1. Introduction
Eye tracking is an experimental method of recording eye motion and gaze orientation across time and specific tasks and is a common method for observing the allocation of visual attention camp [
1]. The eyes are constantly moving to focus and explore the environment performing different movements varying in range and speed, such as fixation, saccades and pursuit, implicating central and peripheral integration.
During fixation, the eyes are stable on a visual target, but since the fovea is small, the eyes need to move frequently to acquire high-quality information. Fixations are relatively short (180-330 milliseconds) but they might vary in length depending on different factors, such as the nature of the visual stimuli, the task’s purpose and complexity, and the skill and attention of the individual [
2]. Even during a fixation, when perception appears stable, the eyes continue to move, with tremors, drifts, and microsaccades [
3] [
4].
On the other hand, saccades can be described as ballistic movements of the eye from one fixation to the next. During saccades, visual input is suppressed, so when the eyes are making a saccade the subject is effectively blind [
5] [
6] [
7]. Saccades velocity and duration are a direct function of the distance travelled [
8]. Saccade measurement has become a key tool in many research fields, as analysis of saccadic function is used to understand cognitive and visual processes [
9] [
10] and in neurological examination and diagnosis [
11] [
12] [
13].
Other important eye movements are smooth pursuit (following a moving visual target) and vergence (bringing the eyes together or apart as a visual target moves closer or further from the participant). The pupil diameter and the optokinetic response do not depend on voluntary control. The former is modulated by the antagonism of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems, the latter is a combination of slow phase and fast phase eye movements: the subject tracks a moving object (pursuit movement), which then moves out of the field of vision, and the eyes move back to the original position (saccadic movement)[
14]. The eye re-orientation can also be induced in response to head motion. In otoneurological practice, the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) has great importance, allowing the eye to maintain a stable retinal image during head movements thanks to the vestibular activations. When it is reduced in function it might cause dizziness and/or oscillopsia [
15].
The eye tracking technology has enhanced applications in a wide array of domains, including measurement of advertising efficacy, instrumentation to enhance reading, automotive safety, pilot training, accessibility interfaces, and providing objective indicators of cognitive, psychiatric and neurological states of individuals [
16]. Abnormal eyes movements can be found indeed in patients with neurodegenerative disorders and their interpretation can be helpful for early diagnosis. Ba and al. demonstrated that patients with Parkinson’s disease have worse stereopsis, with a higher number of fixations and bigger saccade amplitude, suggesting fixation stabilization difficulties [
17]. A meta-analysis performed by Opwonya and al. revealed that prosaccade and antisaccade latencies and frequency of antisaccade errors show significant alterations for both mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s disease dementia (ADD) [
18].
In the past 20 years, the research has developed several methods to track eye movements. Different devices for eye-tracking have been proposed based on different technologies, for example, electro-oculography, infrared camera IR-cam, video-oculography and search coil: to date, the search coil technique is the gold standard in terms of speed and precision, however, its performance is achieved at the expense of a high degree of invasivity [
19].
This paper aims to present preliminary results obtained with a new kind of device that can produce detailed information on both eye and head movement using an array of magnetoresistive detectors fixed on the patient’s head. This prototypic device provides high-rate measurements of the magnetic field produced by a small magnet inserted in a contact lens. The potential of the proposed technique, as well as advantages and disadvantages are here discussed, particularly in what concerns precision of the eye movement reconstruction, invasivity and tolerability for the patient, cost, and completeness of the information that can be extracted.
Similarly to the search-coil technique, our device uses magnetic signals to determine the eye orientation, but the working principle is completely different in the two cases. In fact, the search coil technique is based on the application of a time-dependent field produced by large size external sources and on its detection by means of a (passive) coil inserted in a contact lens; the signal is generated due to the Faraday induction phenomenon. In contrast, our device is based on a small magnet inserted in the contact lens that (actively) produces a magnetostatic field, which is then measured by sensors located in the eye proximity. In this case signal is detected thanks to magnetoresistive effect.
2. Materials and Methods
The tracker operating principle is based on measuring the magnetic field in several positions in proximity of the eye. This field is made by the superposition of an environmental term (the Earth field) and an artificial term, which is generated by a small magnet inserted in a contact lens, tailored to the subject’s cornea curvature.
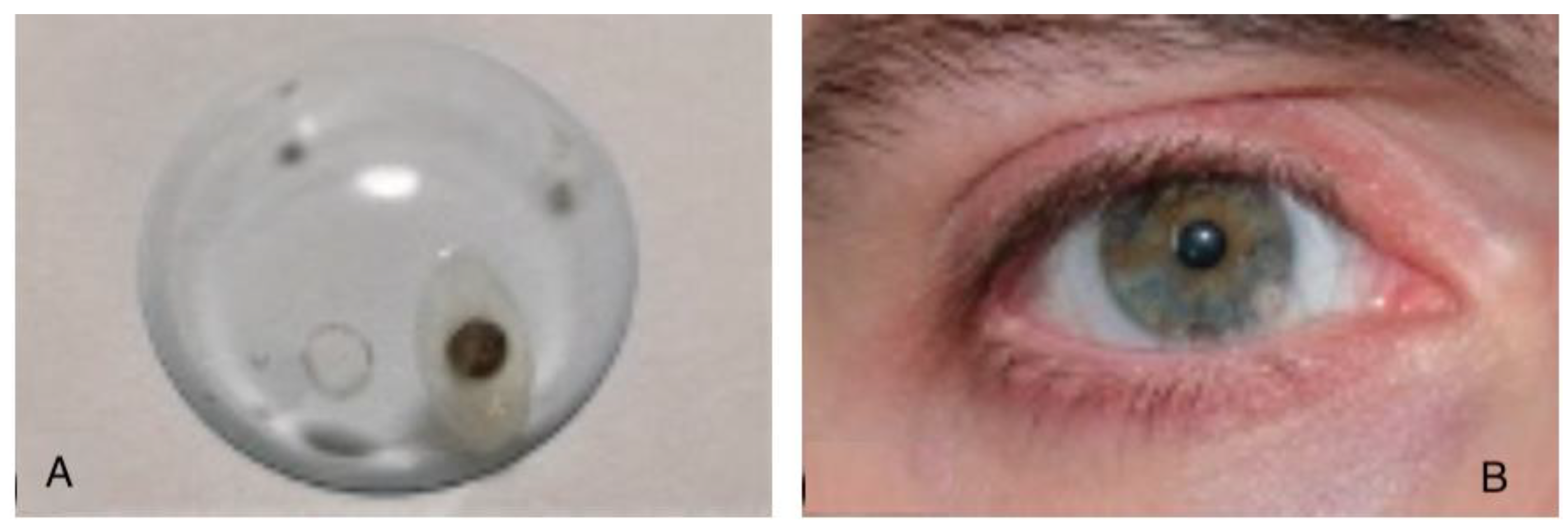
The magnetic source is a coated small disk (0.5 mm in thickness, 2 mm in diameter) in Neodymium-Iron-Boron (Nd-Fe-B) alloy (a state-of-the art material for maximum magnetization level) and it is implanted in a rigid scleral lens, some millimeters away from the optical axis, to not obstruct the line of sight. It is axially magnetized, and in this first implementation it is inserted tangentially to the lens, which means the magnetic dipole is nearly (but not perfectly) aligned with the gaze direction (
Figure 1).
The Earth magnetic field is homogeneous and it has a typical intensity of about 30 microTesla, while the artificial field generated by the magnet is inherently inhomogeneous and is measured with different intensities and orientations by the sensors that are variously located with respect to the magnet. The size of the magnet and the typical distance from the sensors are selected in such way to make the also this inhomogeneous field in the tens of microTesla level. A superposition with similar intensities is a condition that facilitates an accurate determination of both the Earth field (whose components in the sensor reference frame vary with the orientation of the sensor array and hence of the patient head) and of the inhomogeneous one (which varies when the eye orientation changes with respect to the sensor frame).
