1. Introduction
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a condition characterized by urinary urgency, which involves a sudden and intense need to urinate, accompanied by a sensation of bladder irritation, without urinary tract infection or any other obvious cause. It commonly involves both urinary frequency >8 times during the daytime, and nocturia (excessive urination at night) [
1,
2]. The prevalence of OAB in the population aged ≥65 y is 30.9% [
3,
4], and exerts a detrimental effect on physical activity, psychosocial well-being, and the quality of life [
5]. The treatment plan for OAB varies depending on the severity of the symptoms and the patient’s health status; common treatment options include behavioral therapy, pharmacotherapy, surgical treatment, etc.
Pharmacotherapy, along with behavioral therapy, is internationally recognized as the primary treatment for OAB, to relieve symptoms and reduce urge incontinence, and involves treatment with anticholinergics and/or β3-adrenergic receptor agonists. Anticholinergic drug therapy is the first-line treatment to help relax the bladder muscle and reduce the urgency and frequency of urination by blocking the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates bladder contractions. Some examples in this class include oxybutynin, solifenacin, tolterodine, and trospium [
6,
7]. β3-adrenergic receptor agonists such as mirabegron work by stimulating beta-3 adrenergic receptors in the bladder, resulting in the relaxation of the bladder muscle and increasing its capacity to hold urine. β3-adrenergic receptor agonists are used as an alternative to anticholinergic drugs for OAB treatment, especially in patients who cannot tolerate or do not respond well to anticholinergics [
8]. Several studies have reported significant therapeutic effects of monotherapy using both classes of medications [9-11]. However, oral antimuscarinics, commonly used as first-line treatment and in monotherapy, have high discontinuation rates because of bothersome side effects or inadequate clinical response [12-15]. To improve efficacy, clinicians either increase the dose of the drug [
16], switch to a different antimuscarinic, or try a combination of antimuscarinics to improve the therapeutic efficacy at the expense of producing higher rates of side effects [
17]. In cases where medication does not provide satisfactory treatment, procedures such as magnetic stimulation, bladder distension, alcohol injection, botulinum toxin injection, urinary diversion, augmentation cystoplasty, and neuromodulation are performed [
9,
18]. Given these procedures are more invasive or inconvenient treatment options [
18], combination pharmacotherapy may offer an additional promising non-invasive therapeutic management step between single-agent pharmacotherapy and more invasive approaches for the treatment of patients with OAB [
19]. In May 2018, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the combination therapy of a β3-adrenergic agonist and an antimuscarinic, solifenacin, as a pharmacological treatment option for OAB [
20].
Mirabegron, the first β3 adrenergic receptor agonist approved by the FDA for OAB treatment, has gradually gained acceptance in recent years as most clinical trials have reported better pharmacological profiles and improved patient compliance compared to antimuscarinics [21-23]. Tamsulosin, a selective α1 adrenergic receptor antagonist approved for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) [
24], enhances bladder storage function by inhibiting the C-fibers in the urethra, and alleviates sensory nerves’ response to bladder stimulation signals and pain. Thus, its efficacy and effectiveness in treating OAB have been evaluated [
25,
26]. In recent clinical trials, tamsulosin and mirabegron combination therapy for OAB treatment showed improvements in voiding symptoms and the absence of additional side effects [
27,
28]. Consequently, tamsulosin and mirabegron combination therapy is likely to be actively pursued as an alternative to conventional drugs for patients who cannot continue with existing drug therapies due to insufficient efficacy or drug-related side effects.
To validate and provide a basis for mirabegron and tamsulosin combination therapy, the potential drug-drug interactions (DDIs), based on the main metabolic pathway and excretion routes of each drug, should be considered. Mirabegron is metabolized extensively via various mechanisms including phase 1 and 2 metabolism, and is a moderate cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2D6 (CYP2D6) inhibitor, demonstrating an increase in the exposure of CYP2D6 substrates in several DDI studies [
29,
30]. Tamsulosin is primarily metabolized in the liver by cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) and CYP2D6 [
31]. Considering the metabolism of both drugs, there is the possibility of a CYP2D6-mediated DDI. Thus, this study aimed to evaluate the effects of DDIs between tamsulosin and mirabegron on their pharmacokinetics and safety profiles in healthy Korean male subjects.
2. Results
2.1. Demographic characteristics
A total of 36 male participants were enrolled in the study with informed consent. Among them, two participants withdrew from the study. Analysis of the demographic characteristics and safety was conducted for 36 participants who received at least one dose of the investigational product (IP). The mean along with the standard deviation (in parenthesis) of the age, height, weight, and body mass index (BMI) of the participants were 29.00 (7.93) y, 176.17 (6.35) cm, 77.01 (10.55) kg, and 24.76 (2.73) kg/m2, respectively.
