1. Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a global health issue in the modern world and causes more than 600,000 deaths throughout the world per year. Among cancers, HCC is the 5
th most common type of cancer prevailing worldwide, and the mortality is increasing daily due to poor prognosis and therapeutic option availability [
1]. The incidence of HCC is slow and gradual, which is why it can be diagnosed at an early stage, but the survival rate is 60-70% due to ineffective treatment [
2,
3,
4]. Until the FDA approved sorafenib for the systemic treatment of HCC, there were no such therapeutic agents to properly treat the condition. It has been used for more than ten years for the targeted therapy of HCC [
5,
6]. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is actually a group of tumors that originate from the highly diffuse heterogeneous epithelium of renal tubules. After bladder and prostate cancer, it is the third most common urological malignancy and accounts for approximately 3% of all cancers [
7,
8]. The mortality rate is high, i.e.,
˃ 100,000 per anum, and the incidence is ≥ 200,000 cases per anum [
8]. It is more common in men than in women, i.e., 1.5 times higher, and its presentation is higher in patients with a median age of 62 [
9,
10].
Pluronic F-127 has amphiphilic characteristics and is a tri-block (PEO-PPO-PEO), nonionic surfactant property developed from two basic monomeric units, i.e., poly ethylene oxide (hydrophobic) and poly propylene oxide (hydrophilic). Due to its biocompatible and nontoxic nature, it is used as a drug carrier in many forms of cancer and skin diseases. Pluronic F-127 also inhibits the efflux transport protein system (p-glycoprotein), resulting in increased permeation and diffusion (internalization) of active compounds inside the tumor cells and ultimately stability of the compounds [
11]. Pluronic F-127 can overcome multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancers through the glutathione/glutathione-S-transferase detoxification system [
12]. The nanoparticles are usually phagocytized when recognized by the host immune system (reticuloendothelial system) and, as a result, are eliminated from the body. Therapeutic efficacy, particularly in cancerous cells, can be increased by prolonging the circulation half-life and targeting the affected organ by surface modification of nanoparticles with polymers or surfactants. Alternately, biodegradable copolymers such as pluronic/poloxamer, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and polyethylene glycol (PEG) are used as surface modifiers to decrease the opsonization of the nanoparticles [
13].
As a chemotherapeutic agent, sorafenib (SFB) has proven efficacy against diffrent types of cancers, melanoma, cholangiocarcinoma and acute myeloid leukemia [
14]. SFB use is marred by its side effects, which include hand-foot syndrome, decreased heart blood flow, heart attack, intestinal perforations, thyroid hormone alterations, appetite loss, diarrhea, nausea and fatigue. Reduced water solubility, rapid clearance and metabolism are other factors that has limited SFB use. To minimize the side effects of SFB, controlled and targeted drug delivery to the tumor can be achieved by using biodegradable ploymeric nanoformulation technology [
15]. All the above mentioned drawbacks have been over come by the use of PLGA nanopartcle and its composite and can selectively target the tumor tissues. PLGA is a synthetic, biodegradable and biocompatible polymer. Apart from its use in drug delivery systems, it is also used in sutures [
16], bone fixation and screw materials [
17,
18,
19]. The Krebs cycle is responsible for the removal of PLGA from the body without affecting the normal physiology of the body [
