1. Introduction
Destructive effects of carbonmonoxide (CO) gas on human systems have been known since the 19
th century. CO gas is a colorless, odorless, tasteless and nonirritant. CO is an end product of incomplete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels such as charcoal, wood, barbecue, waterpipe, exhaust, natural gas, or kerosene. The affinity of CO gas for hemoglobin (Hb) is 200-280 times higher than that of oxygen, and it leads to the formation of carboxyhemoglobin (COHb) [
1,
2]. CO poisoning causes tissue hypoxia and induce organ damage, such as the hearth, lung, brain, muscles and kidneys. The reason of organ damages is not only hypoxia but also inflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis and neuron necrosis cause organ damages, too [
3,
4].
The symptoms of acute and chronic CO poisoning are wide variety such as dizziness, vomiting, headache, syncope, myalgia, weakness, confusion, changes in consciousness and death [
1]. Long term and/or recurrent exposure to low concentration CO gas is defined as a chronic CO poisoning [
2,
5,
6]. Chronic exposure to CO can be occurred in many situations such as mine workers, kitchen workers, waterpipe, traffic policemen, heavy vehicle operators, and firefighters. Diagnosis of CO poisoning is generally difficult in patients exposed chronic CO poisoning. Chronic CO poisoning can generally be determined after a few hospital admissions [
7].
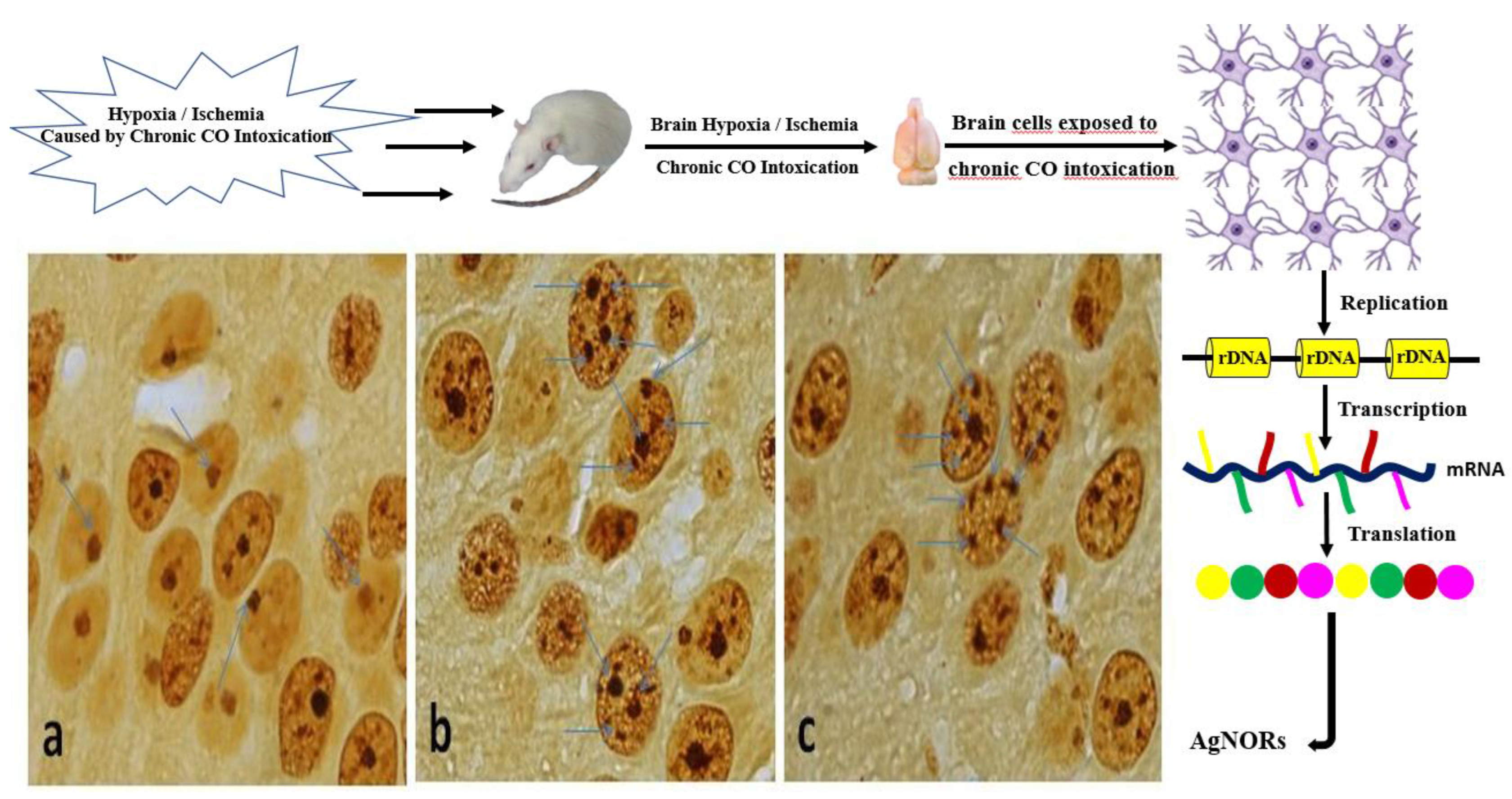
Nucleolar organizer regions (NORs) are chromosomal regions that contain ribosomal genes, which are necessary for protein synthesis that roles in the organization of the nucleolus region. Since these proteins in this region have the affinity to attract and bind silver by interacting with it, it is one of the important biomarkers that can be used for diagnostic purposes to obtain information about the activity of the nucleus and therefore the active capacity of the cell (proliferation, metabolic activity, etc.).
Different studies were done about the using of AgNOR as a biomarkers in Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group E [
8], testicular torsion [
9], different doses of CO poisoning in brain [
10], wound healing [
