden related to hepatitis C” for all sexes and all ages.
2.3. Analysis
Ratio percentage change of the ASIR, ASPR and ASMR for HBV and HCV were estimated dividing the correspondent value for HBV/HCV in order to describe the relative change.
Through Joinpoint regression analysis (segmented regression model) we identified significant changing points in trends of ASPR, ASIR and ASMR of viral hepatitis (HBV and HCV) from 1990 to 2019 for the analyzed period. This model can find and identify points where significant changes occur (breakpoints) where the dependent variable has changed significantly at different times.
For this study, we used the “Methodology for Characterizing Trends” of the National Cancer Institute of the United States [
13] that uses Joinpoint Regression Program, (Version 5.0.2. May, 2023) [
14]. The Joinpoint software uses statistical criteria to determine a) the fewest number of segments necessary to characterize a trend, b) where the segments begin and end; and c) the annual percent change (APC) for each segment (a linear trend on a log scale implies a constant APC) and the average annual percentage change (AAPC) [
13]. HBV and HCV incidence, prevalence and mortality trends were analyzed as follows: “changing less than or equal to 0.5% per year (-0.5 ≤ APC ≤ 0.5), and the APC was not statistically significant, we characterized it as stable; changing more than 0.5% per year (APC < -0.5 or APC > 0.5), and the APC was not statistically significant, we characterized it as non-significant change; changing with a statistically significant APC > 0, we characterized it as rising; and changing with a statistically significant APC < 0, we characterized it as falling” [
13].
3. Results
3.1. HBV and HCV infections prevalence and incidence.
In 2019, there were 439.5 million (95% [uncertainty interval] UI 384.2 – 500.1) people of all ages, living with HBV and HCV (326.2 million [95% UI 292.2 - 361,1] for HBV and 113.2 million [95% UI 92.0 – 139.0] for HCV), worldwide. The ASPR for HBV and HCV was 4,216.3 (3,776.3 – 4,667.2) and 1,463.3 (1,189.0 - 1,796.6) per 100,000 people, respectively. Total percentage change of the ASPR (2019/1990) was -31.4% and -12.8% for HBV and HCV, respectively. The rate ratio (HBV/HCV) was 2.5 in the period. The percentage change of the ASPR for HBV and HCV was highest in countries with middle SDI and lowest in countries with high SDI. For HCV the prevalence rate increased 11.2% in high SDI countries during the period (
Table 1,
Figure S1).
For 2019, the incident cases of HBV were 80.0 million (95% UI 63.9 – 98.2) and for HCV 5.5 million (95% UI 4.8 – 6.3), globally. The ASIR for HBV and HCV was 1,034.2 (827.1 – 1,270.3) and 71.3 (62.8 - 82.6) per 100 000 people, respectively. The total percentage change of the ASIR (2019/1990) was -34.1% and -16.8% for HBV and HCV, respectively. The rate ratio of the percentage change (HBV/HCV) was 2.04 in the period. The percentage of change of ASIR for HBV was highest in countries with middle SDI countries and lowest in countries with low SDI. For HCV, it was highest in countries with middle SDI and lowest in countries with high SDI; in these, the incidence rate increased 9.3% during the period (
Table 1,
Figure S2.).