20]. The effectiveness of PLGA is dependent on the cell environment and fusion with lysosomes [
20,
21]. The previous studies have shown nanoparticles with low drug loading (1.4%), by using the solvent evaporation method which was later on imroved to 5.3% by nanoprecipitation method causing low encapsulatiom efficiency (2.4%). Other attempts including nanocarriers and lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles have been done in the form of drug combination for the synergistic effects; such as the doxorubicin and sorafenib but with low drug loading (2.4%) [
1]. Polymers based nanoformulations improved biodistribution and kinetic parameters, resulting in enhanced efficacy [
22,
23]. Studies have revealed that the EPR effect is responsible for the increased accumulation of nanoparticulates in solid tumors [
24,
25]. Nanoparticles can also modulate the efflux of drugs from tumors by overcoming MDR mediated by P-glycoprotein, resulting in increased levels of the drug inside the tumors [
26,
27]. Polymeric nanoformulations have some drawbacks, such as nongradual and inconsistent drug release, stability problems and hemolytic activity. Embolization of vessels and local toxicities at the site of injection are problems associated with intravenous administration of hydrophobic anticancer drugs such as sorafenib.
In this particular study the PLGA nanoparticles will be prepared by midified solvent evaporation method using pluronic F-127 as a stablizer. The focus will be to prepare nanoparticles with optimum particle size, polydispersity, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency, drug loading, in-vitro drug release (sustained and controlled) and in-vivo pharmacokinetics for the targeted delivery of nanoparticles to liver and kidneys by controlling the physicochemical characteristics.
2. Results
2.1. Physiochemical Characterization
2.1.1. Dynamic Light Scattering
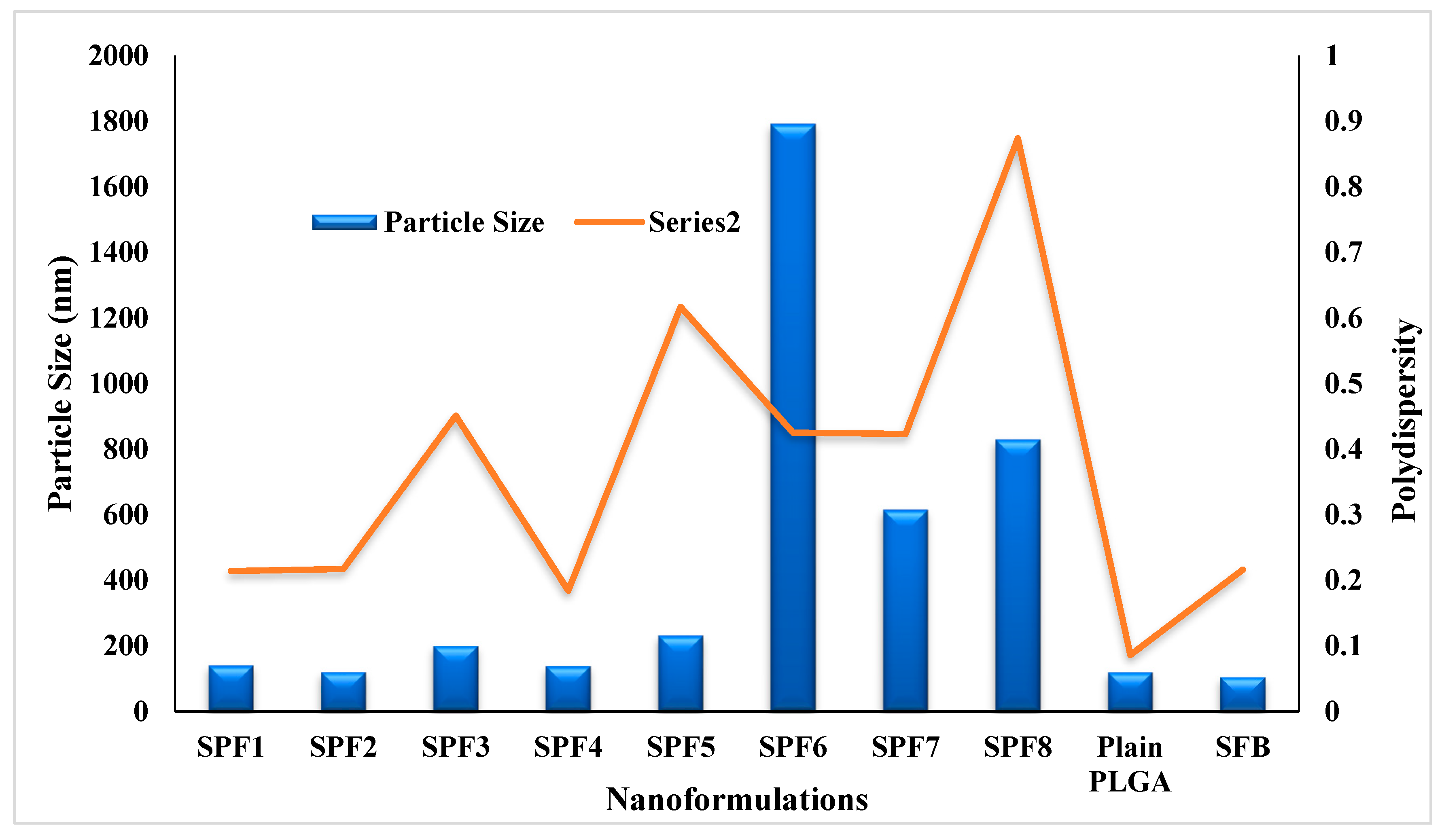
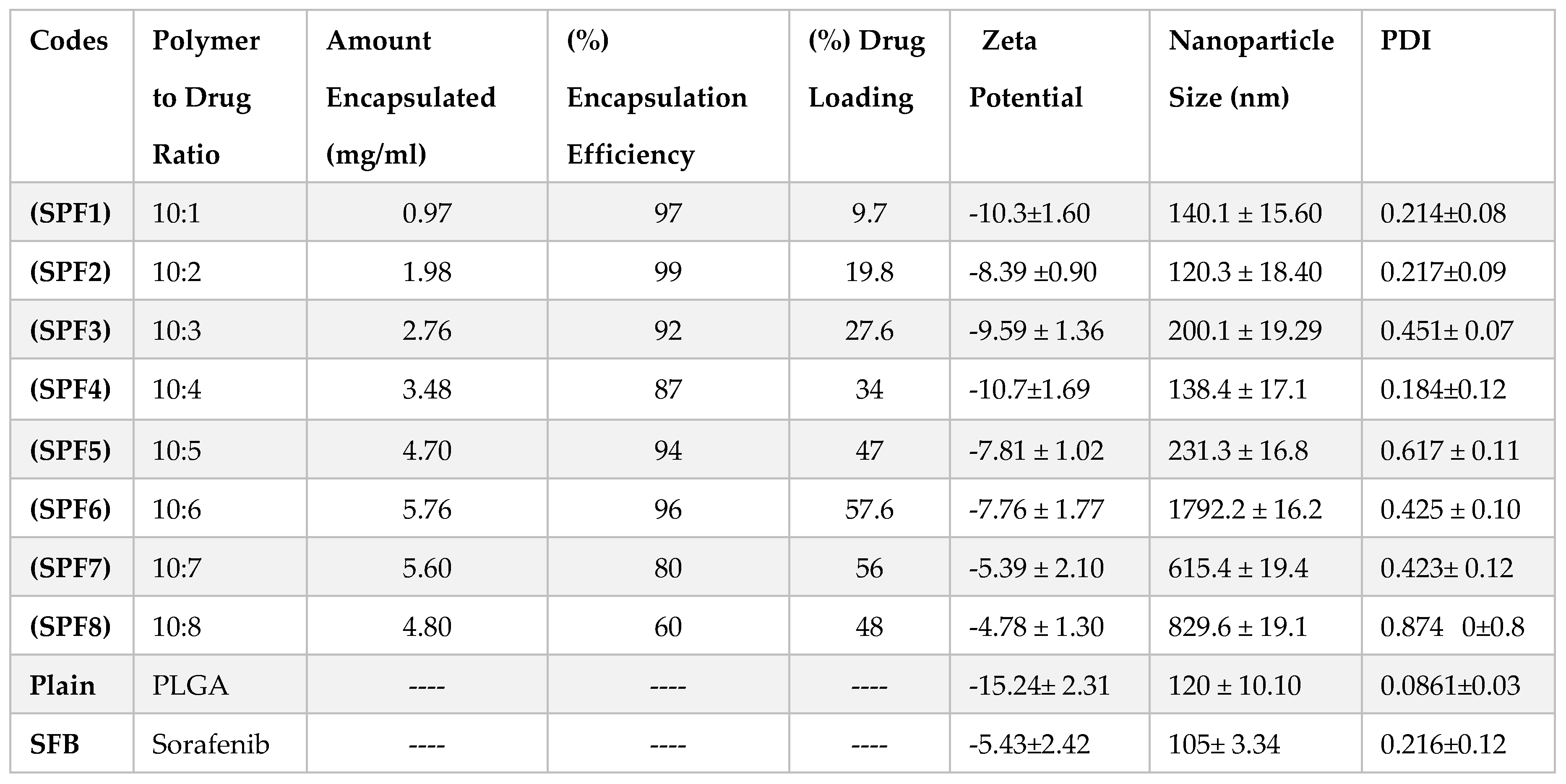
The quantity (10 mg) of Pluronic F-127 (1%) and PLGA was kept constant in the formulations. The particle size and PDI were in the range of 120-1792 nm and 0.184-0.874, resepectively as described in
Table 1 and
Figure 1. The data showed that increasing the concentration of the drug in formulation resulted in the larger size nanoparticles. The increase in nanoparticle size was due to the increased amount of drug in the emulsion nano-droplets. The monodispersity of the particles was changed to polydispersity down the table (0.214 to 0.874) (
Table 1 and
Figure 1) [
28]. The values of zeta potential varied between -10.7 and -4.8 mV (
Table 1). The plain nanoparticles have the size of 120nm, zeta potential of -15 mV
.
2.1.2. Encapsulation Efficiency and Drug Loading
Pluronic is one of the most common stabilizers used because it encapsulates both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs. The values for % EE ranged from 99 % to 60 % while the % DL values were dependent on the drug to polymer ratios and varied in the range of 9.7 to 56.7 as shown in
Table 1.
2.1.3. FTIR Analysis
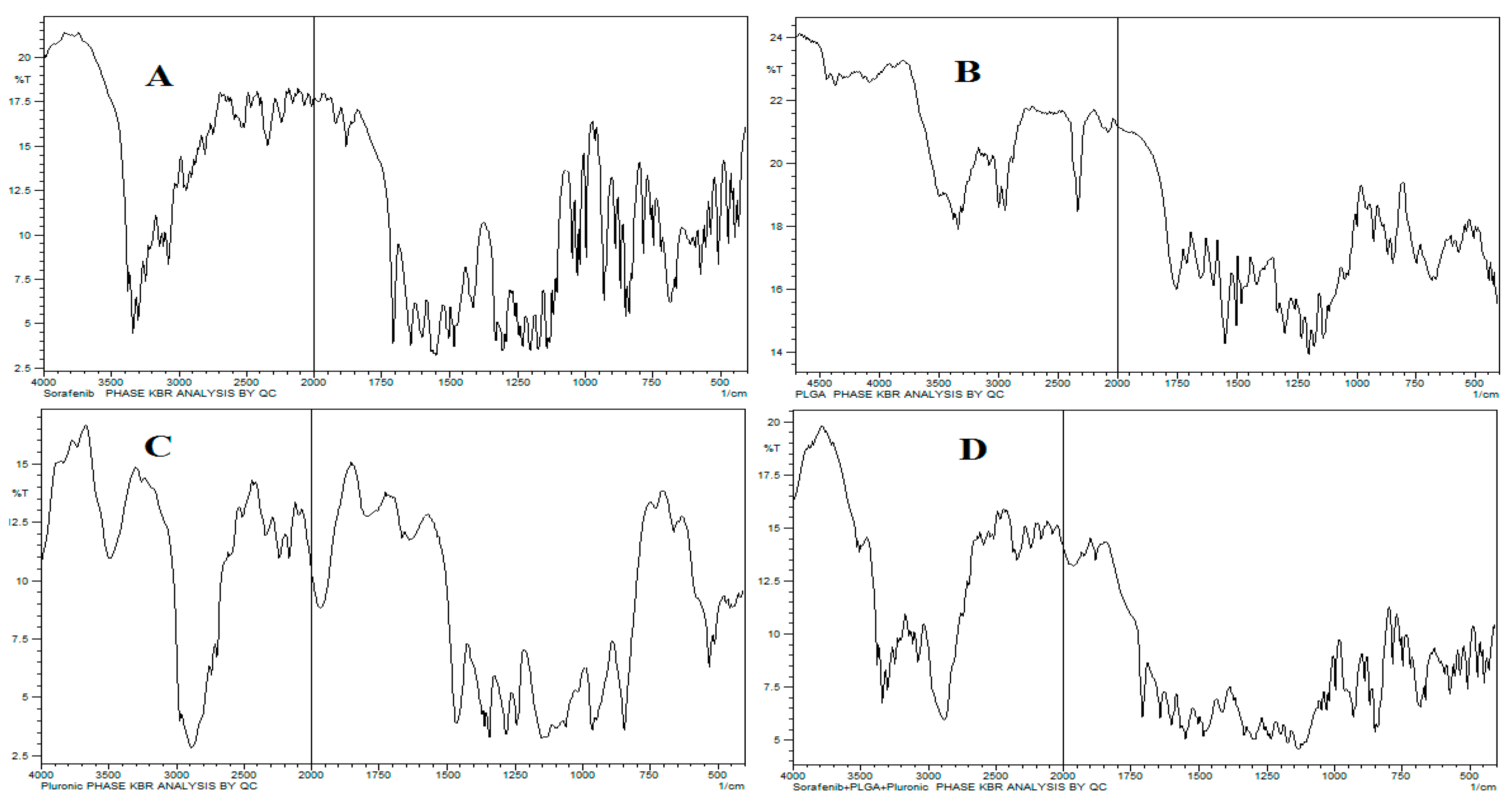
The characteristic wavenumbers for SFB were 1598 cm−1 for carboxylic acid/derivatives, 3080 cm−1 for C=CH2, and 3288 cm−1 for high concentrations of -OH, and the -C=O double bond was observed at approximately 1740 cm-1. The presence of specific IR frequencies at 1166 cm−1 and 1384 cm−1 was for C=C stretching of the aromatic amine group. The 75:25 PLGA gave its characteristic bands, such as OH stretching (3200-3500 cm-1), –CH (2850-3000 cm-1), carbonyl –C=O stretching (1700-1850 cm-1) and C–O stretching (1050-1250 cm-1).
The band located at 1100 cm
-1 was a characteristic peak for C–O–C stretching vibrations, while a -OH group trough was observed at 3200-3500 cm
-1 in pluronic F-127, as shown in
Figure 2.