11], ST segment elevation myocardial infarction [
12], clinical exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [
13], comparison of FNAB and paraffin embedded tissue sections [
14], renal ischemia / reperfusion (I/R) injury [
15], hair root cells of humans [
16,
17], buccal epithelial cells of healthy individuals [
18], developmental stages of Down syndrome infants [
19], discrimination of benign from malign thyroid tissues [
20] etc. Also we showed that the both AgNOR sizes and numbers may be used as a marker for detection of the most reliable dose of rhamnetin [
21], curcumin [
22] and capsaicin [
23].
There are few studies about the evaluation of AgNOR for detection of tissues damage caused by CO intoxication in the literature [
1,
5,
24,
25,
26]. It was reported that the AgNOR number and size increase depending on the increasing of CO exposure because of the hypoxia. So both TAA/NA ratio and mean AgNOR number can be used as a biomarker to obtain knowledge about the level of myocardial injury [
1,
25]. Additionally, it was detected that the sizes of AgNOR increase when the levels of CO exposure increase in lung cells. Thus AgNOR method may give information about the cellular damage rate [
24]. In another study we detected that both AgNOR size and number give information about the level of CO exposure in skeletal muscle cells of rats [
5,
26]. In a study, we investigate the effect of acute doses of CO gas on rat brain tissue [
27]. To our knowledge, no study about the evaluation of the effect of chronic CO poisoning in brain tissue using the AgNOR staining method was performed in the literature. Thus, we performed this study to evaluate the effect of hypoxia caused by different levels of chronic CO exposure (1000 ppm and 3000 ppm) via total AgNOR area / total nuclear area (TAA/TNA) ratio and mean AgNOR number on rat brain tissue.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of Animal Groups and Experiment
The research was carried out on eighteen Albino Wistar adult male rats (weighing 200–300 g). Our study was approved with the letter dated 20/12/2013 and numbered 184 of Atatürk University Animal Experiments Local Ethics Committee Chairmanship.