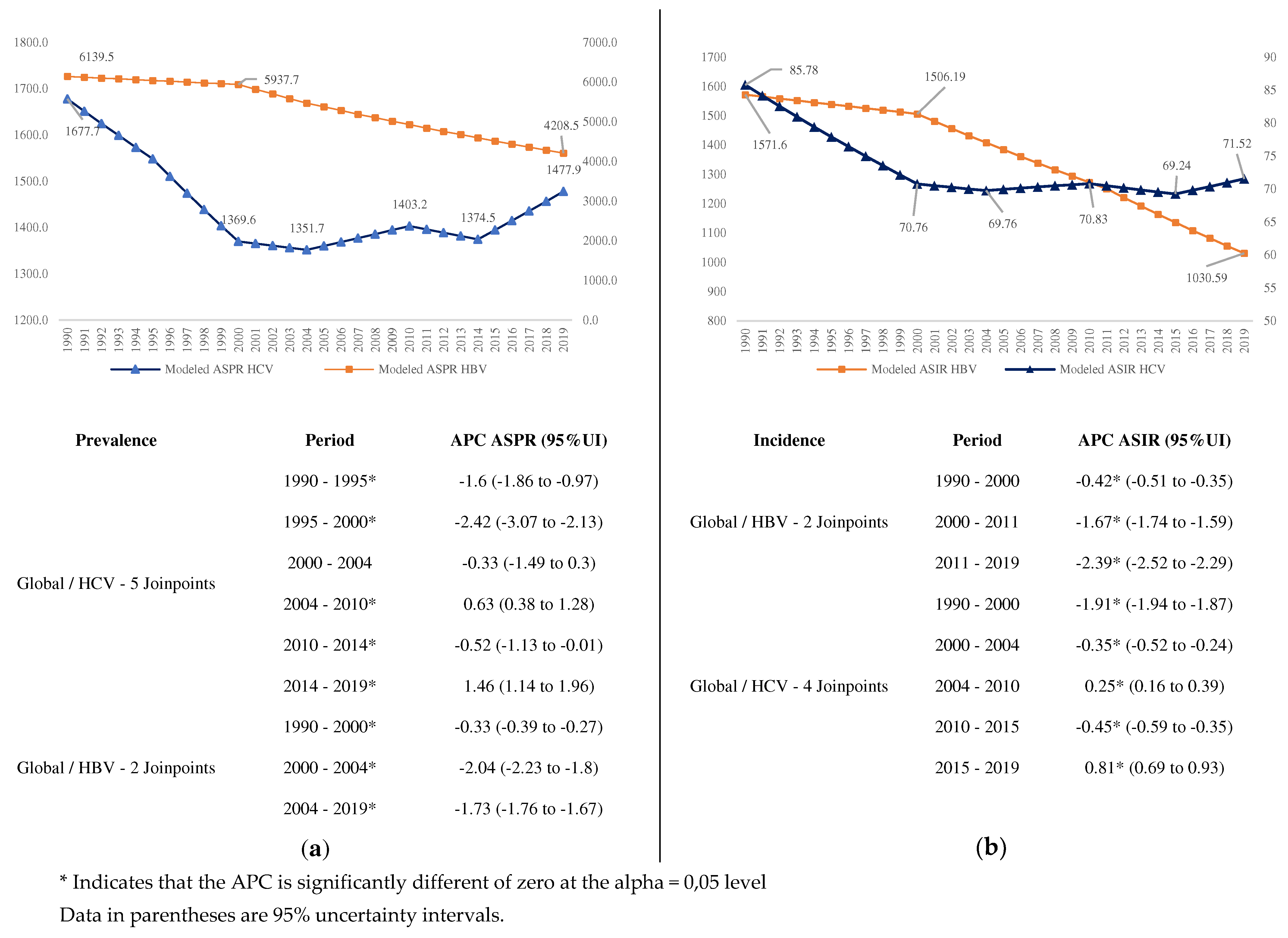
We observed a great decrease in the prevalence (
Figure 1a) and incidence (
Figure 1b) of HBV, starting in 2000, with significant changes in 2000 and 2004. For HCV there were five significant changes. Conversely, the prevalence and incidence of HCV, although it had a significant decrease until 2004, from this year onwards begins a period of increase, with an APC of 1.46% from 2014 to 2019 for prevalence, and 0.81% for incidence (
Figure 1).
The global AAPC for HBV (-1.3%) was 3.25 times that of HCV (-0.4%) during the period. These ratios were different by SDI countries groups. The highest ratio was in low-middle SDI (4.00) and the lowest in the Middle SDI Group (1.89). The highest AAPC for HBV by SDI groups occurred in middle SDI countries, and the lowest in high SDI countries, similar for HCV (
Table S1,
Figure 2).
