Submitted:
18 September 2023
Posted:
22 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test article and chemicals
2.2. Experimental animals
2.3. Experimental design
2.4. Clinical observation
2.5. Body weights and food consumption
2.6. Hematology and biochemistry Analysis
2.7. Necropsy, organ weight and histopathology
2.8. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical observations
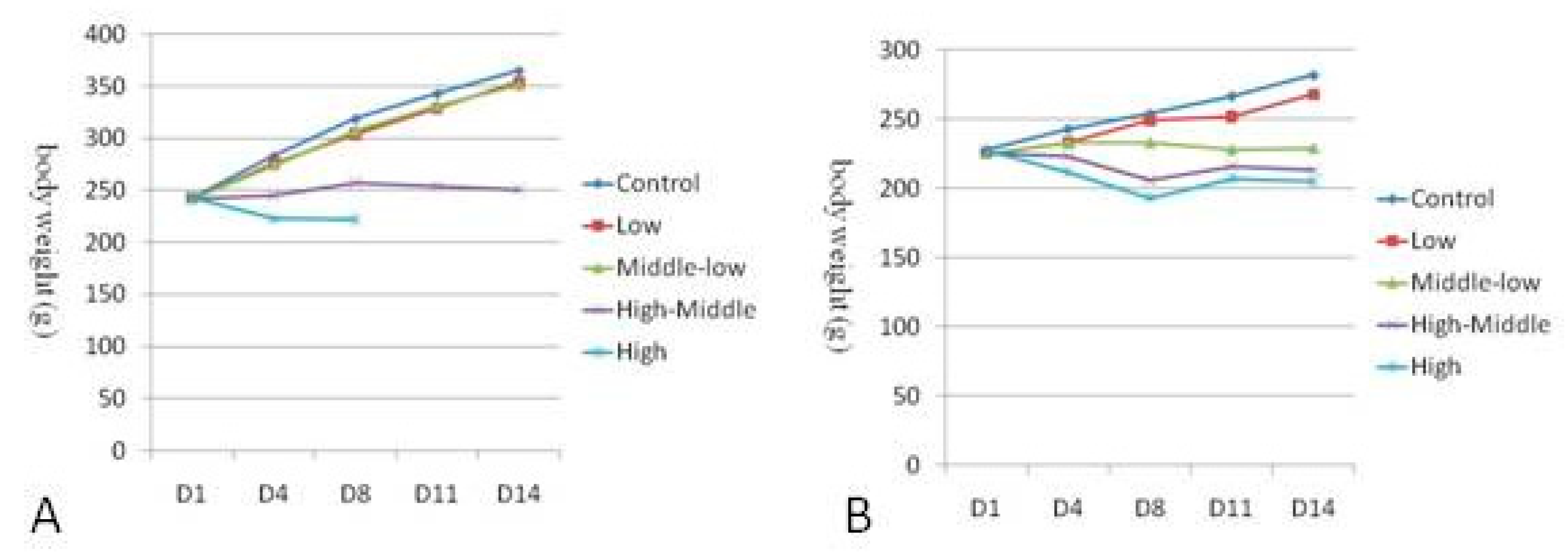
3.2. Body weight
3.3. Hematology
3.4. Serum chemistry
3.5. Blood Coagulation Detection Index
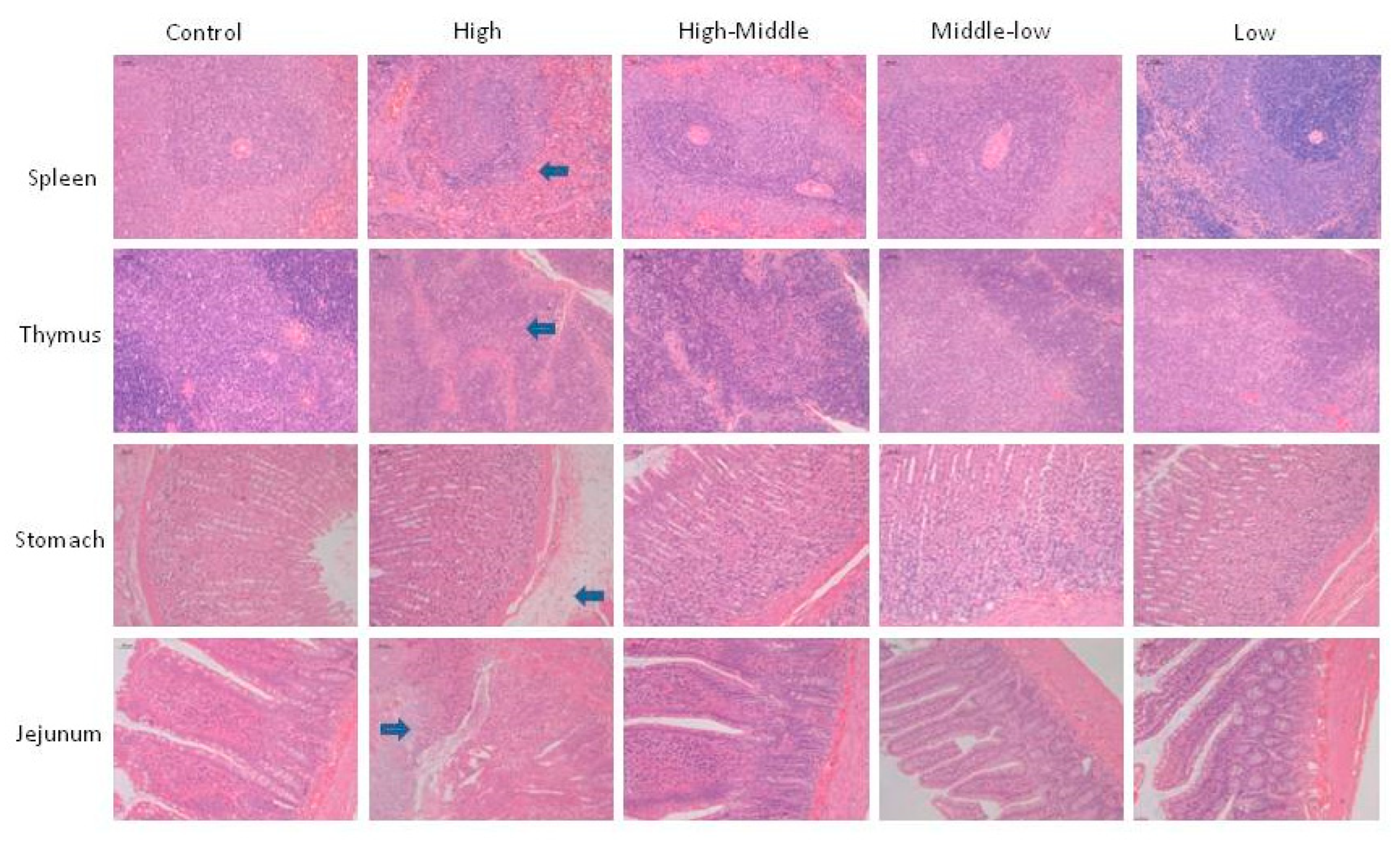
3.6. Necropsy, organ weights and histopathology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
References
- Hudson, T.J.; Anderson, W.; Artez, A.; Barker, A.D.; Bell, C.; Bernabé, R.R.; Bhan, M.K.; Calvo, F.; Eerola, I.; Gerhard, D.S.; et al. International Network of Cancer Genome Projects. Nature 2010, 464, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitulescu, G.M.; Margina, D.; Juzenas, P.; Peng, Q.; Olaru, O.T.; Saloustros, E.; Fenga, C.; Spandidos, D.A.; Libra, M.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Akt inhibitors in cancer treatment: The long journey from drug discovery to clinical use (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 48, 869–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Sun, M.M.; Zhang, G.G.; Yang, J.; Chen, K.S.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, J.F.; Xu, R.; Bencsik, J.R.; Xiao, D.; Kallan, N.C.; Schlachter, S.; Mitchell, I.S.; Spencer, K.L.; Banka, A.L.; Wallace, E.M.; et al. Discovery and Preclinical Pharmacology of a Selective ATP-Competitive Akt Inhibitor (GDC-0068) for the Treatment of Human Tumors. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 8110–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uko, N.E. , Güner, O.F., Matesic, D.F. and Bowen, J.P. Akt Pathway Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. 2020, 20, 883–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.H.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, M.C.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Park, W.