Submitted:
26 May 2023
Posted:
29 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
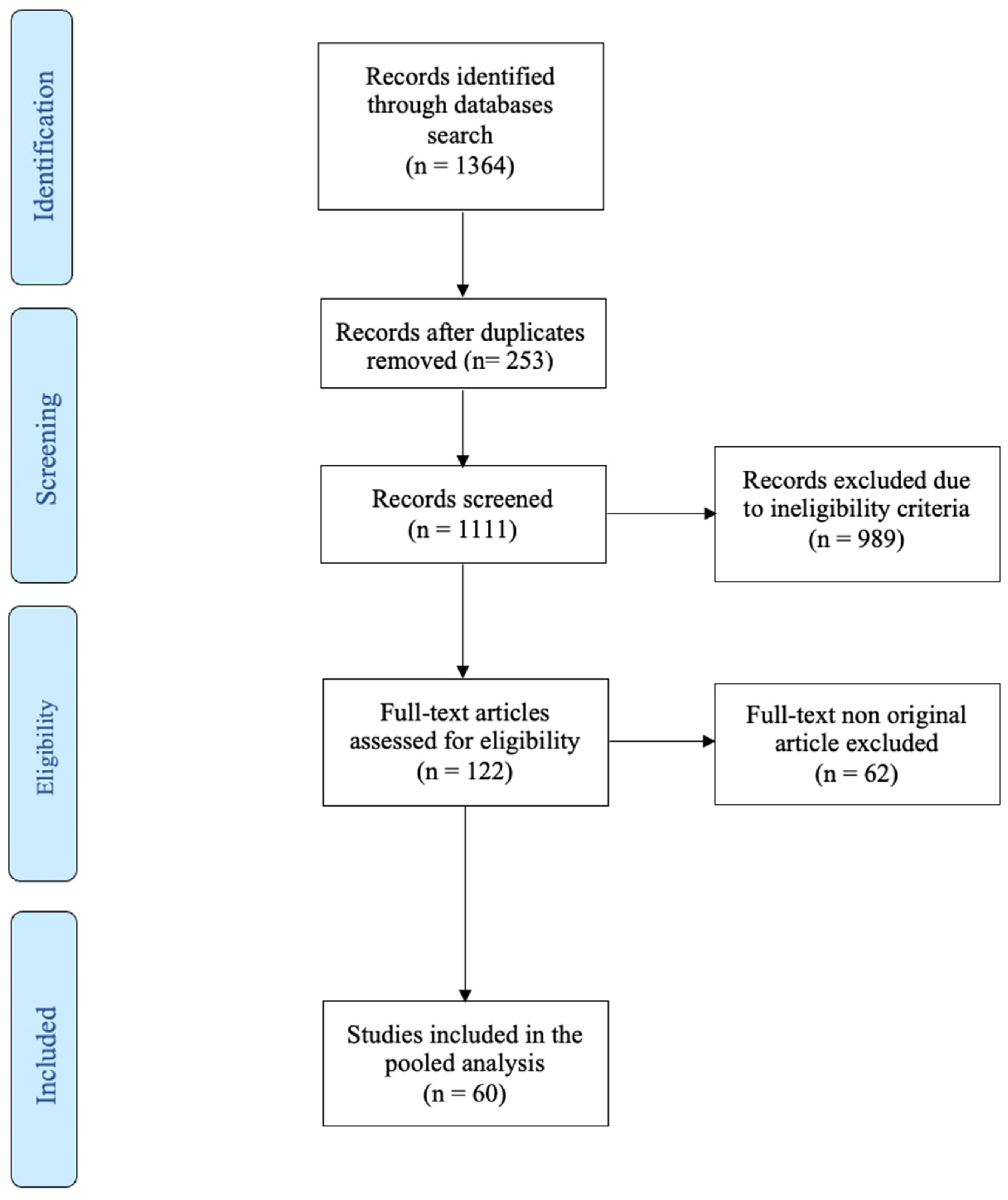
2. Literature search results
3. Results
3.1. The role of micro-rna in the detection of bladder cancer
3.2. The role of micro-RNA in the detection of prostate cancer
3.3. The role of micro-RNA in the detection of renal cancer
3.4. The role of micro-RNA in the detection of upper tract urothelial carcinoma
4. Materials and methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian YQ, Yang JC, Hu JJ, Ding R, Ye DW, Shang JW. Trends and risk factors of global incidence, mortality, and disability of genitourinary cancers from 1990 to 2019: Systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Front Public Health. 2023 Feb 22;11:1119374. [CrossRef]
- Tölle A, Blobel CC, Jung K. Circulating miRNAs in blood and urine as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for bladder cancer: an update in 2017. Biomarkers in Medicine. 2018 Jun;12(6):667–76. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira MCD, Caires HR, Oliveira MJ, Fraga A, Vasconcelos MH, Ribeiro R. Urinary Biomarkers in Bladder Cancer: Where Do We Stand and Potential Role of Extracellular Vesicles. Cancers. 2020 May 29;12(6):1400. [CrossRef]
- Gharib AF, Eed EM, Khalifa AS, Raafat N, Shehab-Eldeen S, Alwakeel HR, et al. Value of Serum miRNA-96-5p and miRNA-99a-5p as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. IJGM. 2022 Mar;Volume 15:2427–36. [CrossRef]
- Visone R, Croce CM. MiRNAs and Cancer. The American Journal of Pathology. 2009 Apr;174(4):1131–8. [CrossRef]
- Wu Z, Chen Q, Qu L, Li M, Wang L, Mir MC, et al. Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Therapy for Urologic Cancer Patients in Clinical Trials: A Collaborative Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. European Urology. 2022 Apr;81(4):414–25. [CrossRef]
- Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, Lee M, Song SJ. Regulatory Mechanism of MicroRNA Expression in Cancer. IJMS. 2020 Mar 3;21(5):1723. [CrossRef]
- Taheri M, Shirvani-Farsani Z, Ghafouri-Fard S, Omrani MD. Expression profile of microRNAs in bladder cancer and their application as biomarkers. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 2020 Nov;131:110703. [CrossRef]
- Endzeliņš E, Melne V, Kalniņa Z, Lietuvietis V, Riekstiņa U, Llorente A, et al. Diagnostic, prognostic and predictive value of cell-free miRNAs in prostate cancer: a systematic review. Mol Cancer. 2016 Dec;15(1):41. [CrossRef]
