1. Introduction
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is defined as any degree of glucose intolerance or development of hyperglycemia throughout pregnancy. GDM affects 2%-10% of pregnancies in the United States and ~17% of pregnancies worldwide. GDM is a known risk factor for a variety of complications, including preeclampsia, macrosomia, respiratory complications such as neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (NRDS), neonatal hypoglycemia, hyperbilirubinemia, and stillbirth. Moreover, mothers diagnosed with GDM are at an increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D), cardiovascular disease (CVD), renal disease, ophthalmic disease, and malignancies. Growing research suggests that GDM pregnancies may have also long-term consequences for the child as they are more likely to live with obesity, CVD, T2D, autism-spectrum disorder and even GDM in their adult lives [
1]. The intergenerational perpetuation of GDM and corresponding comorbidities make the disease a public health dilemma.
Epigenetics explain how the environment is capable of transiently modifying genetic expression through molecular mechanisms such as DNA methylation, histone acetylation, and miRNA expression without altering the DNA sequence. Although the pathophysiology of metabolic syndromes can be attributed to modifiable risk factors (including sedentary lifestyles, diets high in excess calories, smoking, etc.), there also exists genetic variants and polymorphisms that can increase one’s susceptibility to acquiring these syndromes [
2,
3]. This interplay between the environment and genetics can be observed, at least in part, by alterations to genetic expression.
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and epigenetic profiling of maternal blood, umbilical cord blood, adipose tissue, and placental samples of pregnant women and their offspring have revealed the significance of maternal/fetal genetic regulation and the many crossroads that contribute to gestational diabetes [
3]. This narrative review aims to shed light on the interplay of epigenetics, the development of gestational diabetes, and the consequences of these epigenetic changes on the offspring by providing a comprehensive source of the potential molecular markers and epigenetic mechanisms that contribute to the susceptibility and pathologic mechanism of GDM and GDM-related complications. In doing so, we hope to provide more insight to the pathophysiology of GDM that may be used for future prevention and therapy.
2. Materials and Methods
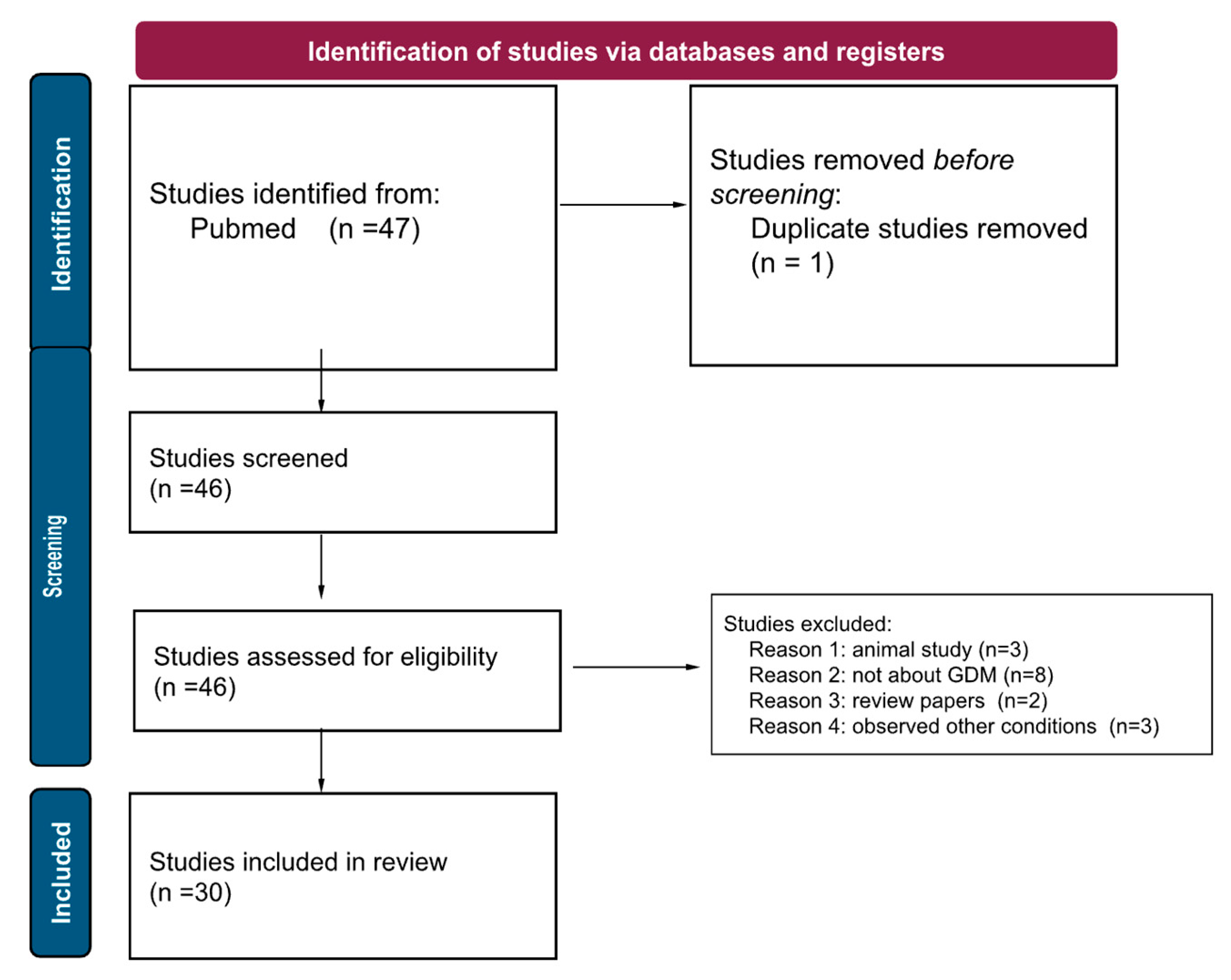
A literature search was performed using PubMed, with the keywords “gestational diabetes AND epigenetics,” from 2017 to 2022. This yielded 47 articles. Due to the number of studies published using human samples, such as maternal blood, umbilical cord blood, and placental samples, we have decided to exclude animal studies (n=3). We additionally excluded papers that did not specifically focus on gestational diabetes (ie maternal diabetes, obesity), to avoid confounding factors (n=8). We excluded papers that were not about epigenetics (n=3), and review papers (n=2). This left us with 30 remaining papers. In this narrative review, we present the current research on epigenetics and GDM, organized by epigenetic mechanism (DNA methylation, histone acetylation, miRNA up/down regulation, immune system involvement, etc), and finally, explore how these epigenetic changes may affect the offspring.