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.B.; et al. Hippo-mediated suppression of IRS2/AKT signaling prevents hepatic steatosis and liver cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1010–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Sheng, X.; Liu, J.; Xiong, H. Cisplatin regulates cell autophagy in endometrial cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3567–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.B.; Jung, M.; Beom, S.H.; Kim, G.M.; Kim, H.R.; Choi, H.J.; Sohn, J.H.; Ahn, J.B.; Rha, S.Y.; Chung, H.C. Phase 2 study of TAS-117, an allosteric akt inhibitor in advanced solid tumors harboring phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog gene mutations. Investig. New Drugs 2021, 39, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roudsari, N.M.; Lashgari, N.-A.; Momtaz, S.; Abaft, S.; Jamali, F.; Safaiepour, P.; Narimisa, K.; Jackson, G.; Bishayee, A.; Rezaei, N.; et al. Inhibitors of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway in Prostate Cancer Chemoprevention and Intervention. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1195–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneum, A.; Said, N. PI3K-AKT-mTOR and NFκB Pathways in Ovarian Cancer: Implications for Targeted Therapeutics. Cancers 2019, 11, 949–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, M.; McGarrigle, S.; Pidgeon, G.P. The next generation of PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway inhibitors in breast cancer cohorts. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Rev. Cancer 2018, 1870, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, X.-H.; Yan, Y.-G.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.-J. PI3K/Akt signaling in osteosarcoma. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 444, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, D.; Sheng, X.; Liu, J.; Xiong, H. Cisplatin regulates cell autophagy in endometrial cancer cells via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3567–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-Y.; Lin, P.-Y.; Weiss, R.H. Targeting the PI3K–Akt pathway in kidney cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2007, 7, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, D.R.; Mell, L.K.; Cohen, E.E. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Cron, P.; Thompson, V.; Good, V.M.; Hess, D.; Hemmings, B.A.; Barford, D. Molecular Mechanism for the Regulation of Protein Kinase B/Akt by Hydrophobic Motif Phosphorylation. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lučić, I.; Rathinaswamy, M.K.; Truebestein, L.; Hamelin, D.J.; Burke, J.E.; Leonard, T.A. Conformational sampling of membranes by Akt controls its activation and inactiva-tion. PNAS. 2018, 115, E3940–E3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bing, S.; Xiang, S.; Xia, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guan, Z.; Che, J.; Xu, A.; Dong, X.; Cao, J.; Yang, B.; et al. AKT inhibitor Hu7691 induces differentiation of neuroblastoma cells. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 1522–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delwatta, S.L.; Gunatilake, M.; Baumans, V.; Seneviratne, M.D.; Dissanayaka, M.L.B.; Batagoda, S.S.; Udagedara, A.H.; Walpola, P.B. Reference values for selected hematological, biochemical and physiological parameters of Sprague-Dawley rats at the Animal House, Faculty of Medicine, University of Colombo, Sri Lanka. Anim. Model. Exp. Med. 2018, 1, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, J.; Dai, X.; Gao, J.; Sheng, H.; Zhan, W.; Lu, Y.; Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Jin, Z.; Chen, B.; et al. Discovery of N-((3S,4S)-4-(3,4-Difluorophenyl)piperidin-3-yl)-2-fluoro-4-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-5-yl)benzamide (Hu7691), a Potent and Selective Akt Inhibitor That Enables Decrease of Cutaneous Toxicity. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 12163–12180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Dosage (mg/kg) | Sex | Clinical observations (a/b) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bristles/matte hair | Red around the nose | Perianal filth | Hunched | Emaciated | Dead | ||
| 0 | ♂ | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 |
| 12.5 | ♂ | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 |
| 50 | ♂ | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 |
| 100 | ♂ | 3/3 | 2/3 | 0/3 | 3/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 |
| 150 | ♂ | 3/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 2/3 |
| 0 | ♀ | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 |
