Submitted:
11 May 2023
Posted:
12 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phytochemical analysis leaf of C. oxyacantha.
2.2. Proportions of polychromatic erythrocytes (PCEs) and micronucleated polychromatic erythrocytes (MNPCEs) in pregnant rats
2.3. Proportion of PCEs, MNPCEs and micronucei (MNs) in neonates of rats
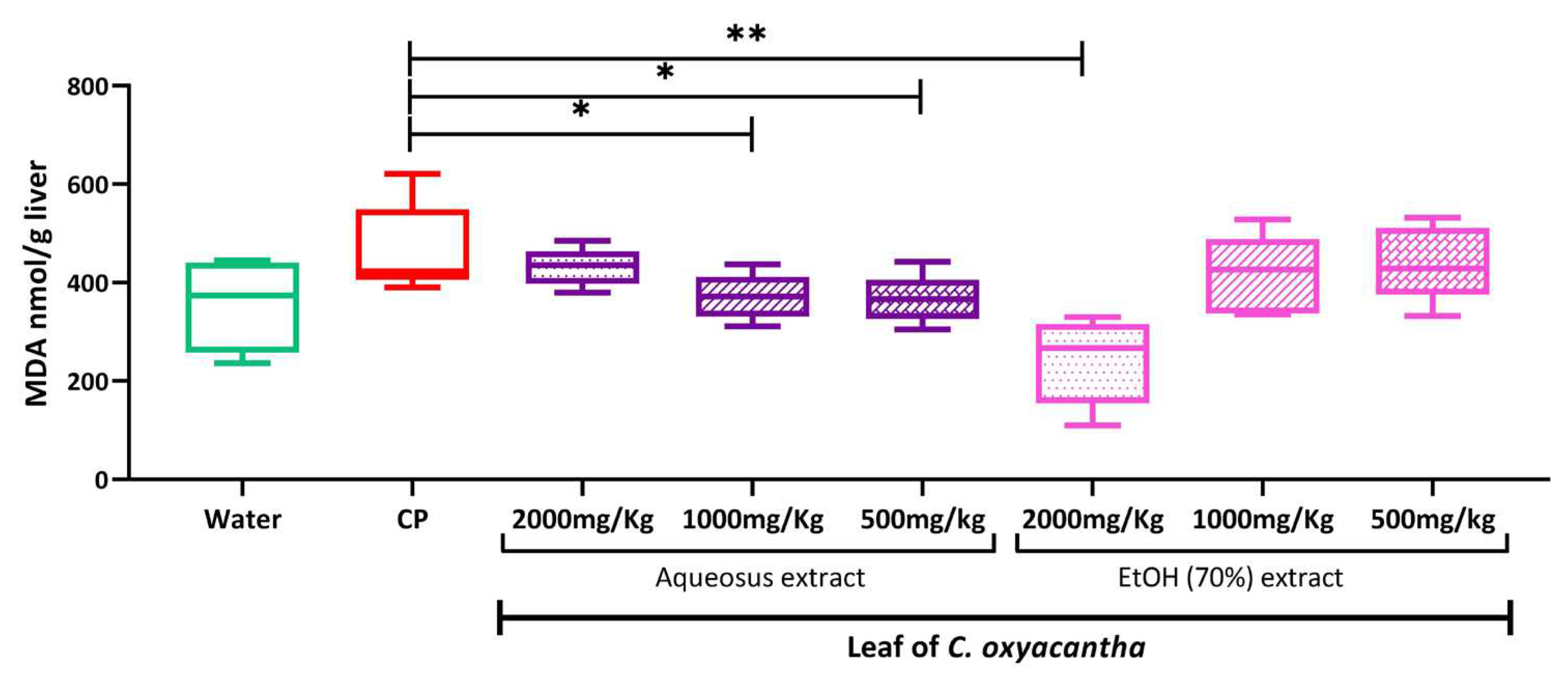