2.2. Pharmacokinetic analysis
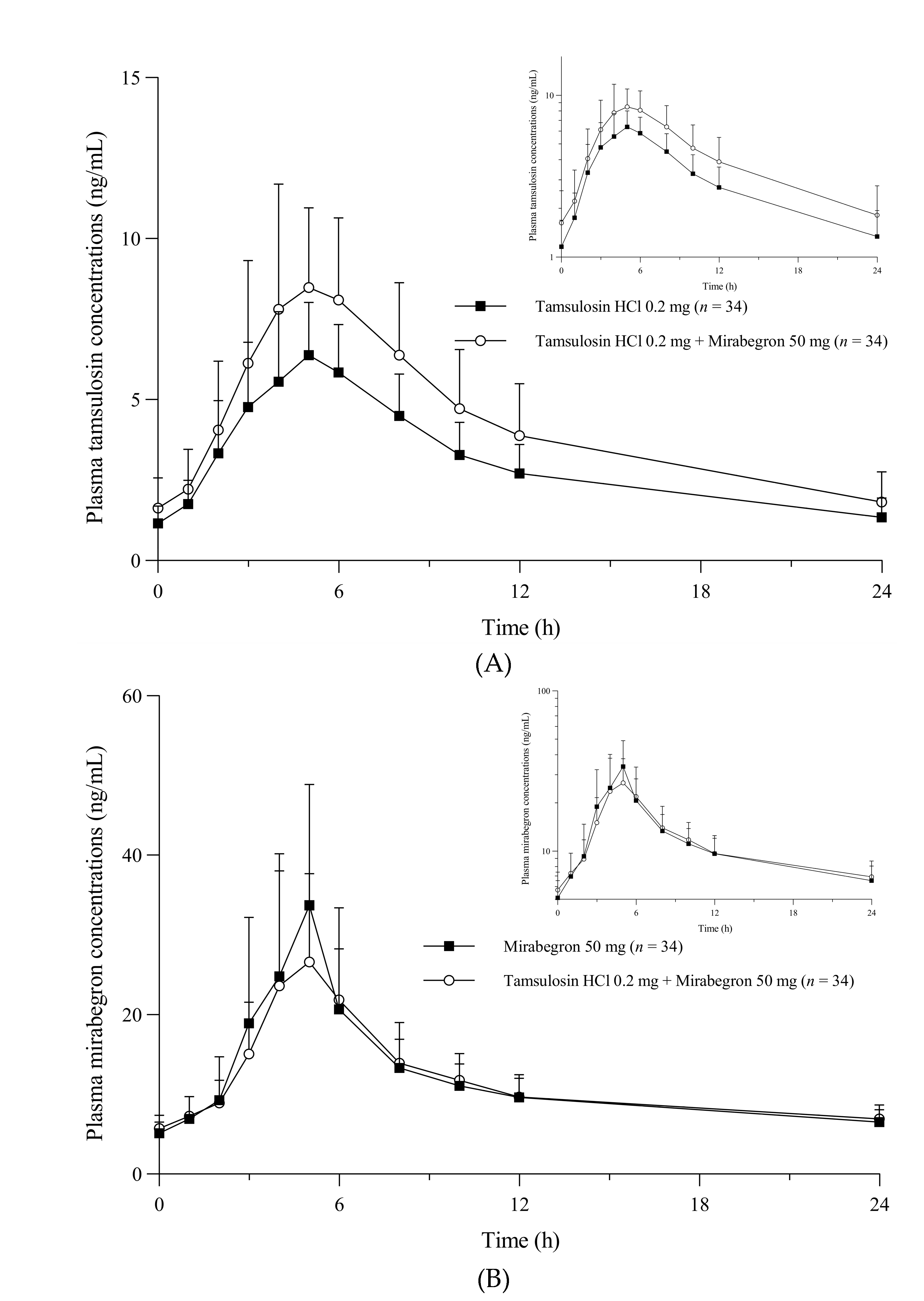
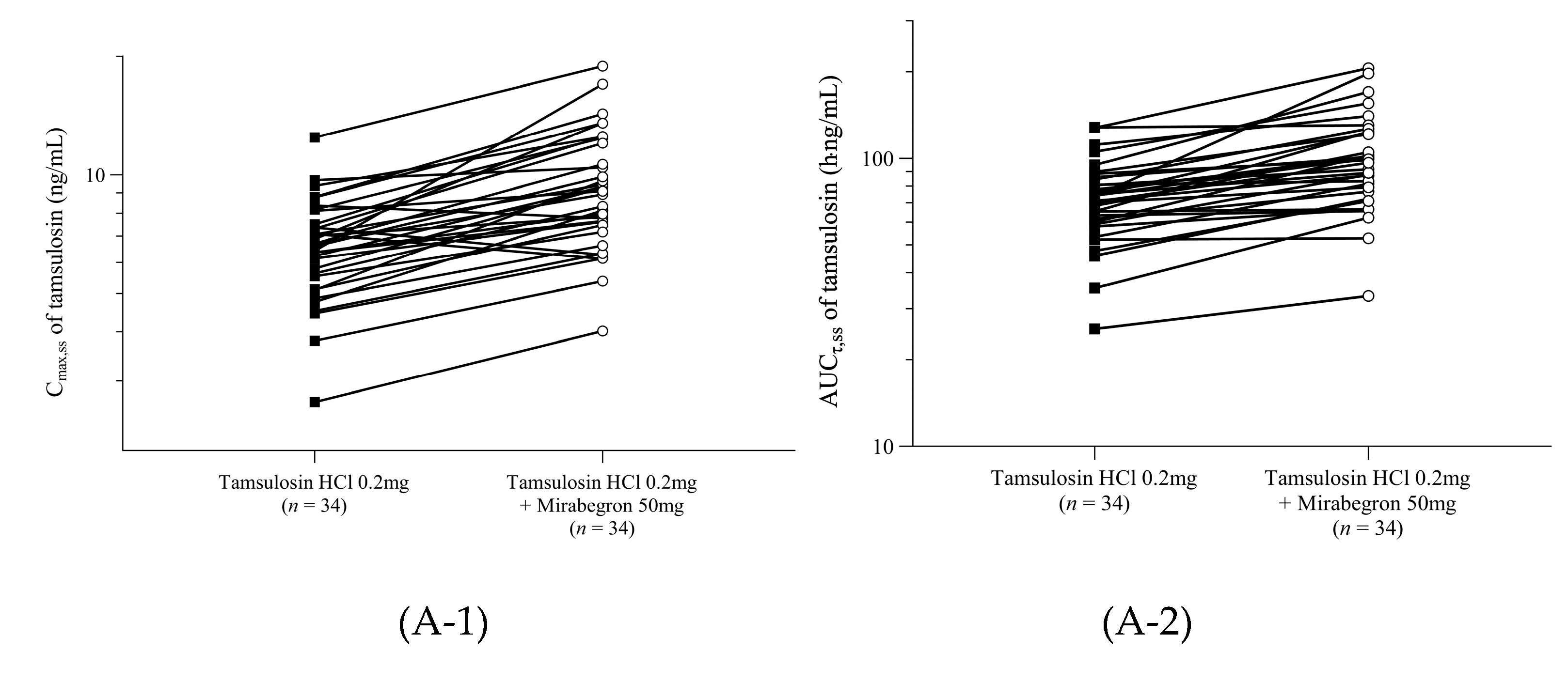
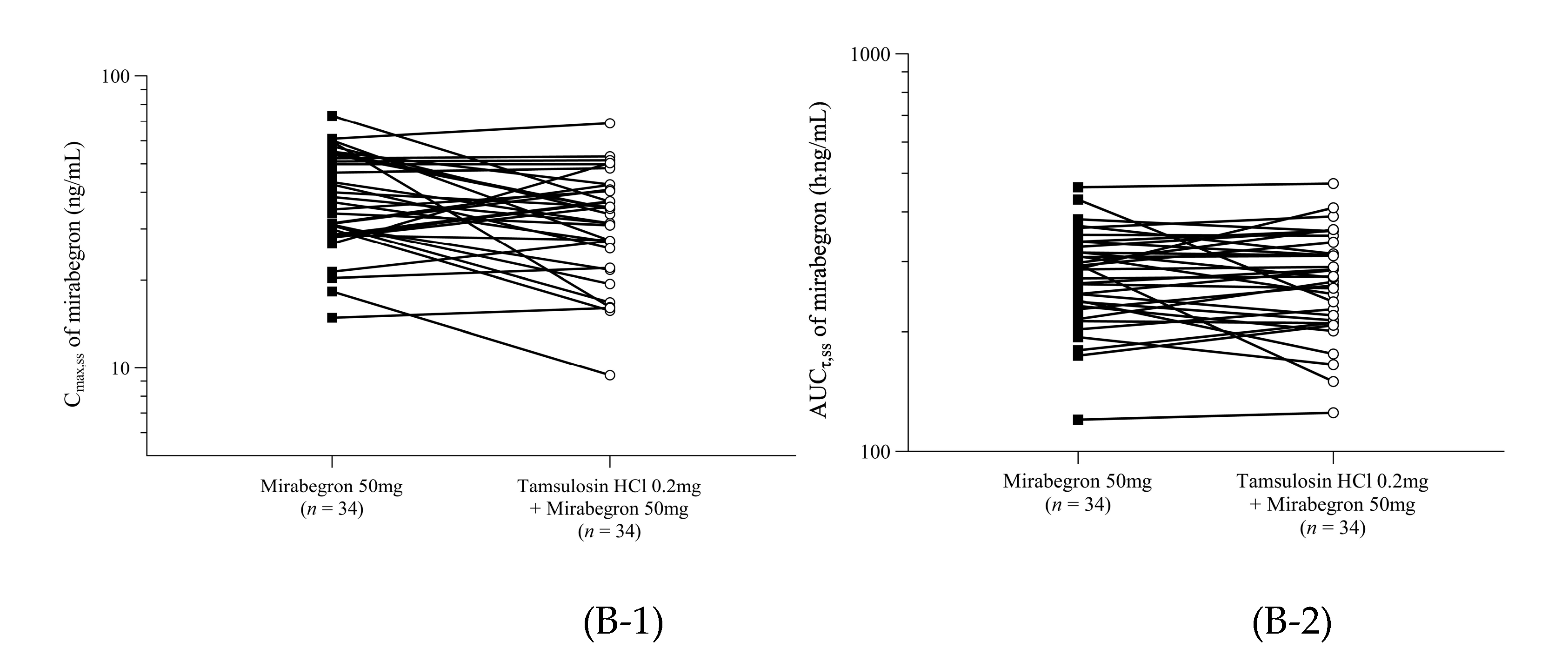
The pharmacokinetic set consisted of the 34 participants who underwent all blood samplings needed to calculate the pharmacokinetic parameters. The pharmacokinetic parameters for tamsulosin and mirabegron when administered alone or in combination are summarized in
Table 1. The mean plasma concentration-time plots for tamsulosin and mirabegron are presented in
Figure 1. The profile of the major pharmacokinetic parameters, the maximum plasma concentration at steady state (C
max,ss) and area under the concentration-time curve within a dosing interval at steady state (AUC
τ,ss), for each participant is presented in
Figure 2.
