1. Introduction
After the start of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, various vaccines have been developed in order to control its spread [
1]. In our setting, the most widely used vaccines have been mRNA-1273/Moderna and BNT162b2/Pfizer. These vaccines have been administered in two doses and the administration of a third booster dose has been recommended.
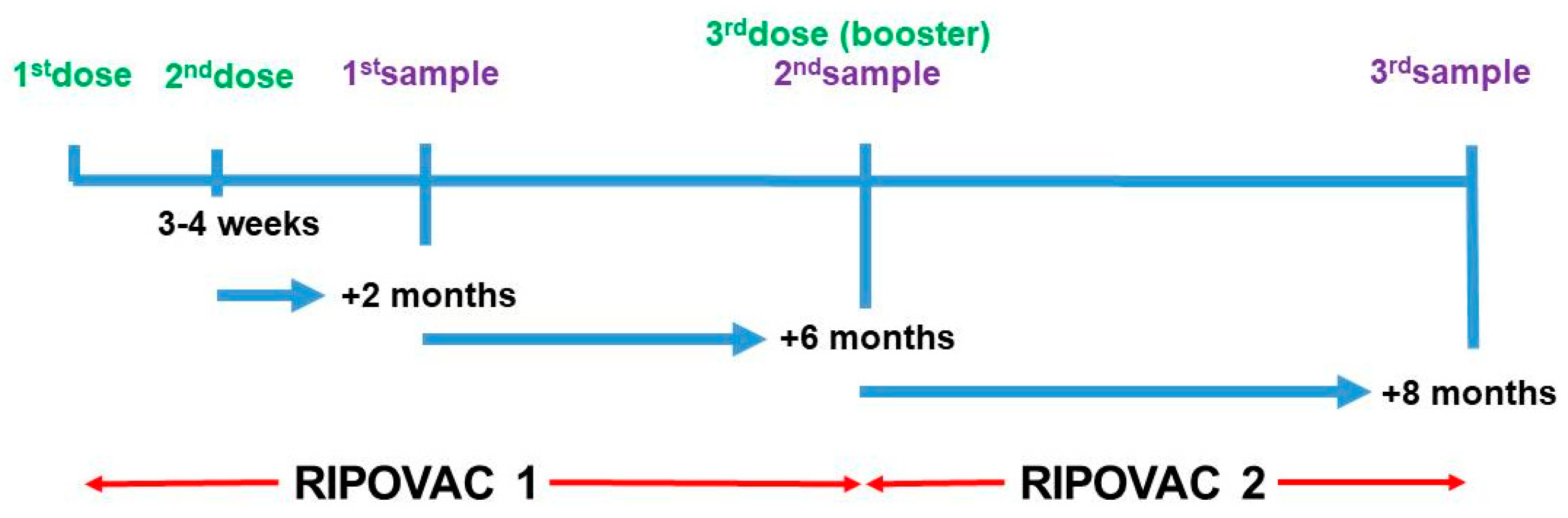
We undertook the RIPOVAC (Respuesta Immune POst-Vacuna Covid) study in 2021 (
Figure 1), in whose first phase we studied the persistence of anti-SARS-CoV-2 post-vaccination antibodies at two and eight months after the second dose in a group of healthcare workers with and without previous infection [
2].
We have now evaluated the immune system response in relation to the presence, intensity, and persistence of SARS-CoV-2 anti-S1 antibodies 8 months after administration of a booster dose in naïve individuals and with evidence of previous infection.
2. Materials and Methods
We show data of second phase of the RIPOVAC study, conducted at the Lozano Blesa University Clinical Hospital of Zaragoza, Spain, the reference center of Sector III of the Aragón Health Service (SALUD). In the second phase of RIPOVAC study (
Figure 1), between December 2021 and January 2022, eight months after the second dose, 389 voluntary, immunocompetent, non-pregnant healthcare workers (55 men and 334 women, mean age of 47.87 years) (
Table 1) received the booster dose of SARS-CoV-2 Moderna (377 cases, regardless of the brand received in the first two doses) or Pfizer (12 cases that had received Pfizer in the first two doses) vaccine. In the booster dose, only half the usual dose in primary vaccination was administered, according to the recommendations of the COVID-19 Vaccination Technical Working Group, of the Report on the Spanish Vaccination Program and Registry of November 2, 2021 [
3].