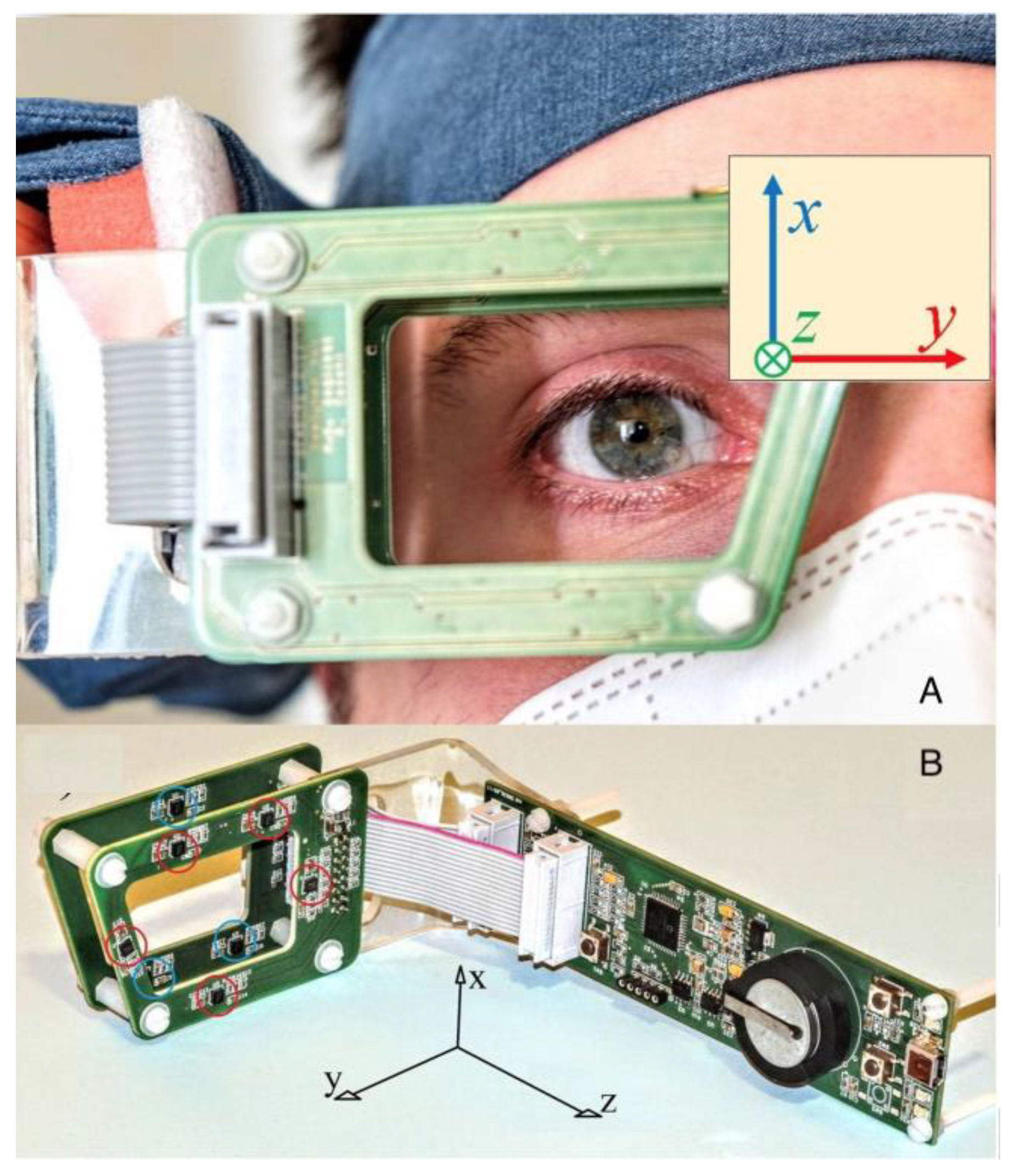
The sensors are placed on a rigid frame (sensor frame, SF) so that their relative positions are known. The SF size is of the order of a few centimetres and is shaped to negligibly hinder the sight (size and shape are similar to common goggles). The SF holds eight vectorial sensors: each sensor measures three components of the magnetic field: each measurement provides 3x8=24 values that correspond to the three components of the magnetic field in 8 different positions around the eye (
Figure 2).
For each measurement, a numeric method (the best fit procedure) is applied to convert those 24 data points into useful information. The latter is made of 9 data that correspond to three three-dimensional vectors, namely the position of the magnet with respect to the SF, the orientation of the magnet with respect to the SF, and the orientation of the SF relative to the Earth field. The numerical procedure runs on an ordinary personal computer (PC) and is fast enough to provide a real-time output, even if the acquisition is performed at the maximum rate (100 Samples/second, for the current implementation).
The first two vectors can be used to infer the eye orientation relative to the SF (and to the patient’s head, which is rigidly linked to the SF), and the third vector allows to infer the orientation of the SF (i.e. of the patients head) relative to the Earth field (the latter use is quite similar to what is commonly done with compasses). In synthesis, the numerical analysis enables simultaneous evaluation of the gaze and head orientation, because it allows distinguishing (and use advantageously) both the Earth and the magnet contributions to the measured fields.
The magnetic sensors used in this instrumentation are highly integrated and advanced devices. They are based on magnetoresistive devices, which are also solid-state and surpass Hall sensors for measurements in the range of tens of micro-tesla [
21]. Nevertheless, they are low-cost devices thanks to the lucky circumstance of their mass production, which is due to their wide application in popular electronics (e.g. to include compasses in smartphones, drones, etc.). They output digitized data at a high rate (over 100 samples/second). A second lucky circumstance is that the speed of currently available personal computers is sufficient to perform the required numerical analysis at the same rate, as to enable a real-time data output [
20] [
22] [
23] [
24].
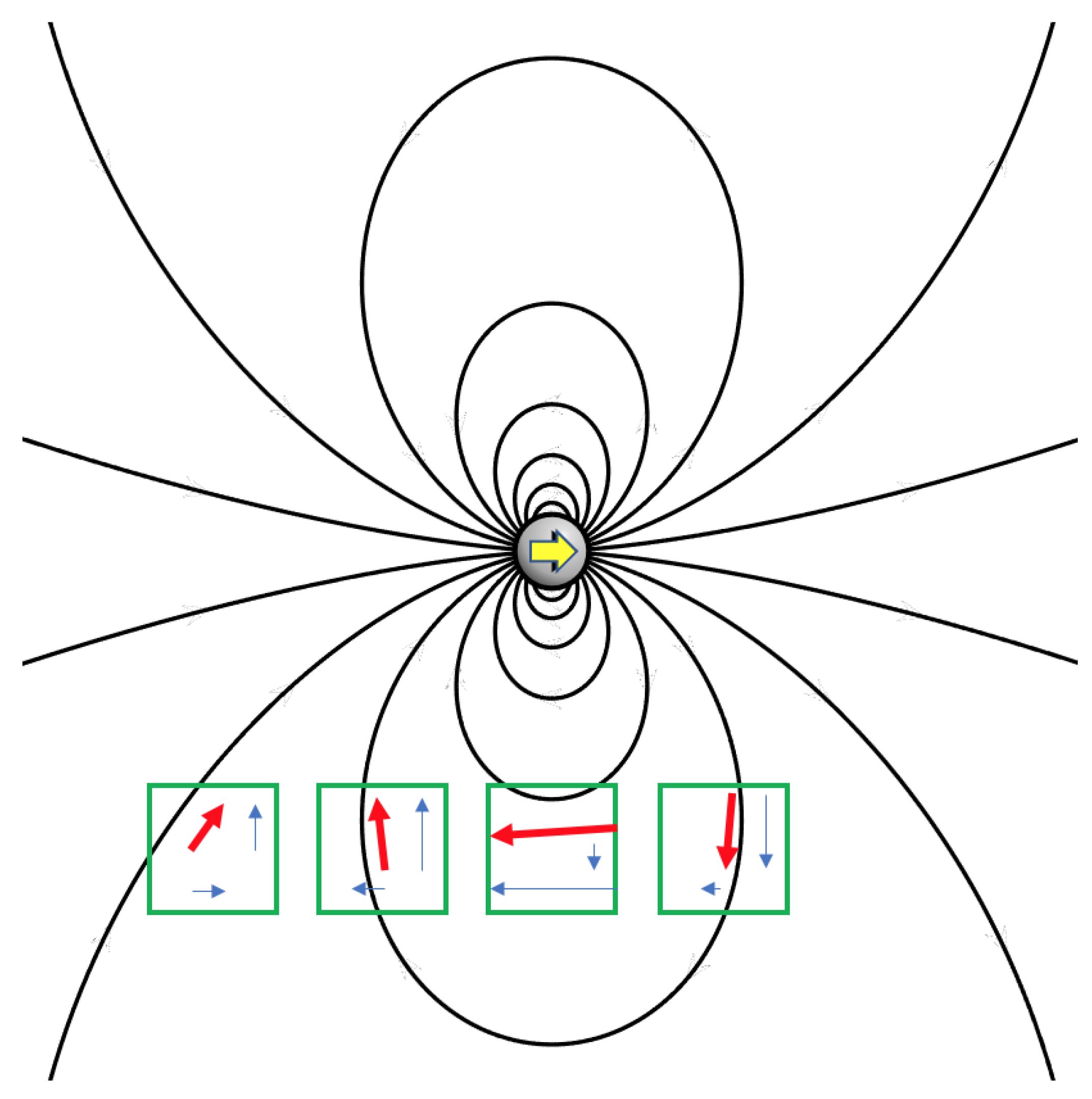
Figure 3 outlines the operating principle of this new device: a magnet produces an inhomogeneous field, whose orientation varies in space and whose strength decreases at an increasing distance from the magnet. Different intensities and different orientations are acquired. Each sensor measures and outputs specific field components depending on where it is located relative to the magnet. Numerical methods permit solving the inverse problem: from the field components measured in several known locations, the position and the orientation of the magnet can be inferred. If an additional homogeneous field is superimposed on the magnet field, those methods enable the characterization of that field, as well. The latter feature provides information about the sensor orientation to the ambient, and it allows tracking the motion of the subject’s head. The real implementation uses eight sensors, and the problem is inherently three-dimensional:
Figure 3 is a simplified image only to illustrate the working principle of the tracker.