3.1. HBV and HCV mortality
In 2019, occurred 1.09 million deaths for HBV and HCV (95% UI 0.96 – 1.23) in all ages and sexes worldwide; 555.4 thousand [95% UI 487.1 – 630.1] for HBV and 542.3 thousand [95% UI 476.7 – 608.8] for HCV. The ASMR per 100,000 persons was 7.18 (95% UI 6.30 – 8.14) and 7.01 (95% UI 6.16 - 7.87) for HBV and HCV, respectively.
The HBV and HCB total percentage change for the ASMR (2019/1990) was -26.7% and 10.0%, respectively. While ASMR for HBV decreased, for HCV increased during period. The percentage change in ASMR of HBV was highest in countries with high-middle SDI and lowest in countries with high SDI. For HCV, the percentage change in ASMR was highest in countries with High SDI (increase) and only in countries with low SDI decreased (
Table 2).
The
Table S2 shows the APC and AAPC of ASMR in HBV and HCV, for all ages and sexes from 1990 to 2019, for global trends as well as by SDI countries grouped.
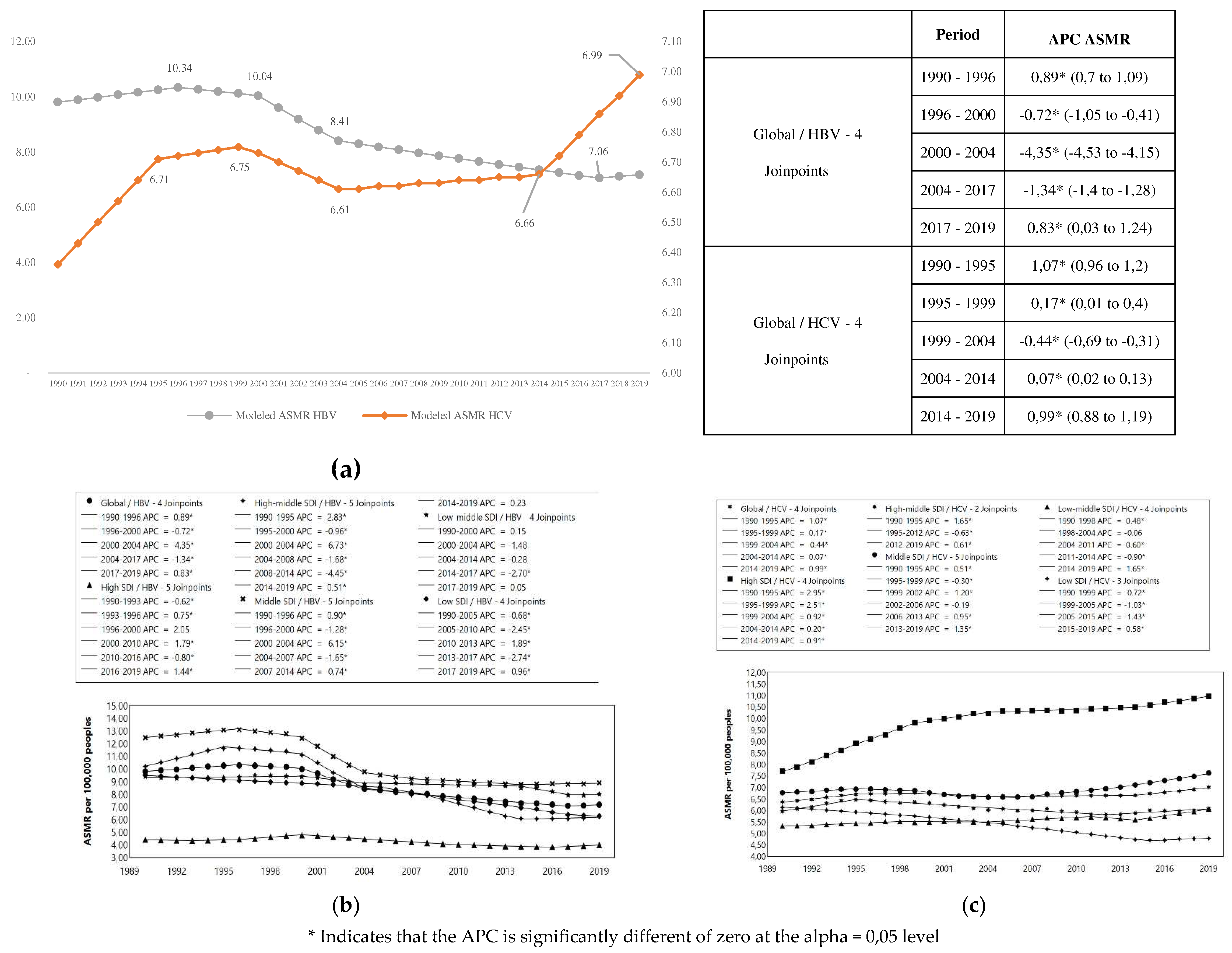
We observed a great decrease in the HBV mortality in high-middle and middle SDI countries, especially between 2000 to 2004 (APC= - 6.15) (
Figure 3a). On the other side, HCV mortality (
Figure 3b) increased for high SDI countries, especially between 1990 to 1999 (APC= 2.51-2.95) and decreased significantly for low SDI countries, between 1999 to 2015 (APC= -1.03 , - 1.43) (
Figure 3).