Rats were randomly divided into three groups according to the different levels of chronic (for 30 min a day during seven days) CO intoxication as each group containing six rats:
Group A: It consists of rats kept in room air as the control group,
Group B: Consisting of rats treated with 1000 ppm CO gas and a mixture of room air,
Group C: Consisting of rats treated with 3000 ppm CO gas and a mixture of room air.
Two tubes of 10 L each containing CO-air mixture gas at concentrations of 1000 ppm and 3000 ppm were procured from Habas (Ind. and Med. Gases Production Industries Inc., Kocaeli-Turkey). Rats in the study group were exposed to CO gas in a closed transparent jar measuring 20X40X60 cm. The jar used had an inlet and outlet with a diameter of 2 cm on opposite sides. CO gas at 1000 ppm concentration was presented to Group B with a flow rate of 4 L/minutes for 30 minutes a day during seven days (chronically exposure). CO gas at 3000 ppm concentration was given to Group C with a flow rate of 4 L/minutes for 30 minutes a day during seven days (chronically exposure). No rats died after exposure. After each application, all of the rats were removed from the transparent jar to provide rats to breathe room air. They were placed in a standard cage, the bottom of which was covered with sawdust. The room temperature was 20 ± 2 0C. All of the rats received adequate food and water throughout the experiment. The rats were anaesthetized with urethane (intraperitoneal 1.25 g/kg) on the study’s 8th day [1-5]. Next, the rats were placed in the supine position for midline thoracotomy. They were sacrificed with intracardiac perfusion. After midline thoracotomy, perfusion fixation was achieved through intracardiac administration of 10% formalin solution, and brain tissues had been taken.
2.2. AgNOR Staining
The samples of brain tissues were taken into a 10% formalin solution for fixation. Following fixation, brain tissues samples were embedded in paraffin blocks (1X1X1 cm) after routine tissue processing protocols. Then, 5 µm thickness segments were acquired from the paraffin blocks, deparaffinized in xylene and rehydrated in graded alcohol series, respectively. After that, the slides, which is including brain tissues samples were air dried at room temperature for 15 minutes and fixed in pure methanol for 5 minutes. Silver staining of brain tissues samples was performed via a slightly modification of Benn and Perle [
28] and Lindner protocol [
29] as the temperature was brought to 37
0C and the time was reduced to 15 minutes [
30].
2.3. Image Analysis of TAA/TNA Ratio and Mean AgNOR Number of Brain Cells
The cerebral cortex region of brain was taken into consideration. The slides which is including silver-stained brain cells were evaluated with a light microscope (Eclipse 80i; Nikon. Tokyo-Japan), and the cells were photographed via a digital camera (Digital Sight DS-Fi1c; Nikon). Images of the silver-stained cells in the cerebral cortex region of brain were transferred to software. (ImageJ, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA.) [
31]. In our studies, we included 18 rats and fifty cells were evaluated for each rat. ImageJ is a license-free, open-source program that has a large worldwide user community and members. The instructions in the program can be automated and custom tools can be created. ImageJ Website has more than 300 macros ang 500 plugins. It is the fastest java image processing program in the world (it can filter a 2048 X 2048 image in 0,1 second. That is 40 million pixels per second). Mean, standard deviation, entire image, minimum and maximum selection, area, lengths and angles can be measured using real world units of measurement, as well as histograms and profile plots can be generated. Rectangle, ellipse or irregular area, line and point selections can be created and edited (
https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/features.html, (accessed on: 30 May 2023)). In the current study, 50 nuclei per slide were evaluated.