- Halaseh SA, Halaseh S, Alali Y, Ashour ME, Alharayzah MJ. A Review of the Etiology and Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer: All You Need To Know. Cureus [Internet]. 2022 Jul 27 [cited 2023 May 4]; Available from: https://www.cureus.com/articles/105534-a-review-of-the-etiology-and-epidemiology-of-bladder-cancer-all-you-need-to-know.
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA A Cancer J Clinicians. 2022 Jan;72(1):7–33. [CrossRef]
- Babjuk M, Burger M, Capoun O, Cohen D, Compérat EM, Dominguez Escrig JL, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (Ta, T1, and Carcinoma in Situ). Eur Urol. 2022 Jan;81(1):75–94. [CrossRef]
- Aveta A, Cacciapuoti C, Barone B, Di Zazzo E, Del Giudice F, Maggi M, et al. The Impact of Meat Intake on Bladder Cancer Incidence: Is It Really a Relevant Risk? Cancers. 2022 Sep 29;14(19):4775. [CrossRef]
- Babjuk M, Burger M, Compérat EM, Gontero P, Mostafid AH, Palou J, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (TaT1 and Carcinoma In Situ) - 2019 Update. European Urology. 2019 Nov;76(5):639–57. [CrossRef]
- Calace FP, Napolitano L, Arcaniolo D, Stizzo M, Barone B, Crocetto F, et al. Micro-Ultrasound in the Diagnosis and Staging of Prostate and Bladder Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Medicina. 2022 Nov 10;58(11):1624. [CrossRef]
- Di Meo NA, Loizzo D, Pandolfo SD, Autorino R, Ferro M, Porta C, et al. Metabolomic Approaches for Detection and Identification of Biomarkers and Altered Pathways in Bladder Cancer. IJMS. 2022 Apr 10;23(8):4173. [CrossRef]
- Kim SM, Kang HW, Kim WT, Kim YJ, Yun SJ, Lee SC, et al. Cell-Free microRNA-214 From Urine as a Biomarker for Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Korean J Urol. 2013;54(11):791. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Zhang Y, Liu X, Fang A, Wang J, Yang Y, et al. Direct quantitative detection for cell-free miR-155 in urine: a potential role in diagnosis and prognosis for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 19;7(3):3255–66. [CrossRef]
- Zhang P, Bill K, Liu J, Young E, Peng T, Bolshakov S, et al. MiR-155 Is a Liposarcoma Oncogene That Targets Casein Kinase-1α and Enhances β-Catenin Signaling. Cancer Research. 2012 Apr 1;72(7):1751–62. [CrossRef]
- Piao XM, Jeong P, Kim YH, Byun YJ, Xu Y, Kang HW, et al. Urinary cell-free microRNA biomarker could discriminate bladder cancer from benign hematuria: Urinary cell-free microRNA biomarker. Int J Cancer. 2019 Jan 15;144(2):380–8. [CrossRef]
- Huang X, Zhao H, Qian X, Qiu J. MiR-20a in cell-free urine as a potential diagnostic biomarker for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: a Chinese population-based study. Int J Clin Exp Med. 11(1):209–16.