4. Discussion
Our analysis showed some encouraging results because incidence and prevalence of HBV and HCV have been decreasing around the world between 1990 and 2019. On the other hand, mortality have decreased for HBV but not for HCV, which is a bit disappointing. However, despite the advances there are still a long way forward to achieve the 2030 goal, a reduction of 90% in incidence and 65% for mortality for both infections. An important challenge is related to find a way to speed the yearly rate at which the decline is happening.
Our data and analysis have some limitations. They are based on data from the Global Burden of Disease repository curated by the Institute of Health Metrics at the University of Washington which have made huge efforts to improve the quality of the information. However, there are still major challenges for information quality including differences in the health coverage services between countries, quality and coverage of death certificate and accuracy of modelling strategies to fill the uncertainties on information between countries. Those aspects may influence the difference observed between developed and developing countries because part of the differences may be due to data quality rather than to diseases behaving in different ways [
15]. For instance, non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases (NAFLD) have been raising fast as an emergent cause of chronic liver disease especially in developing countries and it is likely that, for countries with weaker health care systems, a proportion of cases of NAFLD may be misclassified as chronic liver diseases due to viral hepatitis B or C [
16].
Most of the achievements for the reduction in Hepatitis B incidence, are due to the use of a highly effective vaccine early in childhood. In fact, some WHO regions like Europe (EURO) and The Americas & The Caribbean (PAHO) have achieved the goals of eliminating mother to child transmission [
17]. However, there are less advances for treatment and cure of the people that was infected before the vaccine was available which amount to an estimate of 300 million people. Current available treatments for Hepatitis B virus may stop virus replication but they cannot eliminate the virus from a carrier [
18,
19].
For hepatitis C control, there is a lack of a prophylactic measure and advances in prevention have been linked to improve screening efforts at blood banks which have reduced greatly the main source of infections for many populations. However, this measure alone is unlikely to eliminate Hepatitis C transmission since there is a residual risk of infection of 1 by 100,000 transfusions [
20]. Recently, there have been advances in discovering new antivirals that can eliminate the infection from the liver and have the potential to save lives and boost the decrease in incidence. However, high prices have deterred many low- and middle-income countries of introducing massive search and treatment for hepatitis C. WHO has estimated that it would be needed to invest about
$57 billion dollars to eliminate viral hepatitis from 67 countries [
21].
The European Union HCV Collaborators conducted a study assessing the prevalence of HCV in the EURO and the level of intervention required to achieve WHO targets for HCV elimination. Its final conclusion was that in despite its advanced healthcare infrastructure, the expansion of screening programmes and diagnosis should increase from 88,800 new cases annually in 2015 to 180,000 in 2025 to boost treatment for achieving the WHO targets [
22]. However, Wedemeyer H., et al., consider as of 2021, most countries are not on track to reach the 2030 HCV elimination targets set by the WHO. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in a decrease in HCV diagnoses and fewer direct-acting antiviral treatment initiations in 2020 [
23].
