1. Summary
This study collected 29 nasopharyngeal swab samples from patients undergoing PCR testing for respiratory pathogens at Advanta Genetics (Tyler, TX, USA) between January 2022 and June 2022. Nucleic acids, DNA and RNA were extracted separately using Zymo research reagents and following the protocol in the Explify Respiratory Pathogen ID /AMR Panel User Guide. T7 bacteriophage DNA was added to each sample to determine the absolute concentration of the target copies. Next-generation metagenomic sequencing (mNGS) libraries were prepared using the Illumina®/IDbyDNA Respiratory Pathogen ID /AMR Panel (RPIP) protocol[
1].
The data in this study represents a comprehensive metagenomic analysis of acute upper respiratory infections (URIs), offering comparative insights for researchers and clinicians in respiratory medicine, infectious diseases, epidemiology, and public health. The dataset provides unique precision in identifying URI-related pathogens. It stratifies identified organisms based on their potential to induce lower respiratory infections, presenting new avenues for microbiological diagnostics and treatment[
1]. The study illustrates the multifaceted benefits of this dataset, encompassing comprehensive microbiota characterization, identification of uncharacterized microorganisms, implications for respiratory medicine, infectious diseases, epidemiology, and public health, and its integration potential with other omics datasets. Accordingly, the dataset promises advancements in microbiological diagnostics [
2].
This dataset of URI microbiota offers several clinical benefits that aid in understanding the microbial communities present in the upper respiratory tract. The data provides detailed information on the prevalence, abundance, and diversity of known microbial species, accurately identifying microbes, and shedding light on the etiology and pathogenesis of URIs and their trafficking potential[
3]. Furthermore, the dataset's ability to discern mixed infections involving multiple species is instrumental in addressing polymicrobial pathogenesis. Enabling the detection and differentiation of these mixed infections helps clinicians tailor treatment strategies to manage complex respiratory disease effectively[
4]. The data also offers a snapshot into a better understanding of microbial dysbiosis in microbial communities, aiding in the understanding of how shifts in the microbiota might contribute to infections and related conditions and help scientists and epidemiologists study the prevalence, distribution, and evolution of pathogens causing URIs. Consequently, this information can also aid in monitoring outbreaks and tracking the emergence of new strains[
5].
The metagenomics component of the dataset enables the detection and comprehensive characterization of previously uncharacterized or unculturable microorganisms and provides a potential avenue for biomarker discovery. Microbiota profiling through mNGS can potentially reveal specific microbial signatures or biomarkers associated with different URIs. The discovery of novel microbial species or strains can expand our knowledge of respiratory infections and potentially lead to the development of new diagnostic tools or therapeutic interventions[
6].
This study augments the microbial context of URIs, enriching respiratory disease research. The dataset unveils complex host-microbe interplays, exposing potential pathogenesis, epidemiology, and therapeutic possibilities not readily available by conventional laboratory techniques. Supplementary advantages of the metagenomics data are that it allows clinicians and researchers to identify previously uncultivable or fastidious pathogens, enabling the characterization of dysbiosis, which has been implicated in respiratory diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma[
7]. Furthermore, the dataset illuminates host-microbe interactions, enhancing understanding of immune responses and disease mechanisms. It unravels microbial factors and pathways pivotal for disease, potentially guiding innovative therapeutic strategies. Manipulating these factors might lead to developing novel therapeutic approaches, such as targeting specific virulence factors or modulating dysbiotic microbial populations in many pulmonary diseases[
8].
The data affords epidemiologists and public health experts to gain better insights into URIs epidemiology and transmission patterns. Microbiota composition and lower respiratory trafficking potential data inform surveillance and outbreak investigations. Furthermore, metagenomics-based microbiota characterization offers valuable insights into the distribution and prevalence of specific pathogens across cultures, populations, and geographic domains. This contributes to epidemiological studies that assess patterns of infection spread, potential outbreaks, and transmission dynamics. Such URI data represents a paradigm shift in respiratory disease research and epidemiological investigation and can help guide public health interventions and the development of targeted preventive strategies[
9].
Overall, this dataset's insights into acute URI microbiota contribute to respiratory research, diagnosis, and treatment domains. Integration with omics datasets augments its potential, propelling optimization and advancements in microbiological laboratory workflows and clinical diagnostics[
9]. This work paves the way for a deeper comprehension of URI-related complexities, underscoring the collaborative efforts of respiratory medicine, infectious diseases, epidemiology, and public health.