- Sasaki H, Yoshiike M, Nozawa S, Usuba W, Katsuoka Y, Aida K, et al. Expression Level of Urinary MicroRNA-146a-5p Is Increased in Patients With Bladder Cancer and Decreased in Those After Transurethral Resection. Clinical Genitourinary Cancer. 2016 Oct;14(5):e493–9. [CrossRef]
- Andreu Z, Otta Oshiro R, Redruello A, López-Martín S, Gutiérrez-Vázquez C, Morato E, et al. Extracellular vesicles as a source for non-invasive biomarkers in bladder cancer progression. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2017 Feb;98:70–9. [CrossRef]
- Baumgart S, Meschkat P, Edelmann P, Heinzelmann J, Pryalukhin A, Bohle R, et al. MicroRNAs in tumor samples and urinary extracellular vesicles as a putative diagnostic tool for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov;145(11):2725–36. [CrossRef]
- Yun SJ, Jeong P, Kim WT, Kim TH, Lee YS, Song PH, et al. Cell-free microRNAs in urine as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers of bladder cancer. International Journal of Oncology. 2012 Nov;41(5):1871–8. [CrossRef]
- abdel-Hafiz S, Sherif H, Romeih M, Elesaily K. Urine micro-RNA signature as a potential non-invasive diagnostic biomarker in bladder cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Jan 1;24(1):121–31. [CrossRef]
- Mengual L, Lozano JJ, Ingelmo-Torres M, Gazquez C, Ribal MJ, Alcaraz A. Using microRNA profiling in urine samples to develop a non-invasive test for bladder cancer: miRNA profiling in urine samples. Int J Cancer. 2013 May;n/a-n/a. [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanmehr N, Gharbi S, Korsching E, Tavallaei M, Einollahi B, Mowla SJ. miR-21-5p, miR-141-3p, and miR-205-5p levels in urine-promising biomarkers for the identification of prostate and bladder cancer. Prostate. 2019 Jan;79(1):88–95. [CrossRef]
- Hofbauer SL, De Martino M, Lucca I, Haitel A, Susani M, Shariat SF, et al. A urinary microRNA (miR) signature for diagnosis of bladder cancer. Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations. 2018 Dec;36(12):531.e1-531.e8. [CrossRef]
- Pardini B, Cordero F, Naccarati A, Viberti C, Birolo G, Oderda M, et al. microRNA profiles in urine by next-generation sequencing can stratify bladder cancer subtypes. Oncotarget. 2018 Apr 17;9(29):20658–69. [CrossRef]
- Braicu C, Buiga R, Cojocneanu R, Buse M, Raduly L, Pop LA, et al. Connecting the dots between different networks: miRNAs associated with bladder cancer risk and progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Dec;38(1):433. [CrossRef]
- Cantley LC. The Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Pathway. Science. 2002 May 31;296(5573):1655–7. [CrossRef]
- Lin JT, Tsai KW. Circulating miRNAs Act as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Bladder Cancer in Urine. IJMS. 2021 Apr 20;22(8):4278. [CrossRef]
- Moisoiu T, Dragomir MP, Iancu SD, Schallenberg S, Birolo G, Ferrero G, et al. Combined miRNA and SERS urine liquid biopsy for the point-of-care diagnosis and molecular stratification of bladder cancer. Mol Med. 2022 Dec;28(1):39. [CrossRef]
- Long JD, Sullivan TB, Humphrey J, Logvinenko T, Summerhayes KA, Kozinn S, et al. A non-invasive miRNA based assay to detect bladder cancer in cell-free urine. Am J Transl Res. 2015;7(11):2500–9.