On the other side, Rockstroh JK. et al., consider that, except in a few countries (e.g. Egypt), elimination targets are endangered in the majority of the world—regardless of income level [
24] and state that this is largely because the greater burden of HCV infection is carried by marginalized populations of people who use drugs (PWUD) and people who are incarcerated, who are being left behind in HCV control efforts [
25]. According to data from Polaris observatory (
https://cdafound.org/polaris-regions-database/ ) Australia has detected more than 90% of HCV infected people and is on track to eliminate that virus. Most other continents and countries have detected less than 60% and low- and middle-income countries less than 30%.
The small yearly pace at which both hepatitis agents are reducing its incidence and mortality signals that it is unlikely that elimination goals can be met by 2030. For hepatitis B, the use of vaccines must be supplemented with other measures such as screening and treating pregnant HBsAg+ mothers to reduce the number of children infected at birth and identifying chronic carriers’ adults and treating them to reduce mortality. However, as in the case of treating hepatitis C, most countries cannot bear the costs of doing those actions or do not have in place the technical capacity to do that. On the other hand, hepatitis B vaccine effectiveness is reduced because there many countries who have not introduced the birth dose [
26,
27].
Although the elimination goals were reformulated [
28], the problems and barriers to their achievement persist, especially in low-income countries: a) Little technical capabilities to identify the population carrying the virus; b) Low access to treatment with direct-acting antivirals in people diagnosed; and c) High financial impact on health systems budgets. Thus, Hepatitis B and C elimination may be achieved only if novel mechanisms of financing the cost of antivirals are devised or a dramatic decrease on price can be negotiated with the industry.
5. Conclusion
The global HBV and HCV rates have fallen with different AAPC associated with the SDI. Despite the advances, there is still a long way forward to achieve the 2030 elimination goals. An important challenge is related to finding a way to speed up the yearly rate at which the decline is happening which may include to reduce the costs of hepatitis C antivirals and find better ways to implement population screening to find and treat Hepatitis C or B carriers.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Table S1: Global percent change of age-standardized prevalence and incidence of HBV and HCV, all age and both sex 1990 and 2019. Table S2: Annual percent change of ASMR of HBV and HCV, all age and both sex, global and in countries grouped by SDI. 1990 to 2019.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.A.G., N.A.Z. and F.D.R.; methodology, N.A.G., N.A.Z. and F.D.R.; formal analysis, N.A.G., N.A.Z. and F.D.R.; data curation, N.A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, N.A.G. and F.D.R..; writing—review and editing, N.A.G., N.A.Z. and F.D.R.; visualization, N.A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Andrews JM, Langmuir AD. The philosophy of disease eradication. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1963 Jan;53(1):1–6. [CrossRef]
- Bynum WF. Ronald Ross and the malaria-mosquito cycle. Parassitologia. 1999 Sep;41(1–3):49–52.
- OMS. Enfermedades transmitidas por vectores [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 May 27]. Available from: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/vector-borne-diseases.
- Alvis Guzman N, De la Hoz Restrepo F. Evaluación económica de vacunas. La experiencia en Colombia entre 1999 y 2018 [Internet]. Bogotá D.C.: Universidad Nacional de Colombia; 2023 [cited 2023 May 27]. Available from: https://www.libreriaunal.com/libro/evaluacion-economica-de-vacunas_37750.
- Brilliant LB, Hodakevic LN. Certification of smallpox eradication. Bull World Health Organ. 1978;56(5):722–33.
- Omran AR. The Epidemiologic Transition: A Theory of the Epidemiology of Population Change. Milbank Q. 2005 Dec;83(4):731–57.
- Mahler H. The Meaning of “Health for All by the Year 2000.” Am J Public Health. 2016 Jan;106(1):36–8.
- Recommendations of the International Task Force for Disease Eradication. MMWR Recomm Rep. 1993 Dec 31;42(RR-16):1–38.
- World Health Organization. Global health sector strategy on viral hepatitis 2016-2021. Towards ending viral hepatitis [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/246177.