Comparing treatment with tamsulosin alone (T1) and tamsulosin combined with mirabegron (T3), both showed similar time-concentration graphs indicating a multiphasic elimination phase after reaching peak plasma concentrations at 5 h (
Figure 1A). However, mean C
max,ss and AUC
τ,ss for tamsulosin were 9.53 and 101.96 h·ng/mL in treatment with tamsulosin alone while they were 6.70 and 73.63 h·ng/mL in treatment with tamsulosin combined with mirabegron, respectively. The geometric mean ratio (GMR) and the 90% confidence interval (CI; in parenthesis) for C
max,ss and AUC
τ,ss of the treatment with tamsulosin combined with mirabegron to tamsulosin alone were 1.4018 (1.3127–1.4969) and 1.3609 (1.2786–1.4486), respectively (
Table 1). In T1, C
max,ss and AUC
τ,ss for tamsulosin increased about 1.4 times compared to T3 (
Figure 2A).
Comparing treatment with mirabegron alone (T2) and with tamsulosin combined with mirabegron (T3), both showed similar time-concentration graphs indicating a multiphasic elimination phase after reaching peak plasma concentrations at 5 h (
Figure 1B). For treatment with mirabegron alone and with tamsulosin combined with mirabegron, the mean C
max,ss was 39.50 and 33.48 ng/mL, the mean AUC
τ,ss was 282.75 and 277.63 h·ng/mL, and the mean t
1/2 was 19.72 and 19.81 h, respectively. The GMR (90% CI) for C
max,ss and AUC
τ,ss of treatment with tamsulosin combined with mirabegron to treatment with mirabegron alone were 0.8367 (0.7439–0.9410) and 0.9761 (0.9189–1.0369), respectively (
Table 1). Both C
max,ss and AUC
τ,ss decreased slightly in the combination treatment (T3) compared to T2; however, these changes were not clinically significant (
Figure 2B).
2.3. Safety analysis
Safety analysis was performed on 36 participants who received the IPs at least once. A total 19 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) occurred in 10 participants (27.78%); 5 TEAEs in 5 participants (13.89%) undergoing treatment with tamsulosin alone, 8 TEAEs in 5 participants (14.29%) undergoing treatment with mirabegron alone, and 6 TEAEs in 5 participants (14.71%) undergoing treatment with mirabegron combined with tamsulosin. All TEAEs were mild and resolved spontaneously without any medications, except for one TEAE (otitis media), which was resolved after treatment with antibiotics and painkillers. The details of the TEAEs are summarized in
Table 2. Among the TEAEs, 11 TEAEs occurring in 8 participants (22.22%) were assessed as adverse drug reactions (ADRs); 3 ADRs in 3 participants (13.89%) in T1, 3 ADRs in 3 participants (14.29%) in T2, and 5 ADRs in 5 participants (14.71%) in T3. There were no significant differences in the incidence of TEAEs and ADRs among the treatments (
p = 0.9952 and
p = 0.6696, respectively). In addition, the most common ADRs included headache, dizziness, and retrograde ejaculation (2 participants each); retrograde ejaculation was reported only for T3.
Vital signs and changes from the baseline measured on the screening day were evaluated, wherein the vital sign data measured predose on the last IP administration day for each treatment (days 5, 19, and 26 in T1, T2, and T3, respectively) (
Table 3). In all three treatments, the vital signs were within the normal range, and no significant difference was observed between the treatments regarding changes from the baseline.
No clinically significant changes were observed in the clinical laboratory test results (except for TEAEs), chest X-ray examinations, ECG measurements, or physical examinations.
3. Discussion
This study was designed as a randomized, open-label, multiple-dose, fixed-sequence, 3-period, 3-treatment study to evaluate the DDI between mirabegron and tamsulosin. Since tamsulosin is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 and CYP2D6, and mirabegron is a moderate inhibitor of CYP2D6, DDIs were evaluated in a steady state after multiple doses to maximize the chance of identification. In contrast, considering that this study was conducted in healthy volunteers, it was designed in a fixed sequence to minimize the duration of drug exposure from a risk-benefit perspective. This study was well-designed to evaluate the effects of DDI between the two IPs on their pharmacokinetics and safety.
The results of this study revealed that the combination of tamsulosin and mirabegron increased tamsulosin exposure (AUC
τ,ss, C
max,ss) by approximately 40%, while it only slightly decreased the C
max,ss for mirabegron, by approximately 17%, compared to mirabegron monotherapy. According to the classification of CYP inhibitors by the FDA [
32], a moderate inhibitor increases a sensitive index CYP substrate by 2–5-fold. In this study, the AUC
τ,ss for tamsulosin increased by approximately 1.4-fold only when combined with mirabegron, a moderate inhibitor of CYP2D6. This could be a result of the extensive metabolization of tamsulosin, mainly by CYP3A4 as well as CYP2D6 [
31,
33]. In contrast, mirabegron did not show any pharmacokinetic changes under co-administration with tamsulosin other than a slight decrease in C
max,ss by approximately 17%, which is consistent with the findings of a previous study [
34], and is considered clinically insignificant [
32].
In this study, tamsulosin and mirabegron were administered during the fasting state. According to the prescribing information for each drug, tamsulosin is recommended to be taken approximately one-half hour following a meal [
33] whereas mirabegron can be taken with or without food [
35], based on the results of their food effect studies. Although mirabegron exposures decrease with meals, it demonstrated both safety and efficacy irrespective of food contents and intake [
35]. The C
max,ss for tamsulosin, related to orthostasis, decreased when it was administered in the fed state; thus, it is recommended to take it after meals. In clinical settings, postprandial administration is reasonable when both drugs are taken in combination, and it is speculated that the magnitude of C
max,ss increase observed in this study would reduce.