Scheme 1.
A PRISMA diagram detailing our review method, and demonstrating our screening, exclusion, and final number of papers.
Scheme 1.
A PRISMA diagram detailing our review method, and demonstrating our screening, exclusion, and final number of papers.
3. Epigenetics
3.1. DNA Methylation
DNA methylation is a fundamental epigenetic process known for regulating gene expression and consequently affecting many biological processes. The process centers around DNA methyltransferases (DMNTs), an enzyme that transfers methyl groups to the C-5 position of a cytosine ring. These covalent modifications mostly occur on regions of DNA located on Cytosine to Guanine linkages in a 5’ to 3’ direction, known as CpG sites, with more than 98% occurring in CpG dinucleotide context in somatic cells and a quarter of all methylation appearing in non-CpG context in embryonic stem cells [
4]. Epigenetic DNA methylation is a dynamic process influenced by environmental factors, lifestyle, and disease progression; its involvement in regulating many biological processes, including insulin signaling and glucose metabolism, makes studying differential methylation as a biomarker ideal for the pathogenesis and progression of GDM.
Identifying maternal methylation changes prior to the onset of GDM provides the opportunity for early treatment planning and therapeutic intervention. According to Wu and colleagues, 5 CpGs, within the COPS8, PIK3R5, HAAO, CCDC124, and C5orf34 genes, out of 100 CpGs identified using a genome wide approach in maternal blood, demonstrated potential to be used as clinical biomarkers due to differential methylation in 8 of 11 women who developed GDM relative to matched controls [
5]. While identifying epigenetic changes in maternal blood is less invasive and more accessible, studying tissue-specific methylation changes in the placenta can provide more insight into the cellular mechanism of placental development and its role in insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism in progression to GDM [
6]. Analyzing DNA methylome and gene expression data with normal placenta tissue and GDM patient placenta tissue uncovered a list of genes: Oas 1, Ppie, Polr2g that not only provide targets for early diagnosis of GDM but also shed more light on clinical prevention of abnormal fetal development and type 2 diabetes [
7]. Epigenetic DNA changes can provide information on future adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs) through monitoring the DNA methylation of placenta-specific cell-free nucleic acids during early gestation. Plasma cell-free content is traditionally used to screen for genetic abnormalities during pregnancy, but is currently being studied for its use in predicting APOs. Del Vecchio and colleagues found that placenta-specific DNA was found to be increased in the first trimester prior to the subsequent development of gestational diabetes with no change in patients with preeclampsia and decreased with maternal obesity [
6].
Overall, epigenetic DNA methylation changes provide excellent promise in acting as a biomarker for GDM by providing the opportunity to begin early treatment intervention and management by predicting GDM before the onset of clinical symptoms. Further prospective studies on larger and more diverse patient populations are needed to expand confidence in the clinical utility of differential epigenetic DNA methylation modifications as a biomarker for GDM.
3.2. MicroRNA
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA molecules involved in post-transcriptional gene regulation. MiRNA binds to 3’ untranslated regions (UTR) on mature RNAs (mRNA) and represses protein production by destabilizing and silencing translation of the mRNA. MiRNA regulation of gene expression is the cornerstone in a myriad of biological processes including cell growth, differentiation, development, and disease pathogenesis. The stability of circulating miRNAs in the human body and retrieval through non-invasive procedures allows for their promising use as potential biomarkers [
8]. The invaluable use of miRNAs in the context of GDM is centered around its utility as a biomarker that can predict GDM occurrence later in gestation, monitor its progression and provide a target for potential therapeutic intervention.
MiRNAs can be incorporated early in gestation as a screening tool for future complications including GDM. Wander and colleagues hypothesized that circulating plasma levels of early-mid pregnancy miRNAs can predict future GDM development. Circulating levels of miR-155-5p and miR-21-3p found in weeks 7-23 of gestation, were positively associated with GDM. Among women considered to be overweight or obese miR-21-3p, and miR-210-3p were associated with the development of GDM [
9]. These miRNAs can be monitored to assess the risk and early detection of GDM. Circulating miRNAs located in the plasma of early gestation may also have predictive value of insulin sensitivity (IS) later in pregnancy as well. Légaré and colleagues found 18 circulating miRNAs found in the first trimester associated with Matsuda Index estimated insulin sensitivity later in pregnancy between the 24th and 29th week. Among the 18 miRNAs, the five most significant based on adjusted q values were: hsa-miR215-5p, hsa-miR-141-3p, hsa-miR-200a-3p, hsa-miR-143-3p, and hsa-miR-221-3p. hsa-miR-221-3p was the only one associated with lower IS [
10]. These miRNAs may be involved in the regulation of lipid metabolism and can provide insight into IS adaptations in pregnancy.
Comparing miRNA levels in patients with GDM versus controls allows a closer look into the pathogenesis of GDM on a cellular level through insulin and glucose induced regulation of the miRNAs. After matching for maternal body mass index and maternal age, miRNA levels from maternal and fetal whole blood cells (WBC) of pregnant women with GDM and normal glucose-tolerant women were compared, and the levels miRNA-340 were increased in GDM women [
11]. Strim et al. also showed that insulin increased and glucose reduced miRNA-340 expression levels in lymphocytes derived from maternal blood, providing evidence for insulin-induced epigenetic modification of maternal WBC in women with GDM [
11]. MiRNA-340 can be potentially used as a biomarker to monitor the treatment and progression of GDM and act as a target gene for therapeutic intervention.