- Sun DK, Wang JM, Zhang P, Wang YQ. MicroRNA-138 Regulates Metastatic Potential of Bladder Cancer Through ZEB2. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(6):2366–74. [CrossRef]
- Yang R, Liu M, Liang H, Guo S, Guo X, Yuan M, et al. miR-138-5p contributes to cell proliferation and invasion by targeting Survivin in bladder cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2016 Dec;15(1):82. [CrossRef]
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J Clin. 2021 May;71(3):209–49. [CrossRef]
- Merriel SW, Seggie A, Ahmed H. Diagnosis of prostate cancer in primary care: navigating updated clinical guidance. Br J Gen Pract. 2023 Feb;73(727):54–5. [CrossRef]
- Sekhoacha M, Riet K, Motloung P, Gumenku L, Adegoke A, Mashele S. Prostate Cancer Review: Genetics, Diagnosis, Treatment Options, and Alternative Approaches. Molecules. 2022 Sep 5;27(17):5730. [CrossRef]
- Kasivisvanathan V, Rannikko AS, Borghi M, Panebianco V, Mynderse LA, Vaarala MH, et al. MRI-Targeted or Standard Biopsy for Prostate-Cancer Diagnosis. N Engl J Med. 2018 May 10;378(19):1767–77. [CrossRef]
- M. Hafron J, Yu H, Juang A, Vuong D, Kamer S, Carbonell L, et al. New developments in prostate cancer screening using a novel cancer-specific, non-PSA biomarker assay derived from autoantibody signatures. J Med Therap [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2023 Apr 27];1(4). Available from: http://www.oatext.com/new-developments-in-prostate-cancer-screening-using-a-novel-cancer-specific-non-psa-biomarker-assay-derived-from-autoantibody-signatures.php. [CrossRef]
- Di Minno A, Aveta A, Gelzo M, Tripodi L, Pandolfo SD, Crocetto F, et al. 8-Hydroxy-2-Deoxyguanosine and 8-Iso-Prostaglandin F2α: Putative Biomarkers to assess Oxidative Stress Damage Following Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy (RARP). JCM. 2022 Oct 17;11(20):6102. [CrossRef]
- Luca LD, Crocetto F, Barone B, Creta M, Pesce S, Aveta A, et al. Granulomatous prostatitis mimicking prostate cancer in a patient with psoriatic arthritis: a case report. Future Science OA. 2020 Aug 1;6(7):FSO591. [CrossRef]
- Pandolfo SD, Crauso F, Aveta A, Cilio S, Barone B, Napolitano L, et al. A Novel Low-Cost Uroflowmetry for Patient Telemonitoring. IJERPH. 2023 Feb 13;20(4):3287. [CrossRef]
- Schaefer A, Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ, Wagner I, Stephan C, Jentzmik F, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNA profiling in prostate carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2009;NA-NA. [CrossRef]
- Stephan C, Jung M, Rabenhorst S, Kilic E, Jung K. Urinary miR-183 and miR-205 do not surpass PCA3 in urine as predictive markers for prostate biopsy outcome despite their highly dysregulated expression in prostate cancer tissue. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM) [Internet]. 2015 Jan 1 [cited 2023 Apr 27];53(7). Available from: https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/cclm-2014-1000/html. [CrossRef]
- Salido-Guadarrama AI, Morales-Montor JG, Rangel-Escareño C, Langley E, Peralta-Zaragoza O, Colin JLC, et al. Urinary microRNA-based signature improves accuracy of detection of clinically relevant prostate cancer within the prostate-specific antigen grey zone. Molecular Medicine Reports. 2016 Jun;13(6):4549–60. [CrossRef]
- Leite KRM, Tomiyama A, Reis ST, Sousa-Canavez JM, Sañudo A, Camara-Lopes LH, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles in the progression of prostate cancer—from high-grade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia to metastasis. Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations. 2013 Aug;31(6):796–801. [CrossRef]
