1. Introduction
At the end of 2019, the first cases of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection were diagnosed. SARS-CoV-2 is a Betacoronavirus capable of causing a disease called COVID-19 (COronaVIrus Disease 19), mainly characterized by an influenza-like syndrome. Typical manifestations are fever, dry cough, and dyspnea; other symptoms include headache, dizziness, vomit and diarrhea. [
1,
2] However, SARS-CoV-2 infections may present in various forms, causing mildly symptomatic affections or even Acute Respiratory Distress Syndromes (ARDS), accompanied by a severe systemic inflammation, leading eventually to multiple organ failure (MOF). [
1] It appears that susceptibility to the infection and clinical manifestations severity are associated to patients’ age; typically, older people with comorbidities may develop severe symptomatic infection, eventually leading to hospitalization and even death, while younger subjects may develop mild forms or even asymptomatic infections. [
3,
4]
As for other Betacoronaviruses, human to human transmission happens through respiratory droplets. Median incubation time is four to six days before the onset of symptoms; during this period high viral loads have been identified in the host, or at the symptoms’ onset and during the first week of the disease, determining a high transmission potential even with mildly symptomatic infections. [
1,
3] This led to a rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 worldwide, causing more than 100,000 confirmed cases and over 4000 deaths by early 2020 [
5]. Therefore, on the 11th of March 2020, COVID-19 was declared a pandemic by the WHO Director-General [
5], launching a global effort to develop effective vaccines [
6].
In a short time, already in the course of 2020, various vaccines were developed to pursue and obtain an efficient SARS-CoV-2 prevention tool [
1]. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 (Comirnaty) Vaccine, an mRNA vaccine encoding for the full-length SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein (S), was the first SARS-CoV-2 vaccine approved by both Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in December 2020. At the end of the same month, vaccination campaign against SARS-CoV-2 started, immediately showing a good impact on severe illness.
Several studies demonstrated the immunogenicity of Comirnaty ® vaccine, showing sustained antibody response after vaccination. Originally, the primary vaccination schedule included injection of two doses of BNT162b2, 21 days apart. A 95% protection against COVID-19 has been claimed following administration of two doses of BNT162b2 [
7]. Despite these results, several people have been infected by SARS-CoV-2 after a second dose of BNT162b2, as demonstrated by positive nasopharyngeal swabs.
Most of the SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies (NtAbs) produced after SARS-CoV-2 infection target the spike (S) protein receptor-binding domain (RBD) [8-10]. RBD is a subdomain of SARS-CoV-2 S-protein which is exposed on the virus membrane and has an important role in facilitating viral entry and infection of the host cells [
9,
10]. SARS-CoV-2 has demonstrated the ability to evolve by accumulating mutations in the spike protein in order to escape the humoral response of the host: the rapid emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern (VOC) such as Alpha (B.1.1.7), Gamma (P.1), Delta (B.1.617.2) and Omicron (B.1.1.529) has caused large outbreaks also among previously infected and vaccinated populations [
11].
Since the early months of the pandemics, healthcare workers, have shown a remarkable risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and subsequent morbidity and mortality [
12,
13], higher than the general population, especially for those in the frontline, either using adequate personal protective equipment or not [
14]. This has led to prioritizing healthcare workers’ vaccination at the start of the anti-COVID immunization campaigns worldwide, alongside with elderly patients. [
15] Healthcare workers’ exposure has been shown related to a considerable, although declining, risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection throughout the year 2020 and during the early phases of the vaccination campaign in 2021. [
16]
Keeping these premises in mind, the aim of the present study is to identify factors that might have a role in SARS-CoV-2 infections in vaccinated healthcare workers (HCWs), by analyzing sera from different subjects’ groups.
With the objective of understanding why some vaccinated HCWs were infected, we compared vaccinated subjects’ and not vaccinated infected subjects’ sera and measured the neutralizing antibodies against Wild-Type SARS-CoV-2 and other variants by in vitro live virus neutralization assay.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population