Finally, the software used for data analysis provides information about both the orientation of the eye relative to the sensors and the orientation of the latter relative to the ambient field, so that both eye and head movements are tracked at once. They can be combined (to infer the absolute gaze orientation) or compared (to investigate eye-head correlated movements) and can be drawn up as 2D or 3D images.
The starter patient was asked to complete several tasks concerning measurements of the saccades, with the evaluation of the vestibular-ocular reflex (VOR) on horizontal semicircular canals and the evaluation of the pursuit movements, by following a moving object displayed on a PC monitor or tracking with the eye a pre-arranged shape, pathway or alphabetical letter. Another required task was reading a text on the PC monitor, in order to test and evaluate the combination of all the different kinds of eye movements.
Ethical approval was not requested since the starter patient (an healthy 31-year old man with no vestibular disorders) is one of the authors (M.C.), fully informed about the aims and possible adverse effects of this research.
3. Results
Eye tracking can provide a multitude of different measures for analysis [
25]. The angular uncertainty of the system was assessed through static measurements that estimated the standard deviation of the eye and head angles in statistical samples acquired along time, with a magnet placed on a fixed position with respect to the sensors. Under these conditions, fluctuations of 0.05 degrees in the head orientation and 0.20 degrees in the eye orientation were observed, mainly due to electronic noise and environmental magnetic disturbances.
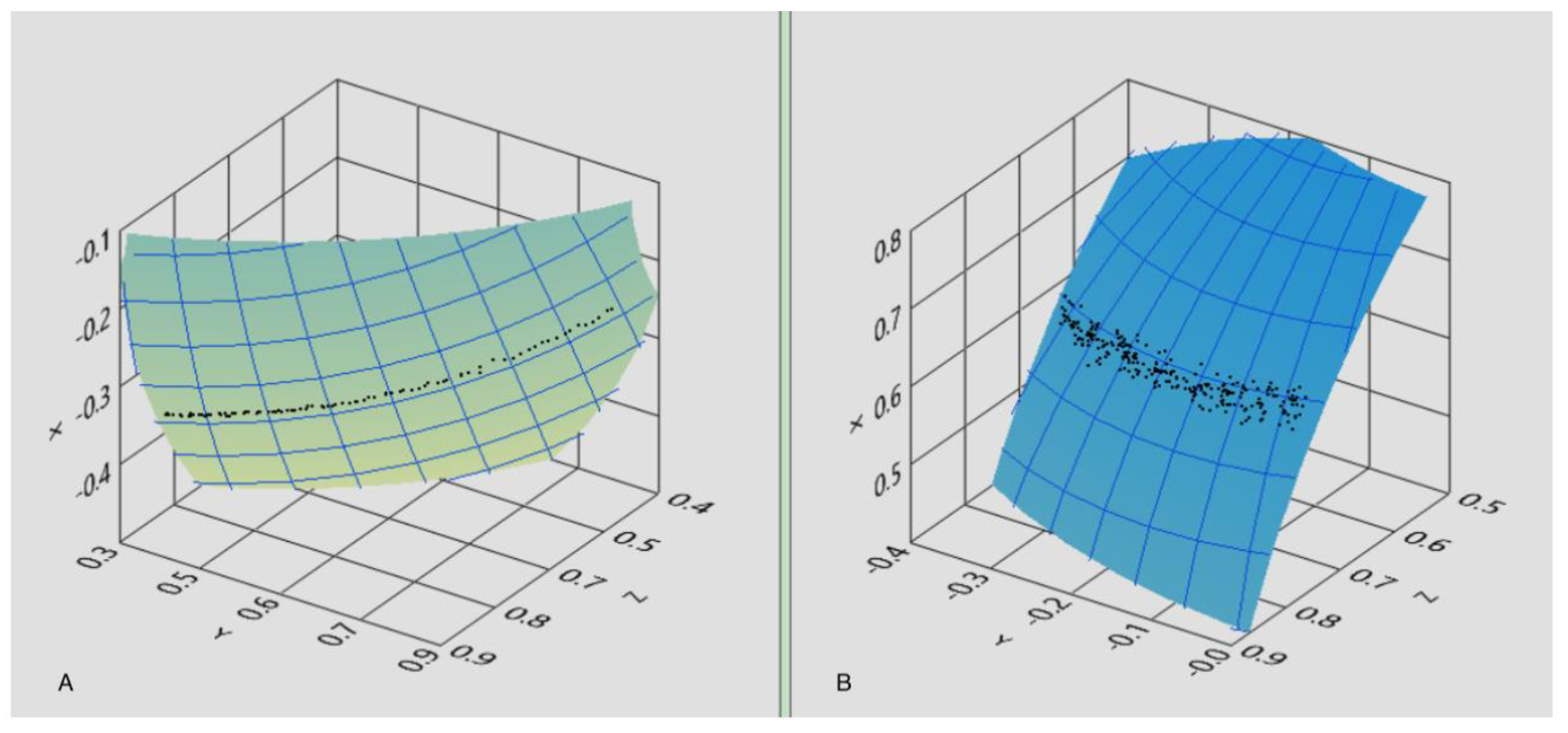
Another estimation of the instrumental uncertainty was performed dynamically. To this aim, the magnet was placed in the proximity of the sensors (simulating the real application case) and the sensor array was rigidly rotated around a fixed axis 1 cm away from the magnet. In this case, the reconstructed trajectory of the magnet orientation is expected to be an arc of circumference, and the standard deviation from ideality provides an estimate of angular uncertainty. Repeated measurements of this kind resulted in an estimated uncertainty of 0.2 degrees. It is important to highlight that the mechanical simulator was designed to reproduce realistically the experimental conditions of in-vivo operation.
Similarly, the in-vivo angular uncertainty was derived from the analysis of pursuit data. In this case, the volunteer was requested to pursue with the eye gaze a small target (red dot) slowly moving along a straight line on a PC screen provided by a dedicated software, while maintaining the head standing. The reconstructed trajectory was then fitted to an arc of circumference, and the standard deviation of the angle from the data points to the curve was evaluated, resulting in 0.6 degrees (
Figure 4).
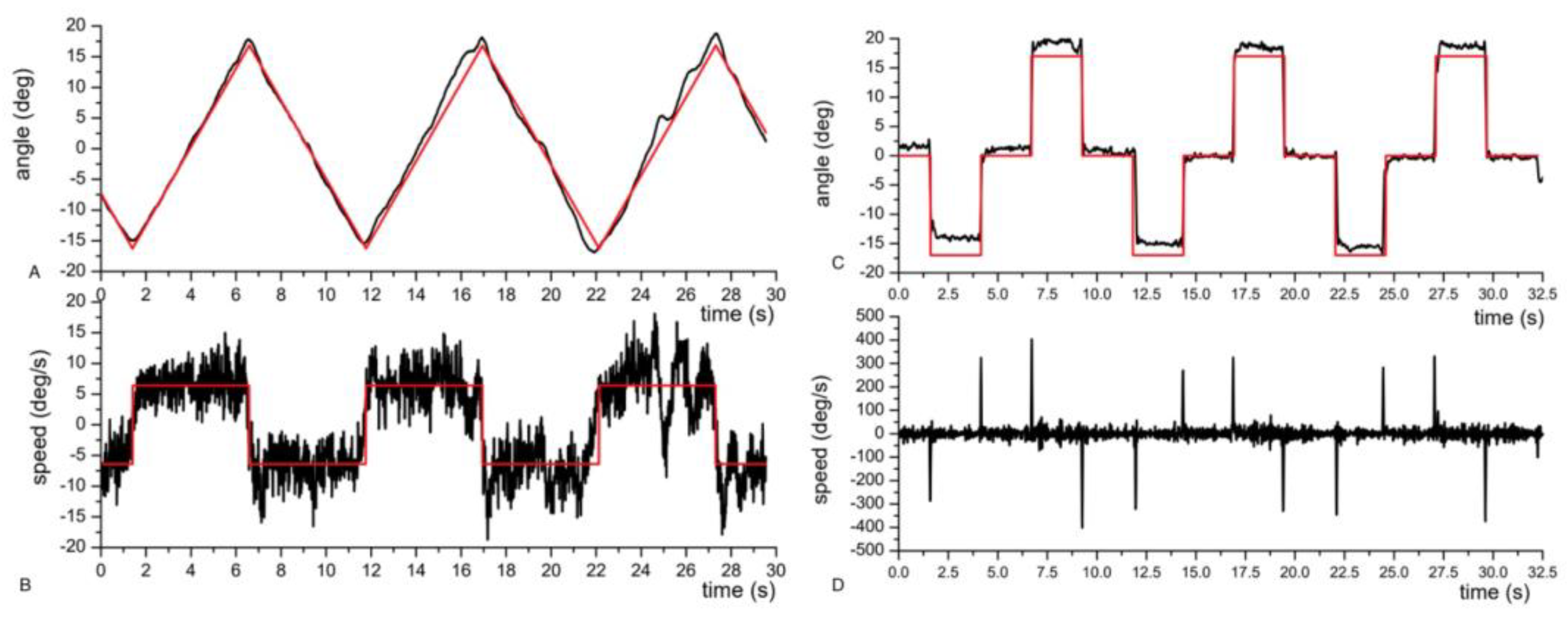
Afterwards, an analysis of pursuit and saccades has been carried out: as shown in
Figure 5, the gaze estimation of the eye tracker strictly recalls the ideal trajectory of the red dot moving on the PC screen.