No serious adverse events or clinically significant safety issues were observed in this study. In addition, given mirabegron, a beta-3 agonist, may increase heart rate and blood pressure, while tamsulosin may cause hypotension by alpha-a1 receptor-mediated vasodilation, the blood pressure and heart rate at steady-state during each treatment were analyzed. However, cardiovascular interactions were not observed, and the characteristics of headache and dizziness, the most common ADRs, were also unrelated to postural change. Namely, cardiovascular interactions between these two drugs were not clinically relevant in this study with a low therapeutic dose in healthy volunteers, similar to that in a previous study with a higher therapeutic dose (tamsulosin 0.4 mg, mirabegron 100 mg) in middle-aged to elderly men [
34]. Meanwhile, two retrograde ejaculations, which are well-known side effects of tamsulosin that are exacerbated in a dose-dependent manner [
33], were observed in the combination treatment. However, since the frequency of incidence and the sample size in this study were too small, it is difficult to infer the association between its incidence and DDIs.
There are some limitations to this study. First, tamsulosin 0.2 mg was administered in this study, while tamsulosin 0.4 mg once daily is the recommended dose for the treatment of the symptoms of BPH. However, tamsulosin exhibited dose-proportional pharmacokinetics, and its safety and efficacy were confirmed in previous studies [
27,
36], in which tamsulosin 0.2 mg and mirabegron 50 mg were co-administered for OAB patients. Therefore, the results of this study provide substantive evidence for pharmacokinetic DDIs. Second, this study was conducted on young male healthy volunteers, and the target condition, OAB, is prevalent in the elderly, especially women. Mirabegron has been reported to have no significant impact by age, but increases body weight corrected systemic exposure by about 20–30% in females; however, no dose adjustment is necessary for the elderly and based on gender [
35]. In contrast, it is suggested that the pharmacokinetics and dispositions of tamsulosin could exhibit a modest prolongation in elderly males, compared to young males. The intrinsic clearance of tamsulosin has been noted to decline concomitantly with advancing age, culminating in a notable 40% elevation in the total systemic exposure (signified by AUC
τ,ss) among individuals aged 55–75 y, in comparison to those aged 20–32 y. Nevertheless, it is noteworthy that no discernible differences in terms of overall safety or efficacy were perceptible between elderly and younger study participants. In addition, another study evaluating the effects of DDIs between mirabegron and tamsulosin in healthy middle-aged to elderly men demonstrated the absence of clinically relevant changes in cardiovascular safety or safety profiles [
34]. Therefore, our results support the findings of previous studies.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants and study design
This study was conducted at the Global Clinical Trials Center of the CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Republic of Korea, with strict adherence to
the key ethical principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki, the Good Clinical Practice Guidelines of the International Council for Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, and local laws and regulations. The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the MFDS and Institutional Review Board (IRB) of CHA University (IRB no. CHAMC 2020-04-051). Furthermore, the study has been registered and can be found on ClinicalTrials.gov (
https://clinicaltrials.gov, accessed on 24 July 2021), with the identifier NCT04485585.
Before the commencement of the clinical trial, the study information and other relevant details were provided to all participants. Screening procedures were conducted exclusively on individuals who voluntarily consented to participate in the clinical trial. The inclusion criteria focused on healthy males aged 19–55 y, who were assessed for their eligibility based on their medical history, vital signs, and the results of physical examination, clinical laboratory tests, and a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG). Meanwhile, the exclusion criteria included individuals with a clinically significant medical history, those who had participated in other clinical trials within the last six months before the screening, and those who were taking prescribed medications that could not be temporarily discontinued for at least two weeks before the screening.