The emergence of using circular RNAs (circRNAs) as a biomarker in predicting GDM is a novel and promising approach. Circular RNAs are known to be more stable than linear RNAs and are expressed at higher levels in tissue making them a more useful biomarker. In pursuit of a more optimal biomarker, Wu and colleagues used reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction to measure the concentration of six circRNAs in the serum and placental tissue, along with the Pearson correlation test to assess the correlation between these circRNAs and clinical variables. Hsa_circRNA_0054633 was found to have the highest diagnostic value in GDM and was highly expressed in the serum in the second and third trimesters and also in the placenta. The researchers additionally found that Hsa_circRNA_0054633 was positively correlated with postprandial blood glucose and may also be used to predict neonatal complications [
12].
The assessment of epigenetic modifications on genes, miRNAs, and circRNAs involved in GDM not only sheds additional light on the pathogenesis of the disease but can also be clinically utilized. With further research, they may prove to be useful in GDM prevention, screening, and treatment. However, to achieve this, a thorough analysis into how these modifications contribute to GDM development is necessary
3.3. Epigenetic Markers and Their Clinical Significance in GDM
The underlying pathophysiology of GDM is tied to pancreatic β-islet cell dysfunction and impaired insulin sensitivity; yet, the molecular mechanisms and contributing factors of the disease are still largely unspecified. As a result, studies have been conducted to assess if the environmental influences and lifestyle decisions related to GDM development can shed light on potential epigenetic markers. The identification of such markers and epigenetic mechanisms can be used to determine therapeutic targets, screening tools for GDM, and provide additional insight into the pathogenesis of the disease. As GDM is a multifactorial disease, it is crucial to assess the multiple signaling and metabolic pathways (e.g. inflammation, lipid metabolism, insulin signaling, etc.) involved
3.3.1. Insulin Metabolism
GDM is defined as varying degrees of maternal glucose intolerance, fetal hyperglycemia and eventual insulin resistance. Therefore, it is important to closely examine whether the genes involved in insulin signaling, secretion, and regulation are subjected to epigenetic modifications [
13].
Adenylyl cyclase is a key enzyme of the G-protein coupled signaling pathway that is involved with a plethora of hormones, including insulin. In a 2019 epigenetic profiling manuscript, placental samples from 82 patients were screened for differentially methylated genes and 3 molecules were identified: CAMK2B, ADCYAP1, and KCNN2 [
14] In addition, a smaller scale study with 24 patients also identified CAMTA1, a transcriptional activator involved in insulin secretion and regulation to be differentially methylated. More specifically, there was decreased methylation of CAMTA1 in the peripheral blood of GDM patients compared to control; further suggesting that disruption of insulin regulation and function is partially responsible for GDM development [
15]. However, it is important to note that the small sample size in this study may warrant further investigation. Lifestyle factors including diet, exercise, and smoking may have also confounded the results discussed despite both studies having matched their sample population. Nonetheless, the epigenetic changes associated with ADCYAP1 and CAMTA1 suggest these genes can serve as potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets of GDM.
Overweight and obesity are chronic conditions linked to dysregulation of adipose tissue, particularly they have been tied to metabolic dysfunction and corresponding comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease, polycystic ovarian disease, and GDM. Only recently have researchers begun to assess epigenetic modifications at the level of visceral (VAT) and subcutaneous (SAT) adipose tissue. A 2021 epigenetic study on 41 patients, identified additional regions of SOCS3, suppressor of cytokine signaling 3, in VAT. Within exon 2 of SOCS3 at CpG5-6, methylation levels were significantly decreased which corresponds to an increase in mRNA and therefore SOCS3 expression in VAT, contributing to GDM development [
16]. SOCS3 has been previously found to have inhibitory effects on leptin and insulin signaling, and therefore correlated with obesity-related insulin resistance. Its reduced expression in GDM patients highlights the importance of assessing both upstream and downstream components of insulin signaling [
17]. A deeper inspection into insulin signaling in VAT was conducted by Rancourt et al. in which they report significantly reduced PI3KR1 expression in VAT of women with GDM [
18]. Regardless, the significant differences in SOCS3 and PI3KR1 expression specifically in VAT are hopeful biomarkers for GDM diagnosis as well as a cofactor to determine if a patient and/or their offspring are at an increased risk of developing the disease.
3.3.2. Lipid Metabolism
Obesity and adiposity have been known to be correlated with GDM development, however the mechanism responsible remains unclear. There have been studies conducted to examine if lipid composition or altered metabolism precede hyperglycemia and insulin resistance in patients. As adiposity and lipid composition are heavily influenced by lifestyle and diet, it is important to assess if epigenetic modulations in the molecular environment of adipose tissue also play a role in GDM development [
19].
ADIPOQ is exclusively expressed in adipose tissue and is responsible for adiponectin function. The hormone adiponectin is a major player in lipid and glucose metabolism. With regards to lipid metabolism, it limits hepatic accumulation of triglycerides and fatty acids, increases their transport into muscle cells, promotes fatty acid catabolism, and is correlated with decreased insulin resistance [
20]. The role adiponectin plays with regards to lipid metabolism is highly interconnected with glucose homeostasis. Ott et al. investigated adiponectin plasma levels and gene expression in SAT and VAT from women with GDM and matched controls. The researchers concluded that the CpG locus sites analyzed were hypermethylated and ADIPOQ gene expression was significantly reduced in both adipose tissue samples of women with GDM. As the groups were matched for BMI, the findings of this study suggest that reduced adiponectin is independent of maternal BMI and may be a cause of, or result of, insulin dysregulation instead [
21].
A 2021 epigenome-wide association study also discovered ADIPOR2, GNAS, and GRB10, genes crucial in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism to be differentially methylated in GDM patients. More specifically, ADIPOR2 exhibited decreased methylation in GDM patients, GNAS was unmethylated in those not exposed to GDM, and GRB10 was shown to be hypermethylated compared to controls [
22]. These results suggest that epigenetic mechanisms are highly specific and are dependent on the gene and/or pathway involved. Overall, it is safe to assume that hypoadiponectinemia is a crucial cofactor in GDM pathogenesis. This is especially important as patients who are overweight or obese are at an increased risk of the disease, therefore the discovery of a pathogenic mechanism and potential cofactors tied to adiposity and insulin resistance may also aid in GDM screening, prevention and treatment.