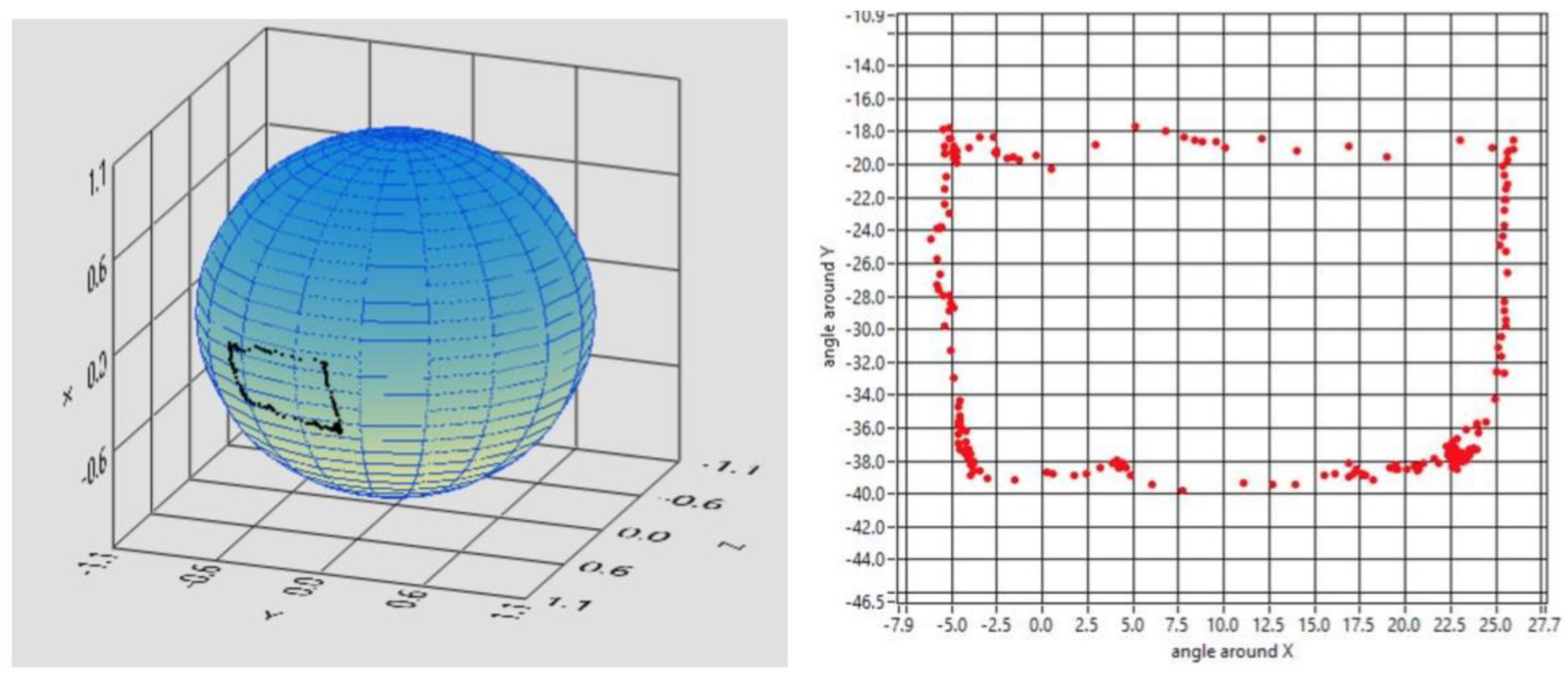
The starter patient was asked to perform different tasks that were analyzed with a dedicated software to establish the tracker’s accuracy, precision and reliability. Possible applications of the tracker might be “drawing” shapes or alphabetical letters that could eventually be used by the subject to communicate with the outer world. Hence, the first task asked to our subject was to draw a rectangle with the following results (
Figure 6).
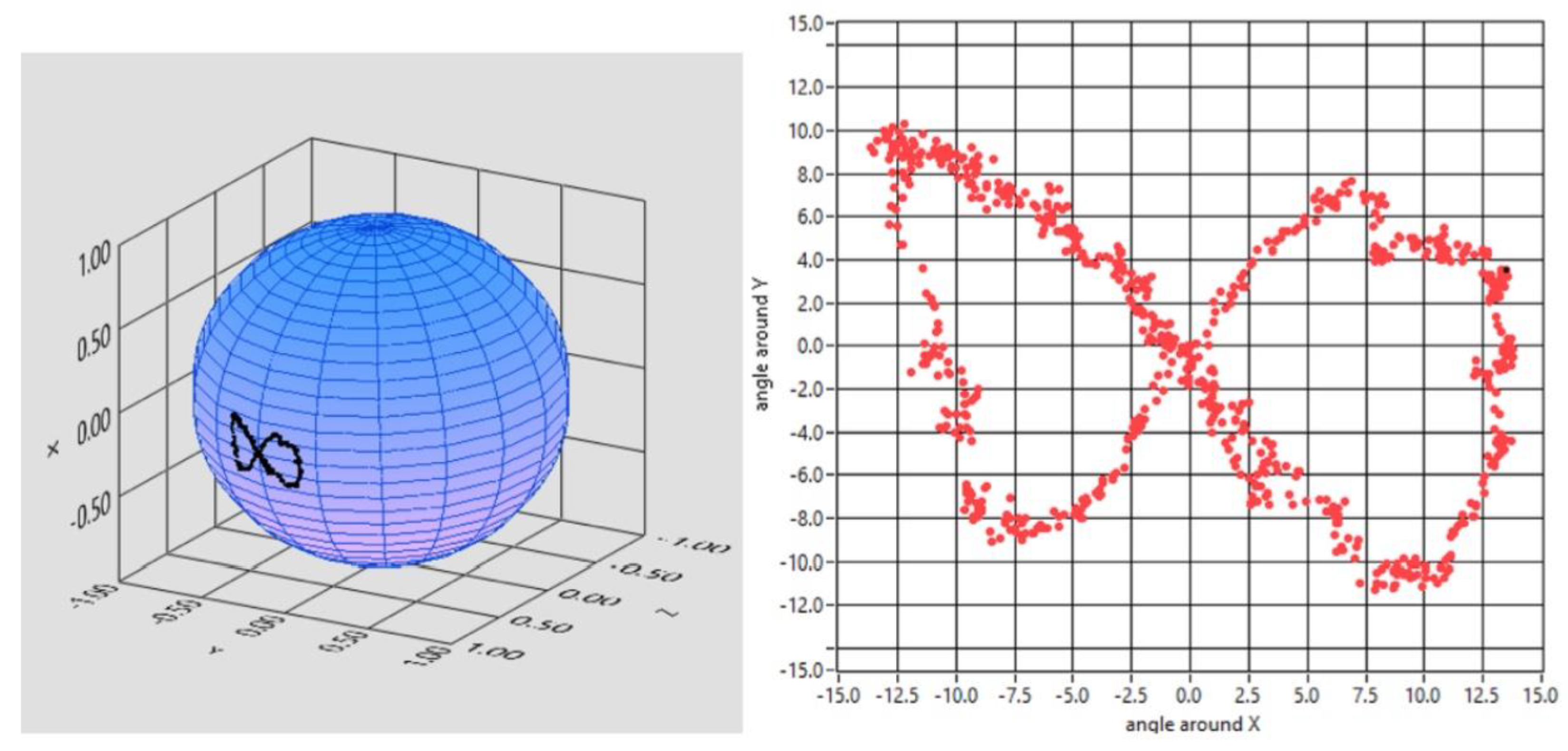
Afterwards, the starter patient was asked to follow a red dot moving on a monitor unaware of the movements that the dot was going to execute: the outcome of his pursuit movement was a ∞, the infinite symbol (
Figure 7).