In this moment a new serum sample was obtained [
2]. All of them were surveyed about if they had had compatible symptoms or if they had been positive in a home antigen test for SARS-CoV-2. Their medical history was also reviewed to see if they had a clinical history of SARS-CoV-2 infection (antigen, PCR, anti-N IgG, or IgM positives).
People with previous positive PCR to SARS-CoV-2 (Alinity m, Abbott; Viasure, Certest Biotec; or GeneXpert, Cepheid), or with previous positive SARS-CoV-2 antigen (PanBio COVID-19 Ag, Abbott) or with presence of anti-N IgG (SARS-CoV-2 IgG, Abbott) or with anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM (SARS-CoV-2 IgM, Abbott) were considered previously infected.
The determination of quantitative anti-S1 IgG (AU/mL) was performed by CMIA (SARS-CoV-2 IgG II Quant) by blinded, trained laboratory staff, using the Alinity i platform (Abbott), following the manufacturer’s instructions. These reagent kits have a specificity of 100% and sensitivity at 15 days of 98.77%, according to the manufacturer.
The analysis was carried out based on the booster dose of vaccine received, and the existence or not of a previous SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The protocol was approved by the Clinical Investigation Ethics Committee of Aragón (EPA 21/000) and the recruited healthcare workers gave their written informed consent, following the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Statistical Analysis: Quantitative variables were described using the mean (standard deviation) and categorical variables were reported using frequencies. Differences in sociodemographic and serological data between the groups were tested using the independent Student´s t-test or the U-Mann Whitney and reported as mean difference (95% confidence interval, CI). Statistical significance was set at p<0.05 for all calculations. Data analysis was performed using SPSS v.19 (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA).
3. Results
All the health workers were anti-S IgG positive 8 months after receiving the booster dose of the vaccine (
Table 2), with a mean of 17040 AU/mL (95% CI, 7790 to 26289), with a range between 483 and >40000 AU/mL. This figure was 4,0 times higher than that obtained 8 months after the second dose of Moderna vaccine, which had been 4297 AU/mL [
2]. The mean number at 8 months after the third dose was 1.6 times higher [(17962 AU/mL (95% CI, 9390 to 26534)] in patients infected at some time than in patients without a history of infection [(11190 AU/mL (95% CI, 795 to 21585)] (
Table 2).
Of the 53 non-infected health workers who were studied eight months after the booster dose, antibody levels increased in 46 (86.8%) and diminished in 7 (13.2%) (
Table 3). Nevertheless, the seven latter showed antibody levels between 920 and 6857 AU/mL (mean of 4104 AU/mL).
In these 46 patients, antibody levels had increased by a mean of 10762 AU/mL at eight months after the booster dose. This figure is 7 times higher than the mean value that these patients had 8 months after the second dose (1506 AU/mL). Fifty one out of 53 cases (96,22%) showed antibody levels >1300 AU/mL.
In the patients who received a Moderna-Moderna-Moderna (MMM) regimen was detected, after the third dose, a mean figure [(12084 AU/mL (95% CI, 3965 to 20203)] higher than that of who received the Pfizer-Pfizer-Moderna (PPM) regimen [(11502 AU/mL (95% CI, -131 to 23135)], but without statistically significant differences (
Table 4).
The lowest figures were detected in the patients who received a Pfizer-Pfizer-Pfizer (PPP) regimen, but the low number of patients in this group precludes assessment of the significance of the difference.