2.1.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
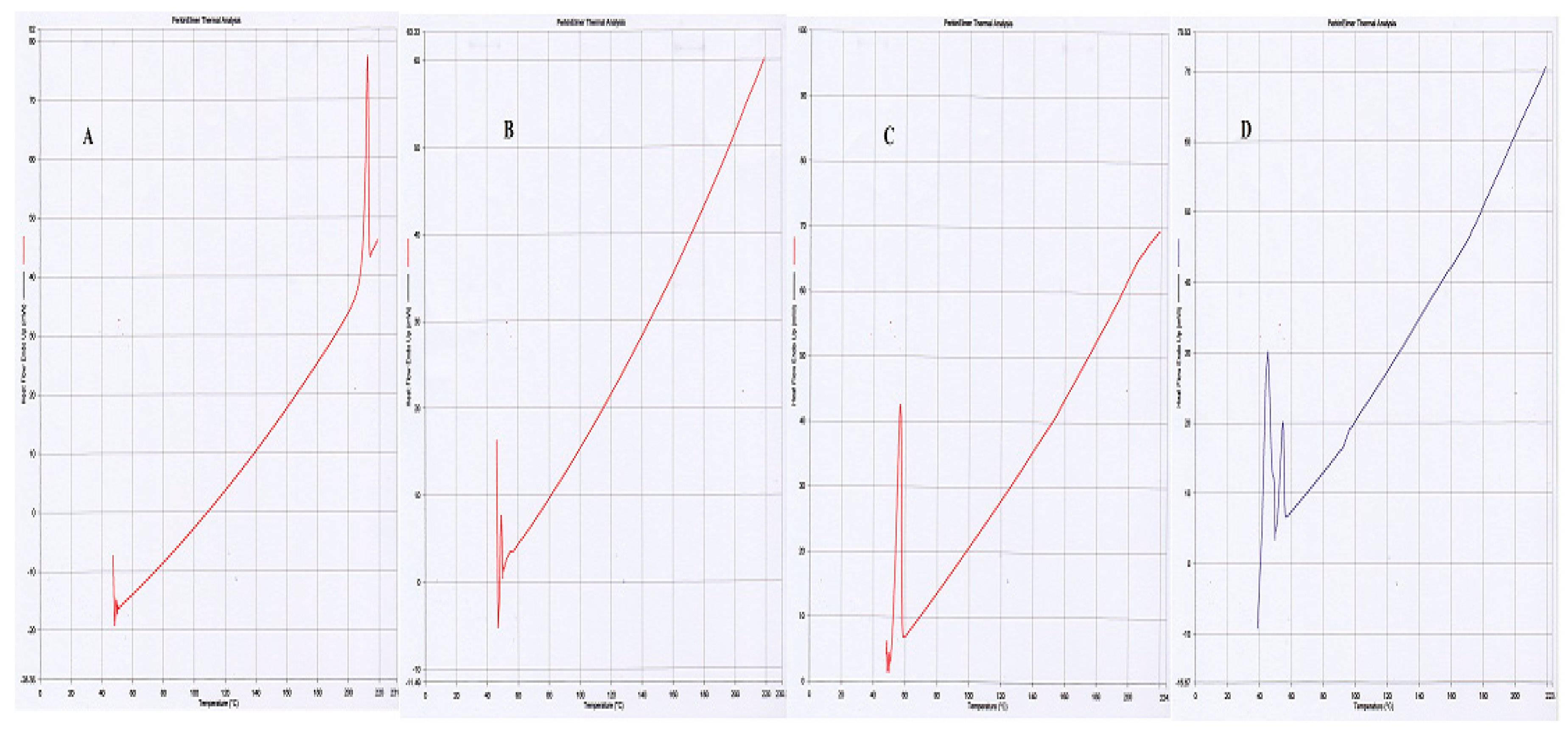
These studies were carried out to determine the crystalline, disordered crystalline, and amorphous nature of PLGA, SFB and pluronic F-127. The endothermic peaks of PLGA at 50 °C, and SFB at 210 °C confirmed their amorphous and crystalline nature, respectively while Pluronic F-127 showed one endothermic peak at 55 °C as shown in
Figure 3 [
29].
2.1.5. X-ray Diffractometry
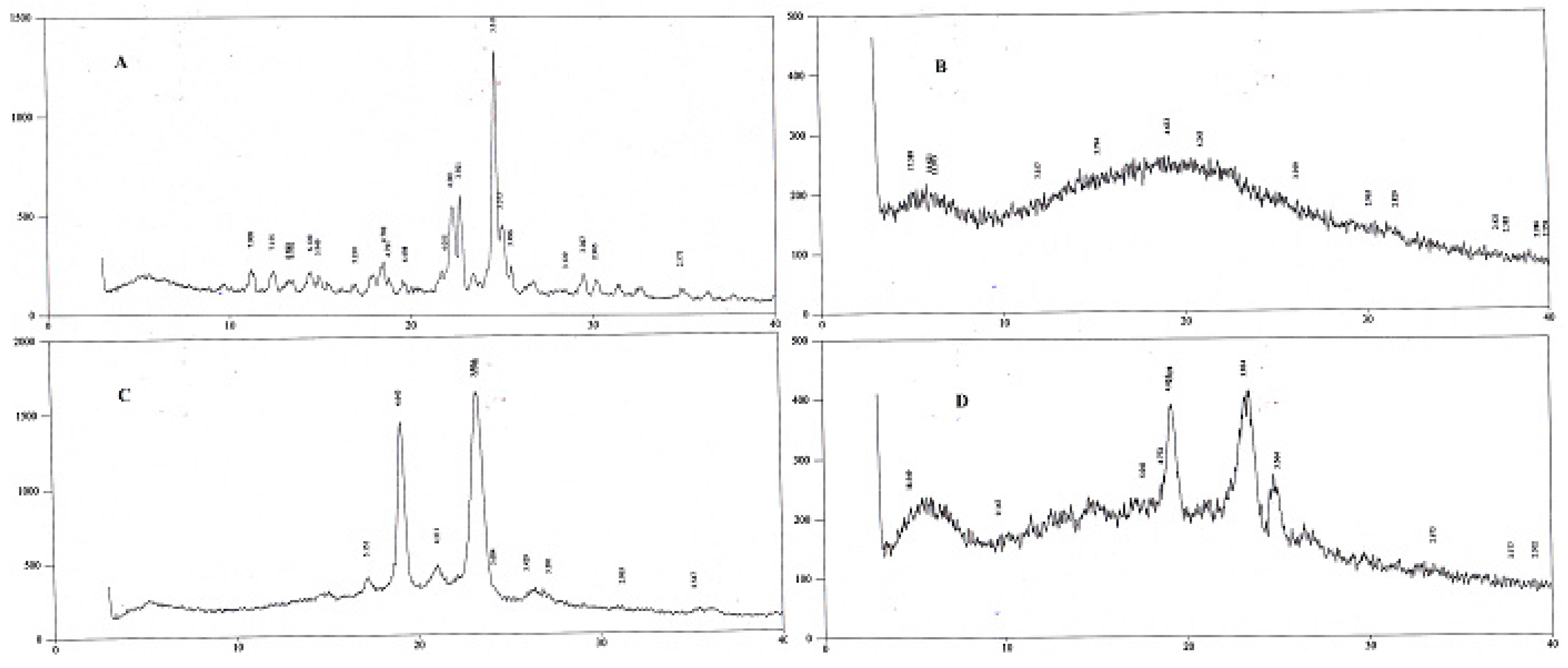
XRD studies were conducted at 3° (2θ) to 40° (2θ) using an XRD. Peaks of SFB were detected at 22.7° and 24.8° (2θ) confirming its crystalline nature, while pluronic was detected at 19˚ and 23˚ (
Figure 4). The peak for PLGA was not detected [
30].
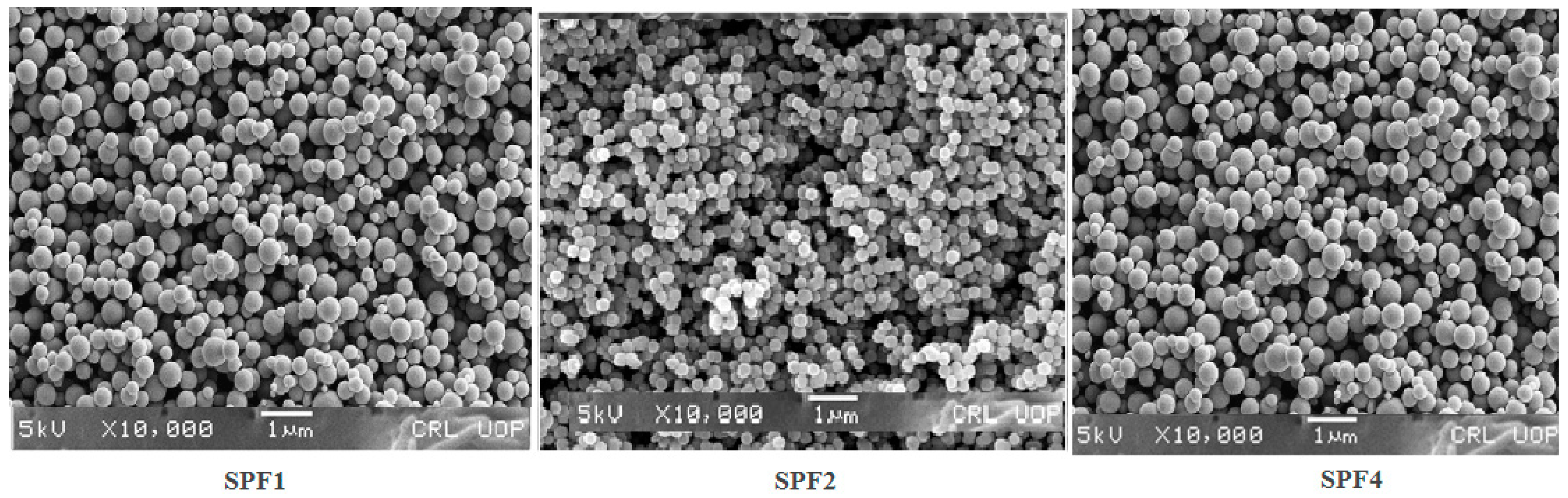
2.1.6. SEM Studies
The circulation, uptake and targeting of the tumor depend on the size, and morphology of the nanoparticles [
31,
32]. The nanoparticles prepared with Pluronic F-127(1%), were spherical in shape (
Figure 5), and remained stable for a longer period as confirmed by scanning electron microscopy. In order to find out the stability, the nanoparticles were freeze dried and then their SEM images were taken, and were then comapred with the freshly prepared nanoformulations. The nanoparticles before and after freeze drying have shown the similar results confirming their stability.