- Porkka KP, Pfeiffer MJ, Waltering KK, Vessella RL, Tammela TLJ, Visakorpi T. MicroRNA Expression Profiling in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Research. 2007 Jul 1;67(13):6130–5. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez M, Bajo-Santos C, Hessvik NP, Lorenz S, Fromm B, Berge V, et al. Identification of non-invasive miRNAs biomarkers for prostate cancer by deep sequencing analysis of urinary exosomes. Mol Cancer. 2017 Dec;16(1):156. [CrossRef]
- Nadiminty N, Tummala R, Lou W, Zhu Y, Shi XB, Zou JX, et al. MicroRNA let-7c Is Downregulated in Prostate Cancer and Suppresses Prostate Cancer Growth. Das GM, editor. PLoS ONE. 2012 Mar 30;7(3):e32832. [CrossRef]
- Foj L, Ferrer F, Serra M, Arévalo A, Gavagnach M, Giménez N, et al. Exosomal and Non-Exosomal Urinary miRNAs in Prostate Cancer Detection and Prognosis: Urinary miRNAs in Prostate Cancer. Prostate. 2017 May;77(6):573–83. [CrossRef]
- Markert L, Holdmann J, Klinger C, Kaufmann M, Schork K, Turewicz M, et al. Small RNAs as biomarkers to differentiate benign and malign prostate diseases: An alternative for transrectal punch biopsy of the prostate? Lobaccaro JMA, editor. PLoS ONE. 2021 Mar 24;16(3):e0247930. [CrossRef]
- Tian L, Fang Y xiang, Xue J lun, Chen J zhong. Four microRNAs promote prostate cell proliferation with regulation of PTEN and its downstream signals in vitro. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e75885. [CrossRef]
- Hasanoğlu S, Göncü B, Yücesan E, Atasoy S, Kayali Y, Özten Kandaş N. Investigating differential miRNA expression profiling using serum and urine specimens for detecting potential biomarkers for early prostate cancer diagnosis. Turk J Med Sci. 2021 Aug 30;51(4):1764–74. [CrossRef]
- Byun YJ, Piao XM, Jeong P, Kang HW, Seo SP, Moon SK, et al. Urinary microRNA-1913 to microRNA-3659 expression ratio as a non-invasive diagnostic biomarker for prostate cancer. Investig Clin Urol. 2021;62(3):340. [CrossRef]
- Kang HW, Byun YJ, Moon SM, Kim K, Piao XM, Zheng CM, et al. Urinary hsv2-miR-H9 to hsa-miR-3659 ratio is an effective marker for discriminating prostate cancer from benign prostate hyperplasia in patients within the prostate-specific antigen grey zone. Investig Clin Urol. 2022;63(2):238. [CrossRef]
- Lee H, Kang SJ, Lee J, Park KH, Rhee WJ. Isolation and Characterization of Urinary Extracellular Vesicles from Healthy Donors and Patients with Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. IJMS. 2022 Jun 27;23(13):7134. [CrossRef]
- Zennami K, Choi SM, Liao R, Li Y, Dinalankara W, Marchionni L, et al. PDCD4 Is an Androgen-Repressed Tumor Suppressor that Regulates Prostate Cancer Growth and Castration Resistance. Molecular Cancer Research. 2019 Feb 1;17(2):618–27. [CrossRef]
- Ashraf NM, Imran K, Kastner DW, Ikram K, Mushtaq A, Hussain A, et al. Potential involvement of mi-RNA 574-3p in progression of prostate cancer: A bioinformatic study. Molecular and Cellular Probes. 2017 Dec;36:21–8. [CrossRef]
- Capitanio U, Bensalah K, Bex A, Boorjian SA, Bray F, Coleman J, et al. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2019 Jan;75(1):74–84. [CrossRef]
- Cinque A, Vago R, Trevisani F. Circulating RNA in Kidney Cancer: What We Know and What We Still Suppose. Genes (Basel). 2021 May 28;12(6):835. [CrossRef]
- Cancer (IARC) TIA for R on. Global Cancer Observatory [Internet]. [cited 2023 Apr 15]. Available from: https://gco.iarc.fr/.
- Ljungberg B, Albiges L, Abu-Ghanem Y, Bedke J, Capitanio U, Dabestani S, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2022 Update. European Urology. 2022 Oct;82(4):399–410. [CrossRef]
- Napolitano L, Manfredi C, Cirillo L, Fusco GM, Passaro F, Abate M, et al. Cytoreductive Nephrectomy and Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Medicina. 2023 Apr 15;59(4):767. [CrossRef]
- Lasorsa F, Di Meo NA, Rutigliano M, Milella M, Ferro M, Pandolfo SD, et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Renal Cell Carcinoma: Molecular Basis and Rationale for Their Use in Clinical Practice. Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 2;11(4):1071. [CrossRef]