2. Data Description
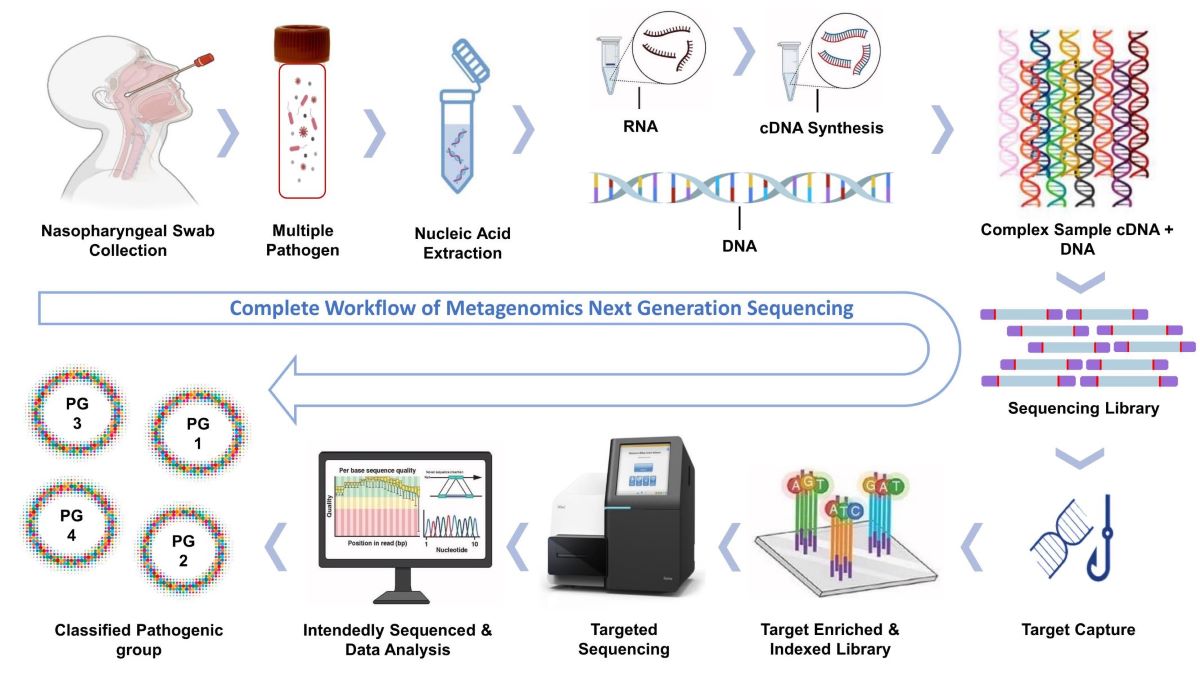
This study used a hybridization-capture-based mNGS workflow to detect an additional 249 microorganisms, comprising 23 viruses, 174 bacteria, and 52 fungi, from clinical samples. The Illumina®/IDbyDNA Respiratory Pathogen ID/AMR Panel (RPIP) was deployed to sequence 29 clinical samples. Raw fastq files were analyzed and interpreted by deciding the cut-off values with the following parameter-
2.1 Samples with less than 0.5 million reads after sequencing were excluded from further analysis. Specific criteria were employed for microorganism detection in clinical sample results: >40% target coverage, a median depth of 1X, and RPKM > 10 in the mNGS assay to be considered positive.