2.1.7. Formulation Optimization
The nanoformulations were prepared as given in (
Table 1). In all eight (08) nanoformulations only three (03) formulations have been optimized for the targeting of liver and kidneys. The nanoformulations SPF1, SPF2 and SPF4 have the required particle size (140.1, 120.3, and 138.4), zeta potential (-10.3, -8.39 and -10.7), PDI (0.214, 0.217 and 0.184), encapsulation efficiency (97, 99 and 87) [
31,
33] and spherical morphology as given in
Figure 5.
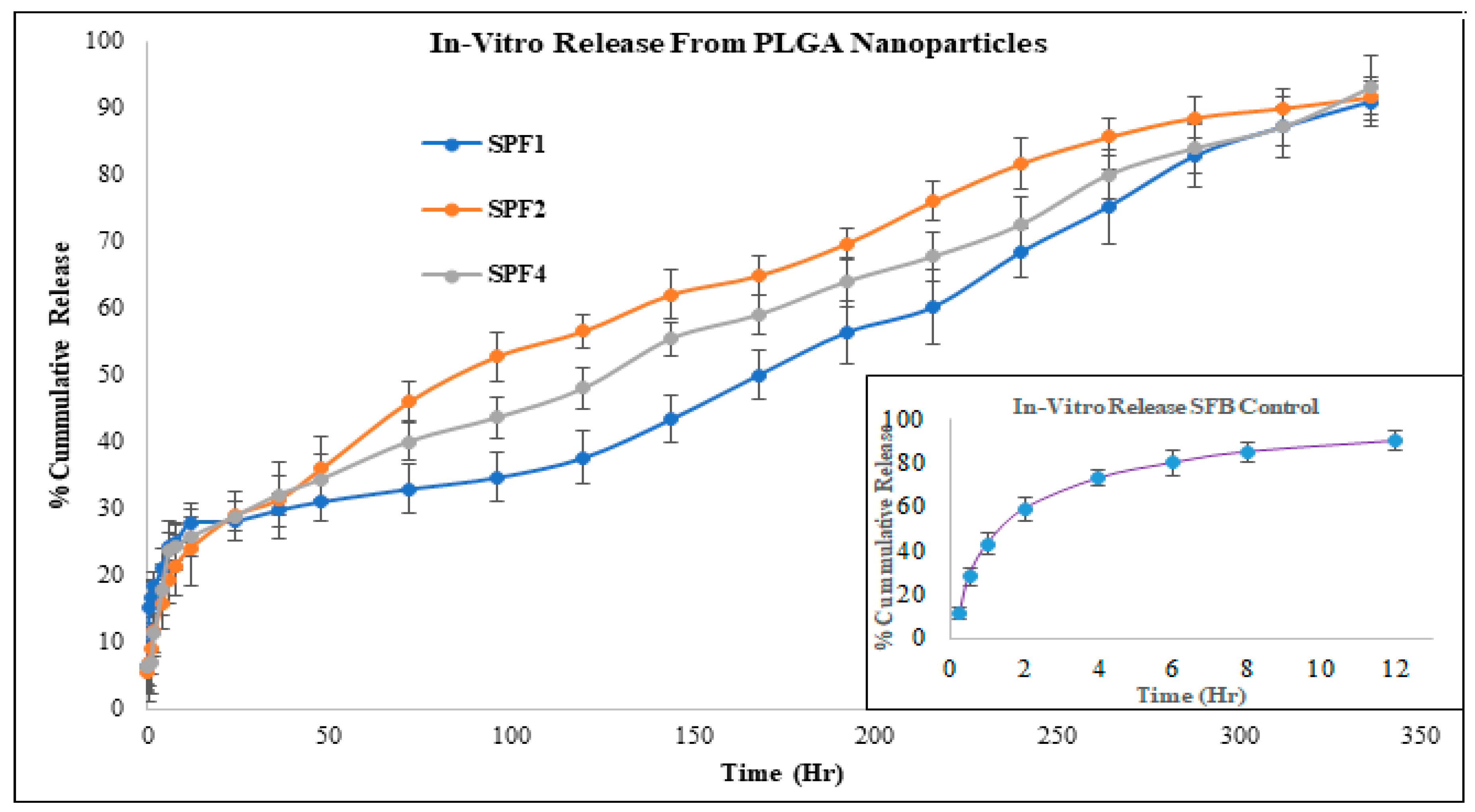
2.1.8. Drug Release Kinetics
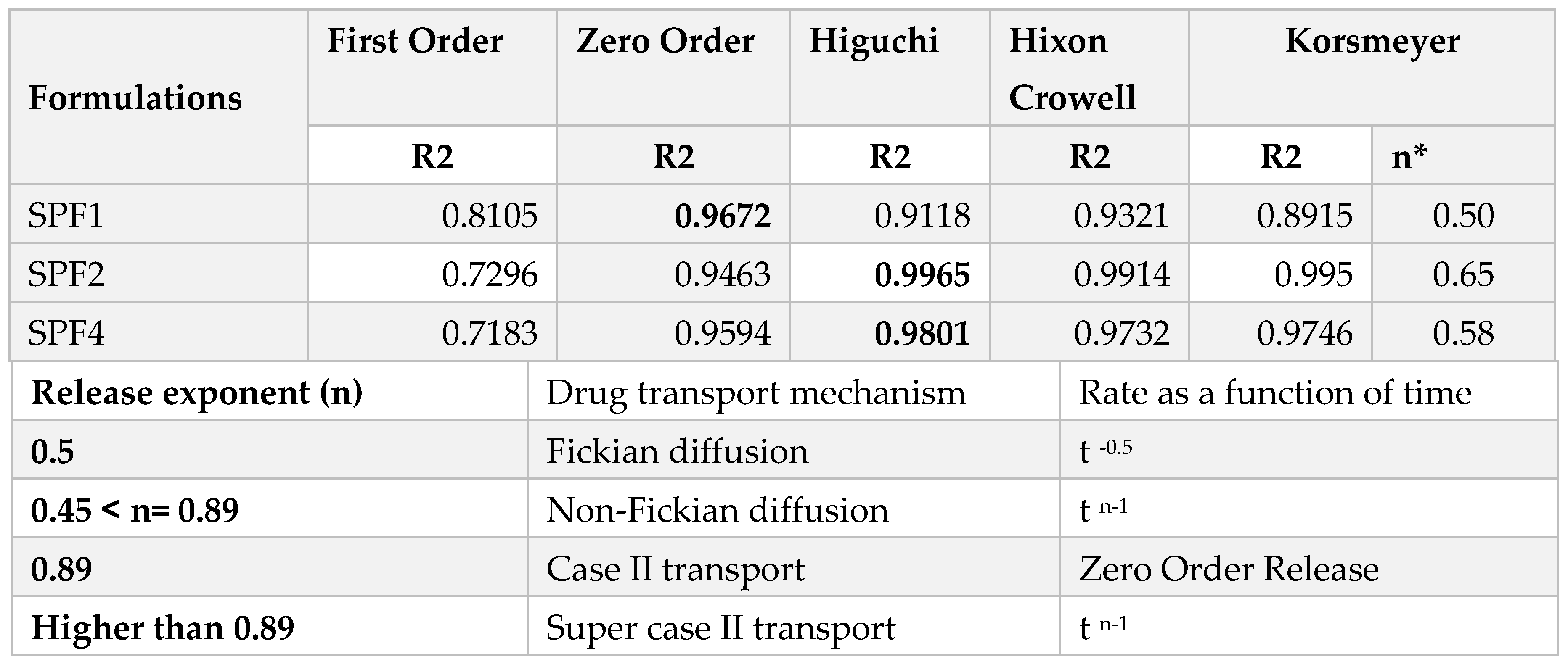
The release kinetics of SPF2 and SPF4 formulations best fit the Higuchi model, while SPF1 followed zero-order kinetics, as represented by regression coefficient (R
2) values. The “n” value represents the release mechanism of SFB from the formulations and is calculated at 60% release concentration as given in
Table 2 and
Figure 6. Diffusion followed by erosion is the most prevailing mechanism [
34].
The Higuchi and zero order models are the best to describe the transport and the release of SFB while the Korsemyer Peppas is a decisive model among all the models [
35].