Fifty nuclei per slides have been evaluated. Each rat’s silver-stained cells in the cerebral cortex region of brain were photographed with a light microscope (Eclipse 80i; Nikon. Tokyo-Japan) attached to a digital camera (Digital Sight DS-Fi1c; Nikon) and the images obtained were analyzed using ImageJ version 1.47t image processing software [
31]. The detection of the mean AgNOR number was recognized by counting, and the measurements of the TAA / TNA ratio were identified using the “freehand selections” tool.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were carried out via the Statistical Package for the Social Science for Windows v. 23 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL). The normality assumption for the continuous variables was analyzed by Shapiro Wilk test. Because the data were not normally distributed (P < 0.05), non-parametric tests were performed for statistical analysis. The Kruskall–Wallis test was used for the comparison of all groups (more than two). For detection of significant difference between groups, the post-hoc (Dunn’s) test was used. The p<0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
3. Results
Demonstrative examples of silver stained NOR (
a:Control,
b:1000 ppm,
c:3000 ppm for cells in the cerebral cortex region of brain) were given in the
Figure 1.
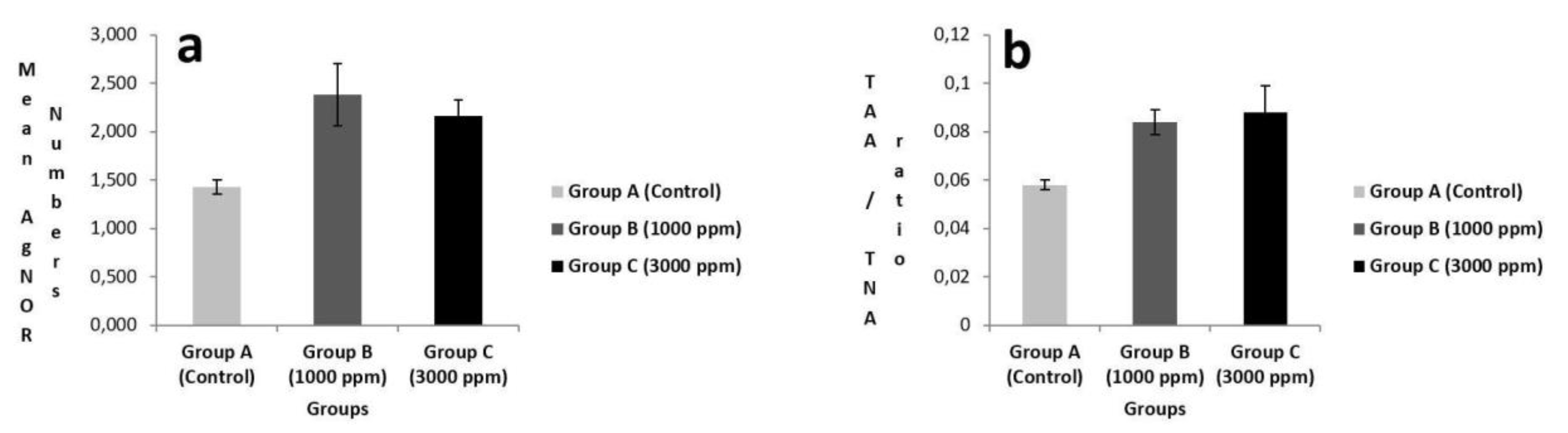
There were statistically differences TAA / TNA ratio and mean AgNOR number in all groups (p<0.05) (
Figure 2 and
Table 1). Pairwise comparisons were made between groups to determine which groups caused this difference. For TAA/TNA ratio, significant differences were detected between Group A (0.058±0.002) and Group B (0.084±0.005) (p<0.05), between Group A (0.058±0.002) and Group C (0.088±0.011) (p<0.05) for TAA/TNA ratio. Conversely, the difference wasn’t significant between Group B (0.084±0.005) and Group C (0.088±0.011) for TAA/TNA ratio (p>0.05) (
Table 2).
According to double comparison, significant differences were also found between Group A (1.428±0.073) and Group B (2.384±0.318) (p<0.05), between Group A (1.428±0.073) and Group C (2.160±0.167) (p<0.05) for mean AgNOR number. Conversely, the difference between Group B (2.384±0.318) and Group C (2.160±0.167) wasn’t statistically significant for mean AgNOR number (p<0.05) (
Table 2).