We retrospectively analyzed differences in neutralizing antibodies response in HCWs of both sexes and aged between 18 and 70, working at the Policlinico University Hospital “P. Giaccone” of Palermo, whose sera were collected from October 2020 to October 2021 at the Microbiology and Virology Laboratory of the University Hospital.
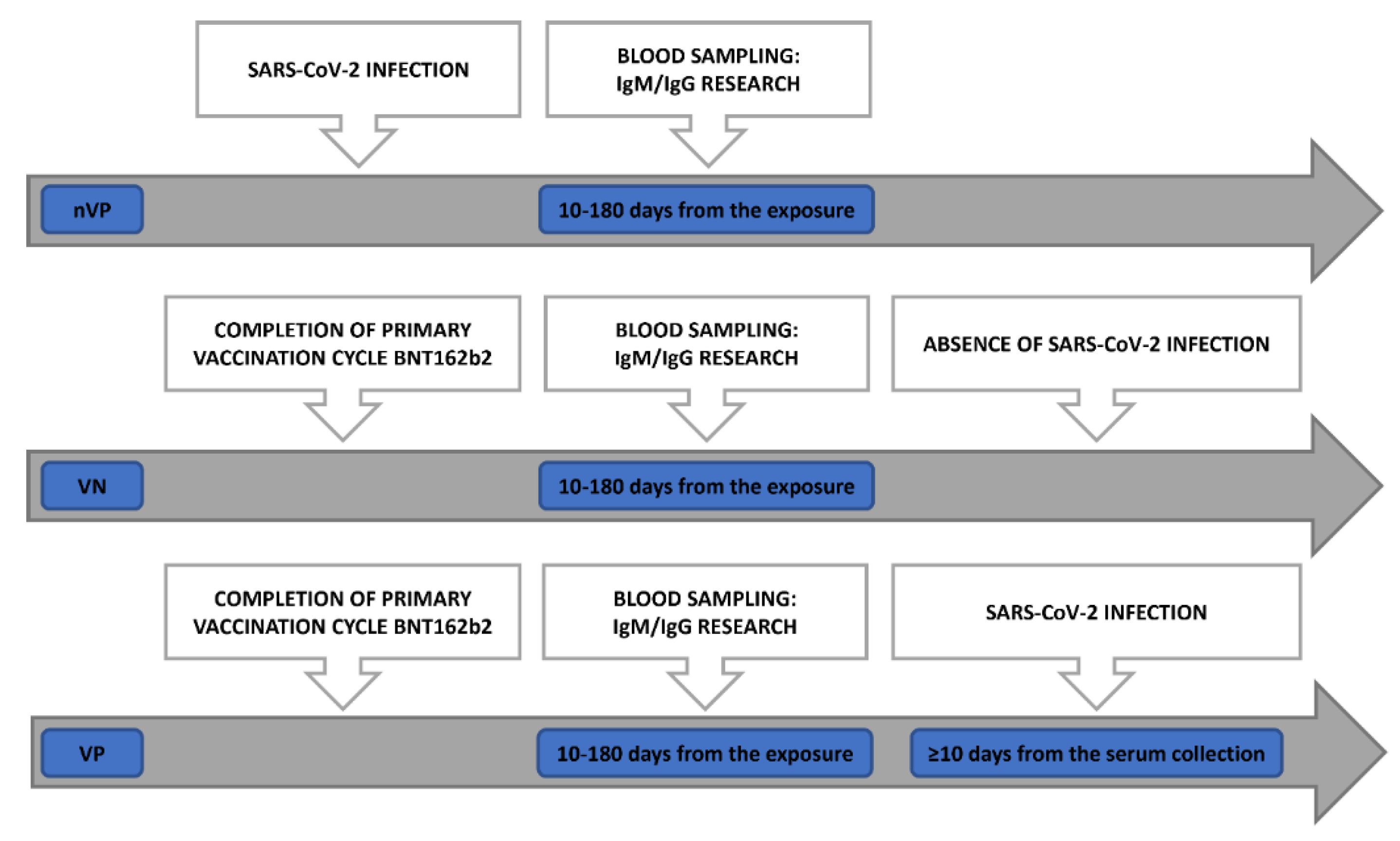
Our study population was divided into 3 cohorts of HCWs (
Figure 1):
Non-Vaccinated Positive (nVP) cohort: Unvaccinated subjects who were diagnosed positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection by molecular test on a nasopharyngeal swab (NPS) sample between August 2020 and March 2021, whose sera were collected 10 to 180 days after a positive test for COVID-19.
Vaccinated Positive (VP) cohort: Subjects who received 2 doses of BNT162b2, and were successively diagnosed positive for SARS-CoV-2 at RT-PCR molecular test on an NPS sample, whose sera were collected 10 to 180 days from administration of the second dose of vaccine, encompassing the humoral response peak and the decline of the humoral response [
17,
18], and at least 10 days before diagnosis of infection (“positivization”).
Vaccinated Non-positive (VN) cohort: Subjects who have received 2 doses of BNT162b2, without evidence of post-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection, with sera collected 10 to 180 days after the second vaccine dose administration.
Subjects included in the three different cohorts were matched by age (± 5 years), sex, and days (± 15) to blood collection from the administration of vaccine, for VN and VP group, or days (± 15) from blood collection to a positive COVID-19 test for nVP group. The date of COVID-19 positivity was retrieved from the national COVID-19 cases database, updated until February 2022.
2.2. Virus neutralization assay
We used a previously described in vitro live virus-neutralization assay to quantify neutralizing antibodies (NtAbs) [
19]. The Vero E6 cell line, cultured and maintained at 37 °C in MEM containing 10% FBS and antibiotics (100 U/mL of penicillin and 100 μg/mL of streptomycin) (Gibco, Life Technologies, USA), were used to isolate Wild-Type SARS-CoV-2 and its VOC (Alpha, Delta, Gamma, and Omicron variants) obtained from clinical samples. Isolation and live virus micro-neutralization assays were performed in a BioSafety Level (BSL)-3 laboratory. Genetic characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 strains were investigated by sequence analysis of spike protein before and after isolation in cell culture. Testing procedures of clinical specimens were carried out through strict observance of the WHO interim guidance [
20]. The titers of NtAbs were determined using separately cells infected with Wild-Type virus and the above-mentioned VOCs. The degree of cytopathic effect (CPE) was evaluated after 3 days of incubation at 37°C 5% CO2. NtAbs titers were defined as the reciprocal value of the sample dilutions (from 1:10 to 1:1280) showing a 50% protection from virus-induced cytopathic effect (ID50). Titers below 10 were reported as “negative”.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Categorical variables were summarized by frequency and relative frequencies (%), whereas continuous variables were shown as mean (standard deviation – SD) if normally distributed and median (interquartile range – IQR) for not normally distributed variables. Moreover, neutralizing antibody titers were summarized by geometric mean and geometric standard deviation (GSD), in accordance with the international scientific literature [
21]. To test for the normal distribution of continuous data, the Shapiro-Wilk test for normality was applied. To compare demographic data among the groups, Pearson’s Chi-squared test was used. Inter-group comparisons were assessed by using the Mann-Whitney U-test.
All statistical analyses were conducted using R for Statistical Computing (R version 4.2.1, Vienna, Austria) within the Rstudio interface (Rstudio, PBC, Boston, MA), and a p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant [
22,
23].
3. Results
The study population comprised 293 HCWs, of which 91 were in the nVP cohort, 102 in the VP cohort and 100 in the VN cohort. Their demographic characteristics are represented in
Table 1.
During the observation period, a few subjects enrolled in the VN cohort became SARS-CoV-2 positive and, therefore, they were moved to the VP cohort, resulting in a total number of 102 HCWs. Their presence did not lead to any statistically significant differences for sex and age between the three cohorts. We then replaced the missing subjects in the VN cohort with other HCWs with the same characteristics.
Female subjects were 56 (61.5%) in nVP cohort, 59 (57.8%) in VP cohort and 62 (62%) in VN cohort. Differences in sex distribution among the groups were not statistically significant. Also the median age (36 in nVP, 32 in VP and 33.5 in VN) and the median of days to blood collection from vaccination or the exposure to the infection (61 in nVP, 51 in VP, 57.5 in VN) showed no statistically significant difference between the cohorts.