The accuracy of the eye tracker was then evaluated for reading text: the different length of the lines is suggested in
Figure 8.
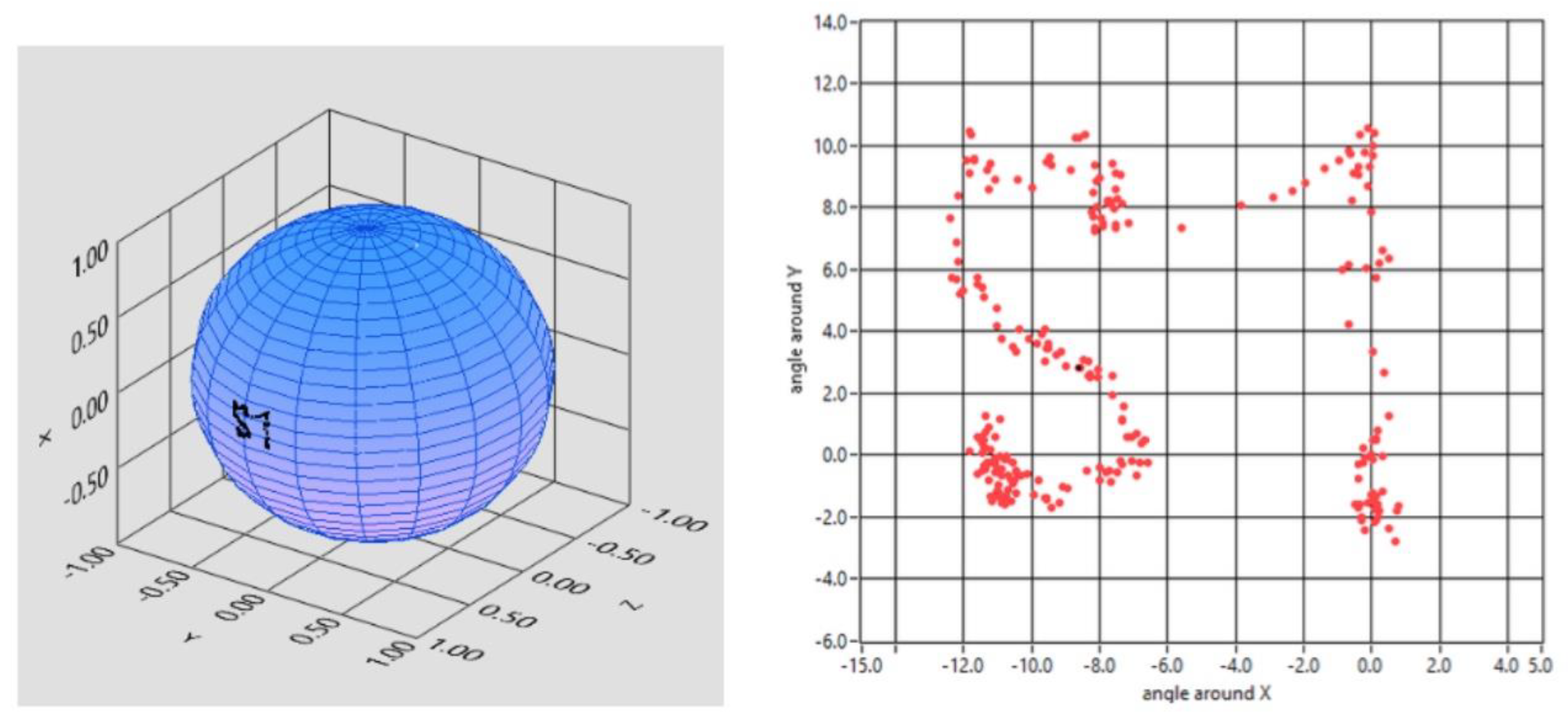
Furthermore, the subject was asked to “write” a simple word, as “YES” in Italian (SI). The tracker was thorough and elaborated the trajectory shown in
Figure 9.
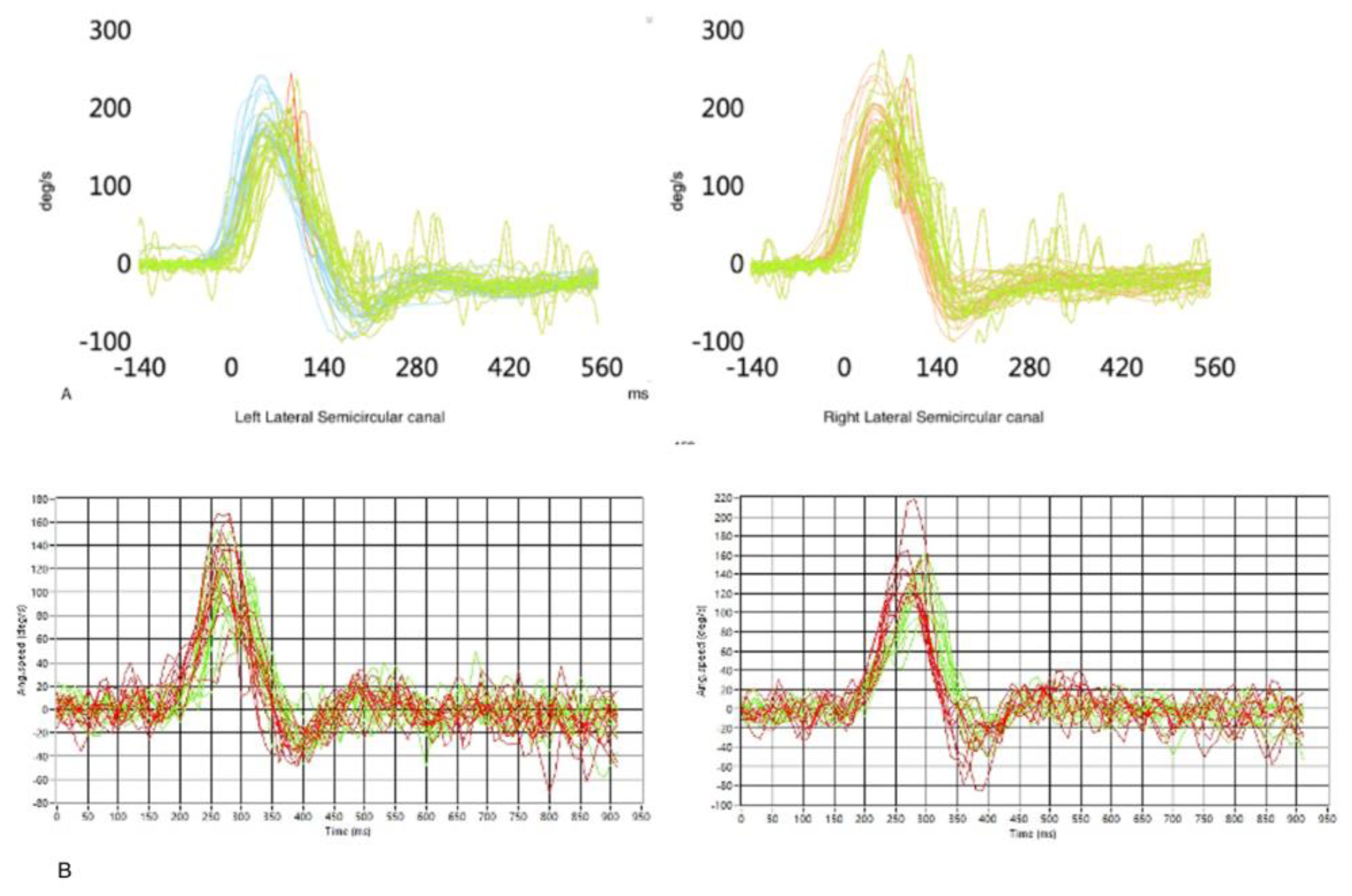
Finally, an HIT (Head Impulse Test) on the horizontal axis has been performed to establish the tracker’s reliability and accuracy in VOR (Vestibular Ocular Reflex) gain estimation. This reflex acts as a compensatory eye movement to keep the image stable on the retina when a head rotation occurs: the eyes will move in the opposite direction of the head, at the same speed and lined up with the axis of rotation of the head [
26]. Even if the search coil is considered the gold standard for VOR measurement, this reflex is usually evaluated by vHIT (video Head Impulse Test) by ICS Impulse - Natus, which has been demonstrated to have the same efficacy [
27]. Thus the subject underwent both vHIT and “mHIT” (HIT with our magnetic eye tracker), to compare the VOR estimations provided by the two devices (
Figure 10).