4. Discussion
CO Poisonings are reported to be cause of most of the fatal poisonings in most countries around the world. Deaths caused by CO are either underdiagnosed or reported lower than certain rate. For this reason, the certain rate of death caused by CO intoxication is not known [
1,
7]. In Turkey, CO poisoning caused from the use of stoves, water heaters and barbecue in areas with insufficient ventilation is very common especially during the winter months, and these patients frequently apply to the emergency services of hospitals. CO poisoning causes hypoxia in various parts of the living body, and the most sensitive area of body to hypoxia is the central nervous system [
7]. The new marker for easy and highly reliable detection of the damage degree to organs and systems of people exposed CO gas is needed.
It was reported that while the COHb level increases depending on the density of CO inhaled increases but it may not be reliable most of the time (the half-life of room air is 4–6 h) in the evaluating the intoxication degree [
32]. We suggested that AgNORs can be used as a marker to obtain more reliable information about CO intoxication levels in forensic medicine when COHb levels appear normal in autopsies with suspected poisoning [
25]. So AgNOR staining methods may be used in vivo or as a supplement of an autopsy for the evaluation of CO intoxication degree. Additionally we performed different studies about the effects of the different levels of both acute and chronic CO intoxication in various tissues and detected that AgNOR protein amounts may give information about the level of cellular damage caused by CO intoxication in lung [
24], chronic [
1] and acute [
25] intoxication in heart, chronic [
5] and acute [
26] CO intoxication in muscle cells. Also we detected significant correlation between AgNOR proteins amount and histopathological examination scores in various tissue samples [
1,
24,
25]. In a study conducted on rats by exposing to acute CO intoxication, we detected that AgNORs may give information about the intensity of CO intoxication and level of brain injury caused by acute exposure to CO [
27].
In our study, we found that statically significant differences among the all groups in term of both TAA / TNA ratio and mean AgNOR number. When the binary comparison of the groups was performed, significant differences were found between Group A and both of Group B and Group C for mean AgNOR number and TAA/TNA ratio. The description of new biomarkers for the detection of the cellular response to dangerous agents such as hypoxia is crucial to improve the diagnostic accuracy. When we take into consideration of our results, it was detected that both AgNOR protein amounts may be used as a marker for easy and reliable detection of the CO poisoning level in brain tissues.
Hypoxia and acidosis (caused by CO intoxication) leads to functional and structural injuries of different tissues such as heart, lung, muscle, brain etc. We know more about acute CO poisoning, but awareness and knowledge of chronic CO intoxication is progressing slowly. The exact number of patients with chronic CO poisoning is not known. Patients with chronic CO poisoning is often overlooked may be misdiagnosed (i.e. depression, chronic fatigue syndrome), because of obscure symptomatology, varieties of presentation, and lack of awareness of the problem [
33,
34].
There are various studies in which AgNOR parameters are evaluated as area index (AI) and coefficient of variation (CV) of AgNOR [
35], mean area, mean number, CV of area, CV of number [
36] and total area of dots in the nucleus [
37,
38]. In the current study, we aimed to determine the success of using AgNOR proteins for diagnostic purposes with a new approach, TAA/TNA measurement method. In dividing and metabolically active cells, not only gene expression but also the morphology of the cell (nuclear volume, etc.) change, too. Therefore, our new approach (the determination of the ratio of the amount of expressed AgNOR protein to the nuclear area) provides us with more certain knowledge about the cell's proliferation and metabolic activity capacity. This shows that our new approach is a more reliable diagnostic marker.
The new and promising markers with highly reliable and easy to apply in order to determine the effect of toxication in different organs and tissues (especially brain tissues) that are chronically exposed to carbon monoxide intoxication are needed. For this purpose we aimed to evaluate the effect of hypoxia caused by different levels of chronic CO exposure via mean AgNOR number and TAA / TNA ratio on rat brain tissue. According to our results, it seems that AgNOR may be used for this purpose. All living cells tend to protect themselves from external and internal dangerous agents such as CO intoxication. Therefore, may the increasing of these proteins’ amounts caused from the continuity of this process or be role the production of others protective proteins on the regulation of gene expression and signaling transduction pathways against chronic CO intoxication? May these proteins to be taken into consideration in treatment of the hypoxia and asphyxia? In individuals at risk for hypoxic and asphyxic births, can the use of these proteins such as folate or B12 reduce the risk of hypoxic and/or asphyxic birth? To obtain the most certain knowledge, additional studies involving large series about the current topic should be performed.