2.1.9. In-Vivo Drug Analysis
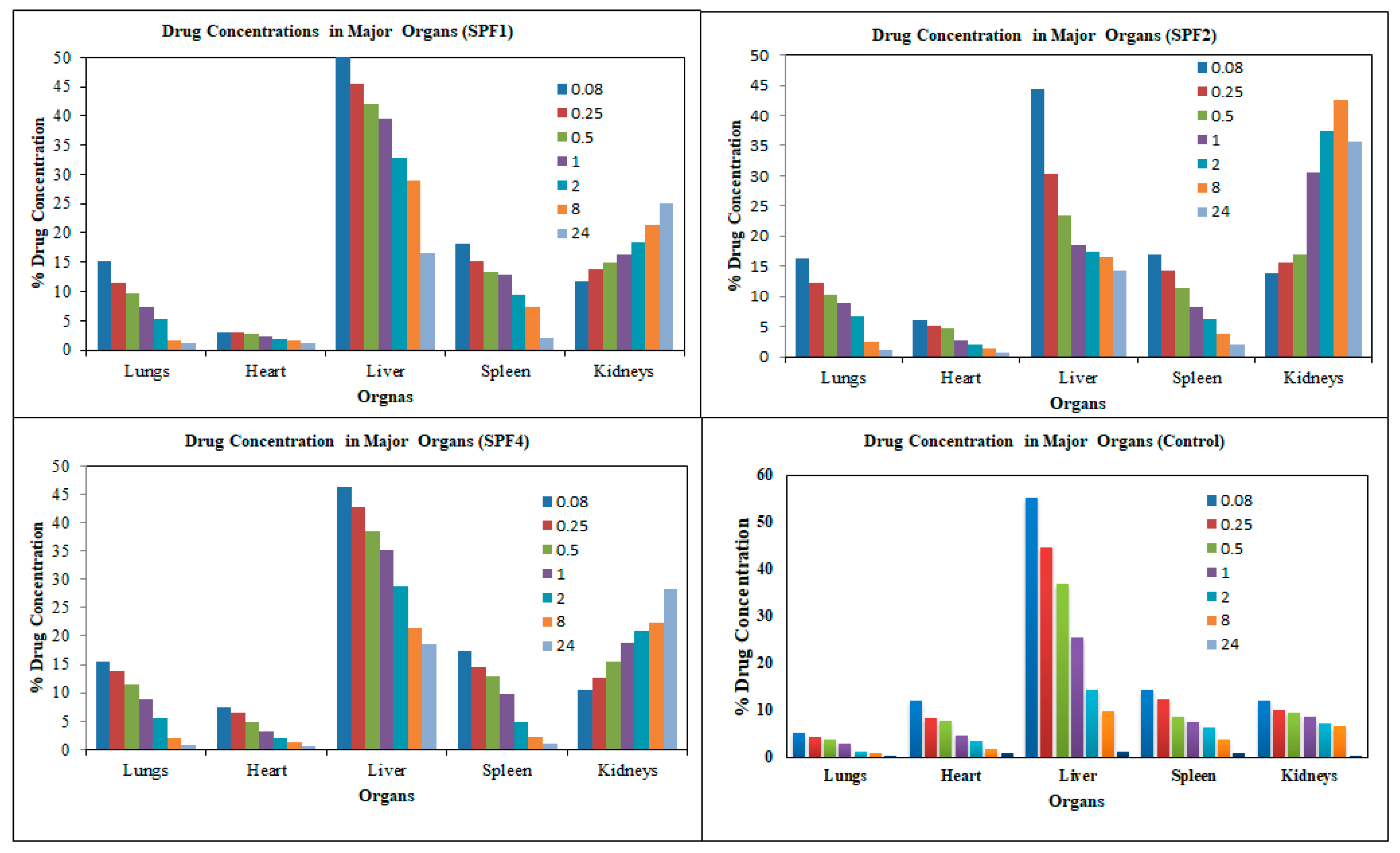
In vivo imaging and pharmacokinetic studies were performed in the test animals. The SFB nanoformulations were injected intravenously into rabbits, and then their distribution was observed by gamma imaging. The pharmacokinetic parameters were evaluated from blood samples.
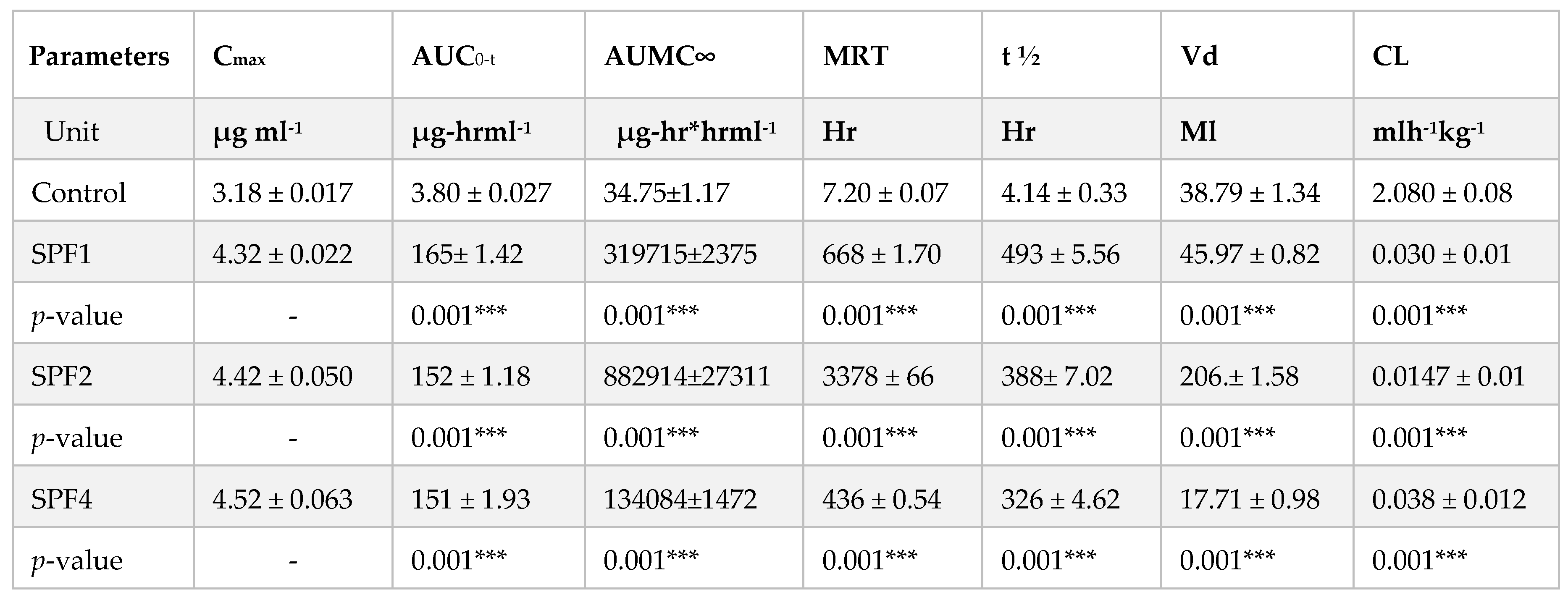
The pharmacokinetic parameters such as their MRT, AUC, Cmax, Vd, elimination half-life (t1/2) have been significantly increased as compared to their SFB control while the clearance of the polymeric nanoparticles has been decreased significantly as compare to SFB control.
The distribution of the control SFB nanosuspension and SFB-PLGA nanoparticles in target organs was different. The clearance of the control (SFB suspension) was quicker than that of its PLGA nanoparticles due to the increased mean residence time (MRT) as well as their size, zeta potential and surface morphology of the nanoformulation (
Table 3).