Table 2 shows the general serological characteristics of the three population groups. In the nVP cohort, the geometric mean NtAbs titers range from 5.92 against Omicron variant to 24.11 against Alpha; in the VP cohort, it ranges from 10.50 against Omicron to 48.45 against Gamma; in the VN cohort, it ranges from 7.45 against Omicron to 60.90 against Alpha. Considerable proportions of the sera analyzed did not have detectable NtAbs against the Omicron variant: 76.92% in the nVP group, 42.16% in the VP group and 56% in the VN group.
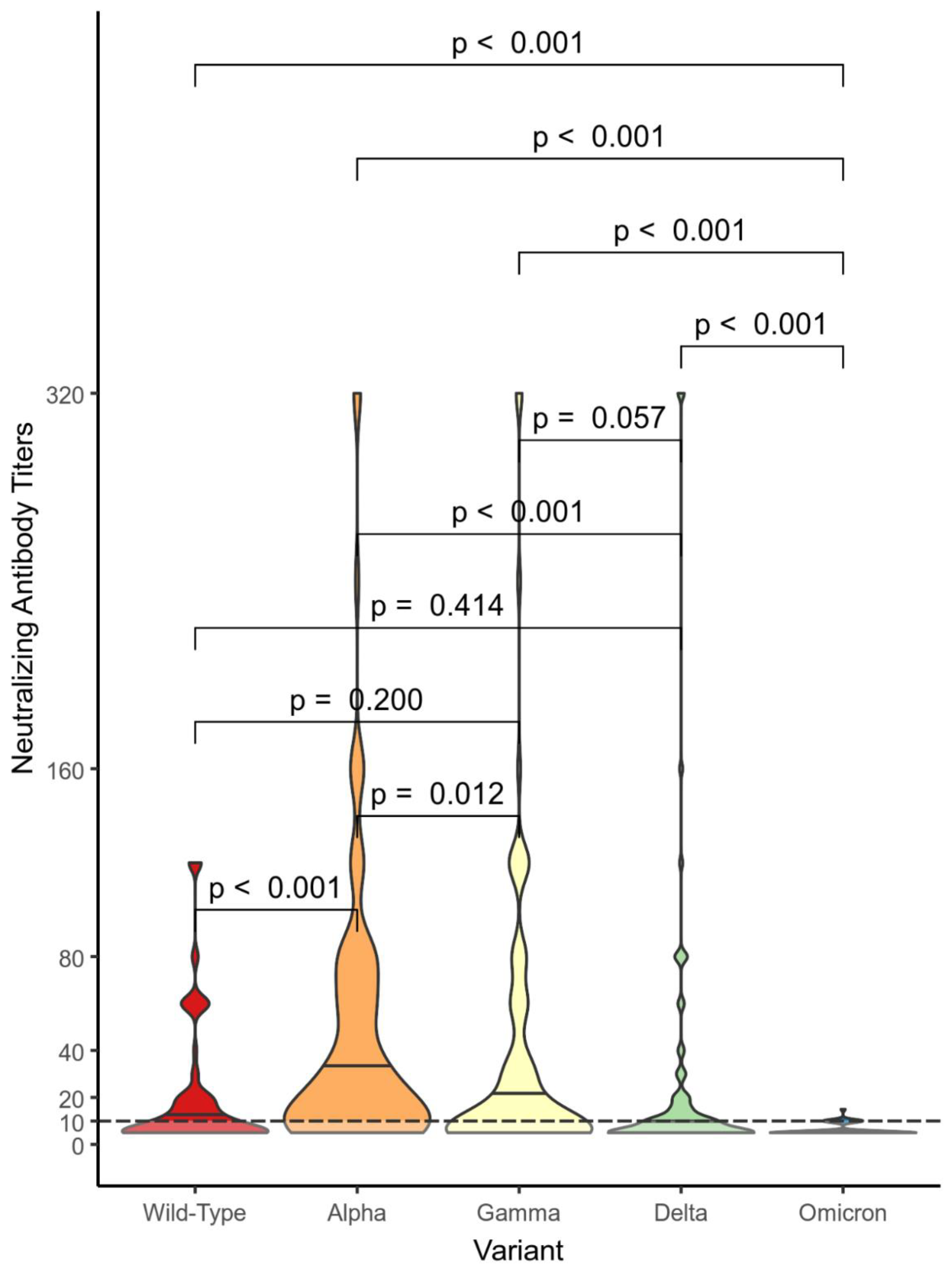
Figure 2,
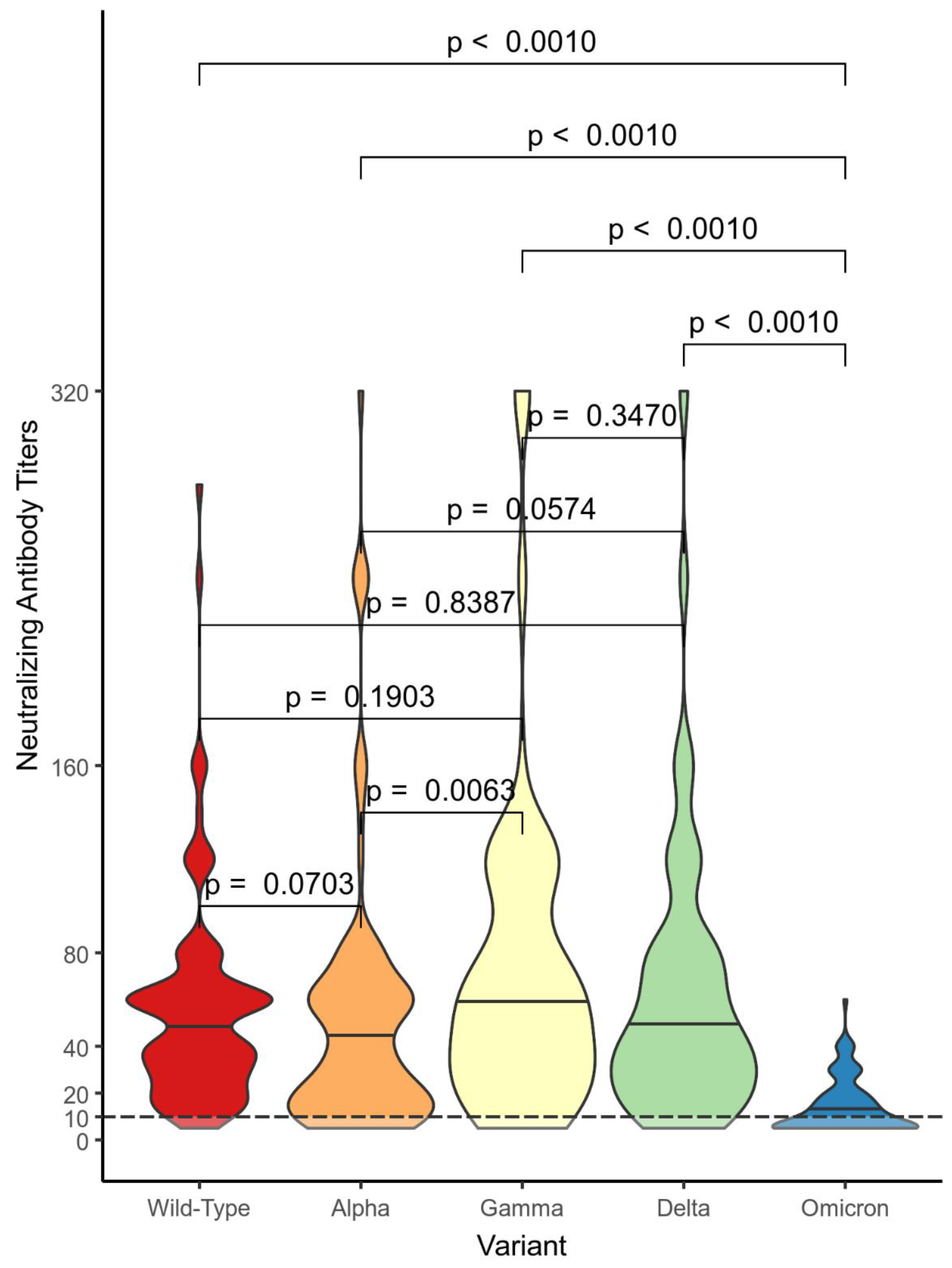
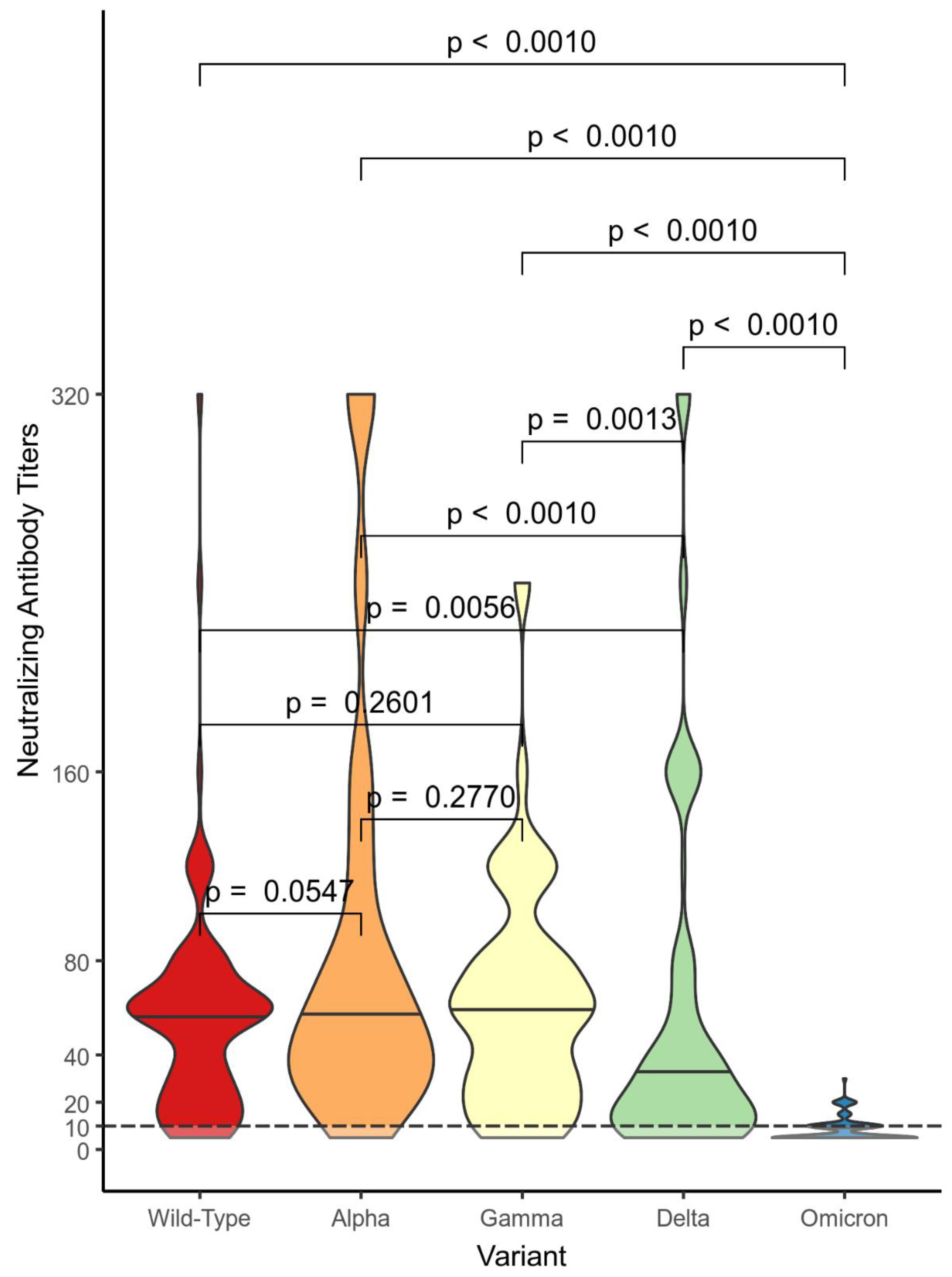
Figure 3 and
Figure 4 show violin plot graphs for each group (nVP –
Figure 2, VP –
Figure 3, VN –
Figure 4) representing the distributions of NtAbs titers against Wild-Type SARS-CoV-2 and VOCs. The subjects in the nVP cohort showed a wide range of NtAbs titers (0 to 320) against Alpha, Gamma, and Delta VOCs, a shorter range against the Wild-Type, while NtAbs against Omicron were almost undetectable (0 to 15). Subjects in the VP cohort showed the following distributions ranges of NtAbs against the VOCs: from 0 to 280 against the Wild-Type, from 0 to 320 against Alpha, Gamma, and Delta, and from 0 to 60 against Omicron. Subjects in the VN group had the following distributions ranges of NtAbs: from 0 to 320 against Wild-Type, Alpha and Delta, from 0 to 240 against Gamma, and from 0 to 40 against Omicron. The differences in NtAbs titers distributions against Omicron and against the other VOCs are statistically significant in all three groups.