| 12.5 | ♀ | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 | 0/3 |
| 25 | ♀ | 0/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 | 1/3 | 1/3 | 0/3 |
| 50 | ♀ | 1/3 | 2/3 | 0/3 | 2/3 | 2/3 | 1/3 |
| 75 | ♀ | 3/3 | 3/3 | 1/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 1/3 |
| Dosage (mg/kg) | Sex |
WBC (109/L) |
%NEUT (%) |
%LYMPH (%) |
%MONO (%) |
%EOS (%) |
RBC (1012/L) |
| 0 | ♂ | 10.93±1.82 | 7.3±1.2 | 90.8±1.3 | 1.4±0.3 | 0.5±0.2 | 7.12±0.44 |
| 12.5 | ♂ | 6.91±1.16 | 7.4±2.6 | 90.4±3.3 | 1.7±1.0 | 0.5±0.2 | 6.84±0.42 |
| 50 | ♂ | 8.73±1.70 | 11.0±2.6** | 85.5±3.7* | 3.0±1.1 | 0.6±0.3 | 7.54±0.12 |
| 100 | ♂ | 11.83±5.38 | 68.9±6.1*** | 25.3±5.2*** | 5.0±2.9 | 0.7±0.4 | 6.51±1.33 |
| 0 | ♀ | 3.44±2.23 | 7.6±4.2 | 89.6±5.1 | 1.7±0.9 | 1.0±0.1 | 7.22±0.21 |
| 12.5 | ♀ | 3.78±1.33 | 12.3±8.8 | 85.2±9.6 | 1.5±0.2 | 1.0±0.7 | 7.29±0.53 |
| 25 | ♀ | 9.92±2.65* | 23.2±19.0 | 73.9±20.1 | 1.9±1.2 | 1.0±0.3 | 6.67±0.16* |
| 50 | ♀ | 10.01±0.91* | 49.5±1.6** | 46.3±1.8** | 3.3±0.0 | 0.9±0.3 | 6.18±0.66 |
| 75 | ♀ | 7.17±3.15* | 53.7±25.2*** | 42.9±23.8*** | 2.0±0.4 | 1.5±1.1 | 5.68±1.79 |
| Dosage (mg/kg) | Sex |
Hb (g/dL) |
HCT (%) |
MCV (fL) |
MCH (Pg) |
MCHC (g/dL) |
PLT (109/L) |
| 0 | ♂ | 14.5±0.3 | 42.5±0.6 | 59.8±2.7 | 20.4±0.9 | 34.1±0.2 | 1,083±31 |
| 12.5 | ♂ | 14.1±0.6 | 40.7±1.3 | 59.6±2.1 | 20.6±0.5 | 34.6±0.4* | 1,036±67 |
| 50 | ♂ | 15.2±0.3 | 43.7±1.2 | 58.0±0.7 | 20.2±0.1 | 34.9±0.3** | 981±100* |
| 100 | ♂ | 13.0±2.7 | 36.0±6.6 | 55.5±1.2 | 19.9±0.1 | 35.9±1.0* | 1,300±304 |
| 0 | ♀ | 13.9±0.7 | 39.4±1.5 | 54.6±0.7 | 19.2±0.4 | 35.1±0.4 | 975±65 |
| 12.5 | ♀ | 14.7±0.7 | 41.0±1.6 | 56.4±2.1 | 20.1±0.8 | 35.8±0.4 | 925±51 |
| 25 | ♀ | 13.7±0.5* | 38.2±1.4 | 57.3±0.8* | 20.5±0.2* | 35.7±0.2* | 1,085±354 |
| 50 | ♀ | 12.1±1.7 | 34.7±3.2 | 56.1±0.8 | 19.6±0.6 | 34.8±1.7** | 1,733±296* |
| 75 | ♀ | 11.1±3.7 | 31.7±10.5 | 55.6±1.0 | 19.5±0.3 | 35.1±0.1* | 1,566±274 |
| Dosage (mg/kg) | Sex |
TP (g/L) |
Alb (g/L) |
ALT (U/L) |
AST (U/L) |
TBIL (umol/L) |
ALP (mmol/L) |
BUN (umol/L) |
| 0 | ♂ | 56.6±1.7 | 41.7±0.6 | 45.0±5.9 | 147.9±10.3 | 0.8±0.3 | 230±9 | 5.3±1.0 |
| 12.5 | ♂ | 56.3±1.7 | 41.9±2.4 | 40.2±5.9 | 106.4±15.2* | 0.8±0.5 | 249±57 | 5.1±1.6 |
