Submitted:
26 May 2023
Posted:
29 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
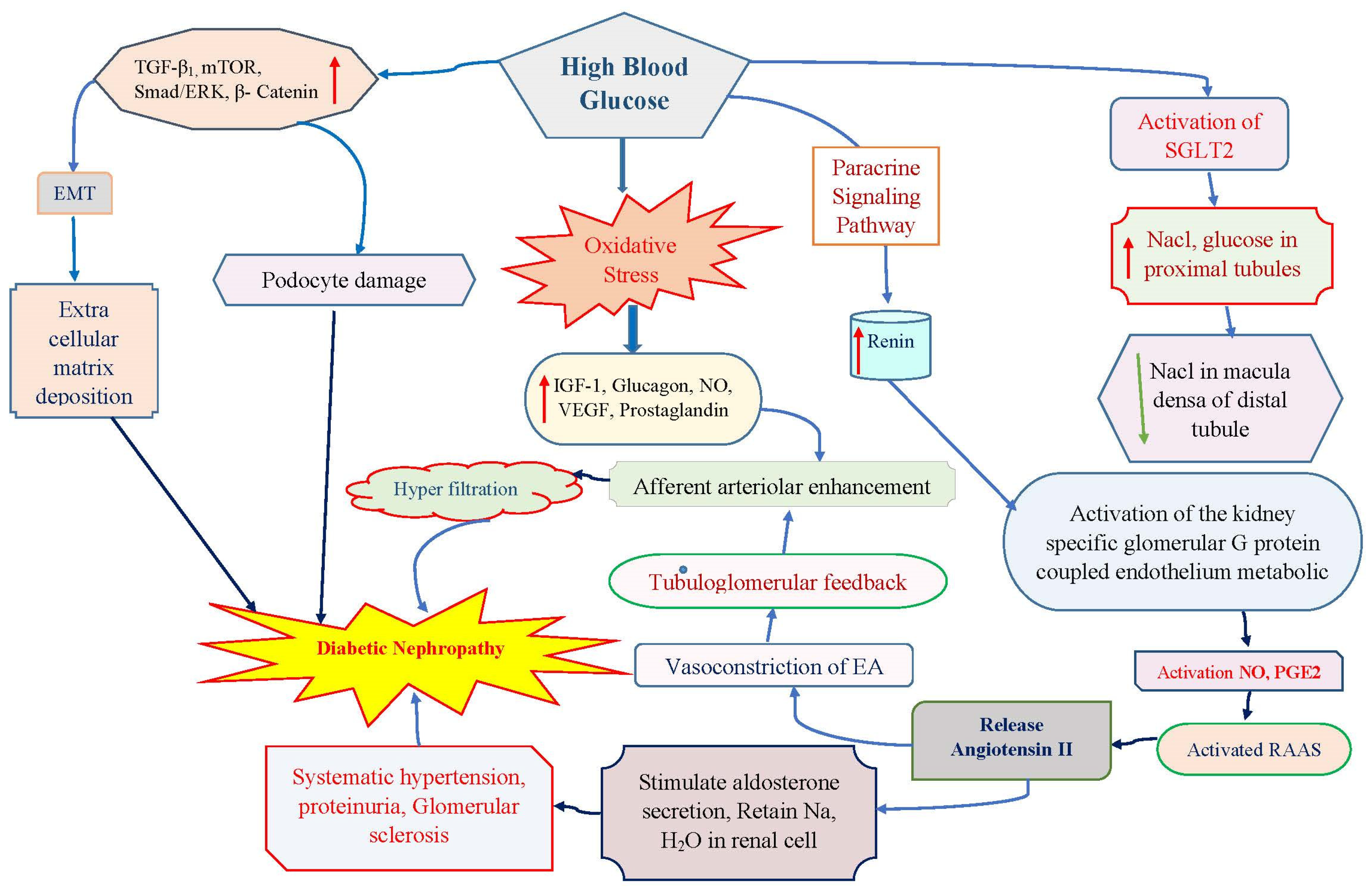
2. Epidemiological Scenario in Diabetic Nephropathy
3. Role of phytocompounds in diabetes nephropathy
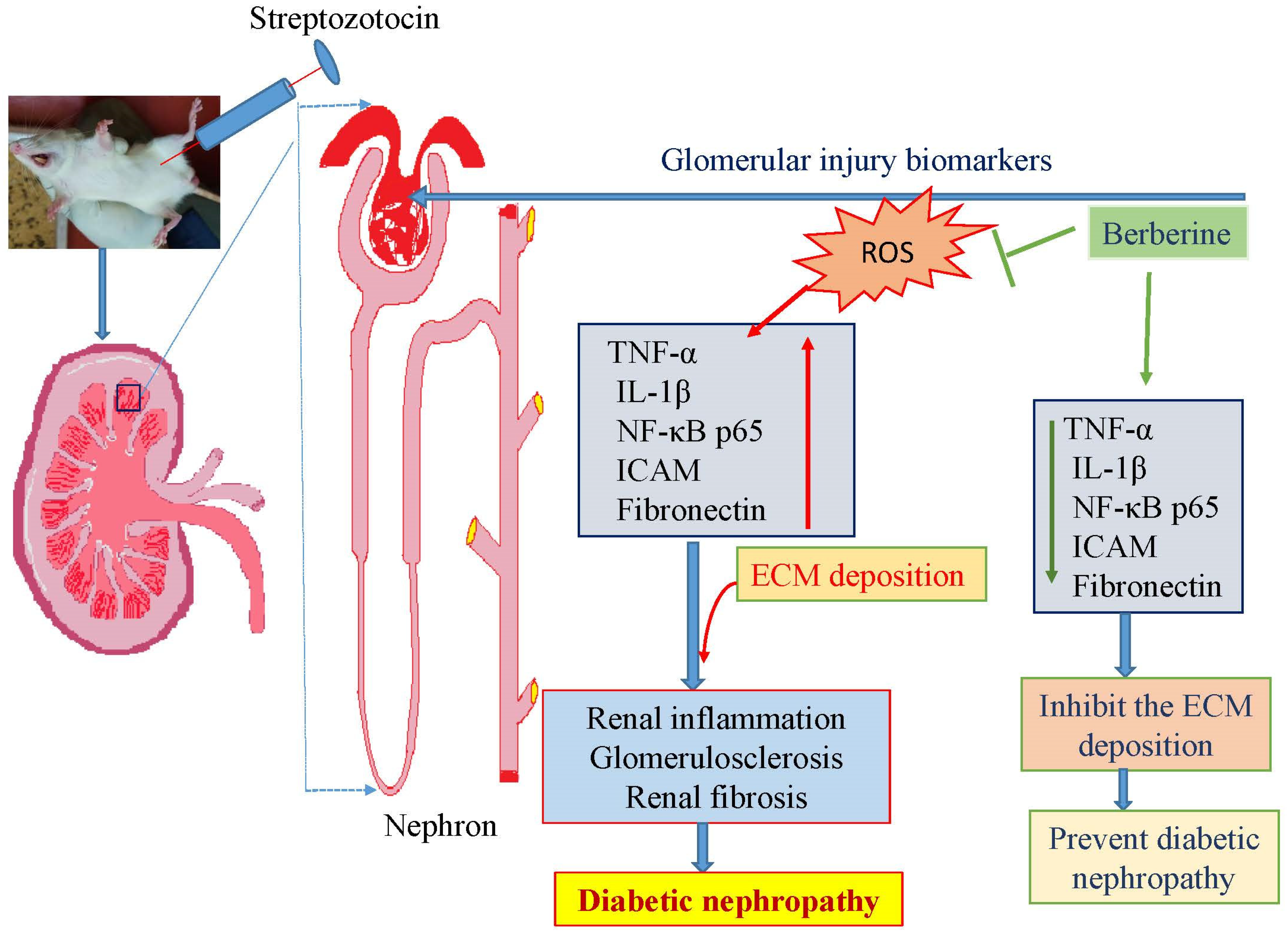
3.1. Berberine
3.2. Resveratrol
3.3. Ellagic acid
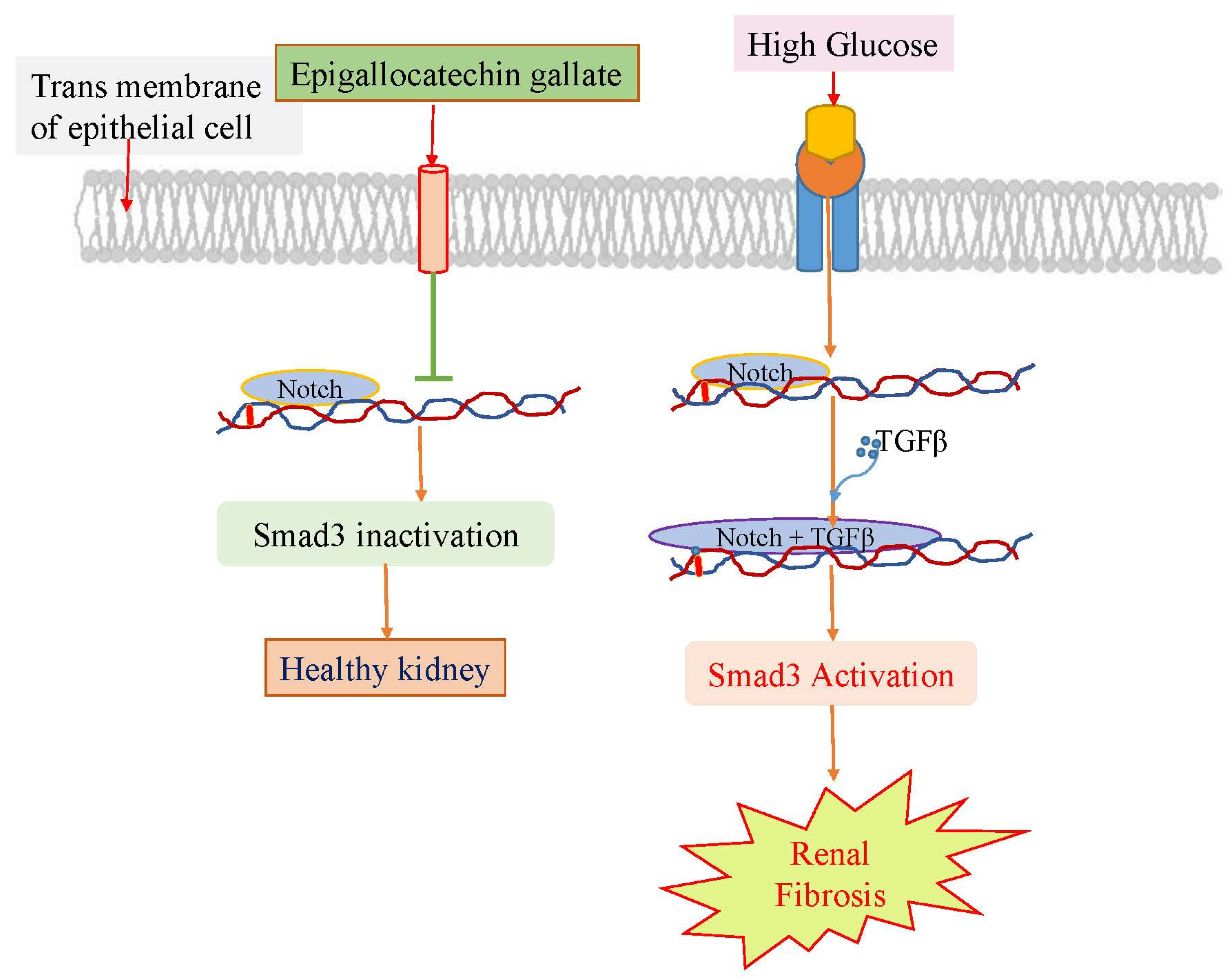
3.4. Epigallocatechin gallate
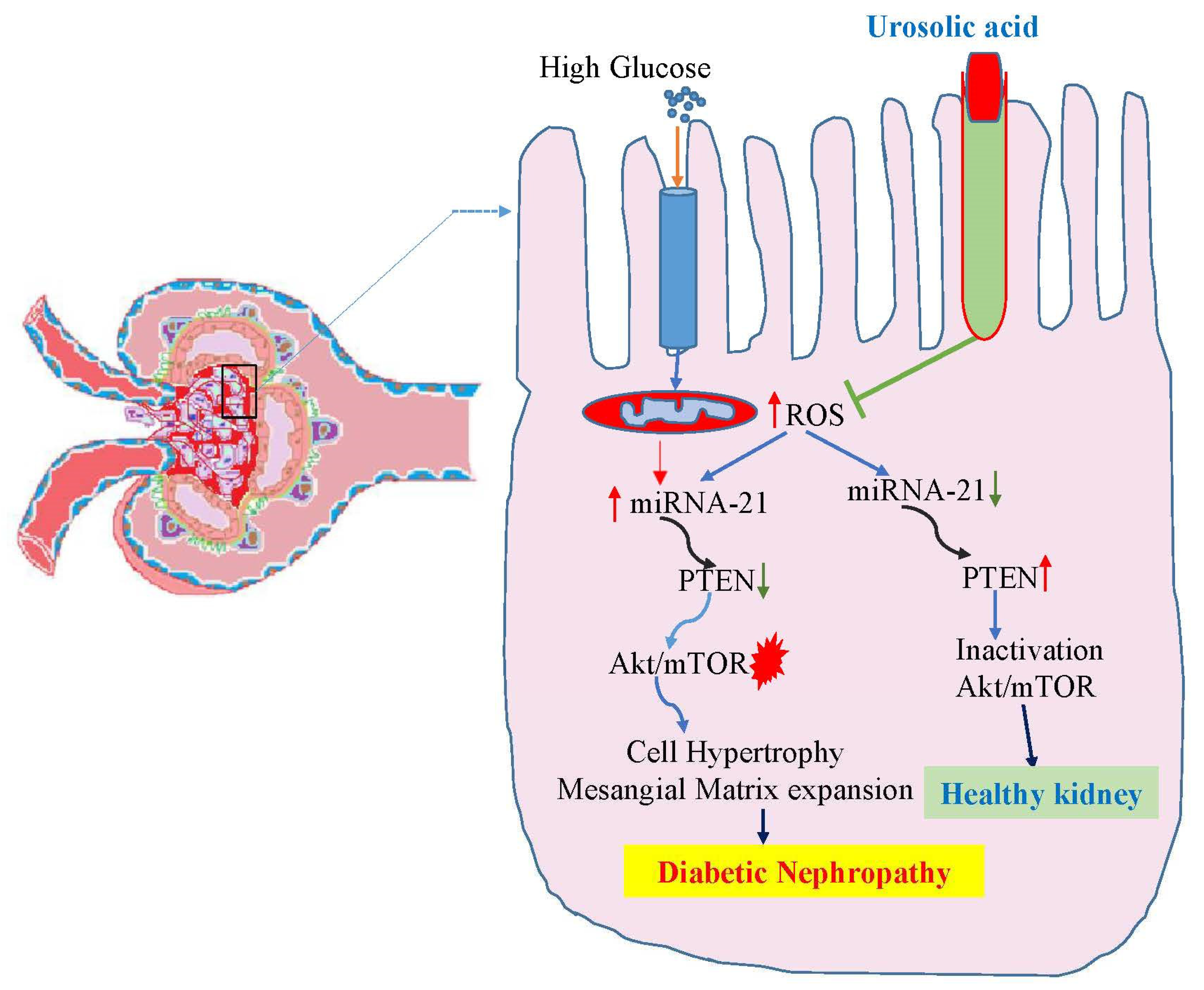
3.5. Ursolic acid
3.6. Ferulic acid
3.7. Quercetin
3.8. Baicalin
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, W. J.; Sobrin, L.; Lee, M. J.; Kang, M. H.; Seong, M.; Cho, H. The relationship between diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy in a population-based study in Korea (KNHANES V-2, 3). Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 6547–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, I. H.; Rue, T. C.; Hall, Y. N.; Heagerty, P. J.; Weiss, N. S.; Himmelfarb, J. (2011). Temporal trends in the prevalence of diabetic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2011, 305, 2532–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianciolo, G.; De Pascalis, A.; Gasperoni, L.; Tondolo, F.; Zappulo, F.; Capelli, I.; Cappuccilli, M.; La Manna, G. The Off-Target Effects, Electrolyte and Mineral Disorders of SGLT2i. Molecules. 2020, 25, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, K. R. Back to the future: glomerular hyperfiltration and the diabetic kidney. Diabetes. 2017, 66, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toma, I.; Kang, J. J.; Sipos, A.; Vargas, S.; Bansal, E.; Hanner, F.; Meer, E.; Peti-Peterdi, J. Succinate receptor GPR91 provides a direct link between high glucose levels and renin release in murine and rabbit kidney. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 2526–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, Z.; Moradi, M.; Nasri, H. A systematic review of the role of renin angiotensin aldosterone system genes in diabetes mellitus, diabetic retinopathy and diabetic neuropathy. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 1090. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H. J.; Wu, Z. Y.; Cao, L.; Zhu, M. Y.; Liu, T. T.; Guo, L.; Lin, Y.; Nie, X. W.; Bian, J. S. Hydrogen Sulfide: Recent Progression and Perspectives for the Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy. Molecules. 