5. Conclusions
The size, number and distribution of AgNORs show the metabolic activities, proliferation index and response to dangerous agents of different cells. In addition, AgNORs can assist the physician in the early diagnosis of both acute and chronic CO poisonings level in organs and systems caused by hypoxic injury and the development of effective treatment strategies for patients exposed to these conditions at a later stage. This technique is also cheap and easy to perform. Perhaps with the current approach, new treatment strategies may be developed in the near future.
Funding:
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.S., S.O. Methodology: A.S., R.E. M.A., S.O. Software: R.E., M.A. Validation: A.S., R.E., S.O. M.A. Formal Analysis: R.E., A.S: M.A. Investigation: A.S., M.A. S.O. Resources: S.O., M.A. Data Curation: S.O., M.A. Writing – Original Draft Preparation: S.O., R.E., M.A., A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Saritas A, Gunes H, Colakoglu S, Eroz R, Akoz A, Oktay M, Buyukkaya A, Kandis H, Ozkan A. Are there any effects of chronic carbon monoxide exposure on argyrophilic nucleolar-organizing region–associated protein synthesis in rat myocardium? Hum Exp Toxicol. 2016;35(9):921–928. [CrossRef]
- Raaijmakers NJ, Bokma AHF, Eggen GG, Prins G, Alsma J. An unhealthy blush - secondary erythrocytosis due to waterpipe smoking. Neth J Med. 2020;78(4):202-205.
- Al-Moamary MS, Al-Shammary AS, Al-Shimemeri AA, Ali MM, Al-Jahdali HH, Awada AA. Complications of carbon monoxide poisoning. Saudi Med J. 2000;21:361–3.
- Kim SG, Woo J, Kang GW. A case report on the acute and late complications associated with carbon monoxide poisoning: Acute kidney injury, rhabdomyolysis, and delayed leukoencephalopathy. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(19):e15551.
- Gunes H, Saritas A, Eroz R, Colakoglu S. Use of argyrophilic nucleolar–organizer region-associated protein synthesis in skeletal muscle cells for prediction of chronic carbon monoxide exposure. Toxin Reviews. 2020;39:349-354. [CrossRef]
- Dorey A, Scheerlinck P, Nguyen H, Albertson T. Acute and Chronic Carbon Monoxide Toxicity from Tobacco Smoking. Military Medicine. 2020;185(1-2):e61–e67. [CrossRef]
- Katirci Y, Kandis H, Aslan S, Kirpinar I. Neuropsychiatric disorders and risk factors in carbon monoxide intoxication. Toxicol Ind Health. 2011;27(5):397-406. [CrossRef]
- Karagun E, Eroz R. Argyrophilic nucleolar organizing regions in patients with Xeroderma Pigmentosum Group E. Exp Dermatol. 2021 Mar;30(3):416-417. doi: 10.1111/exd.14238. Epub 2020 Nov 27. PMID: 33200418. [CrossRef]
- Kabaklıoğlu M, Eroz R, Kaya M. May Argyrophilic Nucleolar Organizer Regions Be Used as a Biomarker for the Detection of the Degree of Ischemic Damage Instead of Tunel in Testicular Torsion? Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Oct 29;57(11):1177. doi: 10.3390/medicina57111177. PMID: 34833395; PMCID: PMC8619308. [CrossRef]
- Yesildag K, Kokulu K, Mutlu H et al. Argyrophilic nucleolar organizer regions as a promising biomarker for the detection of brain hypoxia levels caused by different doses of carbon monoxide poisoning. Gac Med Mex. 2021;157(6):610-617. English. doi: 10.24875/GMM.M21000625. PMID: 35108251. [CrossRef]
- Kaya M, Eroz R, Kabakliogli M. Expression of nucleolin, nucleophosmin, upstream binding transcription factor genes and propolis in wound models. J Wound Care. 2022 Oct 1;31(Sup10):S28-S40. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2022.31.Sup10.S28. PMID: 36240873. [CrossRef]
- Damar İH, Eroz R. Argyrophilic Nucleolar Organizer Regions as New Biomarkers in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022 Feb 14;9(2):58. doi: 10.3390/jcdd9020058. PMID: 35200711; PMCID: PMC8875583. [CrossRef]