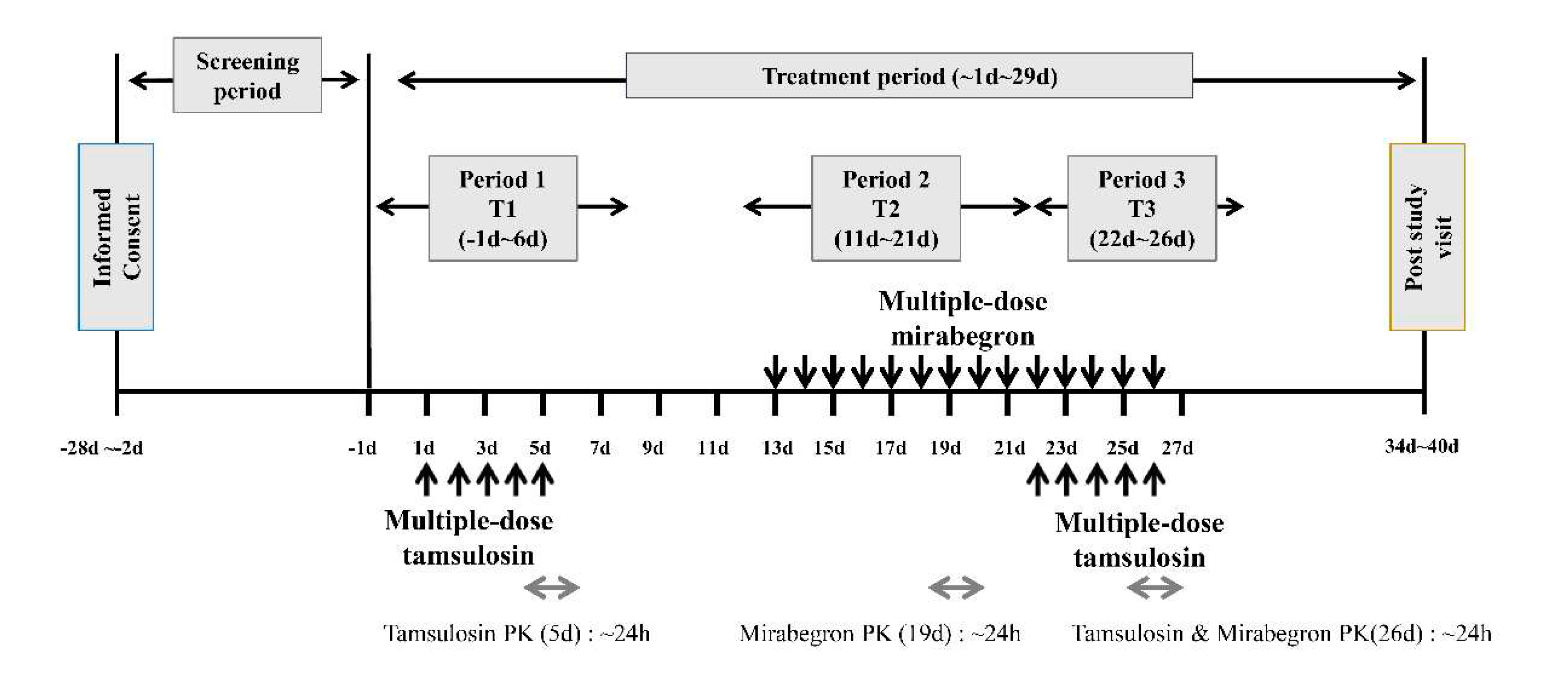
We conducted a randomized, open-label, multiple-dose, fixed-sequence, three-period, 3-treatment study (
Figure 3). The IPs included tamsulosin HCl (0.2 mg, Hanmi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.), and mirabegron (50 mg, Astellas Pharma Korea, Inc.). Eligible participants were divided into fixed sequence groups, and administered 0.2 mg tamsulosin HCl once daily for 5 d (T1). After a 5-day washout period, the participants were administered 50 mg mirabegron once daily for 11 d (T2). Next, the participants were further administered 50 mg mirabegron and 0.2 mg tamsulosin HCl for 5 d (T3). Considering a previous study that included 48 participants (24/arm) to evaluate the pharmacokinetic drug interaction between mirabegron and tamsulosin [
34], the required number of participants was set to 36, considering the dropout rate and to improve the validity of the clinical data. The 5-day washout period between periods 1 and 2 was more than 5 times the terminal half-life of tamsulosin (8.85 ± 2.98 h) [
37]. In contrast, there was no washout period between periods 2 and 3 to maintain a steady mirabegron concentration. During each period, the participants were administered either tamsulosin, mirabegron, or their combination with 150 mL of water during the fasting state. Blood samples were collected at the following time points: pre-dose of 1, 3, and 4 d pre-dose (0 h), and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 24 h post-dose of 5 d for tamsulosin; pre-dose of 11, 17, and 18 d pre-dose (0 h), and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, 24 h post-dose of 19 d for mirabegron; pre-dose of 24 and 25 d (tamsulosin only), and pre-dose (0 h) and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 24 h post-dose of 26 d, for tamsulosin and mirabegron.
4.2. Blood sampling and determination of tamsulosin and mirabegron plasma concentrations
Blood samples were collected in heparinized tubes at each blood sampling time point, and the plasma was separated through centrifugation at 1900× g for 10 min at 4 °C. The collected plasma samples were transferred to 2 Eppendorf tubes at a volume of approximately ≥1.0 mL and stored in a freezer at ≤−70 °C, until further analysis.
The plasma concentrations of tamsulosin and mirabegron were determined through liquid chromatography (tamsulosin: Exion LC, AB SCIEX, Washington D.C., USA; mirabegron: Shimadzu Prominence ultra-fast LC, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) combined with tandem mass spectrometry (tamsulosin: API 4000, AB SCIEX, Washington D.C., USA; mirabegron: QTRAP 6500+, AB SCIEX, Washington D.C., USA), based on validated analytical procedures adopted by the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. For tamsulosin, the calibration curves were linear in the range of 0.1–50 ng/mL (correlation coefficient, r>0.9950), with the lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) as 0.1 ng/mL. The assay range for mirabegron was 0.2–200 ng/mL (r>0.9950), with the LLOQ as 0.2 ng/mL. The accuracy of the assay was within the range of 98.5–105.8% for tamsulosin, and 87.0–111.3% for mirabegron. The precision coefficients of variation for tamsulosin and mirabegron were <6.0% and <13.5%, respectively.
4.3. Pharmacokinetic assessment
Non-compartmental analysis was performed using the Phoenix WinNonlin software version 8.2 (Certara Co., Princeton, NJ, USA), to determine the following pharmacokinetic parameters for tamsulosin and mirabegron: Cmax,ss, the minimum plasma concentration at steady state (Cmin,ss), time to reach Cmax,ss (Tmax,ss), AUCτ,ss, elimination half-life at steady state (t1/2), apparent clearance at steady state (CLss/F), and apparent volume of distribution at steady state (Vdss/F). Plasma drug concentration-time profiles are presented in linear and log-transformed scales. Cmax,ss, Cmin,ss, and Tmax,ss were measured, and AUCτ,ss was calculated by using the linear trapezoidal linear interpolation method. The elimination rate constant (ke) was estimated by performing a linear regression analysis on the data points included in the terminal phase of the log-linear plot of the concentration-time data, and the t1/2 was calculated from the ratio of the natural logarithm of 2 and ke. CLss/F was calculated as Dose/AUCτ, and Vdss/F was calculated as (CLss/F)/ke.