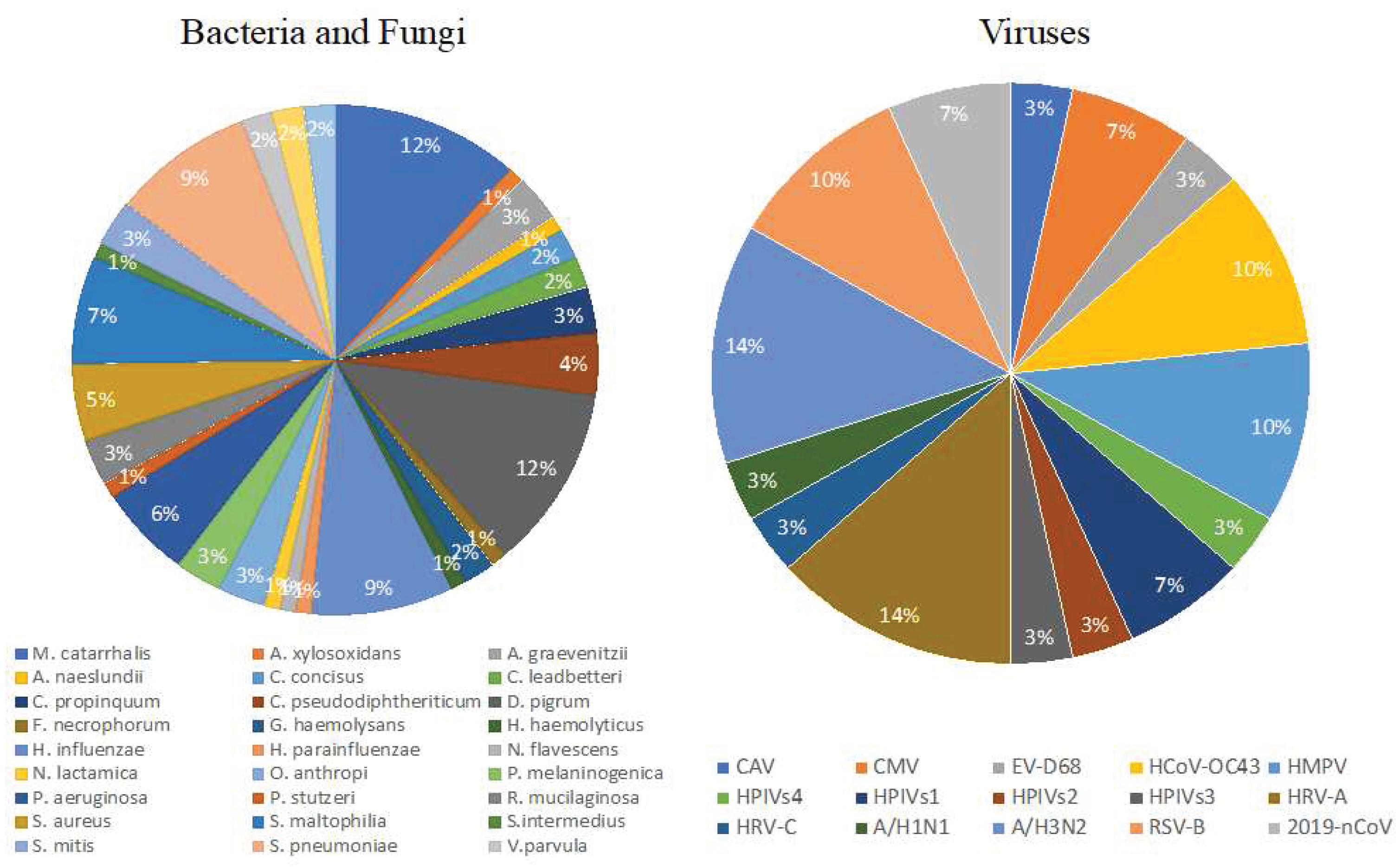
2.2 The mNGS results were then analyzed and the microorganisms were categorized based on their potential to cause infection. The mNGS panel identified 27 bacteria, 2 fungi, and 15 viruses across the 29 samples. The percentage of identified pathogens is shown in
Figure 1.
2.3 The positive microorganisms were further classified into three phenotypic groups based on their infectivity potential: 14/44 (31%) microorganisms were grouped as part of the normal flora, colonizers, or contaminants (phenotypic group 1); 15/44 (34%) microorganisms were grouped as frequently associated with respiratory disease (phenotypic group 2); and 15/44 (34%) microorganisms were grouped as pathogenic for respiratory disease (phenotypic group 3) (Supplementary Table).