3.3.3. Immune Markers
One hypothesis suggests that insulin resistance is associated with an elevated secretion of proinflammatory cytokines and that GDM may be a result of a state of chronic inflammation [
23]. Several studies have also demonstrated that the rise in proinflammatory factors may be the precipitating event causing islet cell dysfunction and subsequent insulin resistance [
24]. Moreover, this mechanism also explains how maternal obesity is strongly correlated with GDM development as obesity is categorized as a low-grade chronic inflammatory state [
23]. As a result, screening for potential epigenetic biomarkers involved in the inflammatory and immune system may provide additional information about GDM.
Pinney et al. performed an epigenome wide analysis on second-trimester amniocytes exposed to GDM in utero for any differentially methylated genes. They found that there was increased expression of genes (e.g. IFIG, IFI44, CMPK2, SERPINA9, etc.) involved in inflammation-related signaling pathways in amniocytes exposed to GDM. Notably, many of the genes identified were members of a family of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) [
25]. The distinct proinflammatory profile of the amniocytes derived from mothers with GDM draw attention to the potential role ISGs play in offspring outcomes and consequences. Another notable gene that was shown to be differentially methylated was MS4A3, which is crucial in myeloid cell differentiation [
6].
Additional studies have also suggested that the proinflammatory environment seen in GDM patients may be attributed to a dysfunctional antigen processing and presentation system. Deng et al. identified significant methylation of genes belonging to the Human Leukocyte Antigens (HLA) class II of the major histocompatibility complex (e.g. HLA-DRB1, HLA-DPB1, HLA-DPA1, HLA-G, etc.) in 26 pregnant women with GDM. In addition, Li et al. identified several hypomethylated hub genes that could serve as potential prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers for GDM, some being HLA genes [
26,
27]. Most notably, they expressed particular interest in HLA-DRB1 which has been established to increase insulin secretion and decrease risks and complications of type 2 diabetes.
The mechanism by which an inflammatory state can disrupt insulin secretion, causing resistance and consequently GDM warrants additional research. However, the epigenetic screening, identification, and analysis of differentially methylated inflammatory-related genes such as IFI6, MS4A3, HLA-DRB1 allow us to further discover the missing pieces necessary to fully understand the pathogenesis of GDM. Such new discoveries are clinically significant in preventing, diagnosing, and treating the disease.
Although additional longitudinal studies are required to further assess the efficacy and safety in utilizing ADCYAP1, SOCS3, PI3KR1, ADIPOQ or HLA genes as potential biomarkers; it is safe to say that the epigenome profiling and analysis done so far are expanding what is known about GDM pathogenesis. The tissue-specific and pathway-specific epigenetic alterations seen in patients once again address the multifactorial aspect of the disease. This suggests that there are multiple methods and sources in which GDM can be screened, diagnosed, and treated. Moreover, the identification and analysis of such biomarkers can also be clinically useful in determining the potential consequences on the children born to mothers with GDM.
3.4. Consequences to the Offspring
GDM is well known to have consequences in both mother and child-from the deeply studied increased risk of pre-eclampsia in the mother, to macrosomia and hypoglycemia in the child [
28]. Emerging research is shedding light on further ramifications GDM may pose to the child. These studies analyzed epigenetic markers found in pregnant women with GDM, and searched for any such similar markers in offspring.
3.4.1. Fetal Period
In an effort to better elucidate the molecular mechanisms behind the correlation between a history of GDM and cardiovascular disease, Cvitic and colleagues studied the epigenetic mechanisms involved with fetal programing of arterial and venous endothelial cells while in the presence of GDM. For this study, genome-wide methylation analysis of fetoplacental arterial endothelial cells (AEC) and venous endothelial cells (VEC) from GDM pregnancies and controls were analyzed. Transcriptome and methylation analyses further identified GDM-specific variations in gene expression, with 408 genes in the AEC and 159 genes in the VEC. Researchers discovered that these genes are associated with programming cell morphology and cellular movement in both endothelial cell types, specifically within actin organization and cell barrier function. It is still unclear if these changes represent vasculature within the fetus itself (the cells are placentally derived), since both placenta and fetus live in the same intrauterine environment, it is a possibility. A similar study analyzing adult adipose [
29].
Kasuga et al. aimed to determine if there are any epigenetic changes between neonates born to mothers who were diagnosed with GDM after 24 gestational weeks (late GDM), compared with neonates born to mothers who were diagnosed before 24 gestational weeks (early GDM). Cord blood samples were taken from 84 early GDM participants, 78 late GDM participants, and 60 controls. Researchers found no significant difference in the methylation of umbilical cord blood between early GDM, late GDM, and normal controls. Researchers detail that in Japan, the country in which this study was conducted, GDM is typically managed before 24 gestational weeks, although the effectiveness of that therapy may be lower than treatment for late GDM [
30].
3.4.2. Neonatal Period
In another investigation, Kasuga et al. furthered their quest in determining the role of epigenetics in fetal hypoglycemia in utero, when their mother has GDM. 128 neonates were included in the study, the cord blood was analyzed for differing patterns of DNA methylation. Using a linear regression analysis, 12 CpG sites were associated with plasma glucose levels taken 1 hour after birth. When controlling for sex, delivery method, and gestational day, methylation at 2 CpG sites near an alternative transcription start site (ZNF696) was significantly associated with decreased plasma glucose following birth [
31].
Wang et al. aimed to determine if epigenetic markers found in the cord blood of postpartum mothers with GDM would have any correlation with fetal birth weight. Using 30 participants with matched controls (infant sex, gestational age at delivery) 7 hypermethylated and 10 hypomethylated genes were validated from the author’s previous epigenome-wide association studies. No significant correlations were found, however, between the gene methylation and the biomarkers. Despite this negative result, the researchers note that data on lifestyle factors of the study participants, such as their dietary habits and physical activity levels, were not collected [
32].