4.4. Safety assessment
Safety was evaluated based on TEAEs, vital signs, and the results of physical examination, 12-lead ECGs, and clinical laboratory tests. TEAEs were either spontaneously reported by the participants or identified through the data collected during scheduled interviews throughout the study period. Vital signs, including systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and heart rate, were measured at the baseline of each visit (0 h), except for visits involving IP administration, as these were measured before IP administration. These measurements were performed with the participant maintaining a stable supine position for at least 3 min, ensuring no sudden positional changes. All TEAEs were coded according to the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities version 23.0, and summarized based on treatment, severity, and association with tamsulosin and mirabegron.
4.5. Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to summarize baseline demographics, such as age, weight, height, and BMI. Pharmacokinetic parameters and safety profiles were also evaluated using descriptive statistics. All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Primary pharmacokinetic endpoints (Cmax,ss and AUCτ,ss) were log-transformed to develop a mixed effects model with the treatment effect as the fixed effect and participant effect as the random effect. GMRs with 90% CIs of the primary pharmacokinetic parameters between the tamsulosin alone vs. tamsulosin and mirabegron, and mirabegron alone vs. tamsulosin and mirabegron treatments were estimated to evaluate the pharmacokinetic drug interactions. Numerical data for these two treatments were compared using the independent t-test or Mann-Whitney U test, and that for all treatments were compared using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). The Scheffe method was used for the post hoc analysis along with ANOVA. Categorical data were compared using the Chi-squared or Fisher’s exact test.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, no clinically relevant DDIs regarding the pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability between tamsulosin and mirabegron were observed. It is expected that the combination therapy of these two drugs could contribute to synergistic effects due to differing mechanisms and increased compliance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.S. and A.K.; Methodology, W.S. and A.K.; Validation, A.K.; Formal analysis, W.S.; Investigation, W.S., A.-Y.Y., H.Y., and A.K.; Resources, A.K.; Data curation, W.S.; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, W.S.; Writing – Review & Editing, W.S., A.-Y.Y., H.Y., and A.K.; Visualization, W.S.; Supervision, A.K.; Project administration, A.K.; Funding Acquisition, A.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Boryung Co., Ltd (grant no. BR-TMC-CT-101).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, the International Conference on Harmonization Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice (ICH-GCP), and the Korean Good Clinical Practice guidelines and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of CHA University, Bundang Medical Center, located in Seongnam, Korea (IRB No. CHAMC 2020-04-051).
Informed Consent Statement
All subjects voluntarily consented to participate in the clinical trial.
Data Availability Statement
The data are not publicly available due to confidentiality reasons.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to all the patients and staff who participated in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Gormley EA, Lightner DJ, Faraday M, Vasavada SP, American Urological A, Society of Urodynamics FPM. Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline amendment. J Urol. 2015, 193, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrijens D, Drossaerts J, van Koeveringe G, Van Kerrebroeck P, van Os J, Leue C. Affective symptoms and the overactive bladder - a systematic review. J Psychosom Res. 2015, 78, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milsom I, Abrams P, Cardozo L, Roberts RG, Thuroff J, Wein AJ. How widespread are the symptoms of an overactive bladder and how are they managed? A population-based prevalence study. BJU Int. 2001, 87, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart WF, Van Rooyen JB, Cundiff GW, Abrams P, Herzog AR, Corey R, et al. Prevalence and burden of overactive bladder in the United States. World J Urol. 2003, 20, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha S, Parsons M. Treatment of overactive bladder in the aging population: focus on darifenacin. Clin Interv Aging. 2006, 1, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussman, DO. Overactive bladder: treatment options in primary care medicine. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2007, 107, 379–385. [Google Scholar]
- Thiagamoorthy G, Cardozo L, Srikrishna S. Drug therapy for an overactive bladder. Womens Health (Lond). 2015, 11, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco E, Bientinesi R. Mirabegron: a review of recent data and its prospects in the management of overactive bladder. Ther Adv Urol. 2012, 4, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold J, McLeod N, Thani-Gasalam R, Rashid P. Overactive bladder syndrome - management and treatment options. Aust Fam Physician. 2012, 41, 878–883. [Google Scholar]
- Nitti VW, Khullar V, van Kerrebroeck P, Herschorn S, Cambronero J, Angulo JC, et al. Mirabegron for the treatment of overactive bladder: a prespecified pooled efficacy analysis and pooled safety analysis of three randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III studies. Int J Clin Pract. 2013, 67, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams P, Andersson KE, Apostolidis A, Birder L, Bliss D, Brubaker L, et al. 6th International Consultation on Incontinence. Recommendations of the International Scientific Committee: EVALUATION AND TREATMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE, PELVIC ORGAN PROLAPSE AND FAECAL INCONTINENCE. Neurourol Urodyn. 2018, 37, 2271–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Souza AO, Smith MJ, Miller LA, Doyle J, Ariely R. Persistence, adherence, and switch rates among extended-release and immediate-release overactive bladder medications in a regional managed care plan. J Manag Care Pharm. 2008, 14, 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Sexton CC, Notte SM, Maroulis C, Dmochowski RR, Cardozo L, Subramanian D, et al. Persistence and adherence in the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome with anticholinergic therapy: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Clin Pract. 2011, 65, 567–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeaw J, Benner JS, Walt JG, Sian S, Smith DB. Comparing adherence and persistence across 6 chronic medication classes. J Manag Care Pharm. 2009, 15, 728–740. [Google Scholar]
- Chancellor MB, Migliaccio-Walle K, Bramley TJ, Chaudhari SL, Corbell C, Globe D. Long-term patterns of use and treatment failure with anticholinergic agents for overactive bladder. Clin Ther. 2013, 35, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman HB, Oelke M, Kaplan SA, Kitta T, Russell D, Carlsson M, et al. Do patient characteristics predict which patients with overactive bladder benefit from a higher fesoterodine dose? Int Urogynecol J. 2019, 30, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang CC, Jiang YH, Kuo HC. Efficacy and Adherence of Flexibly Adding on a Second Antimuscarinic Agent for Patients with Refractory Overactive Bladder. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2017, 9, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkman JS, Smith CP, Staskin DR. Surgical options for drug-refractory overactive bladder patients. Rev Urol. 2010, 12, e97–e110. [Google Scholar]
- El-Zawahry A, Rizk DEE. Combination pharmacotherapy for the treatment of the overactive bladder syndrome: a new solution for an old problem? Int Urogynecol J. 2020, 31, 855–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA Approves Mirabegron, Solifenacin Combo for OAB. Food and Drug Administration2018 [Available from: http://fdadaily.com/2018/05/09/fda-approves-mirabegron-solifenacincombo-for-oab/.