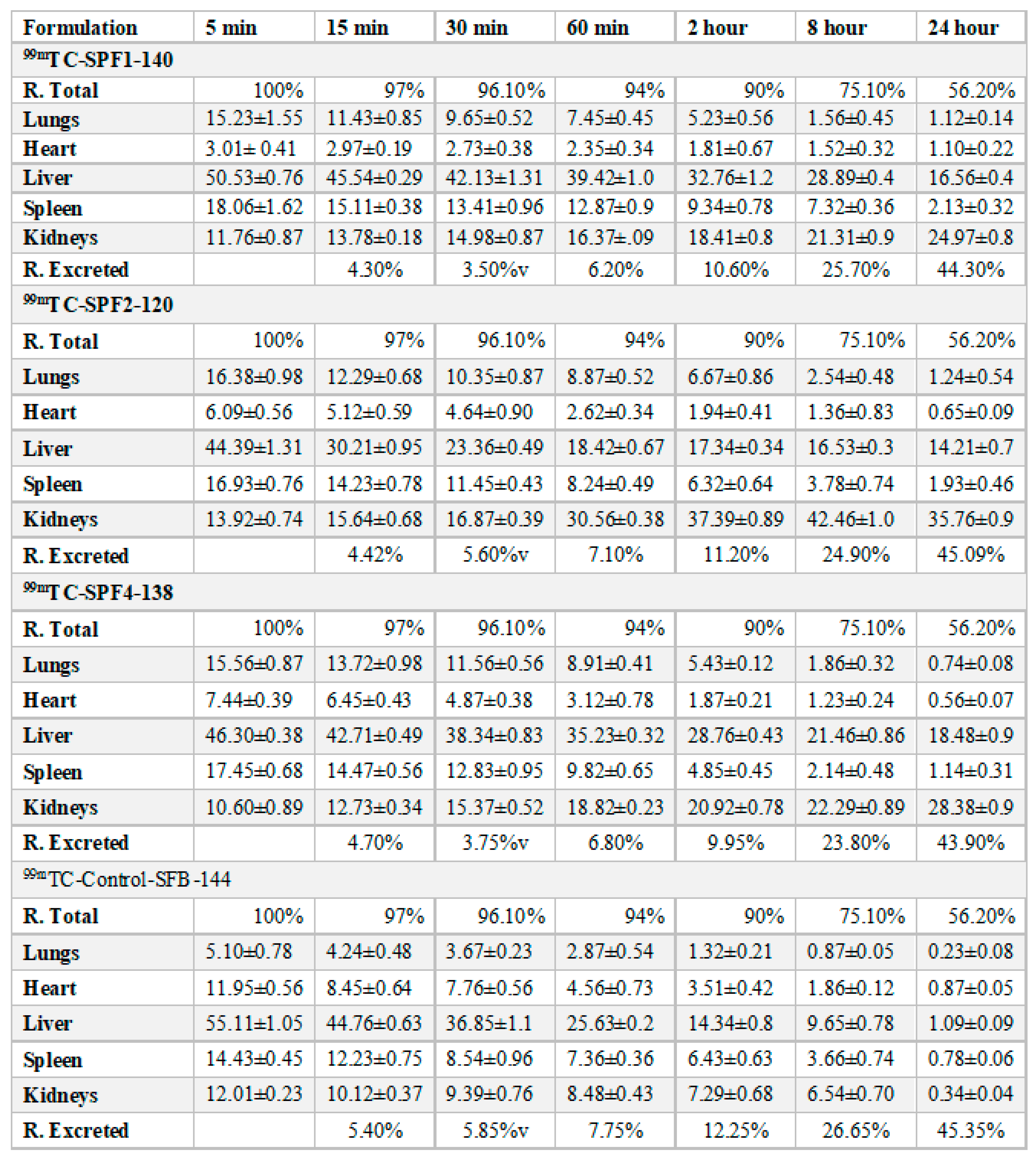
The distribution of the SFB nanoparticles formulation (
Table 3,
Table 4 and
Figure 7) was higher in liver than in the control SFB nanosuspension due to their size (≤ 200 nm). The sterically stabilized small nanoparticles can easily penetrate into the liver. This makes such nanoformulations suitable for targeting and treating the liver carcinoma [
36].
The uptake of the control SFB by the spleen was initially higher than that of SFB nanoformulation. The control SFB was eliminated quickly (in 12 hrs it reaches to below detection level) compared to the nanoformulations. The pharmacokinetic parameters suggest higher circulation time of the SFB nanoparticles for the treatment of local tumors [
37]. The distribution of SFB nanoparticles in the heart was lower than that of free control suspension, however encapsulating SFB in polymeric nanoparticles can significantly reduce cardiotoxicity [
38].
This distribution of SFB-PLGA nanoparticles in the lung was increased while their clearance was decreased compared to the control SFB. The formulation developed can therefore also be used to treat lung cancer [
39].
3. Discussion
The main objective of the study was to develop and optimize PLGA nanoparticles of SFB using pluronic F-125 as an emulsifier for the targeting of liver and kidney. Different concentration of SFB with PLGA were used for the nanoparticle preparation. Among the developed nanoformulations three formulations were optimized for further studies.
The size of the nanoparticle depends upon the quantity of drug in the nanoemulsion and the saturation solubility [
40]. The higher concentration of the SFB in the internal organic phase resulted in viscous and larger emulsion droplets and larger nanoparticles. As the targeting mechnism in this particular study is physical, therefore the key parameters i.e., the particle size (≤ 200 nm), zeta potential (≥ -10 mV), high EE/DL and high yeild are achieved through a controlled manner. The particle size smaller than 100 nm are easily excreted by the kidneys while the particles larger than 300 nm are engulfed by the body defence mechanism (Macrophage system). The tumor targeting in this case is achieved by the enahance permeability and retention effect (EPR).
The FTIR spectra revealed no interaction between the peaks except a slight decrease in -OH stretching. This is because of hydrogen bonding due to –OH group in both PLGA and Pluronic. The main bands of pure PLGA remained the same, demonstrating that there is no interaction among the SFB, excipients and polymer (
Figure 2). It is further supported by thermograms obtained from DSC that the nanoformulations and physical mixtures of PLGA and pluronic F127 are unchanged (
Figure 3). The two peaks observed in the XRD pattern confirmed the crystalline nature of the pluronic, the nanoformulations, and PLGA; however, in the nanoformulations pluronic showed semicrystalline nature as shown in
Figure 4.
The ester group of the PLGA and the long hydrophilic chain of pluronic (PEO-PPO) on the surface particles were responsible for the negative potential of the nanoparticles which has also been reported in other studies [
41]. The presence of a negative charge improves the stability of nanoparticles, electrostatic repulsion, to form agglomerates which results in increased circulation time and increased cellular uptake due to the enhanced nonspecific cell membrane affinity [
42]. For the efficient accumulation of nanoparticles at the tumor site, the particle size should be ~ 200 nm with a zeta potential of ~ -10 mV compared to more negative or positive particles or larger particles [
43]. The % EE (60-99%) has been altered significantly by changing the ratio of SFB to polymer. The drug content is actually affected by the drug-polymer interaction (drug and polymer ratios) and the miscibility of drug in polymer. Higher miscibility leads to higher drug incarporation as reported in the literaure. The % DL to the polymer was efficient compared to other biodegradable polymers [
12].
SEM imaging showed that the nanoparticles were spherical in shape and that spherical particles are more thermodynamically stable, freely circulate in the plasma, sustained drug release, and have greater cellular uptake [
44,
45]. The change in external morphology of the different nanoparticles prepared with different concentrations of sorafenib is insignificant.
The biphasic release pattern shown by the developed nanoformulations (
Table 2) consists of initial burst release in the first 28 hours followed by sustained release, which are supported by the previous study [
46]. This initial phase is due to the entrapped drug on the surface of the formulations, while the second phase involves the diffusion and erosion mechanisms [
47]. The size of polymeric nanoparticles is the major factor which affect the drug release and the degradation of the polymer. Smaller nanoparticles release the drug more rapidly as compared to larger nanoparticles as well as larger diameter particles are degraded slowly as compared to smaller one. However, degradation of the polymer is dependent on the nature and diameter of the polymer, as polymers with larger diameters degrade slowly [
48]. It is concluded that the drug release from the SBF-PLGA nanoparticles might be controlled by diffusion as a result of partitioning between polymeric nanoparticles and surrounding aqueous environment.
The possible mechanism for the higher concentration of PLGA-SFB nanoformulations in target organs (as evident from the imaging studies) might be due to the phagocytic uptake of RES and therefore, it can passively target these organs. The radioactivity of the polymeric SFB nanoparticles in the heart is less than that in other major organs, it is therfore concluded that encapsulating the SFB in PLGA can significantly reduces the cardiotoxicities. The pharmacokinetic data of the nanoformulation revealed that the nanoparticles had improved bioavailability (increased AUC, Cmax, T
1/2 and MRT) while the clearance was decreased (
Table 3) which will help in the treatment of local tumors and will lead to a more controlled and sustained therapeutic response [
37]. In this study, it is obvious that nanoparticles due to their sizes can easily be delivered to the target organs,as well as their greater retention and circulation half-life and low protein binding as compared to plain SFB nanoparticles, will lead to enhance therapeutic efficacy. The enhanced permeability and retetion (EPR) effect is also dependent on the nanoparticles size which in turn affects the drug loading, encapsulation efficiencey, drug release and stability. The morphology of nanoparticles is responsible for the
in-vivo pharmacokinetics of nanoparticles as the spherical nanoparticles will have better rheological properties as compared to other shapes, while in blood circulations [
39]. The relatively higher concentration of the nanoformulations in the liver and kidneys suggests their importance in the treatment of hepatocelleular and renal cell carcinoma.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Equipment
Sorafenib and sodium bicarbonate were purchased from Fluka, while ethanol and dimethyl sulfoxide, dialysis tubing, Pluronic (F-127), potassium chloride, sodium chloride, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, distilled water, HPLC-grade solvents, methanol and acetonitrile were purchased from Sigma‒Aldrich, Germany. PLGA was obtained from Evonik Germany. Ultra-pure distilled and deionized water was used in the study.
Probe Sonicator (Sanyo, UK. ), Vortex Mixer (Fisher Scientific®, USA), Magnetic Stirrer (Benchmark®, USA), Centrifuge (Centurion® Scientific, UK), shaking water bath (Korea), Zeta Sizer (Malvern Zetasizer ZS-90, U.S. K), freeze dryer (Telstar Cryodos-50, USA), differential scanning calorimeter (Perkin Elmer, USA), X-ray diffractometer (JEOL, Japan), The PerkinElmer spectrum BX FTIR (Waltham, MA, USA), scanning electron microscope (JEOL Japan), and UV‒Visible spectrophotometer (Perkin Elmer Series 200, Lambda, 25 using UV) were used in the study.