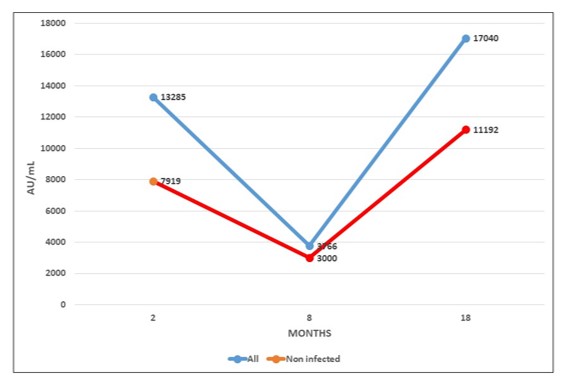
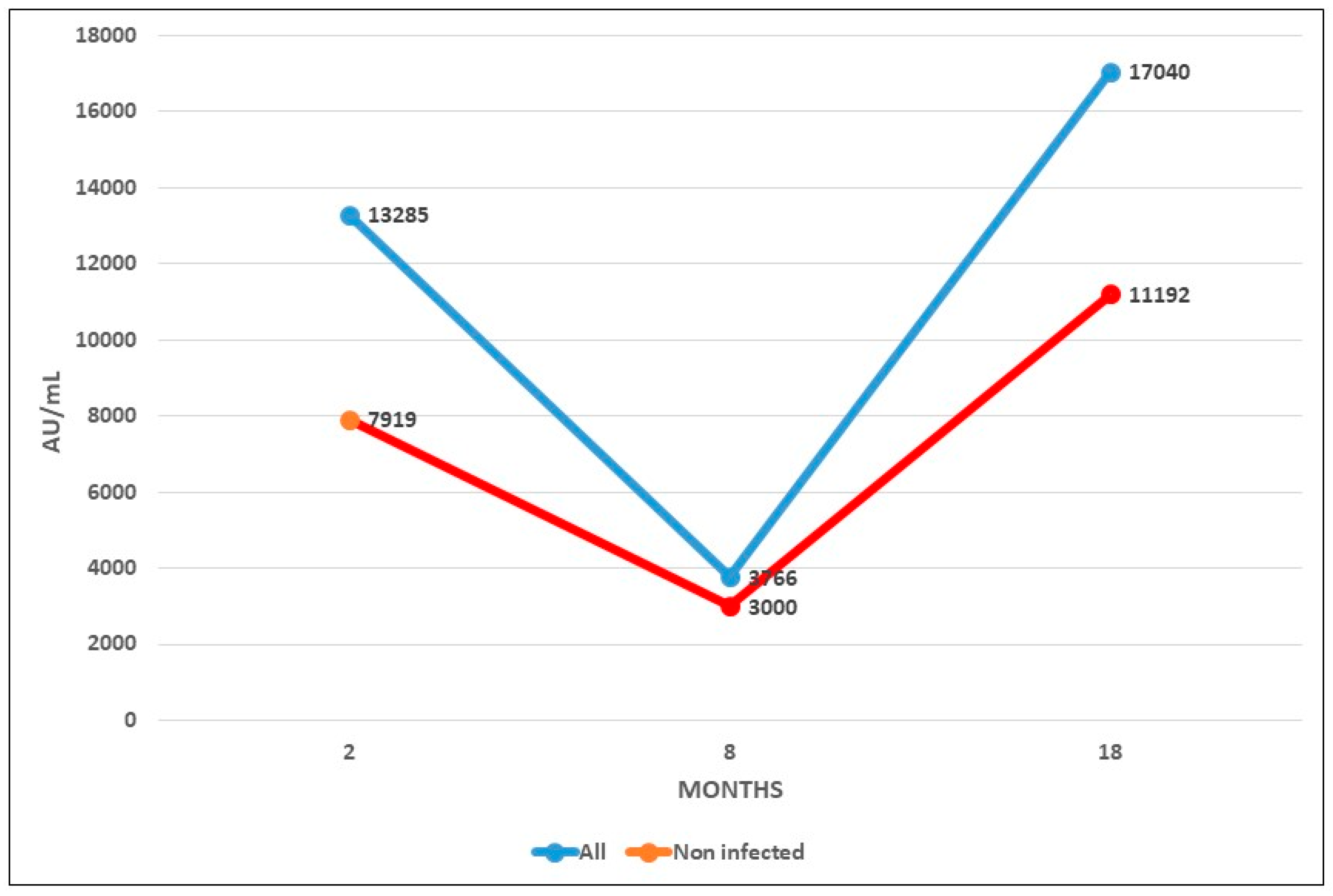
Figure 2 shows the mean evolution of antibody level during both phases of RIPOVAC study in the whole population studied and in non-infected patients. In both populations an increased level of antibodies may be seen after the booster dose.