- Di Meo NA, Lasorsa F, Rutigliano M, Loizzo D, Ferro M, Stella A, et al. Renal Cell Carcinoma as a Metabolic Disease: An Update on Main Pathways, Potential Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Targets. IJMS. 2022 Nov 18;23(22):14360. [CrossRef]
- Cui C, Cui Q. The relationship of human tissue microRNAs with those from body fluids. Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 27;10(1):5644. [CrossRef]
- von Brandenstein M, Pandarakalam JJ, Kroon L, Loeser H, Herden J, Braun G, et al. MicroRNA 15a, inversely correlated to PKCα, is a potential marker to differentiate between benign and malignant renal tumors in biopsy and urine samples. Am J Pathol. 2012 May;180(5):1787–97. [CrossRef]
- Mlcochova H, Hezova R, Stanik M, Slaby O. Urine microRNAs as potential noninvasive biomarkers in urologic cancers. Urol Oncol. 2014 Jan;32(1):41.e1-9. [CrossRef]
- Liu Q, Shin Y, Kee JS, Kim KW, Mohamed Rafei SR, Perera AP, et al. Corrigendum to “Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) point-of-care system for rapid multiplexed detection of microRNAs in human urine specimens” [Biosens. Bioelectron. 71 (2015) 365-372]. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016 Nov 15;85:996. [CrossRef]
- Fedorko M, Juracek J, Stanik M, Svoboda M, Poprach A, Buchler T, et al. Detection of let-7 miRNAs in urine supernatant as potential diagnostic approach in non-metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2017 Jun 15;27(2):411–7. [CrossRef]
- Li G, Zhao A, Péoch M, Cottier M, Mottet N. Detection of urinary cell-free miR-210 as a potential tool of liquid biopsy for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol Oncol. 2017 May;35(5):294–9. [CrossRef]
- Mytsyk Y, Dosenko V, Borys Y, Kucher A, Gazdikova K, Busselberg D, et al. MicroRNA-15a expression measured in urine samples as a potential biomarker of renal cell carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018 May;50(5):851–9. [CrossRef]
- Song S, Long M, Yu G, Cheng Y, Yang Q, Liu J, et al. Urinary exosome miR-30c-5p as a biomarker of clear cell renal cell carcinoma that inhibits progression by targeting HSPA5. J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Oct;23(10):6755–65. [CrossRef]
- Cochetti G, Cari L, Nocentini G, Maulà V, Suvieri C, Cagnani R, et al. Detection of urinary miRNAs for diagnosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 4;10(1):21290. [CrossRef]
- Ferro M, Musi G, Marchioni M, Maggi M, Veccia A, Del Giudice F, et al. Radiogenomics in Renal Cancer Management-Current Evidence and Future Prospects. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 27;24(5):4615. [CrossRef]
- von Brandenstein M, Schlosser M, Herden J, Heidenreich A, Störkel S, Fries JWU. MicroRNAs as Urinary Biomarker for Oncocytoma. Dis Markers. 2018;2018:6979073. [CrossRef]
- Di Meo A, Brown MD, Finelli A, Jewett MAS, Diamandis EP, Yousef GM. Prognostic urinary miRNAs for the assessment of small renal masses. Clin Biochem. 2020 Jan;75:15–22. [CrossRef]
- Rouprêt M, Seisen T, Birtle AJ, Capoun O, Compérat EM, Dominguez-Escrig JL, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: 2023 Update. European Urology. 2023 Mar;S0302283823026520. [CrossRef]
- Wu Z, Li M, Wang L, Paul A, Raman JD, Necchi A, et al. Neoadjuvant systemic therapy in patients undergoing nephroureterectomy for urothelial cancer: a multidisciplinary systematic review and critical analysis. Minerva Urol Nephrol [Internet]. 2022 Sep [cited 2023 May 8];74(5). Available from: https://www.minervamedica.it/index2.php?show=R19Y2022N05A0518. [CrossRef]
- Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Tatarano S, Kawahara K, Uchida Y, Nishiyama K, et al. miR-145 and miR-133a function as tumour suppressors and directly regulate FSCN1 expression in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 2010 Mar 2;102(5):883–91. [CrossRef]