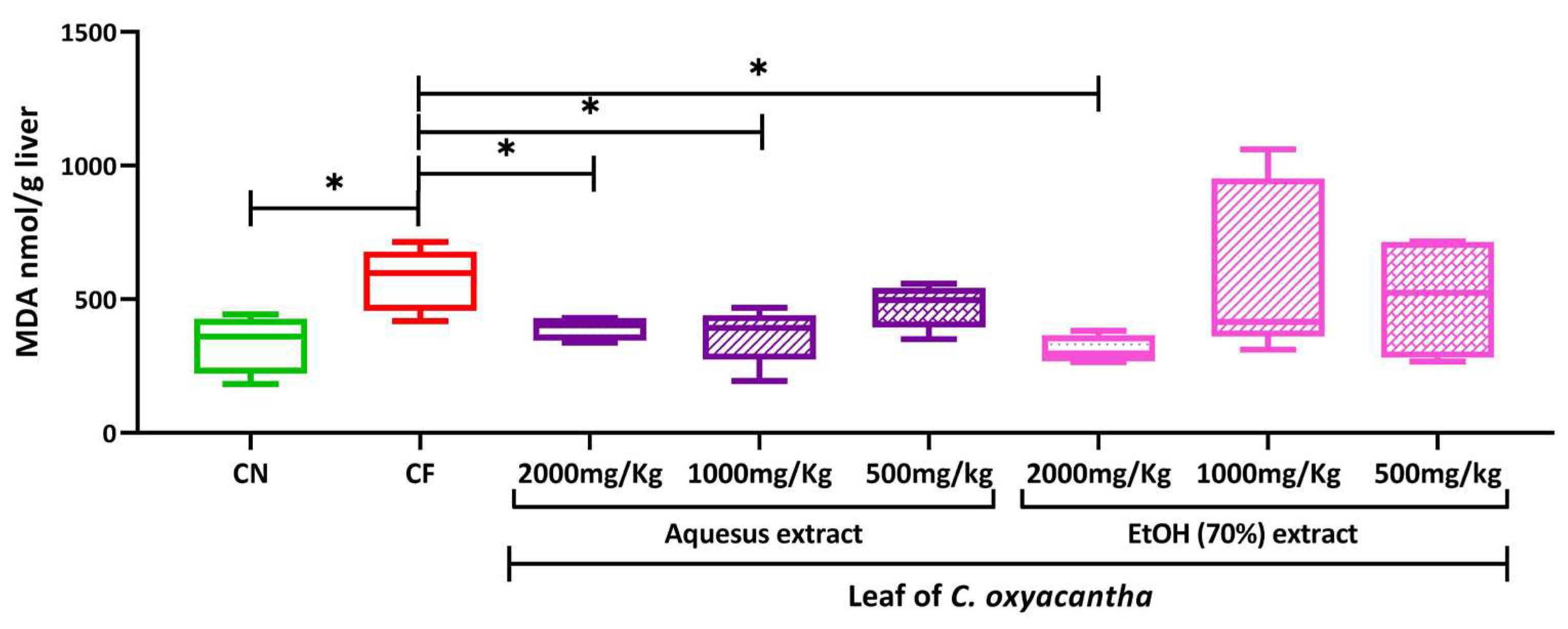
2.4. Hepatic peroxidation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and reagents
4.2. Plant material
4.3. Preparation of the aqueous and hydroalcoholic leaf extracts of C. oxyacantha
4.4. Phytochemical analysis leaf of C. oxyacantha
4.5. Animals
4.6. Study groups
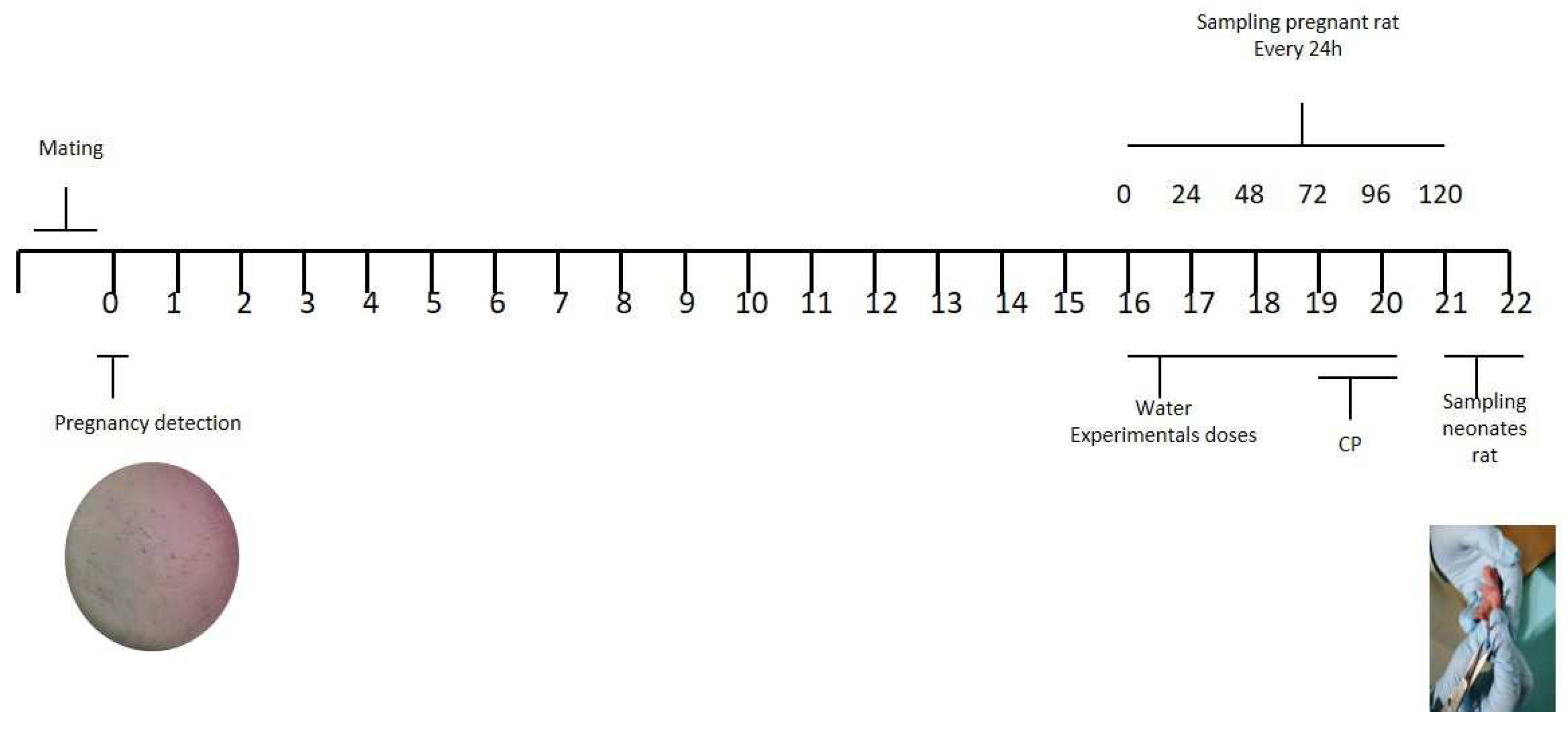
4.7. Mating
4.8. Sample preparation and micronucleus analysis in pregnancy rats and its neonate
4.9. Hepatic peroxidation (Malondialdehyde quantification, MDA)
4.10. Statistical analysis
4.11. Ethical Considerations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Global Centre for Traditional Medicin. Available online: https://www.who.int/initiatives/who-global-centre-for-traditional-medicine (accessed on 3 April 2023).