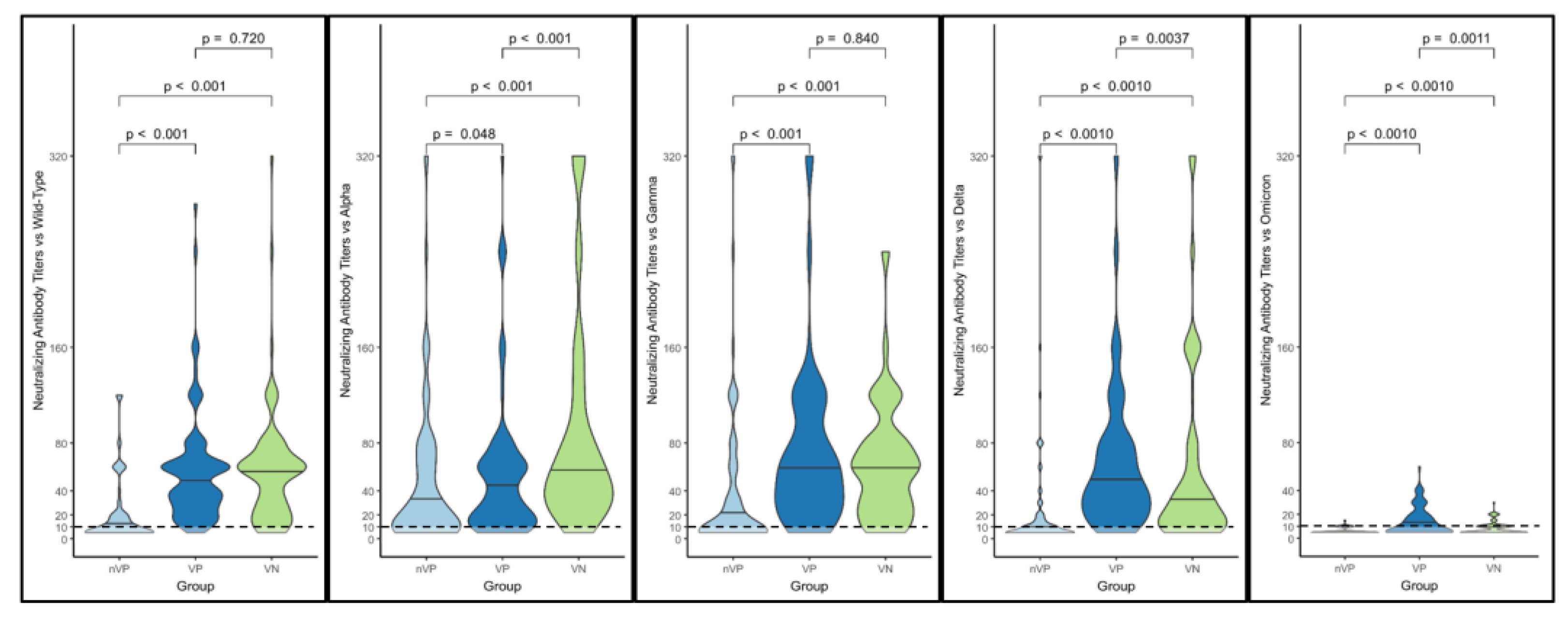
In
Figure 5, the violin plot graph describes the comparisons between distributions of NtAbs titers in each group against each different variant. Almost all differences in the NtAbs distributions for each variant are statistically significant.
4. Discussion
Our study aimed at evaluating the possible determinants of infection in subjects already immunized against SARS-CoV-2 either by a previous infection or by vaccination. HCWs were chosen as the target population of our study because they have been considered at high risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection, morbidity and mortality since the beginning of the pandemic spread [
12,
14]. For the same reason, they have been identified as a priority target group in the earliest phases of vaccination campaigns [
15]. In 2021 new variants of SARS-CoV-2 emerged and spread rapidly, with different infectivity and transmissibility patterns, leading first to a replacement of the Wild-Type SARS-CoV-2 and, then in turn becoming the predominant strain responsible for the subsequent “pandemic waves” [
19]. Therefore, with the aim of speculating on vaccine efficacy against future variants, we assessed the neutralizing efficacy of the immune response against the major SARS-CoV-2 VOCs, compared to the Wild-Type strain, whose spike protein mRNA was included in the vaccine [24-27].
The presence of specific NtAbs has been predictive of adequate protection from SARS-CoV-2 infection by both the Wild-Type and the VOCs, although a decline of neutralizing titers against VOCs has been described elsewhere [
28,
29]. Many studies have described the capacity of Wild-Type strain SARS-CoV-2 and other VOCs to escape the protective host immunity induced by both natural infection and vaccination [
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35]. Overall, the analysis of the HCWs sera showed a generally acceptable neutralizing potency, when compared to results available from previous literature [
28,
36].
In our study, subjects in the nVP cohort showed higher titers against the Alpha variant than against all other strains. The prevalence of Alpha-specific NtAbs was not surprising, as that variant predominantly circulated during the time period in which the nVP population was infected [
37], but the lack of protection from subsequent VOCs somewhat confirmed the escape ability gained by newer variants. On the other hand, vaccinated individuals developed comparable mean neutralizing responses to all VOCs.
As expected, a higher proportion of subjects who did not receive the vaccine did not produce measurable levels of NtAbs. A number of studies in the literature have described that Wild-Type SARS-CoV-2 strain and other variant strains may escape the host protective immunity induced by both natural infection and by vaccination [
31,
33,
34,
35].