For what concerns mHIT, the data analysis software provides information about both eye and head angular speed for each trial and it evaluates the VOR gain as the ratio between eye and head peak angular speeds. Alternatively, the VOR can be estimated in terms of the ratio between eye and head angular displacements [
28]. The starter patient’s VOR gain measurements obtained from vHIT and mHIT included 20 trials each. The mHIT software evaluated the mean VOR gain with either the traditional slope gain (peak velocity) or the angular displacement gain. Results are summarized in
Table 1 together with the standard deviation.
4. Discussion
Eye trackers can be used simply to record where the subject is looking and for how long he or she looked before skipping to another visual stimulus. Moreover, eye trackers can be used for interactive purposes, such as moving a cursor by quadriplegic patients [
3]. Additionally, it can be implemented in the VR systems to reduce the dizziness feeling also known as cybersickness produced by extensive use of the virtual reality system [
29].
Eye tracker performance is usually described in terms of accuracy and precision. Accuracy depends on how much the eye position measured by the tracker corresponds to the actual eye position, while precision is due to consistent measurements of the eye position [
30]. It is important to highlight that the fovea is not strictly lined up with the magnet embedded in the contact lens, so when the software elaborates the eye movements starting from the magnet’s movements, there might be the necessity to correct them with mathematical algorithms, such as Listing’s law [
31]. The details of these corrections are beyond the aim of this paper and they have been discussed in another publication [
32].
This magnetic eye-tracker differs from the other eye tracking technologies for several characteristics: first of all, it does not suffer from the noise produced by facial muscle contraction and the eyes blinking, in contrast to the Electro-Oculography (EOG) [
33], which is an old method based on several electrodes placed around the eye to record the electric potential between cornea and retina. As for EOG, both the devices can record eye movements, even when they are closed or the patient is non-cooperative.
The proposed device needs only a preliminary self-calibration of the sensors, after which it produces absolute angle estimations; moreover, its functioning is not affected by light changes or blinking, differently from IROG (Infrared OculoGraphy), which requires a patient-based recalibration and it is very sensitive to external light changes so that environment light change can produce some biases during data acquisition procedure [
34]. IROG consists of an IR light source that illuminates the eye and an array of photodetectors that collect the reflected light [
35] [
36], thus it cannot produce any signal when the eyes are closed and suffers from artefacts driven by eye-blinking. On the other hand, the magnetic tracker is more invasive compared to other optical devices (IROG, IR cameras) but it not affected by blinking.
The current gold standard for eye tracking is the scleral search coil (SCC) [
37], [
38], a system that measures the voltages induced on a receiving coil by two or three mutually orthogonal alternating magnetic fields. These alternating fields are generated by pairs of large-size coils, surrounding the subject head. The receiving coils are moulded in a soft contact annulus that is attached by suction to the eyeball. The patient’s head is positioned in the centre of the cubic frame [
19]. With this method, the eye orientation is inferred based on how the scleral coil interacts with the alternating magnetic field to generate an electric signal.
Despite being the gold standard for eye tracking, the SSC has the disadvantage of being highly invasive, with the risk of keratitis and corneal damage. The magnetic eye tracker here described is more comfortable than SSC, because the eye-sensor connection is inherently wireless and does not need an electric connection (the exit wire passing on the eyelid of the SSC). Besides, the magnetic eye tracker’s sensor frame is lighter and smaller than the coil systems used to generate the alternating fields necessary for the search coil. All these features make it comfortably wearable, with negligible hindering of the head mobility and no constraints associated with the need of external field generators.
Table 2 summarizes the characteristics of eye tracker technologies presented.
One of the SCC main expressions deals with otoneurology since it is considered the gold standard for VOR gain estimation, although vHIT has been demonstrated comparable with it [
27]. The accuracy and precision of this magnetic eye tracker are comparable to the vHIT infrared method, as inferable from the low standard deviation observed at mHIT, suggesting a possible comparison with SCC in terms of accuracy in the VOR gain estimation, with lower invasivity and the advantage of being self-calibrated.
When performing the HIT on a wooden puppet (sensor frame rotating around a fixed vertical axis), typical results indicate an uncertainty below 5%, meaning that the ratio between head and eye angular displacements (and between angular velocities) resulted in the range of 0.95-1.05. It is worth highlighting that this instrumental error is expected to be an underestimate of the real, in-vivo VOR uncertainty, where other effects (e.g. microsaccades, rotation axis instability, a non-rigid connection between head and sensors etc.) may occur, causing additional imperfections not considered in the assessment described here above [
32].
Another advantage of this technology is that it can determine either the position and the orientation of the eyes. This represents an innovative feature, since this device might measure torsional eye movements, a feature that the other video-base methods usually cannot do or, if they can, is often of low quality. It is important to consider that rotations around the dipole direction cannot be detected. In the current implementation the magnet is axially magnetized, thus the magnetization in nearly parallel to the gaze directions and consequently the system is blind to torsions, while detects efficiently yaw and pitch rotations. Using a magnet with diametral magnetization, would make the dipole transversely oriented: in such way the system would detect efficiently the torsions (e.g. if the dipole is transversely oriented it would measure torsions and pitch, while it would not detect yaw). Small magnet with diametral magnetization are not available commercially; they can be produced on demand but so far we have not provided them ourselves thus we could not test in vivo torsion detection (this will be subject of further, already planned studies). A further possibility is using a lens with two magnets embedded. Theoretically, this might lead to complete (three angular and three position parameters) characterization of the eye pose.
In terms of eye intrusivity, the starter patient showed no discomfort in wearing the contact eye lens and did not require the use of any ocular anaesthetic. The magnet does not obstruct view while the sensor frame partially obstructive. In the current implementation the sensors are distributed on two planes and that makes the frame partially obstructive. However we have evidence that such two-planar distribution could be avoided and we plan to design new prototypes with reduced intrusivity.
The production cost is expected to be quite low, even if the main disadvantage of the device is that the lens must be tailored for a single subject. For this reason, other construction techniques are going to be explored, with the magnet embedded inside the lens using a 3D mould so that common soft contact lenses can be used for our purpose, avoiding the tailoring process [
39].
Since the eye orientation is estimated with respect to the sensor frame while the orientation of the latter is estimated with respect to the ambient field, if the frame is not rigidly connected to the head, this feature may produce artifacts. Further developments are focused to make the sensor frame as light as possible and to improve its mechanical connection to the head.
Concerning the biocompatibility of the used materials, some care is needed to protect the magnet from chemical degradation due to long-term interaction with the lens preserving liquid. Long-lasting experiments are still ongoing, to evaluate the magnet degradation and liquid contamination over time. Several kinds of organic or metallic coatings are being considered to prevent or slow down these processes, and chemical analyses are planned to provide quantitative assessments of diverse potential contaminants.
5. Conclusions
The proposed prototypic device aims at developing new health-oriented technology for a broad range of human well-being applications, ranging from medical diagnosis in neurological and neuro-otological domains to inclusive systems for severely impaired patients. The successful development of a wearable, low invasive, lightweight, accurate, and high-frequency three-dimensional eye tracking system will represent a breakthrough health technology enabling early detection of neurological conditions, such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s diseases, and even rare medical conditions such as progressive supranuclear palsy, including cerebellar.
The head tracking ability of the proposed device will enable its application for diagnosis in neuro-otology by detecting and/or follow-up vestibular impairments, such as BBPV, vestibular migraine or Meniere’s disease episodes. The ability to accurately and reliably estimate gaze in space will allow using the device for a range of inclusive purposes, such as developing interfaces for patients with locked-in syndromes or severe impairment in movement, who might use the technology to communicate through video terminals driven through the eye tracking, by writing some words or by linking specific eye movements to pre-established actions, as well as the ability to drive a wheelchair or other kind of prostheses that might be moved by eye-tracking technology.
The ease of use and versatility of the device would make it suitable for integration in the health care system both by developing a standard battery of screening tests for neurological and neurotological conditions such as stroke or midbrain pathologies to be used in the Emergency Department and as a clinical diagnostic tool in routine procedures for neurology and neuro-otology visits.
This tracker is certainly more invasive than infrared oculographic systems while competing with them in terms of precision, speed and cost-effectiveness, with the advantage of not requiring patient-based calibration. The invasivity aspect is related to the need of wearing a contact lens hosting a small magnet.
Compared to the gold-standard technology for eye-tracking (based on scleral search coils), such invasive detail is dramatically reduced, thanks to the wireless nature of the passive magnetic target. Compared to the search-coil approach, the proposed measurement system has the advantage of being comfortably wearable, facilitating diagnostics that require head movements: the goggles hosting the sensors are small-size and lightweight; no external coils for field generators are needed. An additional feature of the proposed system is the simultaneous evaluation of both eye and head motion. This can be used to infer the absolute direction of the gaze or (with important implications in otoneurological applications) to characterize the eye response to head-motion stimuli. Besides using a magnet with diametral magnetization the system could detect efficiently the torsional eye movements with relatively low invasivity.