- Lamar, A.S.; López, G.F.; Trujillo, N.C.; Fuentes, D.F. Propuesta de ruta crítica para la evaluación genotóxica de plantas medicinales en Cuba. Revista Cubana de Farmacia 2000, 34, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Gentile, J.M.; Gentile, G.J.; Bultman, J.; Sechriest, R.; Wagner, E.D.; Plewa, M.J. An evaluation of the genotoxic properties of insecticides following plant and animal activation. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. 1982, 101, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kier, L.; Brusick, D.; Auletta, A.; Von Halle, E.; Brown, M.; Simmon, V.F.; Rao, T.K. The Salmonella typhimurium/mammalian microsomal assay: A report of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Gene-Tox Program. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. 1986, 168, 69–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames, B.N. The detection of chemical mutagens with enteric bacteria. In Chemical mutagen; Springer: Boston, MA, 1971; pp. 267–282. [Google Scholar]
- Quillardet, P.; Hofnung, M. The SOS Chromotest, a colorimetric bacterial assay for genotoxins: procedures. Mutation Research/Environmental Mutagenesis and Related Subjects 1985, 147, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ni, J.; Liang, Z.; Xue, J.; Fenech, M.F.; Wang, X. The molecular origins and pathophysiological consequences of micronuclei: New insights into an age-old problem. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2018, 779, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedano, A.; Martínez, S.; Escalera, F.; Salgado, S.; Carrillo, F.; Macías, H. La prueba de micronúcleos en sangre como bioindicador de genotóxicos. Abanico veterinario 2012, 2, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, C.I.; Zamora, A.L.; Sosa, M.; Ortiz, Y.M.; Sánchez, R.; Avilés, K.; Pérez, I. Daño al ADN en recién nacidos de madres con sobrepeso. Revista Médica MD 2017, 8, 140–145. [Google Scholar]
- Meda, B.C.; Gonzales, G.Z. Genotoxicidad y potencial teratógeno”. Revista de divulgación científica y tecnológica de la Universidad Veracruzana 2007, 20, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, L.R.; Ford, J.H. Overlap between mutagens and teratogens. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis 1997, 396, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepard, T.H.; Lemire, R.J. Catalog of teratogenic agents, Edited by Thomas H. Shepard, 3rd ed.; Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Arencibia, D.F.; Fernández, R.; Alfredo, L.; Suárez, Y.E.; Delgado, L.; Bourzac, J.F.I. Frecuencia espontánea e inducida de micronúcleos transplacentarios en ratones Balb/c”. Nova Scientia 2011, 3, 01–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M. The micronucleus test—most widely used in vivo genotoxicity test. Genes and Environment 2016, 38, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, V.; Kashyap, C.; Thakur, N. Phytopharmacological Properties and Clinical Applications of Crataegus Oxyacantha (Crataegus Laevigata). American Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine 2012, 7, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul, A.S.; Amin, R.; Suleiman, M.S. Hypotensive effect of Crataegus oxyacantha. International Journal of Crude Drug Research 1987, 25, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Makdessi, S.; Sweidan, H.; Dietz, K.; Jacob, R. Protective effect of Crataegus oxyacantha against reperfusion arrhythmias after global no-flow ischemia in the rat heart. Basic Res. Cardiol. 1999, 94, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenring, F.; Suter, A.; Weber, M.; Saller, R. A randomised double blind placebo controlled clinical trial of a standardised extract of fresh Crataegus berries (Crataegisan®) in the treatment of patients with congestive heart failure NYHA II. Phytomedicine 2003, 10, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalakshmi, R.; Thirupurasundari, C.J.; Devaraj, S.N. Pretreatment with alcoholic extract of shape Crataegus oxycantha (AEC) activates mitochondrial protection during isoproterenol – induced myocardial infarction in rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 292, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Carey, R.; Crofoot, K.; Proteau, P.; Filtz, T. Effect of hawthorn (Crataegus oxycantha) crude extract and chromatographic fractions on multiple activities in a cultured cardiomyocyte assay. Phytomedicine 2006, 13, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, H.; Soner, B.C.; Baysal, T.; Sahin, A.S. Protective effects of Hawthorn (Crataegus oxyacantha) extract against digoxin-induced arrhythmias in rats. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2015, 15, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Durán, R.E.; Medrano-Rodríguez, J.C.; Sánchez-Aguilar, M.; Soria-Castro, E.; Rubio-Ruíz, M.E.; Valle-Mondragón, D.; Ibarra-Lara, L. Extracts of Crataegus oxyacantha and Rosmarinus officinalis Attenuate Ischemic Myocardial Damage by Decreasing Oxidative Stress and Regulating the Production of Cardiac Vasoactive Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbar, K.; Zarrinkalam, E.; Salehi, I.; Komaki, A.; Fayazi, B. Cardioprotective effect of resistance training and Crataegus oxyacantha extract on ischemia reperfusion–induced oxidative stress in diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 100, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanthi, S.; Parasakthy, K.; Deepalakshmi, P.D.; Devaraj, S.N. Hypolipidemic activity of tincture of Crataegus in rats. Indian journal of biochemistry & biophysics 1994, 31, 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Akila, M.; Devaraj, H. Synergistic effect of tincture of Crataegus and Mangifera indica L. extract on hyperlipidemic and antioxidant status in atherogenic rats. Vascular pharmacology 2008, 49, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, C.P.; Arya, V.; Thakur, N. Ethnomedicinal and phytopharmacological potential of Crataegus oxyacantha Linn.–A review. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine 2012, 2, S1194–S1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, C.; Jayachandaran, K.S.; Devaraj, S.N. Hawthorn extract reduces infarct volume and improves neurological score by reducing oxidative stress in rat brain following middle cerebral artery occlusion. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2009, 27, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, C.; Devaraj, S.N. Immunomodulatory effect of Hawthorn extract in an experimental stroke model. J. Neuroinflammation 2010, 7, 97–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, G.; Jeivad, F.; Goharbari, M.; Gheshlaghi, G.H.; Sabzevari, O. Ethanol extract of Crataegus oxyacantha L. ameliorate dietary non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rat. Drug research 2018, 68, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rodríguez, J.L.; Gutiérrez-Hernández, R.; Reyes-Estrada, C.A.; Granados-López, A.J.; Pérez-Veyna, O.; Arcos-Ortega, T.; López, J.A. Hepatoprotective, Antihyperlipidemic and Radical Scavenging Activity of Hawthorn (Crataegus oxyacantha) and Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) on Alcoholic Liver Disease. Alternative Therapies in Health & Medicine 2019, 25, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Mecheri, A.; Benabderrahmane, W.; Amrani, A.; Boubekri, N.; Benayache, F.; Benayache, S.; Zama, D. Hepatoprotective Effects of Algerian Crataegus oxyacantha Leaves. Recent Patents Food, Nutr. Agric. 2019, 10, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, N.A.; Thiruchenduran, M.; Devaraj, S.N. Anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of Crataegus oxyacantha on isoproterenol-induced myocardial damage. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 367, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadic, V.M.; Dobric, S.; Markovic, G.M.; Ðorđevic, S.M.; Arsic, I.A.; Menkovic, N.R.; Stevic, T. Anti-inflammatory, gastroprotective, free-radical-scavenging, and antimicrobial activities of hawthorn berries ethanol extract. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 2008, 56, 7700–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokół-Łętowska, A.; Oszmiański, J.; Wojdyło, A. Antioxidant activity of the phenolic compounds of hawthorn, pine and skullcap. Food chemistry 2007, 103, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olah, N.-K.; Burtescu, R.; Petrescu, S.; Brașovan, A.; Chișe, E.; Cobzac, S.C.A.; Hanganu, D.; SRL, R.R.S.P. Phytochemical screening of different Crataegus Oxyacantha extracts. Studia Universitatis Babes-Bolyai, Chemia 2017, 62, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoudi, M.; Salem, R.B.S.