| 50 | ♂ | 56.9±0.1 | 39.9±1.3 | 43.6±10.2 | 137.3±17.8 | 0.8±0.4 | 162±37* | 4.0±0.5 |
| 100 | ♂ | 52.2±1.6* | 29.5±3.3** | 23.4±8.9 | 99.4±32.1 | 0.2±0.3 | 106±22*** | 10.3±1.3** |
| 0 | ♀ | 60.1±2.3 | 46.7±2.2 | 32.9±4.6 | 110.8±10.8 | 1.4±0.4 | 103±21 | 6.7±0.6 |
| 12.5 | ♀ | 62.2±2.1 | 47.9±2.8 | 33.9±6.7 | 114.6±16.0 | 1.7±0.5 | 100±3 | 6.8±0.8 |
| 25 | ♀ | 61.2±6.5 | 46.6±5.7 | 34.7±9.7 | 100.0±11.2 | 1.1±0.7 | 69±34 | 9.2±1.6 |
| 50 | ♀ | 46.3±0.0* | 26.3±0.6** | 37.0±5.5 | 86.3±11.2 | 0.8±0.3 | 50±2* | 10.4±2.1 |
| 75 | ♀ | 56.3±6.6 | 35.7±9.1 | 38.7±26.0 | 117.7±22.7 | 1.4±0.4 | 79±21 | 12.1±6.1 |
| Dosage (mg/kg) | Sex |
Cr (g/L) |
Glu (g/L) |
K (mmol/L) |
NA (mmol/L) |
CL (umol/L) |
TG (mmol/L) |
TC (mmol/L) |
| 0 | ♂ | 26±1 | 5.50±0.71 | 4.90±0.13 | 142±1 | 100.5±1.6 | 0.51±0.20 | 1.25±1.05 |
| 12.5 | ♂ | 26±2 | 6.23±0.40 | 4.64±0.26 | 144±1 | 102.4±0.9 | 0.55±0.13 | 0.55±0.81 |
| 50 | ♂ | 25±4 | 5.97±0.10 | 4.59±0.09* | 143±1 | 100.5±0.2 | 1.36±0.51 | 2.09±0.32 |
| 100 | ♂ | 29±2 | 4.81±0.59 | 4.74±0.23 | 143±2 | 103.2±1.1 | 1.22±0.54 | 2.83±0.59 |
| 0 | ♀ | 38±6 | 5.64±0.26 | 4.15±0.60 | 142±2 | 99.6±2.3 | 0.40±0.12 | 1.38±0.23 |
| 12.5 | ♀ | 39±2 | 6.32±0.60 | 4.10±0.07 | 143±0 | 101.0±1.1 | 0.38±0.04 | 2.25±0.29* |
| 25 | ♀ | 40±5 | 5.87±0.59 | 3.88±0.12 | 142±2 | 98.9±3.7 | 0.46±0.08 | 1.96±0.63 |
| 50 | ♀ | 34±4 | 4.90±0.67 | 4.92±0.05 | 142±1 | 103.2±1.6 | 2.55±1.68 | 2.26±0.24* |
| 75 | ♀ | 36±4 | 5.84±1.07 | 4.76±0.49 | 144±1 | 102.0±0.9 | 0.73±0.08 | 2.52±0.01** |
| Dosage (mg/kg) | Sex | APTT(s) | PT(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ♂ | 8.0±1.5 | 7.8±0.3 |
| 12.5 | ♂ | 10.5±0.4 | 7.8±0.1 |
| 50 | ♂ | 9.0±2.2 | 7.7±0.1 |
| 100 | ♂ | 8.9±0.5 | 7.7±0.0 |
| 0 | ♀ | 9.8±0.7 | 8.6±0.6 |
| 12.5 | ♀ | 10.6±3.1 | 9.1±1.0 |
| 25 | ♀ | 9.4±1.8 | 8.5±0.2 |
| 50 | ♀ | 10.7±10.1 | 8.1±7.8 |
| 75 | ♀ | 11.4±0.1 | 8.0±0.4 |
| Dosage (mg/kg) | Sex | SPLEEN | LIVER | KIDNEY | ADRENALS | THYMUS |
| 0 | ♂ | 0.7249±0.0476 | 9.8091±0.9568 | 2.5069±0.0579 | 0.0428±0.0100 | 0.7038±0.1141 |
| 12.5 | ♂ | 0.6560±0.0804 | 9.6923±1.2075 | 2.4692±0.1912 | 0.0395±0.0030 | 0.5977±0.1305 |
| 50 | ♂ | 0.5780±0.0685* | 9.9034±0.7158 | 2.3161±0.1122 | 0.0403±0.0056 | 0.3358±0.1020* |
| 100 | ♂ | 0.2030±0.0202*** | 6.6913±0.4170** | 1.5625±0.0597*** | 0.0300±0.0052 | 0.0761±0.0257*** |