Using mother-child dyads, Ott et al. sought to evaluate the underlying molecular mechanism of tissue-specific insulin resistance and if these changes, which may cause GDM in expectant mothers, had any effect on fetal metabolism. In this study, 25 participants (mother-child dyads) with 30 matched controls were observed. Maternal IR gene and protein expression was measured in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue samples. Blood collected from mother-offspring pairs was analyzed for DNA methylation in IR promoter and intronic regions. Researchers found that in women with GDM, IR mRNA and protein expression in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue was significantly reduced compared to the control. Interestingly, the decrease in expression was more pronounced in the visceral adipose tissue, regardless of maternal BMI. The maternal blood samples, however, showed weaker correlations and less variability, indicating that adipose may be a more potent diagnostic tissue. The blood samples from offspring showed patterns of hypermethylation at transcriptor factor binding sites, and hypomethylation at inhibiting transcriptor factor binding sites-however the significance of these alterations are still unclear in the context of metabolism [
33].
Canouil and colleagues similarly studied mother-offspring pairs to determine if the offspring inherited any epigenetic effects from GDM exposure, and if any of these changes had any effect on the offspring. Using a cohort from a previous multicenter study, 536 mother-offspring pairs were included, of which 298 were positive for GDM. Maternal venous blood and offspring cord blood samples were analyzed. Researchers did not find any shared epigenetic markers (differentially methylated CpG probes) between mother and offspring, suggesting that epigenetic heritability in the context of GDM may be more complex than previously thought [
34]. Compared to the Ott et al. study, this study has a dramatically larger sample size, however they focused on general analysis of methylation of CpG sites, whereas Ott et al honed in on specific locations surrounding the Insulin Receptor promoter site and intronic regions.
In perhaps the largest study of its kind to date, Howe and colleagues performed a meta-analysis, including 3,677 mother-newborn pairs, 317 with GDM. Linear regressions were used to find differentially methylated regions. Two hypomethylated regions in newborns exposed to GDM were found, one at the OR2L13 promoter, and another in the gene body of CYP2E1. Interestingly, the OR2L13 gene has been associated with autism spectrum disorder [
35] and CYP2E1 has been shown to be upregulated in type 1 and type 2 diabetes [
36,
37]. It is important to note that causation cannot be determined from this study alone, as autism spectrum disorder, as well as T1DM and T2DM, are complex, multifactorial issues with no one causative agent. Further studies are warranted to better elucidate these mechanisms, and the extent to which they are associated with, or cause, these conditions.
3.4.3. Childhood Through Adolescence
Upon observing the correlation between GDM exposure and obesity in childhood, Gagne-Ouellet et al. aimed to determine if there are any epigenetic markers linking GDM with body composition at 5 years of age. Samples from 24 GDM mothers and 42 controls were analyzed for DNA methylation (especially at the lipoprotein lipase locus), and body composition (height, weight, BMI, body fat, lean mass) was assessed in their children at the age of 5 years old. After adjusting for the sex of the child, maternal age, and pre-pregnancy BMI, researchers found significant positive correlations between maternal LPL DNA methylation levels and birth-weight (r= 0.252) weight at 5 years old (r= 0.314), and fat mass (r= 0.275), and a negative correlation with lean mass (r= -0.306). Interestingly, there was a negative correlation between lipoprotein lipase DNA methylation and mRNA levels in the placenta, which may suggest the regulation of transcriptional activity. Taken together, these findings support fetal metabolic programing via DNA methylation [
38].
In a different study, Gagne-Ouellet further examined the link between fetal DNA methylation of the leptin gene as a consequence of exposure to maternal hyperglycemia, and its association to childhood obesity. Researchers studied DNA methylation of the LEP CpG site, neonatal leptinemia, and adiposity as measured by skinfold thickness in children aged 3 years old. 259 mother-child dyads were included in this study. A multivariate linear analysis was conducted. 3 CpGs associated with neonatal leptinemia were identified, with cg05136031 and cg15758240 being associated with BMI and fat distribution at 3 years of age, respectively [
39].
Shiau and colleagues similarly aimed to detail any potential epigenetic patterns found in the offspring during childhood (ages 3-10 years, median age of 5.6 years) following exposure to a GDM gestation. 578 GDM mother-child pairs, with 578 control mother-child pairs were included in this study. A blood draw was used to harvest DNA, and anthropometric measurements were taken for analysis. For each child, epigenetic age was determined using 2 different epigenetic clock algorithms, Horvath and Hannum. Researchers found that offspring from the GDM group had accelerated aging, or they had DNA methylation patterns deemed older than their chronological age by approximately 5 months using the Horvath method, compared with the control group. This increased DNA age was likewise associated with increased offspring weight, BMI, waist circumference, and body fat percentage [
40]. Epigenetic age has been associated with cardiometabolic risk factors [
41] , suggesting that GDM may have longer ramifications than previously understood.
The following two studies aim to discover if heritable epigenetic variations exist in older children through adolescence (9-16 years). Using the Danish National Birth Cohort, Hjort et al. included 608 GDM offspring and 626 controls. Of the 76 differentially methylated CpGs found in the GDM offspring, 13 of them were found to be independently associated with maternal GDM. 3 of these were additionally found to be hypomethylated BMI-associated CpGs; cg00992687, cg09452568 of ESM1, and cg14328641 of MS4A3. These findings suggest that rather than GDM in isolation, the combination of GDM with pre-pregnancy BMI may be involved in shaping the epigenetic profile of GDM offspring [
42]. Although previously studied in the context of adverse pregnancy events, this study sheds light on the importance of pre-pregnancy BMI as having the potential for altering epigenetic profiles.