3. Methods
This study collected 29 nasopharyngeal swab samples from patients undergoing PCR testing for respiratory pathogens at Advanta Genetics (Tyler, TX, USA) between January 2022 and June 2022. Nucleic acids, DNA and RNA were extracted separately using Zymo research reagents and following the protocol in the Explify Respiratory Pathogen ID /AMR Panel User Guide. The RNA was then reverse-transcribed into cDNA and combined with DNA in equal volumes. T7 bacteriophage DNA was added to each sample to determine the absolute concentration of the target copies. Next-generation metagenomic sequencing (mNGS) libraries were constructed using DNA tagmentation and adapter ligation with an Illumina® RNA Prep with an enrichment kit (Cat# 20040537). The microbial content of the libraries was enriched by hybridization with RPIP probes for 2 hours, followed by amplification and cleanup using AMPure beads (Cat# A63881). For quality control, two NATtrolTM Respiratory Panel 2.1 (RP2.1) Controls (ZeptoMetrix, Cat# NATRPC2.1-BIO) and a blank viral transport medium (VTM) from Criterion Chemistries in Pelham, AL, USA, were included as positive and negative controls, respectively, with each batch of library preparation and sequencing. Final libraries were quantified, then pooled to an equimolar concentration and normalized to 1 nM concentration. The library pool was denatured, neutralized, and further diluted to a loading concentration of 2 pM. The dual-indexed paired-end sequencing with a 75 bp read length was performed using a high-output flow cell (150 cycles) on an Illumina MiniSeq® instrument. Raw fastq files were generated by de-multiplexing, which were further analyzed using the IDbyDNA Explify® Platform (v1.0.1) software, which detects many pathogens and generates the pathogen abundance and clinical significance report. The software generated a report that quantitatively identified viruses, bacteria, and fungi, including AMR markers, in each sample. Microorganisms were categorized into phenotypic groups based on their potential pathogenic status. Target detection accuracy in clinical samples was determined by comparing the results to known microorganisms identified in positive controls.
Dataset
The raw genome sequencing data of Illumina MiniSeq were submitted to NCBI- Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database in FASTQ format with BioSample: SAMN36465186 to SAMN36465214 (29), under BioProject PRJNA995059. Direct URL to data:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA995059.
Dataset License
license under which the dataset is made available CC-BY
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Supplementary Table: sample-wise detected organism and list of respiratory pathogens covered in ID/AMR Panel (RPIP).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and editing, Rob E. Carpenter; Methodology and Project administration, Sadia Almas; Data curation, Writing - Original Draft & editing, Vaibhav K. Tamrakar; Data curation and Formal analysis, Anuradha Singh and Aditya Sharma; Conceptualization, Supervision and Writing, Rahul Sharma.
Funding
This research received no specific grant from public, commercial, or not-for-profit funding agencies.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This research used de-identified residual samples, and the study was exempted by the Institutional Review Board (IRB).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was not applicable due to research conducted on de-identified samples.
Data Availability Statement
The sample-specific fastq files are submitted to the NCBI as Sequence Read Archive (SRA) Data identification number: PRJNA995059. Direct URL to data:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA995059 and mNGS-run BLC files and demultiplexing barcode information are available upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
Not Applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Almas, S., et al., Deciphering Microbiota of Acute Upper Respiratory Infections: A Comparative Analysis of PCR and mNGS Methods for Lower Respiratory Trafficking Potential. Adv Respir Med, 2023. 91(1): p. 49-65. [CrossRef]
- d'Humières, C., et al., The Potential Role of Clinical Metagenomics in Infectious Diseases: Therapeutic Perspectives. Drugs, 2021. 81(13): p. 1453-1466. [CrossRef]
- Gaston, D.C., et al., Evaluation of Metagenomic and Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Workflows for Detection of Respiratory Pathogens from Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Specimens. J Clin Microbiol, 2022. 60(7): p. e0052622. [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z., et al., Metagenomics next-generation sequencing tests take the stage in the diagnosis of lower respiratory tract infections. J Adv Res, 2022. 38: p. 201-212. [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, R.E., et al., SARS-CoV-2 Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) data from clinical isolates from the East Texas Region of the United States. Data Brief, 2023. 49: p. 109312.
- Alnimr, A., Antimicrobial Resistance in Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: Predictive Microbiology and Evidence-Based Therapy. Infect Dis Ther, 2023. 12(6): p. 1527-1552. [CrossRef]
- Tiew, P.Y., O.W. Meldrum, and S.H. Chotirmall, Applying Next-Generation Sequencing and Multi-Omics in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int J Mol Sci, 2023. 24(3). [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, S.A., J.E. McGinniss, and R.G. Collman, The lung microbiome: progress and promise. J Clin Invest, 2021. 131(15). [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, R.E., et al., Confirming Multiplex RT-qPCR Use in COVID-19 with Next-Generation Sequencing: Strategies for Epidemiological Advantage. Glob Health Epidemiol Genom, 2022. 2022: p. 2270965.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).