- Turan Sönmez F, Eröz R. The role of argyrophilic nucleolar organizing region-associated proteins in clinical exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Int Med Res. 2018 Dec;46(12):4995-5003. doi: 10.1177/0300060518788751. Epub 2018 Aug 8. PMID: 30088791; PMCID: PMC6300929. [CrossRef]
- Tasdemir S, Eroz R, Cucer N et al. Comparison of fine needle aspiration biopsy and paraffin embedded tissue sections for measuring AgNOR proteins. Biotech Histochem. 2015 Jul;90(5):395-9. doi: 10.3109/10520295.2015.1013989. Epub 2015 Apr 6. PMID: 25843622. [CrossRef]
- Nisari M, Eroz R, Nisari M et al. Investigation of argyrophilic nucleolar organizing region. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2016;117(6):345-50. doi: 10.4149/bll_2016_068. PMID: 27546367. [CrossRef]
- Eroz R, Tasdemir S, Dogan H. Is there any relationship between decreased AgNOR protein synthesis and human hair loss? Biotech Histochem. 2012 Nov;87(8):494-8. doi: 10.3109/10520295.2012.698307. Epub 2012 Jul 2. PMID: 22747173. [CrossRef]
- Tasdemir S, Eroz R, Dogan H et al. Association Between Human Hair Loss and the Expression Levels of Nucleolin, Nucleophosmin, and UBTF Genes. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2016 Apr;20(4):197-202. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2015.0246. Epub 2016 Feb 11. PMID: 26866305. [CrossRef]
- Selvi B, Demirtas H, Eroz R et al. Reduction of the argyrophilic nucleolar organizing region associated protein synthesis with age in buccal epithelial cells of healthy individuals. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2015 Apr;27(2):201-8. doi: 10.1007/s40520-014-0263-6. Epub 2014 Aug 1. PMID: 25082567. [CrossRef]
- Eroz R, Okur M, Ozkan A et al. Does higher NORs expression affect the developmental stages of Down syndrome infants? Genet Couns. 2012;23(2):249-53. PMID: 22876584.
- Eroz R, Cucer N, Unluhizarci K et al. Tiroid papiller karsinom ve normal tiroid hücre çekirdeklerinde AgNOR sayısının değerlendirilmesi. Erciyes Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi (Journal of health sciences). 2010;102-107. https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/pub/eujhs/issue/44542/552470.
- Ertekin T, Bozkurt O, Eroz R et al. May argyrophilic nucleolar organizing region-associated protein synthesis be used for selecting the most reliable dose of drugs such as rhamnetin in cancer treatments? Bratisl Med Jour. 2016;117 (11): 653-658. [CrossRef]
- Nisari M, Yilmaz S, Eroz R et al. The detection of curcumins' antitumoral effects via argyrophilic nucleolar organizing region-associated protein synthesis in mice with Ehrlich's ascitic carcinoma. Bratisl Med Jour. 2017; 118(1):61-65. [CrossRef]
- Nisari M, Eroz R. Does capsaicin have therapeutic benefits in human colon adenocarcinoma? Selection of the most reliable dose via AgNOR. Turk J Med Sci. 2020;3;50(4):1076-81. [CrossRef]
- Çolakoğlu S, Saritas A, Eroz R, Oktay M, Yaykasli KO, Akoz A, Kaya E, Kandis H. Is one-time carbon monoxide intoxication harmless? Evaluation by argyrophilic nucleolar-organizing regions staining method. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2015;34(1):24-31. [CrossRef]
- Kandiş H, Afacan MA, Eröz R, Colakoglu S, Bayramoglu A, Oktay M, Saritas A, Colak S, Kaya M, Kara İH. Can argyrophilic nucleolar organizing region-associated protein amount be used for the detection of cardiac damage? Hum Exp Toxicol 2015;35: 323-331. [CrossRef]
- Eroz R, Saritas A, Colakoglu S, Oktay M, Kandis H. Evaluation of argyrophilic nucleolar organizing region–associated protein synthesis in femoral muscle cells of rats exposed 3000 ppm carbon monoxide gas. Konuralp Medical Journal. 2016;8: 9-13.