- Yamada Y, Enokida H, Kojima S, Kawakami K, Chiyomaru T, Tatarano S, et al. MiR-96 and miR-183 detection in urine serve as potential tumor markers of urothelial carcinoma: correlation with stage and grade, and comparison with urinary cytology. Cancer Sci. 2011 Mar;102(3):522–9. [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki K, Fujita K, Jingushi K, Kawashima A, Ujike T, Nagahara A, et al. MiR-21-5p in urinary extracellular vesicles is a novel biomarker of urothelial carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 11;8(15):24668–78. [CrossRef]
| Authors | Year of Publication |
Number of Patients (BC/Ctl) |
Study Design | Target (microRNA in PCa) |
Primary Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mamdouh et al. | 2023 | 111/25 |
Retrospective |
miR-200 (↑) miR-145 (↑) miR-21(↑) |
Positive correlation (p=0.02) high and low grade > controls (p=0.01) high and low grade > controls (p=0.05) high and low grade > controls |
| Moisoiu et al. | 2022 | 15/16 |
Retrospective |
Panel of three miRNAs: miR-34a-5p (↑) miR-205-5p (↑) miR-210-3p (↑) |
AUC 0.92 (miRNA + SERS) |
| Lin et al. | 2021 | 180/100 |
Retrospective |
let-7c-5p (↑) miR-146a-5p (↑) miR-149-5p (↑) miR-193a-5p (↑) miR-423-5p (↑) |
Positive correlation BC > Ctl |
| Baugmart et al. | 2019 | 37/0 |
Retrospective |
miR-146 (↑) | Positive correlation High grade > low grade |
| Braicu et al. | 2019 | 23/23 |
Retrospective |
miR-141-3p (↑) miR-205-5p (↑) miR-139-5p (↓) miR-143-5p (↓) miR-200b-3p (↑) |
AUC 0.86 (overall) AUC 0.89 (overall) BC < Ctl BC < Ctl BC > Ctl |
| Pardini et al. | 2018 | 66/48 |
Retrospective |
Panel of three miRNAs: let-7c-5p (↑) miR-30a-5p (↑) miR-486-5p (↓) |
AUC 0.70 (overall) AUC 0.73 (low-grade NMIBC) AUC 0.95 (high-grade NMIBC) AUC 0.99 (MIBC) |
| Huang et al. | 2018 | 80/86 |
Retrospective |
miR-20a (↑) |
Positive correlation (p<0.001) Associated with larger tumour size and advanced tumour grade in NMIBC (all p<0.05) |
| Ghorbanmehr et al. | 2018 | 45/20 |
Retrospective |
miR-21-5p (↑) miR141-3p (↑) mir205-5p (↑) |
Positive correlation 84% SN, 59% SP; AUC 0.76 (overall) 71% SN, 71% SP; AUC 0.74 (overall) 82% SN, 62% SP; AUC 0.73 (overall) |
| Piao et al. | 2018 | 35/20 |
Retrospective |
miR-6124 to miR-4511 ratio (↑) | Positive correlation (AUC: 0.888, 91.5% SN, 76.2% SP) (p < 0.001) |
| Hofbauer et al. | 2018 | 87/115 |
Retrospective |
Panel of six miRNAs: Let-7c (↓) miR-135a (↓) miR-135b (↑) miR-148a (↓) miR-204 (↓) miR-345 (↑) |
AUC 0.88 (overall) AUC 0.91 (MIBC) |
| Andreu et al. | 2017 | 36/9 | Retrospective | miR-146 (↑) | Low grade > high grade |
| Sasaki et al. | 2016 | 28/19 | Retrospective | miR-146a-5p (↑) | Positive correlation (AUC=0.773,95% CI, 0.701-0.892) (p=0.014) (p=0.0436) (high-grade > low-grade) (p=0.1391) (MIBC > NMIBC) |
| Zhang et al. | 2016 | 162/162 | Retrospective |
miR-155 (↑) | Positive correlation (AUC=0.804; 95% CI, 0.756-0.845,80.2% SN, 84.6% SP )(NMIBC) |
| Kim et al. | 2013 | 138/144 | Retrospective | miR-214 (↑) | Positive correlation 20.08±3.21 vs. 18.96±2.68, (p=0.002) (NMIBC) |
| Mengual et al. | 2013 | 181/136 | Retrospective | Panel of six miRNAs: miR-18a (↑) miR-25 (↑) miR-140-5p (↓) miR-187 (↑) miR-142-3p (↓) miR-204 (↓) |
84.8% SN, 86.5% SP; AUC 0.92 (overall) 87.1% SN, 86.5% SP (MIBC) |
| Yun et al. | 2012 | 207/144 |
Retrospective |
miR-145 (↓) miR-200a (↓) |
Negative correlation miR-145 (AUC=0.729;77.8% SN, 61.1% SP) (NMIBC < healthy controls) miR-145 (AUC=0.79;84.1% SN, 61.1% SP) (MIBC < healthy controls) miR-145 (p=0.036) (MIBC<NMIBC) miR-200a (p<0.001) (MIBC and NMIBC<healthy controls) |
| Authors | Year of Publication |
Number of Patients (PCa/Ctl) |