4. Discussion
The efficacy of the administration of two doses of vaccine for SARS-Cov-2 in the general population has been proven in terms of prevention of symptomatic infections [
4,
5] and, in particular, of decrease in the number of both symptomatic and asymptomatic infections in healthcare workers [
6].
However, a decrease in antibody levels to 23.62% and 33.03% has been observed in Moderna or Pfizer vaccinated, respectively, 8 months after vaccination [
2,
7], although there are studies that show that the neutralizing capacity of antibodies can be maintained for up to 6-8 months [
8,
9].
In our current study we have verified that the booster dose produces a robust elevation of the antibody level. These antibodies persist at 8 months with levels up to values significantly higher than those reached after the second dose, both in health workers with previous infection and naïve. These data suggest a persistence of anti-S1 antibodies beyond 8 months.
The increase in the concentration of antibodies after vaccination in people who have passed the infection has been verified in previous studies [
10,
11] and as well in our study it is shown that this is true after the booster dose.
As approximately 18 months have elapsed after the first dose of vaccine was administered to our healthcare workers and the Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant -which is characterized by being easily transmissible and be able to escape the immune response [
12]- was circulating in Spain, the number of uninfected healthcare workers initially included in our study had decreased considerably. However, the study of this group demonstrates the efficacy of the booster dose of the vaccine in terms of its ability to produce specific antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, without the bias of immunological memory conditioned by the stimulus of the immune system produced by previous infection.
Longer studies are needed to verify the maximum persistence time of the antibodies after the booster dose and their efficacy against new variants that may be able to escape immunity and establish, if appropriate, new guidelines or reformulations of the vaccine.
5. Conclusions
The booster dose produces a robust elevation of the antibody level, which persists at 8 months with levels up to values significantly higher than those reached after the second dose, that allow to predict a persistence of more than one year.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A. (Sonia Algarate), L.S. and R.B.; Methodology, J.B., E.A., M.D., S.A. (Sara Arnal) and M.R.; Validation, J.B., S.A. (Sonia Algarate), L.S. and R.B.; Formal Analysis, S.A. (Sonia Algarate), L.S. and R.B.; Investigation, J.B., E.A., M.D., S.A. (Sara Arnal) and M.R.; Resources, B.H-C., M.T. G-B., J.M-M, B.A., A.T., P.S-B. C.Y. Data Curation, E.A., S.A. (Sara Arnal); B.H-C., M.T. G-B., J.M-M, B.A., A.T., P.S-B. C.Y. Writing – Original Draft Preparation, S.A. (Sonia Algarate) and R.B.; Writing – Review & Editing, S.A. (Sonia Algarate), L.S., J.B. and R.B.; Visualization, R.B.; Supervision, R.B..; Project Administration, S.A. (Sonia Algarate) and R.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The protocol was approved by the Clinical in accordance with the ethical standards noted in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All data are contained within the article; for further information please contact the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to particularly acknowledge the recruited healthcare workers for their collaboration.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Krammer, F. SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in development. Nature 2020, 586: 516-527. [CrossRef]
- Serrano, L.; Algarate, S.; Herrero-Cortina, B.; Bueno, J.; González-Barriga, M.T.; Ducons, M.; Montero-Marco, J.; Acha, B.; Taboada, A.; Sanz-Burillo, P.; Yuste, C.; Benito, R. ; RIPOVAC Study Group. Assessment of humoral immune response to two mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccines (Moderna and Pfizer) in healthcare workers fully vaccinated with and without a history of previous infection. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 133: 1969-1974. [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Sanitad. Grupo de trabajo técnico de vacunación COVID-19, Ponencia de Programa y Registro de Vacunaciones de España. Actualización 9 de 2 de noviembre de 2021. https://www.sanidad.gob.es/profesionales/saludPublica/ccayes/ alertasActual/nCov/vacunaCovid19.htm.