2019, 24, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda-Yamahara, M.; Kume, S.; Maegawa, H. Roles of mTOR in diabetic kidney disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, A.; Jin, M.; Kim, S. Y. Bioactive phytochemicals that regulate the cellular processes involved in diabetic nephropathy. Phytomedicine. 2018, 39, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacanli, M.; Dilsiz, S. A.; Başaran, N.; Başaran, A. A. Effects of phytochemicals against diabetes. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 89, 209–238. [Google Scholar]
- Shahidi, F.; Yeo, J. Bioactivities of phenolics by focusing on suppression of chronic diseases: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman Levin, N.; Cohen, M.; Phillip, M.; Tenenbaum, A.; Koren, I.; Tenenbaum-Rakover, Y.; Admoni, O.; Hershkovitz, E.; Haim, A.; Mazor Aronovitch, K.; Zangen, D., Strich, D.; Brener, A.; Yeshayahu, Y.; Schon, Y.; Rachmiel, M.; Ben-Ari, T.; Levy-Khademi, F.; Tibi, R.; Weiss, R.; Shehadeh, N. Youth-onset type 2 diabetes in Israel: A national cohort. Pediatr. Diabetes. 2022, 23, 649–659.
- de Boer, I. H.; Rue, T. C.; Cleary, P. A.; Lachin, J. M.; Molitch, M. E.; Steffes, M. W.; Sun, W.; Zinman, B.; Brunzell, J. D.; Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications Study Research Group, White, N. H.; Danis, R. P.; Davis, M. D.; Hainsworth, D.; Hubbard, L. D.; Nathan, D. M. Long-term renal outcomes of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and microalbuminuria: an analysis of the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications cohort. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 412–420.