6. Patents. V.B. and M.M. appear as inventors in a pending patent No. WO2022018691
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M. and V.B.; methodology, A.D., F.V. and M.C.; software, V.B.; validation, V.B. and M.M.; formal analysis, V.B. and L.B.; investigation, A.D., F.V., M.C. and V.B..; resources, M.M., M.C. and V.B.; data curation, V.B. and L.B..; writing—original draft preparation, A.D. and F.V.; writing—review and editing, A.D., F.V. and V.B.; visualization, A.D. and F.V.; supervision, M.M.; project administration, M.M.; funding acquisition, M.M and V.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study since the starter patient is one of the authors (M.C.), fully informed about the aims and possible adverse effects of this research.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the subject involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
on request to the Authors.
Acknowledgments
Authors are pleased to thank Prof. C. Rossi, G. Bevilacqua and M. Dell’Omodarme for useful discussions. L.B and V.B. acknowledge partial support from Regione Toscana, under the project PhAST (FESR 2014 – 2020).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- B. T. Carter and S. G. Luke, ‘Best practices in eye tracking research’, Int J Psychophysiol, vol. 155, pp. 49–62, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Rayner, ‘Eye movements and attention in reading, scene perception, and visual search’, Q J Exp Psychol (Hove), vol. 62, no. 8, pp. 1457–1506, Aug. 2009. [CrossRef]
- T. Duchowski, Eye Tracking Methodology. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. J. Krauzlis, L. Goffart, and Z. M. Hafed, ‘Neuronal control of fixation and fixational eye movements’, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B, vol. 372, no. 1718, p. 20160205, Apr. 2017. [CrossRef]
- D. C. Burr, M. C. Morrone, and J. Ross, ‘Selective suppression of the magnocellular visual pathway during saccadic eye movements’, Nature, vol. 371, no. 6497, pp. 511–513, Oct. 1994. [CrossRef]
- E. Castet and G. S. Masson, ‘Motion perception during saccadic eye movements’, Nat Neurosci, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 177–183, Feb. 2000. [CrossRef]
- M. Rolfs, ‘Attention in Active Vision: A Perspective on Perceptual Continuity Across Saccades’, Perception, vol. 44, no. 8–9, pp. 900–919, 2015. [CrossRef]
- A. T. Bahill, M. R. Clark, and L. Stark, ‘The main sequence, a tool for studying human eye movements’, Mathematical Biosciences, vol. 24, no. 3–4, pp. 191–204, Jan. 1975. 1975. [CrossRef]
- S. B. Hutton, ‘Cognitive control of saccadic eye movements’, Brain Cogn, vol. 68, no. 3, pp. 327–340, Dec. 2008. [CrossRef]
- M. Ibbotson and B. Krekelberg, ‘Visual perception and saccadic eye movements’, Current Opinion in Neurobiology, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 553–558, Aug. 2011. [CrossRef]
- P. Termsarasab, T. Thammongkolchai, J. C. Rucker, and S. J. Frucht, ‘The diagnostic value of saccades in movement disorder patients: a practical guide and review’, J Clin Mov Disord, vol. 2, p. 14, 2015. [CrossRef]
- S. Stuart, A. Hickey, B. Galna, S. Lord, L. Rochester, and A. Godfrey, ‘iTrack: instrumented mobile electrooculography (EOG) eye-tracking in older adults and Parkinson’s disease’, Physiol Meas, vol. 38, no. 1, pp. N16–N31, Jan. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Stuart, S. Lord, B. Galna, and L. Rochester, ‘Saccade frequency response to visual cues during gait in Parkinson’s disease: the selective role of attention’, Eur J Neurosci, vol. 47, no. 7, pp. 769–778, Apr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Distler and K.-P. Hoffmann, ‘The optokinetic reflex’, in The Oxford handbook of eye movements., in Oxford library of psychology. New York, NY, US: Oxford University Press, 2011, pp. 65–83.
- S. Somisetty and J. M Das, ‘Neuroanatomy, Vestibulo-ocular Reflex’, in StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2022. Accessed: Mar. 22, 2022. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545297/.
- Brousseau, J. Rose, and M. Eizenman, ‘Hybrid Eye-Tracking on a Smartphone with CNN Feature Extraction and an Infrared 3D Model’, Sensors (Basel), vol. 20, no. 2, p. E543, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- F. Ba, T. T. Sang, W. He, J. Fatehi, E. Mostofi, and B. Zheng, ‘Stereopsis and Eye Movement Abnormalities in Parkinson’s Disease and Their Clinical Implications’, Front Aging Neurosci, vol. 14, p. 783773, 2022. 3773; 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Opwonya et al., ‘Saccadic Eye Movement in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis’, Neuropsychol Rev, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 193–227, Jun. 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. Eggert, ‘Eye movement recordings: methods’, Dev Ophthalmol, vol. 40, pp. 15–34, 2007. [CrossRef]
- G. Bevilacqua et al., ‘A Wearable Wireless Magnetic Eye-Tracker, in-vitro and in-vivo tests’, IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, vol. PP, Jun. 2023. [CrossRef]
- V. Biancalana et al., ‘Validation of a Fast and Accurate Magnetic Tracker Operating in the Environmental Field’, Instruments, vol. 5, no. 1, p. 11, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- V. Biancalana, R. Cecchi, P. Chessa, M. Mandalà, and Pratichizzo, ‘System for Tracking an Object’, 20DO001.
- V. Biancalana, R. Cecchi, P. Chessa, G. Bevilacqua, Y. Dancheva, and A. Vigilante, ‘Fast, Cheap, and Scalable Magnetic Tracker with an Array of Magnetoresistors’, Instruments, vol. 5, no. 1, p. 3, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. Bellizzi et al., ‘An innovative eye-tracker: Main features and demonstrative tests’, Review of Scientific Instruments, vol. 93, no. 3, p. 035006, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Holmqvist, Ed., Eye tracking: a comprehensive guide to methods and measures. Oxford ; New York: Oxford University Press, 2011.
- M. Boleas-Aguirre, A. A. Migliaccio, and J. P. Carey, ‘[Vestibulo-oculomotor reflex recording using the scleral search coil technique. Review of peripheral vestibular disorders]’, Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp, vol. 58, no. 7, pp. 321–326, Sep. 2007.
- H. G. MacDougall, K. P. Weber, L. A. McGarvie, G. M. Halmagyi, and I. S. Curthoys, ‘The video head impulse test: Diagnostic accuracy in peripheral vestibulopathy’, Neurology, vol. 73, no. 14, pp. 1134–1141, Oct. 2009. [CrossRef]
- L. A. McGarvie, H. G. MacDougall, G. M. Halmagyi, A. M. Burgess, K. P. Weber, and I. S. Curthoys, ‘The Video Head Impulse Test (vHIT) of Semicircular Canal Function – Age-Dependent Normative Values of VOR Gain in Healthy Subjects’, Front. Neurol., vol. 6, Jul. 2015. [CrossRef]
- R. Hussain, M. Chessa, and F. Solari, ‘Mitigating Cybersickness in Virtual Reality Systems through Foveated Depth-of-Field Blur’, Sensors (Basel), vol. 21, no. 12, p. 4006, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Reingold, ‘Eye tracking research and technology: Towards objective measurement of data quality’, Visual Cognition, vol. 22, no. 3–4, pp. 635–652, Apr. 2014. [CrossRef]
- T. Haslwanter, ‘Mathematics of three-dimensional eye rotations’, Vision Research, vol. 35, no. 12, pp. 1727–1739, Jun. 1995. [CrossRef]
- V. Biancalana and P. Chessa, ‘A Non-Inductive Magnetic Eye-Tracker: From Dipole Tracking to Gaze Retrieval’, Instruments, vol. 7, no. 1, p. 8, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. E. Kolder, ‘Electro-oculography’, Ophthalmologica, vol. 169, no. 1–3, pp. 127–140, 1974. [CrossRef]
- H. R. Chennamma and X. Yuan, A Survey on Eye-Gaze Tracking Techniques, arXiv:1312.6410 [cs], Dec. 2013, Accessed: Mar. 22, 2022. [Online]. [CrossRef]
- Siriwadee Aungsakun, ‘Development of robust electrooculography (EOG)-based human-computer interface controlled by eight-directional eye movements’, Int. J. Phys. Sci., vol. 7, no. 14, Mar. 2012. [CrossRef]
- A. Kumar and G. Krol, Binocular Infrared Oculography:, The Laryngoscope, vol. 102, no. 4, pp. 367–378, Apr. 1992. [CrossRef]
- D. A. Robinson, A Method of Measuring Eye Movemnent Using a Scieral Search Coil in a Magnetic Field, IEEE Trans. Bio-med. Electron., vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 137–145, Oct. 1963. [CrossRef]
- H. Collewijn, F. van der Mark, and T. C. Jansen, Precise recording of human eye movements, Vision Research, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 447-IN5, Mar. 1975. [CrossRef]
- A. Tanwear et al., Spintronic Sensors Based on Magnetic Tunnel Junctions for Wireless Eye Movement Gesture Control, IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst., vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 1299–1310, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
A)Nd-Fe-B magnet embedded in the contact lens. B) The contact lens worn by the subject.