-B.; Ben Salem, M.; Brahmi, N.; Badraoui, R.; Nasri, M.; El Feki, A. Beneficial effects of crataegus oxyacantha extract on neurobehavioral deficits and brain tissue damages induced by an insecticide mixture of deltamethrin and chlorpyrifos in adult wistar rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmalek, Y.; Yahia, O.A.; Belkebir, A.; Fardeau, M.L. Anti-microbial and anti-oxidant activities of Illicium verum, Crataegus oxyacantha ssp monogyna and Allium cepa red and white varieties. Bioengineered 2013, 4, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeouk, I.; Balouiri, M.; Bekhti, K. Antistaphylococcal Activity and Phytochemical Analysis of Crude Extracts of Five Medicinal Plants Used in the Center of Morocco against Dermatitis. Int. J. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanus, M.; Lafon, J.; Mathieu, M. Double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a fixed combination containing two plant extracts (Crataegus oxyacantha and Eschscholtzia californica) and magnesium in mild-to-moderate anxiety disorders. Curr. Med Res. Opin. 2004, 20, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabach, R.; Mattei, R.; Carlini, E.L. Pharmacological evaluation of a phytotherapeutic product-CPV (dry extract of Crataegus oxyacantha L., Passiflora incarnata L. and Valeriana officinalis L.) in laboratory animals. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2009, 19, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijarro, J.M. Los parámetros de seguridad en Fitoterapia. Revista de fitoterapia 2005, 5, 117–134. [Google Scholar]
- Luengo, M.T.L. Plantas medicinales: interacciones con medicamentos y con otros fármacos vegetales. Offarm: farmacia y Sociedad 2008, 27, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Saad, B.; Zaid, H.; Shanak, S.; Kadan, S.S. Introduction to Medicinal Plant Safety and Efficacy. In Anti-diabetes and Anti-obesity Medicinal Plants and Phytochemicals; Springer Cham Published, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 21–55. ISBN 9783319541013. [Google Scholar]
- Chamorro-Cevallos, G.; Mojica-Villegas, M.A.; García-Martínez, Y.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, S.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.; Vargas-Mendoza, N.; Morales-González, J.A.; Cristóbal-Luna, J.M. A Complete Review of Mexican Plants with Teratogenic Effects. Plants 2022, 11, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomson, T.; Landmark, C.J.; Battino, D. Antiepileptic drug treatment in pregnancy: Changes in drug disposition and their clinical implications. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heddle, A.; Cimino, M.C.; Hayashi, M.; Romagna, F.; Shelby, M.D.; Tucker, J.D.; MacGregor, J.T. Micronuclei as an index of cytogenetic damage: past, present, and future. Environmental and molecular mutagenesis 1991, 18, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; MacGregor, J.T.; Gatehouse, D.G.; Adler, I.D.; Blakey, D.H.; Dertinger, S.D.; Krishna, G.; Morita, T.; Russo, A.; Sutou, S. In vivo rodent erythrocyte micronucleus assay. II. Some aspects of protocol design including repeated treatments, integration with toxicity testing, and automated scoring. Environ Mol Mutagen 2000, 35, 234–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Meda, B.C.; Zúñiga-González, G.M.; Zamora-Perez, A.; Ramos-Ibarra, M.L.; Batista-González, C.M.; Torres-Mendoza, B.M. Folate supplementation of cyclophosphamide-treated mothers diminishes micronucleated erythrocytes in peripheral blood of newborn rats. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2004, 44, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga-González, G.M.; Gómez-Meda, B.C.; Zamora-Perez, A.L.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Bautista-Bejarano, M.A.; Patiño-Valenzuela, S.; Armendáriz-Borunda, J.; Lazalde-Ramos, B.P.; Sánchez-Parada, M.G.; Gallegos-Arreola, M.P. Micronucleated erythrocytes in newborns rats exposed to three different types of ultraviolet-A (UVA) lamps from commonly uses devices. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B: Biol. 2016, 165, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, M.K.; Avila, D.; Zhang, J.; Barve, S.; Arteel, G.; McClain, C.; Joshi-Barve, S. Acrolein cytotoxicity in hepatocytes involves endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Toxicology and applied pharmacology 2012, 265, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Lin, J.H.; Yang, C.H.; Haung, C.H.; Weng, C.W.; Lin, A.M.Y.; Tang, M.S. Acrolein induces mtDNA damages, mitochondrial fission and mitophagy in human lung cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 70406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Rodríguez, F.R.; Zamora-Perez, A.L.; Galván-Moreno, C.L.; Gutiérrez-Hernández, R.; Estrada, C.A.R.; Esparza-Ibarra, E.L.; Lazalde-Ramos, B.P. Cytotoxic and Genotoxic Evaluation of the Aqueous and Hydroalcoholic Leaf and Bark Extracts of Crataegus oxyacantha in Murine Model. Plants 2021, 10, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.J.; Singh, S.M. Transplacental teratogenesis and mutagenesis in mouse fetuses treated with cyclophosphamide. Teratog. Carcinog. Mutagen. 