- Webster, A. C.; Nagler, E. V.; Morton, R. L.; Masson, P. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2017, 389, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, M. Z.; Aktas, G.; Duman, T. T.; Atak, B. M.; Savli, H. Is Uric Acid elevation a random finding or a causative agent of diabetic nephropathy? Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2019, 65, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethuram, L.; John, T.; Mukherjee, A.; Natarajan, C. A review on contemporary nanomaterial-based therapeutics for the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) with special reference to the Indian scenario. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 2367–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Habib, A.; Najmi, A. K. Limited knowledge of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in India. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019, 16, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, R.; Rema, M.; Pradeepa, R.; Deepa, M.; Shanthirani, C. S.; Deepa, R.; Mohan, V. Prevalence and risk factors of diabetic nephropathy in an urban South Indian population: the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES 45). Diabetes Care. 2007, 30, 2019–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, C.; Kaushik, R.; Kaushik, R. M. Awareness of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Indian scenario. J. of Nephro. 2018, 7, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Siddiqui, S.; Husain, S. A.; Mazurek, S.; Iqbal, M. A. Phytocompounds targeting metabolic reprogramming in cancer: an assessment of role, mechanisms, pathways, and therapeutic relevance. J Agric Food Chem. 2021, 69, 6897–6928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Han, J.; Yuan, R.; Xue, L.; Pang, W. Berberine ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neag, M. A.; Mocan, A.; Echeverría, J.; Pop, R. M.; Bocsan, C. I.; Crişan, G.; Buzoianu, A. D. Berberine: Botanical occurrence, traditional uses, extraction methods, and relevance in cardiovascular, metabolic, hepatic, and renal disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C.; Lopez, A. Berberine improves glucose homeostasis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats in association with multiple factors of insulin resistance. ISRN Endocrinol. 2011, 2011, 519371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chueh, W. H.; Lin, J. Y. Protective effect of isoquinoline alkaloid berberine on spontaneous inflammation in the spleen, liver and kidney of non-obese diabetic mice through downregulating gene expression ratios of pro-/anti-inflammatory and Th1/Th2 cytokines. Food Chemistry. 2012, 131, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, T.; Jiang, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, S.; Hua, W.; Li, Z.; Huang, H.; Ruan, X.; Du, X. Berberine Protects Against Palmitate-Induced Apoptosis in Tubular Epithelial Cells by Promoting Fatty Acid Oxidation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W. J.; Ding, H. H.; Tang, L. Q. Berberine as a promising anti-diabetic nephropathy drug: An analysis of its effects and mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 760, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Geng, S.; Hou, X.; Ma, X.; Xu, H.; Yang, F.; Liu, K.; Liang, W.; Ma, G. Berberine Reduces Renal Cell Pyroptosis in Golden Hamsters with Diabetic Nephropathy through the Nrf2-NLRP3-Caspase-1-GSDMD Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021, 2021, 5545193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Yang, H.; Ma, L.; Fu, P. The roles of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated signaling pathways in hyperuricemic nephropathy. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, S.; Guo, X.; Sun, B.; Wang, Q.; Chen, L. Berberine protects diabetic nephropathy by suppressing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition involving the inactivation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Ren. Fail. 2022, 44, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, S. B.; Pandey, R. P.; Park, Y. I.; Sohng, J. K. Biotechnological advances in resveratrol production and its chemical diversity. Molecules. 2019, 24, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Meng, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Guan, G. Resveratrol ameliorates hyperglycemia-induced renal tubular oxidative stress damage via modulating the SIRT1/FOXO3a pathway. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017, 126, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowd, V.; Kang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Chen, F.; Cheng, K. W. Resveratrol: evidence for its nephroprotective effect in diabetic nephropathy. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y. H.; Fan, Y. J. Resveratrol improves lipid metabolism in diabetic nephropathy rats. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2020, 25, 1913–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, O. D.; Kulkarni, Y. A. Mini-review of analytical methods used in quantification of ellagic acid. Rev. Ana. Chem. 2020, 39, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B. H.; Qiu, Z. P.; Yi, H. L.; Zhou, D. S.