Figure 1.
A)Nd-Fe-B magnet embedded in the contact lens. B) The contact lens worn by the subject.
Figure 2.
Worn sensor frame and sensors’ position.
A. The sensor array is rigidly fixed to the patient’s head and tracks the movements of his right eye.
B. It contains eight three-axial magnetoresistive sensors in two sets distributed on two parallel printed circuit boards (PCBs). Red and blue circles highlight the two sets. A third PCB hosts a microcontroller and other electronics that interface the sensors to a personal computer. The Cartesian axes with respect to the sensor array are shown in both the pictures. Nominally, when the head is erect and front oriented, zˆ is back-directed, xˆ is vertical and yˆ is transverse-horizontal.
(This Figure is already present in [
20]
).
Figure 2.
Worn sensor frame and sensors’ position.
A. The sensor array is rigidly fixed to the patient’s head and tracks the movements of his right eye.
B. It contains eight three-axial magnetoresistive sensors in two sets distributed on two parallel printed circuit boards (PCBs). Red and blue circles highlight the two sets. A third PCB hosts a microcontroller and other electronics that interface the sensors to a personal computer. The Cartesian axes with respect to the sensor array are shown in both the pictures. Nominally, when the head is erect and front oriented, zˆ is back-directed, xˆ is vertical and yˆ is transverse-horizontal.
(This Figure is already present in [
20]
).
Figure 3.
The inhomogeneous magnetic field produced by a magnet (yellow arrow). The orientation varies in space and strength depending on the distance from the magnet. The black lines describe the field orientation, the red arrows represent a sample of field measurements performed in a set of locations, where a set of sensors (green boxes) are located. The blue arrows highlight the vectorial nature of the measured quantities. The schematics in this figure simplify the real condition, where the sensors are 8 (not 4) and each of them measures 3 (not 2) components of the field. Furthermore, an additional homogeneous field (the Earth field) sums to those illustrated.
Figure 3.
The inhomogeneous magnetic field produced by a magnet (yellow arrow). The orientation varies in space and strength depending on the distance from the magnet. The black lines describe the field orientation, the red arrows represent a sample of field measurements performed in a set of locations, where a set of sensors (green boxes) are located. The blue arrows highlight the vectorial nature of the measured quantities. The schematics in this figure simplify the real condition, where the sensors are 8 (not 4) and each of them measures 3 (not 2) components of the field. Furthermore, an additional homogeneous field (the Earth field) sums to those illustrated.
Figure 4.
Estimated uncertainty of the system in dynamic conditions: the reconstructed trajectory of the magnet orientation is expected to be an arc of circumference and the standard deviation from ideality provides an estimate of angular uncertainty. (A) Estimated uncertainty measured rotating the sensors frame around a fixed axis with a mechanic simulator. (B) Estimated uncertainty measured on the starter patient wearing the lens.
Figure 4.
Estimated uncertainty of the system in dynamic conditions: the reconstructed trajectory of the magnet orientation is expected to be an arc of circumference and the standard deviation from ideality provides an estimate of angular uncertainty. (A) Estimated uncertainty measured rotating the sensors frame around a fixed axis with a mechanic simulator. (B) Estimated uncertainty measured on the starter patient wearing the lens.
Figure 5.
Analysis of pursuit (A-B) and saccades (C-D). Red line = ideal trajectory followed by a small target moving on the PC screen. Black line = trajectory reconstructed by the magnetic eye tracker (A) Comparison between the eye and the target’s angular displacement during pursuit. (B) Comparison between the eye and the target’s angular speed. (C) Comparison between the eye and the target’s angular displacement during saccades (D) Eye’s angular variation speed during saccades.
Figure 5.
Analysis of pursuit (A-B) and saccades (C-D). Red line = ideal trajectory followed by a small target moving on the PC screen. Black line = trajectory reconstructed by the magnetic eye tracker (A) Comparison between the eye and the target’s angular displacement during pursuit. (B) Comparison between the eye and the target’s angular speed. (C) Comparison between the eye and the target’s angular displacement during saccades (D) Eye’s angular variation speed during saccades.
Figure 6.
Outcome of drawing a rectangle and reconstruction in 3D and 2D.
Figure 6.
Outcome of drawing a rectangle and reconstruction in 3D and 2D.
Figure 7.
Reconstruction of the eye tracking while the patient was following a moving dot on the monitor. The total pathway was the infinite symbol, here edited in 3D and 2D.
Figure 7.
Reconstruction of the eye tracking while the patient was following a moving dot on the monitor. The total pathway was the infinite symbol, here edited in 3D and 2D.
Figure 8.
The starter patient was asked to read a three lines text. The tracker recognizes the different position and length of the lines.
Figure 8.
The starter patient was asked to read a three lines text. The tracker recognizes the different position and length of the lines.
Figure 9.
The subject writes the Italian word for YES, “SI”.
Figure 9.
The subject writes the Italian word for YES, “SI”.
Figure 10.
A) Reconstruction and evaluation of the VOR gain of the starter patient with vHIT for lateral semicircular canals. Green line = VOR. Red line = saccades. Blue line = head movement in left vHIT. Orange = head movement in right vHIT. B) Same measurements performed with the magnetic eye tracker. Green line = VOR. Red line = head movement.
Figure 10.
A) Reconstruction and evaluation of the VOR gain of the starter patient with vHIT for lateral semicircular canals. Green line = VOR. Red line = saccades. Blue line = head movement in left vHIT. Orange = head movement in right vHIT. B) Same measurements performed with the magnetic eye tracker. Green line = VOR. Red line = head movement.
Table 1.
Mean VOR gain estimation with a commercial instrumentation (vHIT) and with the described device (mHIT). The mHIT provides mean VOR gain measurements slightly higher than the vHIT mainly due to a non-rigid connection between head and sensors. Nevertheless the standard deviations (σ) in all the three scenarios are similar, supporting the reliability of the magnetic eye tracker measurements.
Table 1.
Mean VOR gain estimation with a commercial instrumentation (vHIT) and with the described device (mHIT). The mHIT provides mean VOR gain measurements slightly higher than the vHIT mainly due to a non-rigid connection between head and sensors. Nevertheless the standard deviations (σ) in all the three scenarios are similar, supporting the reliability of the magnetic eye tracker measurements.
| |
Mean VOR
Right LSC |
σ |
Mean VOR
Left LSC |
σ |
| vHIT |
0,95 |
0,06 |
0,87 |
0,06 |
|
mHIT1Position Gain (Angles) |
0,87 |
0,15 |
0,97 |
0,15 |
|
mHIT1 Slope Gain (Velocity) |
0,89 |
0,16 |
0,84 |
0,16 |
Table 2.
Main features of currently available eye-tracking technologies
Table 2.
Main features of currently available eye-tracking technologies
| Eye tracker |
Technology |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| EOG (Electro-Oculography) |
Several electrodes placed around the eye to record the electric potential between cornea and retina |
Can record closed eyes movements (even when the patient is not cooperative) |
Noise produced by facial muscles contraction and eyes blinking. |
| IROG (Infrared OculoGraphy) |
IR light source that illuminates the eye + array of photodetectors (or video camera) which collect the light reflected towards |
Not invasive |
Patient-based recalibrationSensitive to external light changes (environment light can produce bias) |
| SSC (Scleral Search Coil) |
2-3 pairs of large-size coils, mounted in a cubic frame that produce alternating fields inducing electric signals in the scleral coil |
Current gold standard (high accuracy and precision).Mature technology, developed since 1963 [37], [38] |
Requires special corneal lenses.Highly invasive, with risk of keratitis and corneal damage.Needs an external field generator. |
| Magnetic Eye Tracker |
8 sensors placed on a rigid frame: each sensor measures the magnetic field produced by a magnet embedded in a contact lens. Numerical method provides information about the magnet pose |
High accuracy and precisionWireless sensor connectionCan record closed eye movementsOne time calibration of the lensDo not depend on environmental light |
Requires special corneal lenses.Invasive for the presence of the lens (but reduced invasivity compared to SSC)Currently available as a prototype: further development needed |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).