Study Design | Target (microRNA in PCa) |
Primary Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lee et al. | 2022 | 6/8 | Retrospective | miR-21-5p, miR-574-3p, and miR6880-5p (↑) | Positive correlation in CRPC miR-21-5p, miR-574-3p (p <0.05) miR6880-5p (p <0.01) |
| Kang et al. | 2022 | 63/53 | Retrospective | miR-H9 to miR-3659 ratio (↑) | Positive correlation (AUC=0.803,95% CI) (p= 0.001) |
| Byun et al. | 2021 | 14/5 | Retrospective | miR-1913 to miR-3659 ratio (↑) | Positive correlation (AUC=0.7,95% CI, 61.4% SN, 71.8% SP) |
| Hasanoglu et al. | 2021 | 8/30 | Retrospective | miR-320a (↑) | Positive correlation p=0.0168 |
| Markert et al. | 2021 | 28/25 | Retrospective | miR-19b and miR-26a (↓) | Negative correlation AUC=0.7 |
| Ghorbanmehr et al. | 2020 | 23/42 | Retrospective | miR-21-5p (↑) mi-R-141-3p (↑) miR-205p (↑) |
Positive correlation p=0.001 p=0.005 p=0.020 |
| Foj et al. | 2017 | 60/10 | Retrospective | miR-21, miR-141, and miR-375 (↑) let-7c |
Positive correlation miR-21 (p=0.001) miR-141(p=0.033); higher Gleason score (p=0.034) miR-375 (p=0.038) let-7c (no correlation) |
| Rodriguez et al. | 2017 | 28/19 | Retrospective | miR-196a-5p and miR-501-3p (↓) | Negative correlation miR-196a-5p (AUC=0.73,95% CI 0.56 to 0.86) miR-501-3p (AUC=0.69%, 95% CI 0.52 to 0.85) |
| Salido-Guadarrama et al. | 2016 | 73/70 | Retrospective | miR-100 and miR-200b (↑) | Positive correlation (p=0.0355; Spearman coefficient=0.18) |
| Stephan et al. | 2015 | 38/38 | Retrospective | miR-183 and miR-205 | No correlation |
| Authors | Year of Publication |
Number of Patients (RCC/Ctl) |
Study design | Target (microRNA in RCC) |
Primary Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Di Meo et al. | 2020 | 6/8 | Retrospective | miR-432-5p and miR-532-5p (↑↑) miR-10a-5p, miR-144-3p, miR-28-3p, miR-326, miR-328-3p, miR-603, and miR-93-3p (↑) |
Positive correlation miR-432-5p (AUC: 0.71, 95% CI: 0.59 to 0.83, p=0.003) miR-532-5p (AUC: 0.70, 95%CI: 0.57–0.82, p=0.007) miR-10a-5p (AUC: 0.66, 95% CI: 0.53–0.79) miR-144-3p (AUC: 0.68, 95% CI: 0.55–0.81) miR-28-3p (AUC: 0.65, 95% CI: 0.52–0.78) miR-326 (AUC: 0.68, 95% CI: 0.55–0.81) miR-328-3p (AUC: 0.65, 95% CI: 0.52–0.78) miR-603 (AUC: 0.67, 95% CI: 0.55–0.80), and miR-93-3p (AUC: 0.68, 95% CI: 0.54–0.81), all p<0.05 |
| Cochetti et al. | 2020 | 13/14 | Retrospective | Panel of: miR-122, miR-1271, miR-15b (↑) |
(100% SN (95% CI 75–100%), and 86% SP (95% CI 57–98%), AUC of 0.96 and p<0.001) |
| Song et al. | 2019 | 70/30 | Retrospective | miR-30c-5p (↓) | Negative correlation (68.57% SN and 100%SP) |
| von Brandenstein et al. | 2018 | 26/17 | Retrospective | miR-498, miR-183, miR-205, and miR-31(↑) | Positive correlation with Oncocytoma |
| Mytsyk et al. | 2018 | 67/15 | Retrospective | miR-15a (↑) | Positive correlation between miR-15a levels and tumour size (98.1% SP, 100% SN, AUC=0.955, p<0.001) |
| Li et al. | 2017 | 75/45 | Retrospective | miR-210 (↑) | Positive correlation P<0.001 (SN of 57.8% and SP of 80.0%) |
| Fedorko et al. | 2017 | 69/36 | Retrospective | all let-7 miRNAs (let-7a, let-7b, let-7c, let-7d, let-7e and let-7g (↑) | Positive correlation (AUC=0.8307, 71% SN, 81% SP), all p<0.05. |
| von Brandenstein et al. | 2012 | 25/5 | Retrospective | miR-15a (↑) | Positive correlation (p not reported) |
| Authors | Year of Publication |
Number of Patients (UTUC/Ctl) |
Study design | Target (microRNA in UTUC) |
Primary Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matsuzaki et al. | 2017 | 36/26 | Retrospective | miR-155-5p, miR-15a-5p, miR-21-5p, miR-132-3p and miR-31-5p (↑) | Positive correlation in UTUC (all p<0.001) miR-21-5p (AUC=0.900) |
| Yamada et al. | 2011 | <104/74 | Retrospective | miR-190 (=) miR-96 and miR-183 (↑) |
Positive correlation (p=0.006) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