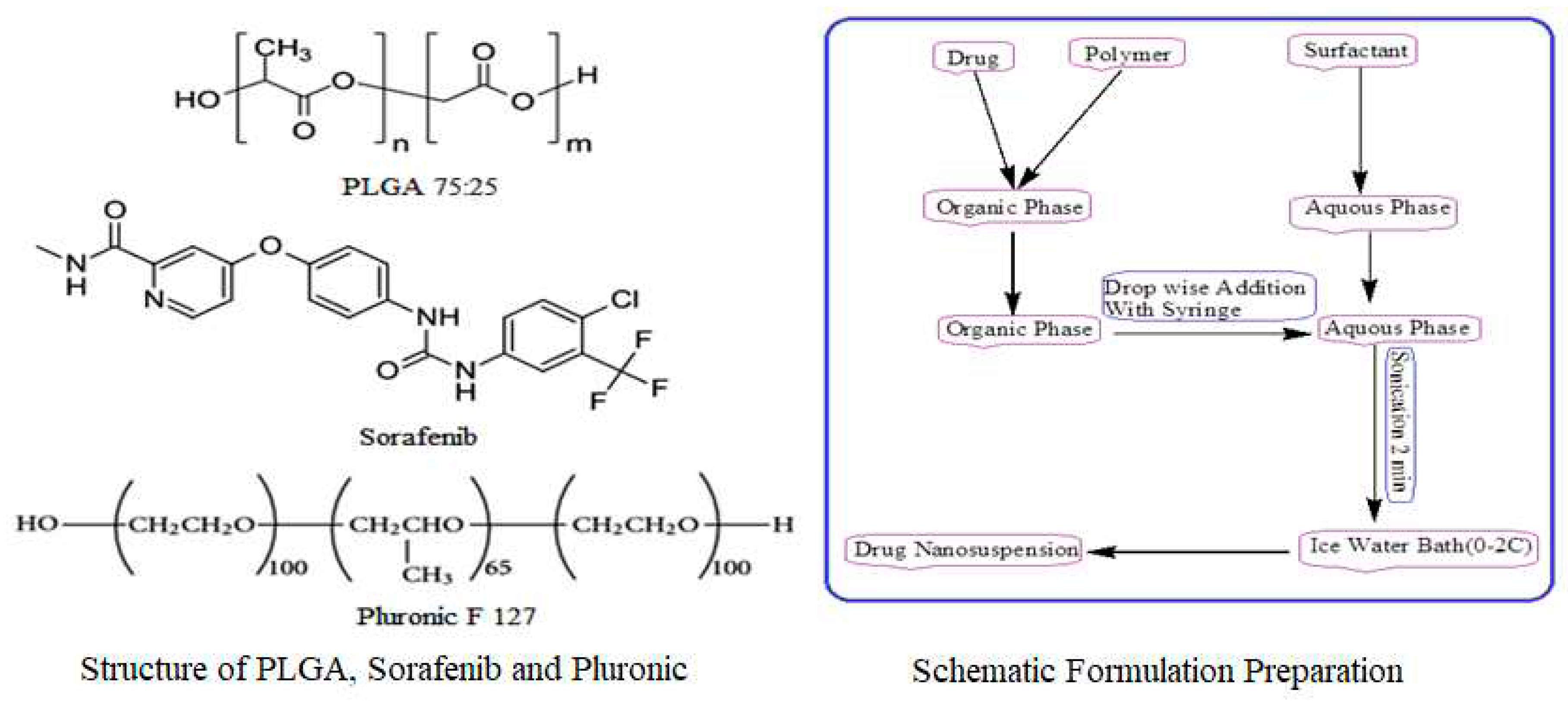
4.2. Preparation of Plain and Drug Loaded Nanoparticles
A modified solvent evaporation method was used for the preparation of nanoformulations. PLGA (75:25), 10 mg was dissolved in 3 ml ethyl acetate and 2 ml acetonitrile with varying concentrations of sorafenib (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 mg). A 1% solution of stabilizer was prepared in water, and 10 ml of stabilizer was utilized for formulation preparation as shown in
Figure 8. This was followed by adding 5 ml of the organic phase dropwise to 10 ml of an aqueous stabilizer solution with slow magnetic stirring at 70-80 rpm. The organic and aqueous mixture was then sonicated for 2 min by using a probe sonicator set at 99% level in an iced water bath using 15 W power. The organic phase was then removed through slow magnetic stirring, followed by high-speed centrifugation at 15000 rpm for 30 min at 4 °C for nanoparticle collection. The nanoparticles were first washed three times with sterile water and then lyophilized for future use and stability studies. Similar procedure was adopted for the preparation of sorafenib nanosuspension as 10 mg of sorafenib was dissolved in 3 ml ethyl acetate and 2 ml ACN and was added drop wise to 1% stabilizer solution with slow magnetic stirring followed by the same procedure as that of nanoformulation preparation. PLGA nanoparticles without SFB were prepared in the same way.
4.3. Physicochemical Characterization
4.3.1. Dynamic Light Scattering
A Malvern zeta sizer was used to determine the size, polydispersity (PDI) and zeta potential of the nanoparticles using the dynamic light scattering technique. The nanoformulation samples can be analyzed as such or can be diluted if required with distilled water, and the analysis is carried out at 25 °C with a 90° scattering angle. By using Malvern software, the average diameter and PDI were calculated. Statistical calculations for size and PDI were carried out in triplicate. The instrument software was adjusted in such a way that it took the average of three readings, and each reading was passed through 100 runs. The zeta potential actually determines the nanoparticle stability in dispersion.
4.3.2. Fourier Transform Infra-Red Analysis
FTIR spectroscopy was performed to confirm the polymer, drug and excipients and to evaluate their compatibility. The PerkinElmer spectrum BX FTIR (Waltham, MA, USA) was used for analysis, and the sample was prepared by a potassium bromide (KBr) disc. For sample preparation, 2 mg of SFB was mixed with 100 mg KBr in a mortar and pestle. The mixture was compressed to obtain a pellet. The samples were analyzed at 4000-400 cm-1 against a blank KBr pellet with a resolution of 1.0 cm-1, and baseline correction was performed.
4.3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
Sorafenib (API), PLGA, pluronic F-127, their physical mixture and lyophilized nanoformulation powder were analyzed by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). In the aluminum pan, a 10 mg sample was placed and sealed. Scanning was performed using a similar empty pan as a reference under nitrogen at a 10 °C/min heating rate. The temperature and energy scale of the instrument is calibrated using a standard aluminum material.
4.3.4. X-Ray Diffractometry
The crystalline/semicrystalline or amorphous nature of SFB, PLGA, Pluronic F-127, the physical mixture and NP formulations was determined through XRD at 3° (2θ) to 40° (2θ). To control the curves, the amount of power must be in the same quantity.
4.3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
The lyophilized powder was placed on the brass stub and the sputtering technique was used to coat the sample with gold, and this procedure was carried out for 1.30 min at 40 dm Amp under vacuum (argon gas). Then, it was placed in the sample holder of a scanning electron microscope (JSM-5910, Jeol Japan) to analyze its morphology (7 samples at a time).
4.3.6. Drug Entrapment Efficiency
To determine the drug entrapment efficiency, the percent encapsulation efficiency (% EE) and percent drug loading (% DL) were determined. The developed nanoformulations were evaluated by centrifuging the sample at 4 °C and 15000 rpm for 30 min. After centrifugation, the free amount of SFB present in the supernatant was detected by spectrophotometer at 271.10 nm. The following equations were used for %EE of SFB and %DL [
49]:
4.3.7. Formulation Optimization
The parameters set for the optimization of nanoparticles were; nanopaticle size (100-200 nm), polydispersity (PDI, 0.137-0.244), zeta potential (≥± 30 mV), drug loading and encapsulations efficiency (≥ 86%), for targeting Renal Cell Carcinoma and Hepatocellular Cell Carcinoma [
31,
33].
4.3.8. Drug Release Kinetics
The release kinetics of the developed nanoparticles was studied by redispersing the lyophilized nanoparticles in 2 ml of PBS (pH 7.4) and placing them in a cellulose membrane (MW cut-off = 12-14 kDa) immersed in 100 ml of PBS at 37 °C in a water bath with gentle shaking at 100 rpm. The volume was replaced with PBS as the samples were withdrawn. The content of SFB was measured in triplicate by a UV‒visvisible spectrophotometer and the cumulative percent drug release was measured.
4.3.9. In-Vivo Drug Analysis
4.3.9.1. Imaging Studies
The nanoformulations of SFB (150 μl) were incubated with 80 μl reducing agent (stannous chloride) at ambient temperature for 20 min and further incubated for 10 min with technetium-99 m (300 μl). The loading efficiency of the radiolabelled formulation (2 ml) was evaluated by TLC. The percent radioactivity of the formulation was determined by the gamma counter [
50].
4.3.9.2. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation
In vivo studies were carried out in rabbit models weighing 2± 0.5 kg obtained from the National Institute for Health (NIH), Islamabad, Pakistan. Approval of the experiments was obtained from the Departmental Ethical Committee; University of Peshawar vide letter number Pharm/8567. Water and food were provided, and animals with any discomfort were excluded from the study.