In our study, the subjects in the nVP cohort showed higher NtAbs titers specifically against the Alpha variant than against the other strains, and significantly lower or no antibody production against the Omicron variant, somewhat confirming the escaping ability of this variant. The prevalence of Alpha-specific NtAbs might be attributable to the circulation of that variant during part of the time range in which the nVP population had been infected. An increasing incidence of infections by the Alpha VOC, although never dominating, has characterized a wave of COVID cases during the last weeks of 2020 and the first months of 2021 in Sicily [
37], and this might explain our results. Such hypothesis can only be presumed but not confirmed due to unavailability of genotyping on the biological samples.
However, in our study neutralizing response against different viral strains was encouraging in general, all the groups showed wide ranges of NtAbs titers against the Wild-Type and the VOCs, except against the Omicron strain. Antibodies against the latter were significantly lower in all groups, and a remarkable number of subjects didn’t have detectable levels of NtAbs against the Omicron strain. This result aligns with previous studies describing considerably reduced humoral response against the Omicron strain and almost no vaccine effectiveness against symptomatic disease after two doses of BNT162b2 [
38]. Omicron sub-variants have generally higher immune escape ability than other SARS-CoV-2 VOCs [
34,
39], even though the earlier Omicron sub-variants (BA.1 and BA.2) appeared to have stronger binding affinities than other VOCs [
39]. The Omicron variant is characterized by great antigenic variability due to the selection of 37 mutations in the spike protein, the main immunogenic protein of the virus and capable of inducing the production of neutralizing antibodies [
40,
41]. However, significant protection against Omicron has been shown at least within a short time after booster dose, but initial elevation of the NtAbs titers was followed by a remarkable decline over time [
38,
42,
43]. These results raise concerns about the potential protective efficacy of antibodies against Omicron over time [
44,
45], justifying the need for periodic administration of booster doses and production of vaccines based on newly emerging variants. This has been furtherly confirmed by a recent literature review, analysing several studies which implied how booster doses administration increased Nt Abs production and conferred a stronger protection against severe COVID-19 [
46].
The analysis of the HCWs sera collected in this study showed a generally acceptable neutralizing potency, confirming the results of several studies that focused on the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection and/or COVID-19 vaccination [
19,
30]. However, a significantly lower neutralizing response following natural infection was recorded in the unvaccinated group (nVP) compared to the vaccinated HCWs, once again confirming the importance of promoting these professionals’ immunization, keeping in mind that their role exposes them to a higher risk of infection than the general population and to becoming a potential vehicle for virus transmission virus to subjects with comorbidities and a weaker immune system.
It is worth noting that, since our study involved a sample of HCWs, being more exposed to infectious agents, these results might not be fully applicable to the general population. On the other hand, since fewer and fewer healthcare workers have remained unvaccinated, also due to the mandatory vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 for such professionals, approved in Italy as an emergency decree on April 1, 2021, further enrollment in the nVP cohort will be more and more difficult.
It has been estimated that higher titers are required for protection from severe infection than the ones required to protect from any symptomatic infection and mild/moderate symptomatic infection [
28]. Unfortunately, it was not possible to collect information on the clinical status of the infected participants both in the nVP and VP group, limiting our capability to correlate humoral immunity with development of symptomatic infection. Lastly, another limitation of our study was not to examine other immune responses (e.g., innate, or cellular immunity) which are commonly involved in contrasting viral infections and elicited by COVID vaccination [
18], preventing from assessing any potential correlation between the different types of immune responses.
Despite this, it is critical to underline that these data underscore the need of promoting COVID-19 vaccination on a routine basis. This is due to the emergence of novel VOCs, as well as evidence indicating that antibody protection conferred by vaccinations based on SARS-CoV-2 variations genetically distant from the circulating version is insufficient. Recent advancements have resulted in the approval of a vaccine formulation based on mRNAs encoding the SARS-CoV-2 VOC XBB.1.5 Spike protein [
47]; this Omicron sub-lineage has been shown to resist immune response induced by one of the latest vaccines, based on both Wild-type and Omicron BA.4/BA.5 [
47,
48]. Based on these findings and a plethora of additional information, it is the role of professionals working in public health to educate the general population about the benefits of having SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations in the following months, and to maintain an active surveillance system to detect the emergence of new VOCs, evaluate the risks for the community and be prepared to contrast the undesired spread of the virus. This is aimed at preventing an increase in the number of patients suffering from respiratory diseases caused by SARS-CoV-2 infections.
5. Conclusions
The results of the present study offer supplemental evidence to confirm antibodies protection against the predominant SARS-CoV-2 VOCs, in both unvaccinated and vaccinated subjects. However, the humoral response of people infected and unvaccinated appeared to be less adequate to contrast different variants of SARS-CoV-2. Therefore, future constant research might be accompanied by investigation of the clinical features of SARS-CoV-2 infection in immunized subjects. These findings confirm the need to promote booster vaccination for both previously infected and vaccinated people. The procedures illustrated in this paper could be applied to evaluation of the several vaccine platforms available and developed in the future, and their immunizing potential. Moreover, the low immunity against Omicron variants elicited by both previous infection and vaccination pushes to continue monitoring VOCs circulation, to detect newly emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and contrast their spread with proper public health measures.