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N. ; Creech. C,B,; McGettigan, J.; Khetan, S.; Segal, N.; Solis, J.; Brosz, A.; Fierro, C.; Schwartz, H.; Neuzil, K.; Corey, L.; Gilbert, P.; Janes, H.; Follmann, D.; Marovich, M.; Mascola, J.; Polakowski, L.; Ledgerwood, J.;, Graham, B.S.; Bennett, H.; Pajon, R.; Knightly. C.; Leav, B.; Deng, W.; Zhou, H.; Han, S.; Ivarsson, M.; Miller, J.;, Zaks, T.; COVE Study Group. Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384: 403-416. [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K.A.; Roychoudhury, S.; Koury, K.; Li, P.; Kalina, W.V.; Cooper, D.; Frenck, R.W. Jr.; Hammitt, L.L.; Türeci, Ö.; Nell, H.; Schaefer, A.; Ünal, S.; Tresnan, D.B.; Mather, S.; Dormitzer, P.R.; Şahin, U.; Jansen, K.U.; Gruber, W.C. ; C4591001 Clinical Trial Group. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 31: 2603-2615. [CrossRef]
- Núñez López, C.; González de Abreu, J.M. : Pérez-Blanco, V.; de Miguel Buckley, R.; Romero Gómez, M.P.; Díaz-Menéndez, M.; La Paz Health Care Workers Vaccination Study Group; Appendix. La Paz Health Care Workers Vaccination Study Group. Effectiveness of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in Spanish healthcare workers. Enf. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. (Engl Ed) 2023, 41: 33-35. [CrossRef]
- Mestre-Prad, M.T.; Recio-Comí, G.; Molina-Clavero, M.C.; Olona-Cabases, M.M. Reinfection confirmed by SARS-CoV-2 in a healthcare professional detected by an in-hospital infection control program. Enf. Infecc. Microbiol. Clin, 2023, 41: 50-61. [CrossRef]
- Robbiani, D.F.; Gaebler, C.; Muecksch, F.; Lorenzi, J.C.C.; Wang, Z.; Cho, A.; Agudelo, M.; Barnes, C.O.; Gazumyan, A.; Finkin, S.; Hägglöf, T.; Oliveira, T.Y.; Viant, C.; Hurley, A.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Millard, K.G.; Kost, R.G.; Cipolla, M.; Gordon, K.; Bianchini, F.; Chen, S.T.; Ramos, V.; Patel, R.; Dizon, J.; Shimeliovich, I.; Mendoza, P.; Hartweger, H.; Nogueira, L.; Pack, M.; Horowitz, J.; Schmidt, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Michailidis, E.; Ashbrook, A.W.; Waltari, E.; Pak, J.E.; Huey-Tubman, K.E.; Koranda, N.; Hoffman, P.R.; West, A.P. Jr.; Rice, C.M.; Hatziioannou, T.; Bjorkman, P.J.; Bieniasz, P.D.; Caskey, M. ; Nussenzweig. M,C. Convergent antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in convalescent individuals. Nature 2020, 584: 437-442. [CrossRef]
- Dan, J.M.; Mateus, J.; Kato, Y.; Hastie, K.M.; Yu, E.D.; Faliti, C.E.; Grifoni, A.; Ramirez, S.I.; Haupt, S.; Frazier, A.; Nakao, C.; Rayaprolu, V.; Rawlings, S.A.; Peters, B.; Krammer, F.; Simon, V.; Saphire, E.O.; Smith, D.M.; Weiskopf, D.; Sette, A.; Crotty, S. Immunological memory to SARS-CoV-2 assessed for up to 8 months after infection. Science 2021, 371(6529):eabf4063. [CrossRef]
- Krammer, F.; Srivastava, K.; the PARIS team Simon, V. Robust spike antibody responses and increased reactogenicity in seropositive individuals after a 2 single dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. medRxiv. 2021 Available in: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.01.29.21250653v1.full. pdf.
- Krammer, F.; Srivastava, K.; Alshammary, H.; Amoako, A.A.; Awawda, M.H.; Beach, K.F. Antibody responses in seropositive persons after a single dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. N Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384: 1372-1374. [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.Y.; Wang, W.B.; Gao, R.D.; Zhou, A.M. Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) of SARS-CoV-2: Mutation,
infectivity, transmission, and vaccine resistance. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10: 1-11. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).