The next study, after identifying DNA methylation at the ESM1 and MS4A3 genes Manitta and colleagues sought to determine if the altered methylation and expression of these genes were detectable in blood and in subcutaneous adipose tissue. A different cohort of offspring were analyzed, one arm exposed to GDM, and one arm exposed to GDM, and the other exposed to Type 1 DM, both compared to a control group. Interestingly, researchers did not find the same pattern of hypomethylation along the ESM1 and MS4A3 genes. However, researchers identified higher MS4A3 DNA methylation in the adipose tissue of offspring exposed to Type 1 Diabetes, and decreased ESM1 expression in the adipose tissue of offspring exposed to GDM. Another gene identified in a previous study by the group, TSPAN14, was found to have lower expression in the adipose tissue of offspring exposed to GDM, and was the only gene in this study that was positively associated with maternal pre-pregnancy BMI, and the offspring’s HbA1C levels and adiposity [
43]. This study furthers understanding regarding the complex interplay of pre-pregnancy BMI and it's association with altered epigenetic profiles, especially how the heritable profiles may shape metabolism of the offspring, even as the child ages. Research in this field is still at its infancy, and it is still unclear as to what ramifications these altered epigenetic profiles may have on the offspring. Metabolic diseases are notoriously multifactorial, and the environment the mother and offspring are exposed to, including sleep, dietary, and exercise habits are additional factors to be considered.
4. Discussion
The field of epigenetics, despite being in its infancy, is steadily growing. Although its clinical utility may still be limited, chronicling the epigenetic profiles associated with GDM is quite a worthwhile endeavor; in addition to contributing to science for its own sake, epigenetic profiles may soon become clinically useful. These profiles can target specific genes for gene therapy, or they can be used as screening tools to help prevent downstream complications. By assessing patients’ susceptibilities to developing GDM, preventative measures may be employed earlier, thus potentially mitigating harmful effects. Since GDM is a highly multifactorial condition, modification of lifestyle is among the most powerful effectors; additionally, the genetic susceptibilities of individuals may vary highly [
2]. Therefore, using epigenetic profiles is a logical next step in the determination of screening at-risk individuals.
Limitations to this investigation include the immense variability of the included studies. Many of them begin by sequencing the genomes of GDM mothers against healthy control mothers, looking for areas of hyper/hypomethylation and how they differ. We can note that between studies, different researchers have focused on different genes-that is to say, we have not found overlap in the specific markers found by the researchers. Interestingly, many of these different markers are related to adipose metabolism, insulin receptor synthesis and degradation, inflammation, and leptin and ghrelin metabolism. Further limitations include the lack of diversity in generalizing populations. Most of the participants from each study were taken as convenience samples, such as patients who were diagnosed, or had given birth in a specific hospital. Researchers note this, particularly in studies performed in homogenous populations, such as a single province in Japan-may not generalize to diverse populations. Many of the studies also have not taken into account specific lifestyle factors of the expectant and new mothers. Some studies note that the mothers had not been smoking nor drinking alcohol, however activity levels, diet, and family history were not described. As GDM is highly multifactorial, we cannot say with certainty to what extent these epigenetic changes have on causation or association of GDM.
Future studies may take into account the participants’ lifestyles, such as diet, exercise frequency, smoking history, and how these effectors may play a role in epigenetic modifications regarding GDM. Additionally, larger sample sizes involving individuals of varying ages and ethnicities would allow researchers to better generalize their findings.
5. Conclusions
In this review, we present a summary of various studies aiming to identify different epigenetic markers relating to GDM, assess the clinical utility of said markers, and explore any association between GDM-specific traits and possible consequences to offspring. Although the science of epigenetics is still in its infancy, researchers worldwide have begun to elucidate the various mechanisms at play, creating an epigenetic map to characterize certain conditions. Breakthroughs in this field may allow clinicians to better screen for GDM, and give patients an opportunity to enact various preventative health measures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Camila Araujo, Vivian Tieu; Methodology, Camila Araujo, Vivian Tieu; Data curation, Camila Araujo, Vivian Tieu, Garbel Zeynalvand; Writing—Original draft preparation, Camila Araujo, Vivian Tieu, Garbel Zeynalvand.; Writing—review and editing, Camila Araujo, Vivian Tieu, Garbel Zeynalvand.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Susan Yazdanmehr and Dr. Mukesh Agarwal for their advice and support in the creation of this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sheiner, E. "Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Long-Term Consequences for the Mother and Child Grand Challenge: How to Move on Towards Secondary Prevention?". Front Clin Diabetes Healthc 1 (2020): 546256. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36993989. [CrossRef]
- Plows, J. F., J. L. Stanley, P. N. Baker, C. M. Reynolds, and M. H. Vickers. "The Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus." Int J Mol Sci 19, no. 11 (Oct 26 2018). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30373146. [CrossRef]
- 3Dalfra, M. G., S. Burlina, G. G. Del Vescovo, and A. Lapolla. "Genetics and Epigenetics: New Insight on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus." Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 11 (2020): 602477. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33335512. [CrossRef]
- Lister, R., M. Pelizzola, R. H. Dowen, R. D. Hawkins, G. Hon, J. Tonti-Filippini, J. R. Nery, et al. "Human DNA Methylomes at Base Resolution Show Widespread Epigenomic Differences." Nature 462, no. 7271 (Nov 19 2009): 315-22.