| 0 | ♀ | 0.6360±0.0877 | 7.7315±0.6535 | 1.9792±0.2029 | 0.0631±0.0111 | 0.5214±0.1420 |
| 12.5 | ♀ | 0.4255±0.0225* | 6.8255±0.1239 | 1.7739±0.0321 | 0.0557±0.0036 | 0.4555±0.0892 |
| 25 | ♀ | 0.3973±0.1707 | 6.3344±0.7277 | 1.5645±0.1521* | 0.0542±0.0107 | 0.2082±0.0900* |
| 50 | ♀ | 0.3414±0.0619* | 6.6504±0.3591 | 1.3779±0.1180* | 0.0488±0.0005 | 0.1233±0.1055* |
| 75 | ♀ | 0.2458±0.0670* | 6.4443±0.0599 | 1.4232±0.3043 | 0.0353±0.0006* | 0.0970±0.0851* |
| Dosage (mg/kg) | Sex | HEART | BRAIN | TESTICLE | EPIDIDIMS | OVARIES |
| 0 | ♂ | 1.2545±0.0688 | 1.8932±0.1410 | 2.6549±0.0202 | 0.6507±0.0917 | |
| 12.5 | ♂ | 1.2089±0.0494 | 1.8676±0.0664 | 2.8478±0.1281 | 0.6631±0.0919 | |
| 50 | ♂ | 1.1532±0.0469 | 1.9459±0.0988 | 2.8200±0.4947 | 0.6440±0.0882 | |
| 100 | ♂ | 0.8343±0.0399*** | 1.9045±0.0321 | 3.0220±0.3458 | 0.6166±0.0506 | |
| 0 | ♀ | 1.0607±0.0609 | 1.9342±0.0258 | 0.1396±0.0049 | ||
| 12.5 | ♀ | 0.9025±0.0885 | 1.8307±0.0090** | 0.1147±0.0185 | ||
| 25 | ♀ | 0.8658±0.1433 | 1.7825±0.1327 | 0.1126±0.0099* | ||
| 50 | ♀ | 0.8210±0.1025* | 1.8012±0.0477* | 0.0872±0.0306 | ||
| 75 | ♀ | 0.8776±0.0246* | 1.9177±0.0360 | 0.0864±0.0081** |
| Dosage (mg/kg) | Sex | SPLEEN | LIVER | KIDNEY | ADRENALS | THYMUS |
| 0 | ♂ | 0.2109±0.0115 | 2.8544±0.2808 | 0.7295±0.0186 | 0.0125±0.0030 | 0.2047±0.0320 |
| 12.5 | ♂ | 0.1968±0.0135 | 2.9350±0.5525 | 0.7418±0.0045 | 0.0119±0.0006 | 0.1798±0.0393 |
| 50 | ♂ | 0.1773±0.0230* | 3.0327±0.1533 | 0.7097±0.0303 | 0.0124±0.0020 | 0.1034±0.0334* |
| 100 | ♂ | 0.0882±0.0107*** | 2.9074±0.2773 | 0.6774±0.0030** | 0.0130±0.0026 | 0.0328±0.0097*** |
| 0 | ♀ | 0.2417±0.0379 | 2.9308±0.1816 | 0.7522±0.0913 | 0.0240±0.0043 | 0.1994±0.0620 |
| 12.5 | ♀ | 0.1684±0.0155* | 2.6983±0.1569 | 0.7006±0.0150 | 0.0220±0.0023 | 0.1802±0.0366 |
| 25 | ♀ | 0.1857±0.0878 | 2.9489±0.6734 | 0.7286±0.1627 | 0.0248±0.0037 | 0.0983±0.0507 |
| 50 | ♀ | 0.1701±0.0105 | 3.3385±0.2218 | 0.6904±0.0240 | 0.0246±0.0032 | 0.0589±0.0457 |
| 75 | ♀ | 0.1268±0.0143* | 3.3985±0.5195 | 0.7381±0.0389 | 0.0186±0.0027 | 0.0475±0.0366 |
| Dosage (mg/kg) | Sex | HEART | BRAIN | TESTICLE | EPIDIDIMS | OVARIES |
| 0 | ♂ | 0.3651±0.0219 | 0.2047±0.0320 | 0.7725±0.0052 | 0.1896±0.0286 | |