5. Conclusions
The PLGA based nanoparticles of Sorafenib were developed applying modified emulsion solvent evaporation method using pluronic F-127 as a stabilizer and coating agent to get high encapsulation and drug loading, enhanced internalization and sustained/controlled drug delivery, in order to achieve better therapeutic response. The pre-formulation study was conducted for the compatibility of drug and excipients, while stability at higher temperature was evaluated with DSC. The physicochemical properties of the formulations i.e., size (≤ 200 nm), PDI (≤ 0.2), tunable surface charge (≤ -10) [
51], drug loading (≥ 20%), encapsulation efficiency (≥ 87%), morphology, and
in-vitro sustained release studies were caried out. The
in-vivo studies (both imaging and pharmacokinetic) of the optimized nanoformulations were conducted. It has been concluded that small sized nanoparticles of Sorafenib with surface modified by pluronic F-127 may easily be targeted to liver and kidneys. This study will open new horizon for the targeted drug delivery of sorafenib to liver and kidneys to achieve the therapeutic response in comparison to conventional formulations of Sorafinib.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.K.; Z.I. and A.K.; methodology, I.K.; formal analysis, L.A.; data curation, A.K.; writing—original draft preparation, I.K.; writing—review and editing, A.K. and S.A.K.; supervision, Z.I.; funding acquisition, M.D.H. and M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to extend sincere appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project Number RSP2023R301, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. We are also thankful to the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan for facilitating the scholar.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of Department of Pharmacy, University of Peshawar vide letter number Pharm/8567, dated November 25, 2014.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The quantitative laboratory data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article. The supporting data of this study are available from the corresponding author, Dr. Abad Khan upon request.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the Nuclear Oncology and Radiotherapy Institute Islamabad (NORI) and Central Research Lab (CRL) Peshawar for their support in the physicochemical characterization. The authors would like to extend sincere appreciation to the Researchers Supporting Project Number RSP2023R301, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Caputo, T.M., et al., Sorafenib-Loaded PLGA Carriers for Enhanced Drug Delivery and Cellular Uptake in Liver Cancer Cells. International Journal of Nanomedicine 2023, 4121–4142. [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J. and J.M. Llovet, Major achievements in hepatocellular carcinoma. The Lancet 2009, 373, 614–616. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J. and M. Sherman, Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1208–1236. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J., et al., Conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference: European Association for the Study of the Liver. J Hepatol, 2001, 35, 421–430.
- Llovet, J.M. and J. Bruix, Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology, 2003, 37, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, P., A. Villanueva, and J. Llovet, Systematic review: evidence-based management of hepatocellular carcinoma–an updated analysis of randomized controlled trials. Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics, 2006, 23, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, H.T. and F. J. McGovern, Renal-cell carcinoma. New England Journal of Medicine, 2005, 353, 2477–2490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I., S. C. Campbell, and B. Escudier, Renal cell carcinoma. The Lancet, 2009, 373, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, J.M. , et al. , Rising incidence of small renal masses: a need to reassess treatment effect. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 2006, 98, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, J.M. , et al. , Five-year survival after surgical treatment for kidney cancer: a population-based competing risk analysis. Cancer, 2007, 109, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo, B.A.G., F.L. Motta, and M.H.A. Santana, The interactions between humic acids and Pluronic F127 produce nanoparticles useful for pharmaceutical applications. Journal of nanoparticle research 2015, 17, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Menon, J.U. , et al. , Effects of surfactants on the properties of PLGA nanoparticles. Journal of biomedical materials research Part A, 2012, 100, 1998–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.K. , et al. , Neutrophil activation by plasma opsonized polymeric microspheres: inhibitory effect of Pluronic F127. Biomaterials, 2000, 21, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L. , et al. , Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer research, 2006, 66, 11851–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-q., et al., Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of sorafenib suspension, nanoparticles and nanomatrix for oral administration to rat. International journal of pharmaceutics 2011, 419, 339–346. [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.Y., C.K. Poh, and W. Wang, Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) as a controlled release delivery device. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 2009, 20, 1669–1675. [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K. , et al. , Guided bone regeneration by poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) grafted hyaluronic acid bi-layer films for periodontal barrier applications. Acta Biomaterialia, 2009, 5, 3394–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vij, N. , et al. , Development of PEGylated PLGA nanoparticle for controlled and sustained drug delivery in cystic fibrosis. Journal of nanobiotechnology, 2010, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csaba, N., A. Sanchez, and M. J. Alonso, PLGA: poloxamer and PLGA: poloxamine blend nanostructures as carriers for nasal gene delivery. Journal of Controlled Release, 2006, 113, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafee, N. , et al. , Relevance of the colloidal stability of chitosan/PLGA nanoparticles on their cytotoxicity profile. International journal of pharmaceutics, 2009, 381, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, D. , et al. , Poly (ethylene oxide)-modified poly (β-amino ester) nanoparticles as a pH-sensitive system for tumor-targeted delivery of hydrophobic drugs. 1. In vitro evaluations. Molecular pharmaceutics, 2005, 2, 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Couvreur, P. , et al. , Tissue distribution of antitumor drugs associated with polyalkylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 1980, 69, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolland, A. , Clinical pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin in hepatoma patients after a single intravenous injection of free or nanoparticle-bound anthracycline. International journal of pharmaceutics, 1989, 54, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, J.-C. Leroux, J.-C., et al., Biodegradable nanoparticles—from sustained release formulations to improved site specific drug delivery. Journal of Controlled Release 1996, 39, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsky, W.L. , et al. , Augmentation of transvascular transport of macromolecules and nanoparticles in tumors using vascular endothelial growth factor. Cancer Research, 1999, 59, 4129–4135. [Google Scholar]
- Bennis, S. , et al. , Enhanced cytotoxicity of doxorubicin encapsulated in polyisohexylcyanoacrylate nanospheres against multidrug-resistant tumour cells in culture. European Journal of Cancer, 1994, 30, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowinsky, E.K. and R. C. Donehower, Paclitaxel (taxol). New England journal of medicine, 1995, 332, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyulai, G. , et al. , Preparation and characterization of cationic Pluronic for surface modification and functionalization of polymeric drug delivery nanoparticles. Express Polymer Letters, 2016, 10, 216–226. [Google Scholar]
- Detroja, C., S. Chavhan, and K. Sawant, Enhanced antihypertensive activity of candesartan cilexetil nanosuspension: formulation, characterization and pharmacodynamic study. Scientia pharmaceutica, 2011, 79, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.X. , et al. , Bioavailability enhancement of a COX-2 inhibitor, BMS-347070, from a nanocrystalline dispersion prepared by spray-drying. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences, 2005, 94, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E., H. Shen, and M. Ferrari, Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nature biotechnology, 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, N.P. , et al. , The importance of nanoparticle shape in cancer drug delivery. Expert opinion on drug delivery, 2015, 12, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, F. , et al. , Development and characterization of parenteral nanoemulsions containing thalidomide. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2011, 42, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, S. , et al. , Kinetic modeling on drug release from controlled drug delivery systems. Acta Pol Pharm, 2010, 67, 217–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costa, and J. M.S. Lobo, Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2001, 13, 123–133. [CrossRef]
- Stolnik, S. , et al. , Polylactide-poly (ethylene glycol) micellar-like particles as potential drug carriers: production, colloidal properties and biological performance. Journal of drug targeting, 2001, 9, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, G. and M. Amiji, Biodistribution and targeting potential of poly (ethylene glycol)-modified gelatin nanoparticles in subcutaneous murine tumor model. Journal of drug targeting 2004, 12, 585–591. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snehalatha, M. , et al. , Etoposide loaded PLGA and PCL nanoparticles II: biodistribution and pharmacokinetics after radiolabeling with Tc-99m. Drug delivery, 2008, 15, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollis, C.P. , et al. , Biodistribution and bioimaging studies of hybrid paclitaxel nanocrystals: lessons learned of the EPR effect and image-guided drug delivery. Journal of Controlled Release, 2013, 172, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N., P. Madan, and S. Lin, Effect of process and formulation variables on the preparation of parenteral paclitaxel-loaded biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles: A co-surfactant study. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2016, 11, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, E., et al., PLGA nanospheres for the ocular delivery of flurbiprofen: drug release and interactions. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences 2008, 97, 5306–5317. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, É. , et al. , Tuneable surface modification of PLGA nanoparticles carrying new antitubercular drug candidate. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2014, 458, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morachis, J.M., E. A. Mahmoud, and A. Almutairi, Physical and chemical strategies for therapeutic delivery by using polymeric nanoparticles. Pharmacological reviews, 2012, 64, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. , et al. , Shape-memory nanoparticles from inherently non-spherical polymer colloids. Nature materials, 2005, 4, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. , et al. , The shape of things to come: importance of design in nanotechnology for drug delivery. Therapeutic delivery, 2012, 3, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halayqa, M. and U. Domańska, PLGA biodegradable nanoparticles containing perphenazine or chlorpromazine hydrochloride: effect of formulation and release. International journal of molecular sciences, 2014, 15, 23909–23923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrigan, O.I. and X. Li, Quantifying drug release from PLGA nanoparticulates. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2009, 37, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redhead, H., S. Davis, and L. Illum, Drug delivery in poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles surface modified with poloxamer 407 and poloxamine 908: in vitro characterisation and in vivo evaluation. Journal of Controlled Release, 2001, 70, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassin, A. , et al. , Optimization of 5-fluorouracil solid-lipid nanoparticles: a preliminary study to treat colon cancer. Int J Med Sci, 2010, 7, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Patricio, B., M. de Souza Albernaz, and R. Santos-Oliveira, Development of nanoradiopharmaceuticals by labeling polymer nanoparticles with tc-99m. World journal of nuclear medicine, 2013, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S., et al., In vivo biodistribution, biocompatibility, and efficacy of sorafenib-loaded lipid-based nanosuspensions evaluated experimentally in cancer. International journal of nanomedicine 2016, 2329–2343. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).