- PAHO/WHO | Countries of the Americas take action to eliminate hepatitis [Internet]. Pan American Health Organization / World Health Organization. 2017 [cited 2023 Aug 18]. Available from: https://www3.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=13529:paises-americas-implementan-acciones-hacia-eliminacion-hepatitis&Itemid=0&lang=en#gsc.tab=0.
- Vos T, Lim SS, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abbasi M, Abbasifard M, et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet. 2020 Oct 17;396(10258):1204–22.
- Global Burden of Disease (GBD) [Internet]. [cited 2023 Aug 18]. Available from: https://www.healthdata.org/research-analysis/about-gbd.
- Methodology for Characterizing Trends | Cancer Trends Progress Report [Internet]. [cited 2023 Aug 17]. Available from: https://progressreport.cancer.gov/methodology.
- Joinpoint Regression Program, Version 5.0.2 - May 2023; Statistical Methodology and Applications Branch, Surveillance Research Program, National Cancer Institute [Internet]. [cited 2023 Aug 17]. Available from: https://surveillance.cancer.gov/joinpoint/.
- Zhang X, Zhang X, Liu M, Zhu L, He Z. Global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis and other chronic liver diseases due to alcohol use, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2019. BMC Gastroenterology. 2022 Nov 23;22(1):484. [CrossRef]
- Paik JM, Golabi P, Younossi Y, Mishra A, Younossi ZM. Changes in the Global Burden of Chronic Liver Diseases From 2012 to 2017: The Growing Impact of NAFLD. Hepatology. 2020 Nov;72(5):1605. [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Hincapié CY, Murad-Rivera R, Tohme RA, Ropero AM, Gómez B, Librado Cardona D, et al. Progress towards the elimination of hepatitis B in children in Colombia: A novel two-phase study approach. J Viral Hepat. 2022 Sep;29(9):737–47. [CrossRef]
- Chen DS. Toward elimination and eradication of hepatitis B. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Jan;25(1):19–25. [CrossRef]
- Nayagam S, Thursz M, Sicuri E, Conteh L, Wiktor S, Low-Beer D, et al. Requirements for global elimination of hepatitis B: a modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016 Dec;16(12):1399–408.
- van der Poel CL. Hepatitis C virus and blood transfusion: past and present risks. J Hepatol. 1999;31 Suppl 1:101–6.
- Cox AL, El-Sayed MH, Kao JH, Lazarus JV, Lemoine M, Lok AS, et al. Progress towards elimination goals for viral hepatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Sep;17(9):533–42. [CrossRef]
- European Union HCV Collaborators. Hepatitis C virus prevalence and level of intervention required to achieve the WHO targets for elimination in the European Union by 2030: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 May;2(5):325–36.
- Wedemeyer H, Tergast TL, Lazarus JV, Razavi H, Bakoyannis K, Baptista-Leite R, et al. Securing wider EU commitment to the elimination of hepatitis C virus. Liver Int. 2023 Feb;43(2):276–91. [CrossRef]
- Cui F, Blach S, Mingiedi CM, Gonzalez MA, Alaama AS, Mozalevskis A, et al. Global reporting of progress towards elimination of hepatitis B and hepatitis C. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;8(4):332–42. [CrossRef]
- Rockstroh JK, Swan T, Chang J, Elamouri F, Lloyd AR. The path to hepatitis C elimination: who are we leaving behind and why? J Int AIDS Soc. 2023 Jul;26(7):e26136.
- Hoz FDL, Choconta-Piraquive LA, Guzman NA. PIN85 GLOBAL COMPLIANCE WITH HEPATITIS B VACCINE BIRTH DOSE AND FACTORS RELATED TO TIMELY SCHEDULE. A LITERATURE REVIEW. Value in Health. 2019 May 1;22:S208. [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer A, Akmatov MK, Krause G. Hepatitis B vaccination timing: results from demographic health surveys in 47 countries. Bull World Health Organ. 2017 Mar 1;95(3):199-209G. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global health sector strategies on, respectively, HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections for the period 2022-2030 [Internet]. Available from: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/hq-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-library/full-final-who-ghss-hiv-vh-sti_1-june2022.pdf?sfvrsn=7c074b36_13.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).