Author Contributions
“Conceptualization, P.I., A.C., M.G.V., G.C. and G.M.G.; methodology, E.A., D.F, S.D., F.C; formal analysis, D.G and E.A..; investigation, D.F., S.D., P.I. and V.P.; data curation, E.A.; writing—original draft preparation, V.P.; writing—review and editing, P.I, V.P., D.F and G.L.; visualization, D.G.; supervision, G.M.G..; project administration, P.I.; funding acquisition, P.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee “Palermo 1” (protocol code 08/2021 and date of approval 15/09/2021).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bakhiet, M.; Taurin, S. SARS-CoV-2: Targeted Managements and Vaccine Development. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 58, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu H, Chan JF, Yuen TT, Shuai H, Yuan S, Wang Y, Hu B, Yip CC, Tsang JO, Huang X, Chai Y, Yang D, Hou Y, Chik KK, Zhang X, Fung AY, Tsoi HW, Cai JP, Chan WM, Ip JD, Chu AW, Zhou J, Lung DC, Kok KH, To KK, Tsang OT, Chan KH, Yuen KY. Comparative tropism, replication kinetics, and cell damage profiling of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV with implications for clinical manifestations, transmissibility, and laboratory studies of COVID-19: an observational study. Lancet Microbe. 2020 May;1(1):e14-e23. [CrossRef]
- Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P, Shi ZL. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021 Mar;19(3):141-154. [CrossRef]
- Lu X, Zhang L, Du H, Zhang J, Li YY, Qu J, Zhang W, Wang Y, Bao S, Li Y, Wu C, Liu H, Liu D, Shao J, Peng X, Yang Y, Liu Z, Xiang Y, Zhang F, Silva RM, Pinkerton KE, Shen K, Xiao H, Xu S, Wong GWK; Chinese Pediatric Novel Coronavirus Study Team. SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 23;382(17):1663-1665. [CrossRef]
- WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19–- 11 March 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/Director-General/Speeches/Detail/Who-Director-General-s-Opening-Remarks-at-the-Media-Briefing-on-Covid-19---11-March-2020 (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Jackson, L.A.; Anderson, E.J.; Rouphael, N.G.; Roberts, P.C.; Makhene, M.; Coler, R.N.; McCullough, M.P.; Chappell, J.D.; Denison, M.R.; Stevens, L.J.; et al. An MRNA Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 — Preliminary Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1920–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 MRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Su, B.; Guo, X.; Sun, W.; Deng, Y.; Bao, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, C.; et al. Potent Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Identified by High-Throughput Single-Cell Sequencing of Convalescent Patients’ B Cells. Cell 2020, 182, 73–84.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, P.J.M.; Caniels, T.G.; van der Straten, K.; Snitselaar, J.L.; Aldon, Y.; Bangaru, S.; Torres, J.L.; Okba, N.M.A.; Claireaux, M.; Kerster, G.; et al. Potent Neutralizing Antibodies from COVID-19 Patients Define Multiple Targets of Vulnerability. Science 2020, 369, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C.; Adams, A.C.; Hufford, M.M.; de la Torre, I.; Winthrop, K.; Gottlieb, R.L. Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies for Treatment of COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.W.X.; Chia, T.; Young, B.E. SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern and Vaccine Escape, from Alpha to Omicron and Beyond. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2022, 16, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amnesty Analysis Reveals over 7,000 Health Workers Have Died from COVID-19 [Website]. London: Amnesty International; 3 September 2020. Available online: https://www.amnesty.org.uk/press-releases/More-7000-Health-Worker-Deaths-Covid-19-Globally-Uk-Deaths-Third-Highest (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Gholami M, Khamis AH, Ho SB. Response to”"RE: COVID-19 and healthcare workers: A systematic review and meta-analysis”". Int J Infect Dis. 2021 May;106:140-141. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Drew, D.A.; Graham, M.S.; Joshi, A.D.; Guo, C.-G.; Ma, W.; Mehta, R.S.; Warner, E.T.; Sikavi, D.R.; Lo, C.-H.; et al. Risk of COVID-19 among Front-Line Health-Care Workers and the General Community: A Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e475–e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO)–-WHO SAGE ROADMAP FOR PRIORITIZING USES OF COVID-19 VACCINES IN THE CONTEXT OF LIMITED SUPPLY. An Approach to Inform Planning and Subsequent Recommendations Based upon Epidemiologic Setting and Vaccine Supply Scenarios, 13 November 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/Docs/Default-Source/Immunization/Sage/Covid/Sage-Prioritization-Roadmap-Covid19-Vaccines.Pdf?Status=Temp&sfvrsn=bf227443_2 (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Gholami M, Fawad I, Shadan S, Rowaiee R, Ghanem H, Khamis AH and Ho SB (2023) The COVID-19 Pandemic and Health and Care Workers: Findings From a Systematic Review and MetaAnalysis (2020–2021). Int J Public Health 68:1605421. [CrossRef]
- Grupel, D.; Gazit, S.; Schreiber, L.; Nadler, V.; Wolf, T.; Lazar, R.; Supino-Rosin, L.; Perez, G.; Peretz, A.; Ben Tov, A.; et al. Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Anti-S IgG after BNT162b2 Vaccination. Vaccine 2021, 39, 5337–5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sheboul, S.A.; Brown, B.; Shboul, Y.; Fricke, I.; Imarogbe, C.; Alzoubi, K.H. An Immunological Review of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccine Serology: Innate and Adaptive Responses to MRNA, Adenovirus, Inactivated and Protein Subunit Vaccines. Vaccines 2022, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonura, F.; De Grazia, S.; Bonura, C.; Sanfilippo, G.L.; Giammanco, G.M.; Amodio, E.; Ferraro, D. Differing Kinetics of Anti-Spike Protein IgGs and Neutralizing Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 after Comirnaty (BNT162b2) Immunization. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 3987–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Laboratory Biosafety Guidance Related to Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Interim Guidance, 28 January 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/Publications/i/Item/WHO-WPE-GIH-2021.1 (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Reverberi, R. The Statistical Analysis of Immunohaematological Data. Blood Transfus. 2008. [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2021. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- rStudio Team (2020). rStudio: Integrated Development for R. rStudio, PBC, Boston, MA. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/; (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Istituto Superiore Di Sanità (ISS)–- Prevalenza e Distribuzione Delle Varianti Del Virus SARS-CoV-2 Di Interesse per La Sanità Pubblica in Italia. Rapporto 19 Maggio 2021. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/Coronavirus/Pdf/Sars-Cov-2-Monitoraggio-Varianti-Rapporti-Periodici-19-Maggio-2021.Pdf; (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Istituto Superiore Di Sanità (ISS)–- Prevalenza e Distribuzione Delle Varianti Del Virus SARS-CoV-2 Di Interesse per La Sanità Pubblica in Italia. Rapporto n. 2 Dell’11 Giugno 2021. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/Coronavirus/Pdf/Sars-Cov-2-Monitoraggio-Varianti-Rapporti-Periodici-11-Giugno-2021.Pdf; (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Istituto Superiore Di Sanità (ISS)–- Prevalenza e Distribuzione Delle Varianti Di SARS-CoV-2 Di Interesse per La Sanità Pubblica in Italia. Rapporto n. 11 Del 15 Ottobre 2021. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/Coronavirus/Pdf/Sars-Cov-2-Monitoraggio-Varianti-Rapporti-Periodici-15-Ottobre-2021.Pdf; (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Istituto Superiore Di Sanità (ISS)–- Prevalenza e Distribuzione Delle Varianti Di SARS-CoV-2 Di Interesse per La Sanità Pubblica in Italia Rapporto n. 15 Del 10 Dicembre 2021. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/Coronavirus/Pdf/Sars-Cov-2-Monitoraggio-Varianti-Rapporti-Periodici-10-Dicembre-2021.Pdf; (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing Antibody Levels Are Highly Predictive of Immune Protection from Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cromer, D.; Steain, M.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Khoury, D.S.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralising Antibody Titres as Predictors of Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Variants and the Impact of Boosting: A Meta-Analysis. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e52–e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, D.; Saunders, N.; Maes, P.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; Bolland, W.-H.; Porrot, F.; Staropoli, I.; Lemoine, F.; et al. Considerable Escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to Antibody Neutralization. Nature 2022, 602, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Antibody Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Variants B. 1.351 and B.1.1.7. Nature 2021, 593, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCallum, M.; Bassi, J.; De Marco, A.; Chen, A.; Walls, A.C.; Di Iulio, J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Navarro, M.-J.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Saliba, C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Immune Evasion by the B. 1.427/B.1.429 Variant of Concern. Science 2021, 373, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, R. Host Protective Immunity against Severe Acute Respiratory Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and the COVID-19 Vaccine-Induced Immunity against SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants. Viruses 2022, 14, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotaki, R.; Adachi, Y.; Moriyama, S.; Onodera, T.; Fukushi, S.; Nagakura, T.; Tonouchi, K.; Terahara, K.; Sun, L.; Takano, T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron-Neutralizing Memory B Cells Are Elicited by Two Doses of BNT162b2 MRNA Vaccine. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabn8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Azman, A.S.; Sun, R.; Lu, W.; Zheng, N.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Q.; Deng, X.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Neutralizing Antibodies Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Variants Induced by Natural Infection or Vaccination: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Wang, J.J.; Selva, K.J.; Reynaldi, A.; Tan, H.-X.; Lee, W.S.; Wragg, K.M.; Kelly, H.G.; Esterbauer, R.; et al. Evolution of Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 in Mild-Moderate COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, E.; Genovese, D.; Fallucca, A.; Ferro, P.; Sparacia, B.; D’Azzo, L.; Fertitta, A.; Maida, C.M.; Vitale, F. Clinical Severity in Different Waves of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Sicily: A Model of Smith’s “Law of Declining Virulence” from Real-World Data. Viruses 2022, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreño, J.M.; Alshammary, H.; Tcheou, J.; Singh, G.; Raskin, A.J.; Kawabata, H.; Sominsky, L.A.; Clark, J.J.; Adelsberg, D.C.; Bielak, D.A.; et al. Activity of Convalescent and Vaccine Serum against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron. Nature 2022, 602, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, K.; Zhu, X.; Yan, J.; Xu, P.; Hu, L.; Bai, C. A Systematic Study on the Binding Affinity of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein to Antibodies. AIMS Microbiol. 2022, 8, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.E.; Zhang, X.; Case, J.B.; Winkler, E.S.; Liu, Y.; VanBlargan, L.A.; Liu, J.; Errico, J.M.; Xie, X.; Suryadevara, N.; et al. Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Variants to Neutralization by Monoclonal and Serum-Derived Polyclonal Antibodies. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Tian, M.; Huang, M.; Liu, S.; Xie, Y.; Han, P.; Bai, C.; Han, P.; Zheng, A.; et al. Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Mutations Stabilize Spike up-RBD Conformation and Lead to a Non-RBM-Binding Monoclonal Antibody Escape. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alidjinou, E.K.; Demaret, J.; Corroyer-Simovic, B.; Vuotto, F.; Miczek, S.; Labreuche, J.; Goffard, A.; Trauet, J.; Lupau, D.; Dendooven, A.; et al. Serum Neutralization of SARS Coronavirus 2 Omicron Sublineages BA. 1 and BA.2 and Cellular Immune Responses 3 Months after Booster Vaccination. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 258.e1–258.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, N.; Stowe, J.; Kirsebom, F.; Toffa, S.; Rickeard, T.; Gallagher, E.; Gower, C.; Kall, M.; Groves, N.; O’Connell, A.-M.; et al. Covid-19 Vaccine Effectiveness against the Omicron (B. 1.1.529) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1532–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusvarghi, S.; Pollett, S.D.; Neerukonda, S.N.; Wang, W.; Wang, R.; Vassell, R.; Epsi, N.J.; Fries, A.C.; Agan, B.K.; Lindholm, D.A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Neutralization by Therapeutic Antibodies, Convalescent 177 Sera, and Post-MRNA Vaccine Booster. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron Escapes the Majority of Existing SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenchula S, Karunakaran P, Sharma S, Chavan M. Current evidence on efficacy of COVID-19 booster dose vaccination against the Omicron variant: a systematic review. J Med Virol. 2022;94:2969-2976. [CrossRef]
- He C, Alu A, Lei H, et al. A recombinant spike-XBB.1.5 protein vaccine induces broad-spectrum immune responses against XBB.1.5-included Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2. MedComm. 2023;4:e263. [CrossRef]
- Link-Gelles R, Ciesla AA, Roper LE, Scobie HM, Ali AR, Miller JD, Wiegand RE, Accorsi EK, Verani JR, Shang N, Derado G, Britton A, Smith ZR, Fleming-Dutra KE. Early Estimates of Bivalent mRNA Booster Dose Vaccine Effectiveness in Preventing Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection Attributable to Omicron BA.5- and XBB/XBB.1.5-Related Sublineages Among Immunocompetent Adults - Increasing Community Access to Testing Program, United States, December 2022-January 2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023 Feb 3;72(5):119-124. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).