- Yesildag K, Kokulu K, Mutlu H, Eroz R, Taha-Sert E, Saritas A. Argyrophilic nucleolar organizer regions as a promising biomarker for the detection of brain hypoxia levels caused by different doses of carbon monoxide poisoning. Gac Med Mex. 2021;157(6):610-617. English. doi: 10.24875/GMM.M21000625. PMID: 35108251. [CrossRef]
- Benn PA, Perle M. Chromosome staining and banding techniques In: Rooney DE, Czepulkowski BH. (eds). Human Cytogenetics, Constitutional Analysis, practical approach, Vol 1 Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1986; p.91–118.
- Lindner LE. Improvements in the silver-staining technique for nucleolar organizer regions (AgNOR). Journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry 1993; 41(3):439–445. [CrossRef]
- Imamoglu N, Eroz R, Canatan H, Demirtas H and Saatci C. Nuclear AgNOR Protein Enhancement in Nucleoplasms of Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes of Babies/Children With Down Syndrome. Microsc Res Tech. 2016;79(3):133-9. [CrossRef]
- Rasband WS (1997–2016) ImageJ U. S. National Institutes of Health. Bethesda. Maryland. USA. https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/.
- Kandis H, Katırcı Y, Cakır Z, Aslan S, Uzkeser M, Bilir O. A retrospective analyze of the patients admitted to emergency service for carbon monoxide intoxication. Eurasian J Emerg Med. 2007;6(3):21-25.
- Myers RA, DeFazio A, Kelly MP. Chronic carbon monoxide exposure: a clinical syndrome detected by neuropsychological tests. J Clin Psychol. 1998;54(5):555-67.
- Heckerling PS. Occult carbon monoxide poisoning: a cause of winter headache. Am J Emerg Med. 1987;5:201–204. [CrossRef]
- Kobyakov D, Klimachev V, Avdalyan A, Bobrov I, Bychkova E, Kruglova N, Lazarev A, Lushnikova E, Nepomnyashchikh L. Association between Argyrophilic Proteins of Nucleolar Organizer Regions, Clinicomorphological Parameters, and Survival in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer Int. 2014;2014:891917. doi: 10.1155/2014/891917. Epub 2014 Jan 2. PMID: 26316948; PMCID: PMC4437406. [CrossRef]
- Bànkfalvi A, Ofner D, Schmid KW, Schmitz KJ, Breukelmann D, Krech R, Böcker W. Standardized in situ AgNOR analysis in breast pathology: diagnostic and cell kinetic implications. Pathol Res Pract. 1999;195(4):219-29. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(99)80038-7. PMID: 10337659. [CrossRef]
- Slowinska-Klencka D, Klencki M, Popowicz B, et al. AgNOR quantification in the diagnosis of follicular pattern thyroid lesions. Analysis and Quantitaive Cytology and Histology 2003;25:347–352.
- Slowi’nska-Klencka D, Klencki M, Popowicz B, et al. Multiparameter analysis of AgNOR in thyroid lesions: comparison with PCNA expression. Histol Histopathol 2004;19:785–792. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).