- Wu, P., W. E. Farrell, K. E. Haworth, R. D. Emes, M. O. Kitchen, J. R. Glossop, F. W. Hanna, and A. A. Fryer. "Maternal Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Profiling in Gestational Diabetes Shows Distinctive Disease-Associated Changes Relative to Matched Healthy Pregnancies." Epigenetics 13, no. 2 (2018): 122-28. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27019060. [CrossRef]
- Del Vecchio, G., Q. Li, W. Li, S. Thamotharan, A. Tosevska, M. Morselli, K. Sung, et al. "Cell-Free DNA Methylation and Transcriptomic Signature Prediction of Pregnancies with Adverse Outcomes." Epigenetics 16, no. 6 (Jun 2021): 642-61. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33045922. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., T. Zhang, and Y. Chen. "Comprehensive Analysis of Gene Expression Profiles and DNA Methylome Reveals Oas1, Ppie, Polr2g as Pathogenic Target Genes of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus." Sci Rep 8, no. 1 (Nov 2 2018): 16244. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30389953. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Q. Lu, and C. Chang. "Epigenetics in Health and Disease." Adv Exp Med Biol 1253 (2020): 3-55. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32445090. [CrossRef]
- Wander, P. L., E. J. Boyko, K. Hevner, V. J. Parikh, M. G. Tadesse, T. K. Sorensen, M. A. Williams, and D. A. Enquobahrie. "Circulating Early- and Mid-Pregnancy Micrornas and Risk of Gestational Diabetes." Diabetes Res Clin Pract 132 (Oct 2017): 1-9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28783527. [CrossRef]
- Legare, C., V. Desgagne, C. Poirier, K. Thibeault, F. White, A. A. Clement, M. S. Scott, et al. "First Trimester Plasma Micrornas Levels Predict Matsuda Index-Estimated Insulin Sensitivity between 24th and 29th Week of Pregnancy." BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 10, no. 2 (Mar 2022). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35246451. [CrossRef]
- Stirm, L., P. Huypens, S. Sass, R. Batra, L. Fritsche, S. Brucker, H. Abele, et al. "Maternal Whole Blood Cell Mirna-340 Is Elevated in Gestational Diabetes and Inversely Regulated by Glucose and Insulin." Sci Rep 8, no. 1 (Jan 22 2018): 1366. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29358694. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H., S. Wu, Y. Zhu, M. Ye, J. Shen, Y. Liu, Y. Zhang, and S. Bu. "Hsa_Circrna_0054633 Is Highly Expressed in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Closely Related to Glycosylation Index." Clin Epigenetics 11, no. 1 (Feb 8 2019): 22. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30736847. [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla Rodriguez, B. S., and H. Mahdy. "Gestational Diabetes." In Statpearls. Treasure Island (FL) relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Heba Mahdy declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies., 2023.
- Li, X., W. Yang, and Y. Fang. "Epigenetic Profiles Reveal That Adcyap1 Serves as Key Molecule in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus." Comput Math Methods Med 2019 (2019): 6936175. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31485258. [CrossRef]
- Dias, S., S. Adam, P. Rheeder, J. Louw, and C. Pheiffer. "Altered Genome-Wide DNA Methylation in Peripheral Blood of South African Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus." Int J Mol Sci 20, no. 23 (Nov 20 2019). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31757015. [CrossRef]
- Rancourt, R. C., R. Ott, K. Schellong, T. Ziska, K. Melchior, W. Henrich, and A. Plagemann. "Altered Socs3 DNA Methylation within Exon 2 Is Associated with Increased Mrna Expression in Visceral Adipose Tissue in Gestational Diabetes." Epigenetics 16, no. 5 (May 2021): 488-94. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32752921. [CrossRef]
- Rancourt, R. C., R. Ott, T. Ziska, K. Schellong, K. Melchior, W. Henrich, and A. Plagemann. "Visceral Adipose Tissue Inflammatory Factors (Tnf-Alpha, Socs3) in Gestational Diabetes (Gdm): Epigenetics as a Clue in Gdm Pathophysiology." Int J Mol Sci 21, no. 2 (Jan 12 2020). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31940889. [CrossRef]
- 18. Rancourt, R. C., R. Ott, K. Schellong, K. Melchior, T. Ziska, W. Henrich, and A. Plagemann. "Visceral Adipose Tissue Alteration of Pi3kr1 Expression Is Associated with Gestational Diabetes but Not Promoter DNA Methylation." Adipocyte 8, no. 1 (Dec 2019): 339-46. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31608772. [CrossRef]
- Furse, S., A. Koulman, S. E. Ozanne, L. Poston, S. L. White, and C. L. Meek. "Altered Lipid Metabolism in Obese Women with Gestational Diabetes and Associations with Offspring Adiposity." J Clin Endocrinol Metab 107, no. 7 (Jun 16 2022): e2825-e32. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35359001. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T. M. D. "Adiponectin: Role in Physiology and Pathophysiology." Int J Prev Med 11 (2020): 136. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33088464. [CrossRef]
- 21. Ott, R., J. H. Stupin, K. Melchior, K. Schellong, T. Ziska, J. W. Dudenhausen, W. Henrich, R. C. Rancourt, and A. Plagemann. "Alterations of Adiponectin Gene Expression and DNA Methylation in Adipose Tissues and Blood Cells Are Associated with Gestational Diabetes and Neonatal Outcome." Clin Epigenetics 10, no. 1 (Oct 24 2018): 131. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30355290. [CrossRef]
- Lu, T., A. Cardenas, P. Perron, M. F. Hivert, L. Bouchard, and C. M. T. Greenwood. "Detecting Cord Blood Cell Type-Specific Epigenetic Associations with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Early Childhood Growth." Clin Epigenetics 13, no. 1 (Jun 26 2021): 131. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34174944. [CrossRef]
- Pinto, Y., S. Frishman, S. Turjeman, A. Eshel, M. Nuriel-Ohayon, O. Shrossel, O. Ziv, et al. "Gestational Diabetes Is Driven by Microbiota-Induced Inflammation Months before Diagnosis." Gut 72, no. 5 (May 2023): 918-28. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/36627187. [CrossRef]
- Pan, X., X. Jin, J. Wang, Q. Hu, and B. Dai. "Placenta Inflammation Is Closely Associated with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus." [In eng]. Am J Transl Res 13, no. 5 (2021): 4068-79.