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y. [Research progress of ellagitannin intestinal metabolite urolithins]. Zhongguo. Zhong. Yao. Za. Zhi. 2016, 41, 2968–2974. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhao, M.; Lu, Q. TLR2 and TLR4 in autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allergy. Immunol. 2014, 47, 136–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Jiang, S. Ellagic acid attenuates streptozocin induced diabetic nephropathy via the regulation of oxidative stress and inflammatory signaling. Food. Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 123, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X. The role of PI3K/AKT/FOXO signaling in psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2019, 311, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Liu, G.; Kang, X.; Guo, P.; Shang, Y.; Du, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Yue, R.; Kong, F.; Zhu, Q. Ellagic acid inhibits high glucose-induced injury in rat mesangial cells via the PI3K/Akt/FOXO3a signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S. G.; Han, S. S.; Toborek, M.; Hennig, B. EGCG protects endothelial cells against PCB 126-induced inflammation through inhibition of AhR and induction of Nrf2-regulated genes. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 261, 181–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, F.; Yang, T.; Guo, W.; Wu, J.; Jin, H.; Wu, H. Epigallocatechin gallate upregulates NRF2 to prevent diabetic nephropathy via disabling KEAP1. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 108, 840–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Yamamoto, M. Stress-sensing mechanisms and the physiological roles of the Keap1–Nrf2 system during cellular stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 16817–16824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, T.; Narasimhan, K. K. S.; Ravi, D. B.; Velusamy, P.; Chandrasekar, N.; Chakrapani, L. N.; Srinivasan, A.; Karthikeyan, P.; Kannan, P.; Tamilarasan, B.; Johnson, T.; Kalaiselvan, P.; Periandavan, K. Role of Nrf2 dysfunction in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy: Therapeutic prospect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 160, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y. W.; Zhu, Q. Q.; Yang, X. Y.; Xu, H. H.; Sun, B.; Wang, X. J.; Sheng, J. Wound healing can be improved by (—)-epigallocatechin gallate through targeting Notch in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Fang, C.; Song, S.; Li, C.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.; Yan, L.; Hao, S.; Wang, X.; Sheng, J. (-)-Epigallocatechin Gallate Targets Notch to Attenuate the Inflammatory Response in the Immediate Early Stage in Human Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q. Q.; Yang, X. Y.; Zhang, X. J.; Yu, C. J.; Pang, Q. Q.; Huang, Y. W.; Wang, X. J.; Sheng, J. EGCG targeting Notch to attenuate renal fibrosis via inhibition of TGFβ/Smad3 signaling pathway activation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Food. Funct. 2020, 11, 9686–9695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Hortas, L.; Pérez-Larrán, P.; González-Muñoz, M. J.; Falqué, E.; Domínguez, H. Recent developments on the extraction and application of ursolic acid. A review. Food. Res. Int. 2018, 103, 130–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. L.; Wang, X. T.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, J. G.; Zhou, Y. J.; Yang, J. J.; Qi, M. Y. Ursolic acid improves diabetic nephropathy via suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation in streptozotocin-induced rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Cao, P.; Wang, H. Tetrandrine mediates renal function and redox homeostasis in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy rat model through Nrf2/HO-1 reactivation. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yang, H.; Deng, J.; Fan, D. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rg5 against kidney injury via inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and the MAPK signaling pathway in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, H.; Wan, Z.; Wang, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Guo, H.; Qi, C.; Jiao, X.; Li, X. The combination of ursolic acid and empagliflozin relieves diabetic nephropathy by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress and renal fibrosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S. T.; Su, H.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, H. Q.; Wang, C. J.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, W.; Zhu, H. Q.; Wang, Y. Sitagliptin inhibits endothelin-1 expression in the aortic endothelium of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes by suppressing the nuclear factor-κB/IκBα system through the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 1558–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, D.; Fan, L.; Xiao, Q.; Zuo, H.; Li, Z. CAPE-pNO2 ameliorated diabetic nephropathy through regulating the Akt/NF-κB/iNOS pathway in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Oncotarget. 