- Hsu FC, Weeks CE, Selph SS, Blazina I, Holmes RS, McDonagh MS. Updating the evidence on drugs to treat overactive bladder: a systematic review. Int Urogynecol J. 2019, 30, 1603–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelleher C, Hakimi Z, Zur R, Siddiqui E, Maman K, Aballea S, et al. Efficacy and Tolerability of Mirabegron Compared with Antimuscarinic Monotherapy or Combination Therapies for Overactive Bladder: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Eur Urol. 2018, 74, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staskin D, Herschorn S, Fialkov J, Tu LM, Walsh T, Schermer CR. A prospective, double-blind, randomized, two-period crossover, multicenter study to evaluate tolerability and patient preference between mirabegron and tolterodine in patients with overactive bladder (PREFER study). Int Urogynecol J. 2018, 29, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepor, H. Alpha blockers for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Rev Urol. 2007, 9, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevisani M, Campi B, Gatti R, Andre E, Materazzi S, Nicoletti P, et al. The influence of alpha1-adrenoreceptors on neuropeptide release from primary sensory neurons of the lower urinary tract. Eur Urol. 2007, 52, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama O, Yusup A, Oyama N, Aoki Y, Miwa Y, Akino H. Improvement in bladder storage function by tamsulosin depends on suppression of C-fiber urethral afferent activity in rats. J Urol. 2007, 177, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichihara K, Masumori N, Fukuta F, Tsukamoto T, Iwasawa A, Tanaka Y. A randomized controlled study of the efficacy of tamsulosin monotherapy and its combination with mirabegron for overactive bladder induced by benign prostatic obstruction. J Urol. 2015, 193, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada N, Iuchi H, Kita M, Hashizume K, Matsumoto S, Kakizaki H. Urodynamic Efficacy and Safety of Mirabegron Add-on Treatment with Tamsulosin for Japanese Male Patients with Overactive Bladder. Low Urin Tract Symptoms. 2016, 8, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura Y, Iitsuka H, Toyoshima J, Kuroishi K, Hatta T, Kaibara A, et al. Pharmacokinetic drug interaction study between overactive bladder drugs mirabegron and tolterodine in Japanese healthy postmenopausal females. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2016, 31, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauwinkel W, Dickinson J, Schaddelee M, Meijer J, Tretter R, van de Wetering J, et al. The effect of mirabegron, a potent and selective beta3-adrenoceptor agonist, on the pharmacokinetics of CYP2D6 substrates desipramine and metoprolol. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2014, 39, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Salinas G, de la Rosette JJ, Michel MC. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of tamsulosin in its modified-release and oral controlled absorption system formulations. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2010, 49, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Drug Interaction Studies — Cytochrome P450 Enzyme- and Transporter-Mediated Drug Interactions Guidance for Industry. Food and Drug Administration2020 [Available from: https://www.fda.gov/media/134581/download.
- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION, FLOMAX (tamsulosin hydrochloride) capsules. Initial U.S. Approval: 1997 Food and Drug Administration1997 [Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2009/020579s026lbl.pdf.
- van Gelderen M, Tretter R, Meijer J, Dorrepaal C, Gangaram-Panday S, Brooks A, et al. Absence of clinically relevant cardiovascular interaction upon add-on of mirabegron or tamsulosin to an established tamsulosin or mirabegron treatment in healthy middle-aged to elderly men. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2014, 52, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION, MYRBETRIQ (mirabegron extended-release tablets) for oral use. Initial U.S. Approval: 2012 Food and Drug Administration2012 [Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/202611s011lbl.pdf.
- Kakizaki H, Lee KS, Yamamoto O, Jong JJ, Katou D, Sumarsono B, et al. Mirabegron Add-on Therapy to Tamsulosin for the Treatment of Overactive Bladder in Men with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: A Randomized, Placebo-controlled Study (MATCH). Eur Urol Focus. 2020, 6, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park S-I RS-j, Jang I-J, Yu K-S, Yim S-V, Kim B-H. Bioequivalence of the pharmacokinetics between two formulations of 0.2 mg tamsulosin hydrochloride in healthy subjects. Translational and Clinical Pharmacology. 2015, 23, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).