- Pinney, S. E., A. Joshi, V. Yin, S. W. Min, C. Rashid, D. E. Condon, and P. Z. Wang. "Exposure to Gestational Diabetes Enriches Immune-Related Pathways in the Transcriptome and Methylome of Human Amniocytes." J Clin Endocrinol Metab 105, no. 10 (Oct 1 2020): 3250-64. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgaa466. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32687192. [CrossRef]
- Li, E., T. Luo, and Y. Wang. "Identification of Diagnostic Biomarkers in Patients with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Based on Transcriptome Gene Expression and Methylation Correlation Analysis." Reprod Biol Endocrinol 17, no. 1 (Dec 27 2019): 112. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31881887. [CrossRef]
- Deng, X., Y. Yang, H. Sun, W. Qi, Y. Duan, and Y. Qian. "Analysis of Whole Genome-Wide Methylation and Gene Expression Profiles in Visceral Omental Adipose Tissue of Pregnancies with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus." J Chin Med Assoc 81, no. 7 (Jul 2018): 623-30. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29685721. [CrossRef]
- Moon, J. H., and H. C. Jang. "Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications." Diabetes Metab J 46, no. 1 (Jan 2022): 3-14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35135076. [CrossRef]
- Cvitic, S., B. Novakovic, L. Gordon, C. M. Ulz, M. Muhlberger, F. I. Diaz-Perez, J. E. Joo, et al. "Human Fetoplacental Arterial and Venous Endothelial Cells Are Differentially Programmed by Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Resulting in Cell-Specific Barrier Function Changes." Diabetologia 61, no. 11 (Nov 2018): 2398-411. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30091044. [CrossRef]
- Kasuga, Y., T. Kawai, K. Miyakoshi, A. Hori, M. Tamagawa, K. Hasegawa, S. Ikenoue, et al. "DNA Methylation Analysis of Cord Blood Samples in Neonates Born to Gestational Diabetes Mothers Diagnosed before 24 Gestational Weeks." BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 10, no. 1 (Jan 2022). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35046013. [CrossRef]
- Kasuga, Y., T. Kawai, K. Miyakoshi, Y. Saisho, M. Tamagawa, K. Hasegawa, S. Ikenoue, et al. "Epigenetic Changes in Neonates Born to Mothers with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus May Be Associated with Neonatal Hypoglycaemia." Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 12 (2021): 690648. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34267729. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. J., R. Huang, T. Zheng, Q. Du, M. N. Yang, Y. J. Xu, X. Liu, et al. "Genome-Wide Placental Gene Methylations in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Fetal Growth and Metabolic Health Biomarkers in Cord Blood." Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 13 (2022): 875180. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35721735. [CrossRef]
- Ott, R., K. Melchior, J. H. Stupin, T. Ziska, K. Schellong, W. Henrich, R. C. Rancourt, and A. Plagemann. "Reduced Insulin Receptor Expression and Altered DNA Methylation in Fat Tissues and Blood of Women with Gdm and Offspring." J Clin Endocrinol Metab 104, no. 1 (Jan 1 2019): 137-49. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30260402. [CrossRef]
- Canouil, M., A. Khamis, E. Keikkala, S. Hummel, S. Lobbens, A. Bonnefond, F. Delahaye, et al. "Epigenome-Wide Association Study Reveals Methylation Loci Associated with Offspring Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Exposure and Maternal Methylome." Diabetes Care 44, no. 9 (Sep 2021): 1992-99. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34116986. [CrossRef]
- Dall'Aglio, L., T. Muka, C. A. M. Cecil, W. M. Bramer, Mmpj Verbiest, J. Nano, A. C. Hidalgo, O. H. Franco, and H. Tiemeier. "The Role of Epigenetic Modifications in Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Systematic Review." Neurosci Biobehav Rev 94 (Nov 2018): 17-30. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30067938. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., S. D. Hall, J. F. Maya, L. Li, A. Asghar, and J. C. Gorski. "Diabetes Mellitus Increases the in Vivo Activity of Cytochrome P450 2e1 in Humans." Br J Clin Pharmacol 55, no. 1 (Jan 2003): 77-85. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12534643. [CrossRef]
- Howe, C. G., B. Cox, R. Fore, J. Jungius, T. Kvist, S. Lent, H. E. Miles, et al. "Maternal Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Newborn DNA Methylation: Findings from the Pregnancy and Childhood Epigenetics Consortium." Diabetes Care 43, no. 1 (Jan 2020): 98-105. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31601636. [CrossRef]
- 38. Gagne-Ouellet, V., A. A. Houde, S. P. Guay, P. Perron, D. Gaudet, R. Guerin, B. Jean-Patrice, et al. "Placental Lipoprotein Lipase DNA Methylation Alterations Are Associated with Gestational Diabetes and Body Composition at 5 Years of Age." Epigenetics 12, no. 8 (Aug 2017): 616-25. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28486003. [CrossRef]
- 39. Gagne-Ouellet, V., E. Breton, K. Thibeault, C. A. Fortin, A. Cardenas, R. Guerin, P. Perron, M. F. Hivert, and L. Bouchard. "Mediation Analysis Supports a Causal Relationship between Maternal Hyperglycemia and Placental DNA Methylation Variations at the Leptin Gene Locus and Cord Blood Leptin Levels." Int J Mol Sci 21, no. 1 (Jan 3 2020). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31947745. [CrossRef]
- Shiau, S., L. Wang, H. Liu, Y. Zheng, A. Drong, B. T. Joyce, J. Wang, et al. "Prenatal Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Exposure and Accelerated Offspring DNA Methylation Age in Early Childhood." Epigenetics 16, no. 2 (Jan-Feb 2021): 186-95. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32614694.
- 41. Huang, R. C., K. A. Lillycrop, L. J. Beilin, K. M. Godfrey, D. Anderson, T. A. Mori, S. Rauschert, et al. "Epigenetic Age Acceleration in Adolescence Associates with Bmi, Inflammation, and Risk Score for Middle Age Cardiovascular Disease." J Clin Endocrinol Metab 104, no. 7 (Jul 1 2019): 3012-24. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30785999. [CrossRef]
- Hjort, L., D. Martino, L. G. Grunnet, H. Naeem, J. Maksimovic, A. H. Olsson, C. Zhang, et al. "Gestational Diabetes and Maternal Obesity Are Associated with Epigenome-Wide Methylation Changes in Children." JCI Insight 3, no. 17 (Sep 6 2018). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30185669. [CrossRef]
- Manitta, E., I. C. Fontes Marques, S. Stokholm Bredgaard, L. Kelstrup, A. Houshmand-Oeregaard, T. Dalsgaard Clausen, L. Groth Grunnet, et al. "DNA Methylation and Gene Expression in Blood and Adipose Tissue of Adult Offspring of Women with Diabetes in Pregnancy-a Validation Study of DNA Methylation Changes Identified in Adolescent Offspring." [In eng]. Biomedicines 10, no. 6 (May 26 2022). [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).