| 12.5 | ♂ | 0.3645±0.0302 | 0.1798±0.0393 | 0.8575±0.0476 | 0.1999±0.0315 | |
| 50 | ♂ | 0.3536±0.0197 | 0.1034±0.0334* | 0.8643±0.1515 | 0.1975±0.0284 | |
| 100 | ♂ | 0.3616±0.0054 | 0.0328±0.0097*** | 1.3080±0.1040*** | 0.2676±0.0247* | |
| 0 | ♀ | 0.4027±0.0274 | 0.1994±0.0620 | 0.0530±0.0040 | ||
| 12.5 | ♀ | 0.3563±0.0329 | 0.1802±0.0366 | 0.0452±0.0059 | ||
| 25 | ♀ | 0.4017±0.0932 | 0.0983±0.0507 | 0.0518±0.0047 | ||
| 50 | ♀ | 0.4166±0.1013 | 0.0589±0.0457 | 0.0430±0.0101 | ||
| 75 | ♀ | 0.4642±0.0880 | 0.0475±0.0366 | 0.0452±0.0031 |
| Dosage (mg/kg) | Sex | SPLEEN | LIVER | KIDNEY | ADRENALS | THYMUS |
| 0 | ♂ | 38.3281±1.4699 | 518.1590±34.5187 | 132.8023±7.9521 | 2.2943±0.7151 | 37.0121±3.5065 |
| 12.5 | ♂ | 35.2493±5.5822 | 518.7932±58.5405 | 132.5686±15.1094 | 2.1220±0.2353 | 32.0979±7.5437 |
| 50 | ♂ | 29.7780±4.2084* | 508.6051±11.9040 | 119.1164±5.4313 | 2.0837±0.3797 | 17.4630±6.0305** |
| 100 | ♂ | 10.6696±1.2342*** | 351.6505±28.0513** | 82.0323±2.3705*** | 1.5767±0.2993 | 3.9878±1.2975*** |
| 0 | ♀ | 32.8470±4.1430 | 399.7410±33.6162 | 102.3844±11.2781 | 3.2684±0.6109 | 26.9221±7.0784 |
| 12.5 | ♀ | 23.2407±1.1581* | 372.8430±6.4049 | 96.9035±2.0308 | 3.0424±0.1934 | 24.8936±4.9750 |
| 25 | ♀ | 22.0046±8.6217 | 355.1793±29.4804 | 87.8005±6.6001 | 3.0611±0.7300 | 11.5635±4.7535* |
| 50 | ♀ | 18.9152±2.9385* | 369.0860±10.1691 | 76.4363±4.5296 | 2.7078±0.0991 | 6.7703±5.6781* |
| 75 | ♀ | 12.8502±3.7331* | 336.1378±9.4321 | 74.3752±17.2626 | 1.8414±0.0641 | 5.0982±4.5316* |
| Dosage (mg/kg) | Sex | HEART | TESTICLE | EPIDIDIMS | OVARIES | WOMB |
| 0 | ♂ | 66.6880±8.6860 | 140.7071±9.5896 | 34.6570±6.6415 | ||
| 12.5 | ♂ | 64.8128±4.2740 | 152.7603±12.1614 | 35.5677±5.4317 | ||
| 50 | ♂ | 59.3902±4.4840 | 144.9807±25.1509 | 33.1594±4.9988 | ||
| 100 | ♂ | 43.7945±1.4480* | 158.6207±17.0399 | 32.4007±3.0500 | ||
| 0 | ♀ | 54.8691±3.7782 | 7.2153±0.2069 | 19.0245±3.2897 | ||
| 12.5 | ♀ | 49.2874±4.6447 | 6.2701±1.0382 | 21.6684±2.6783 | ||
| 25 | ♀ | 48.4052±5.3772 | 6.3180±0.3267* | 19.8641±6.5851 | ||
| 50 | ♀ | 45.6720±6.9008 | 4.8176±1.5724 | 16.2426±6.2479 | ||
| 75 | ♀ | 45.7604±0.4243* | 4.5077±0.5086** | 11.8367±1.0334 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