2017, 8, 114506–114525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, N.; Yan, S.; Liu, M.; Sun, B.; Lu, Y.; Shao, Y. Ursolic acid alleviates inflammation and against diabetes-induced nephropathy through TLR4-mediated inflammatory pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 4675–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, N.; Ghosh-Choudhury, N.; Kasinath, B. S.; Choudhury, G. G. TGFβ-stimulated microRNA-21 utilizes PTEN to orchestrate AKT/mTORC1 signaling for mesangial cell hypertrophy and matrix expansion. PLoS One. 2012, 7, e42316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Fan, Q.; Xu, L.; Li, L.; Yue, Y.; Xu, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, L. Ursolic acid attenuates diabetic mesangial cell injury through the up-regulation of autophagy via miRNA-21/PTEN/Akt/mTOR suppression. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0117400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento-Silva, A.; Patto, M. C. V.; do Rosário Bronze, M. Relevance, structure and analysis of ferulic acid in maize cell walls. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 360–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M. E. Autophagy in kidney disease. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2020, 82, 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Klionsky, D. J. Autophagy and disease: unanswered questions. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 858–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhao, W. Geniposide alleviates diabetic nephropathy of mice through AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 886, 173449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, F.; Chu, C.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Xiao, W. Use of Ferulic Acid in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Molecules. 2022, 27, 6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, D.; Chengcheng, L.; Xuan, Q.; Yibing, C.; Lei, W.; Hao, Y.; Xizhi, L.; Yuan, L.; Xiaoxing, Y.; Qian, L. Quercetin inhibited mesangial cell proliferation of early diabetic nephropathy through the Hippo pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 146, 104320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Ji, X. J.; Zhou, Y. X.; Yao, X. Q.; Liu, Y. Q.; Zhang, F.; Yin, X. X. Quercetin inhibits the mTORC1/p70S6K signaling-mediated renal tubular epithelial–mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 237–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigeoka, A. A.; Mueller, J. L.; Kambo, A.; Mathison, J. C.; King, A. J.; Hall, W. F.; Correia, J.daS.; Ulevitch, R. J.; Hoffman, H. M.; McKay, D. B. An inflammasome-independent role for epithelial-expressed Nlrp3 in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6277-85.
- Wang, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Q. Y.; Wang, F. M.; Kong, L. D. Quercetin and allopurinol ameliorate kidney injury in STZ-treated rats with regulation of renal NLRP3 inflammasome activation and lipid accumulation. PLoS One. 2012, 7, e38285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Gurung, P.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, H.; Guo, R.; Han, Q.; Zhang, J.; Lei, S.; Liu, F. The relationship between the thickness of glomerular basement membrane and renal outcomes in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Acta. Diabetol. 2018, 55, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Ge, J.; Li, N. Quercetin improves lipid metabolism via SCAP-SREBP2-LDLr signaling pathway in early stage diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Ko, W.K.; Hwang, D.S.; Heo, D.N.; Lee, S.J.; Heo, M.; Lee, K.S.; Ahn, J.Y.; Jo, J.; Kwon, I.K. Use of baicalin-conjugated gold nanoparticles for apoptotic induction of breast cancer cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 381. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Wu, F.; Shao, Q.; Chen, G.; Xu, L.; Lu, F. Baicalin alleviates oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy via Nrf2 and MAPK signaling pathway. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 3207–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, L.; Liang, R.; Yang, C.; Wang, P. Baicalin suppresses renal fibrosis through microRNA-124/TLR4/NF-κB axis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy mice and high glucose-treated human proximal tubule epithelial cells. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 76, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Zhang,W.; Chen, S.; Deng, H. Baicalin improves podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Open Med. (Wars). 2021, 16, 1286–1298. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J. E.; Jo, S. Y.; Ahn, C. W.; & Kim, Y. S.; & Kim, Y. S. Baicalin attenuates fibrogenic process in human renal proximal tubular cells (HK− 2) exposed to diabetic milieu. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