1988, 8, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorvatovičová, D.; Ujhàzy, E. Transplacental effect of stobadine on cyclophosphamide induced micronucleus frequency in mice. Mutagenesis 1995, 10, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Mariscal, K.; Gómez-Meda, B.C.; Zamora-Perez, A.L.; Sánchez-Parada, M.G.; Gallegos-Arreola, M.P.; Zúñiga-González, G.M. Micronuclei Induction in Amniotic Fluid Cells from Cyclophosphamide Treated Rats. Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science 2018, 48, 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Velazquez, G.; Lazalde-Ramos, B.P.; Gómez-Meda, B.C.; Zúñiga-González, G.M.; Ortiz-García, Y.M.; Gutiérrez-Hernández, R.; Guerrero-Velazquez, C.; de la Rosa, S.V.S.; Zamora-Perez, A.L. Genome Damage in Rats after Transplacental Exposure to Jatropha dioica Root Extract. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 2962950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkes, E. Cyclophosphamide teratogenesis: A review. 1985, 5, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JDer Elst, J.P.S.-V.; Van Der Heide, D.; Rokos, H.; De Escobar, G.M.; Köhrle, J. Synthetic flavonoids cross the placenta in the rat and are found in fetal brain. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 1998, 274, E253–E256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benabderrahmane, W.; Lores, M.; Lamas, J.P.; Benayache, S. Matrix solid-phase dispersion as a tool for phytochemical and bioactivities characterisation: Crataegus oxyacantha L._A case study. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 32, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svedström, U.; Vuorela, H.; Kostiainen, R.; Huovinen, K.; Laakso, I.; Hiltunen, R. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of oligomeric procyanidins from dimers up to the hexamer in hawthorn. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 968, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, S.; Ringl, A.; Huefner, A.; Pemp, E.; Kopp, B. 4-Acetylvitexin-2 -O-rhamnoside, Isoorientin, Orientin, and 8-Methoxykaempferol-3-O-glucoside as Markers for the Differentiation of Crataegus monogyna and Crataegus pentagyna from Crataegus laevigata (Rosaceae). Chem Biodivers 2007, 4, 2920–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Liu, P. Composition and health effects of phenolic compounds in hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) of different origins. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 2012, 92, 1578–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Der Elst, J.P.S.-V.; Van Der Heide, D.; Rokos, H.; De Escobar, G.M.; Köhrle, J. Synthetic flavonoids cross the placenta in the rat and are found in fetal brain. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 1998, 274, E253–E256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh, L.; Seifi, N.; Shahinfard, N.; Sedighi, M.; Kheiri, S.; Shirzad, H.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. Antioxidant activity and teratogenicity evaluation of Lawsonia Inermis in BALB/c mice. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research: JCDR 2015, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fateh, A.H.; Mohamed, Z.; Chik, Z.; Alsalahi, A.; Zin, S.R.M.; Alshawsh, M.A. Prenatal developmental toxicity evaluation of Verbena officinalis during gestation period in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Chemico-biological interactions 2019, 304, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyselova, Z. Toxicological aspects of the use of phenolic compounds in disease prevention. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2011, 4, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, G.; P. J. O'Brien. Potential toxicity of flavonoids and other dietary phenolics: significance for their chemopreventive and anticancer properties. Free Radic Biol Med 2004, 37, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Quadros, A.P.O.; Mazzeo, D.E.C.; Marin-Morales, M.A.; Perazzo, F.F.; Rosa, P.C.P.; Maistro, E.L. Fruit extract of the medicinal plant Crataegus oxyacantha exerts genotoxic and mutagenic effects in cultured cells. J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. Part A 2017, 80, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleĭnik, A.V. Effect of cyclophosphane on bile formation and lipid peroxidation in the liver. Farmakologiia i toksikologiia 1986, 49, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Aladaileh, S.H.; Abukhalil, M.H.; Saghir, S.A.; Hanieh, H.; Alfwuaires, M.A.; Almaiman, A.A.; Mahmoud, A.M. Galangin activates Nrf2 signaling and attenuates oxidative damage, inflammation, and apoptosis in a rat model of cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Jeon, J.H.; Shin, S.; Joo, S.S.; Kang, D.-H.; Moon, S.-H.; Kim, Y.B. Green tea extract increases cyclophosphamide-induced teratogenesis by modulating the expression of cytochrome P-450 mRNA. Reprod. Toxicol. 2009, 27, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Dakdoky, M.H. Influence of mefloquine administration during early pregnancy on rat embryonic development. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2015, 25, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, J.C.; de Oliveira, P.R.; Camargo-Mathias, M.I.; Perazzo, F.F.; Rosa, P.C.P.; Gaivão, I.O.d.M.; Maistro, E.L. Hepatic and splenic cytotoxic evaluation after Crataegus oxyacantha fruit extract administration on mice. J. Histol. Histopathol. 2019, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhees, K.; Godschalk, R.W.; Sanders, A.; Doorn-Khosrovani, S.B.v.W.v.; van Schooten, F.J. Maternal quercetin intake during pregnancy results in an adapted iron homeostasis at adulthood. Toxicology 2011, 290, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karampour, N.S.; Arzi, A.; Varzi, H.N.; Mohammadian, B.; Rezaei, M. Quercetin Preventive Effects on Theophylline-Induced Anomalies in Rat Embryo. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2014, 9, e17834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesser, M.N.; Keen, C.L.; Lanoue, L. Reproductive and developmental outcomes, and influence on maternal and offspring tissue mineral concentrations, of (−)-epicatechin, (+)-catechin, and rutin ingestion prior to, and during pregnancy and lactation in C57BL/6J mice”. Toxicology Reports 2015, 2, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harborne, J.B. Phytochemical Methods: a guide to modern techniques of plant analysis, 3rd ed.; Springer, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, W. The micronucleus test. Mutat Res 1975, 31, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihara, M.; Uchimara, M. Determination of Malonaldehyde Precursor in Tessues by Thiobarbituris Acis Test”. Analytical Biochemistri. 1978, 86, 271–278. [Google Scholar]
| Test | Leaf | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroalcoholic Extract | Aqueous Extract | ||
| Flavonoids | ShinodaHCl(c) | - | - |
| NaOH | + | + | |
| Tannins | Gelatin | - | - |
| FeCl3 | Green + Black + |
Green + Black + |
|
| Potassium ferrocyanide | - | - | |
| Quinines | NH4OH | + | + |
| H2 SO4 | - | - | |
| Bornträger reaction | Yellow + | - | |
| PCEs/1000 TEs | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 96 h | 120 h | |||
| Controls | SW | 30.40 ±4.33 | 29.80±5.16 | 28.00±3. 53 | 30.40±3.57 | 30.20±2.58 | 28.60±2.70 | |
| p-value | ----- | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| CP | 53.00 ±5.35 | 52.00±5.35 | 55.00±9.27 | 52.00±12.30 | 46.75±14.50 | 12.00±4.54 | ||
| p-value | ------ | 1.00 | 0.610 | 1.00 | 0.346 | 0.0001 | ||
| C. oxyacantha | Aqueous Ext of leaf | 2000 mg/kg | 39.40±2.19 | 31.20±2.38 | 28.00±2.91 | 25.00±2.34 | 22.60±3.28 | 22.40±3.50 |
| p-value | ------ | 0.002 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | ||
| 1000 mg/kg | 40.20±4.38 | 34.40±3.64 | 31.00±1.58 | 29.00±2.54 | 32.40±4.03 | 29.40±4.92 | ||
| p-value | ------ | 0.065 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.033 | 0.002 | ||
| 500 mg/kg | 38.00±4.41 | 40.20±4.91 | 33.60±2.96 | 34.40±2.79 | 35.00±2.34 | 27.80±3.03 | ||
| p-value | ------ | 1.00 | 0.172 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.004 | ||
| Hydroalcoholic Ext of leaf |
2000 mg/kg p-value |
39.80±3.83 ------ |
38.00±2.91 1.00 |
36.00±2.12 0.405 |
32.60±3.04 0.025 |
28.80±1.92 0.001 |
24.80±1.64 0.0001 |
|
|
1000 mg/kg p-value |
41.40±2.60 | 37.20±2.16 | 34.20±1.09 | 31.00±1.58 | 27.20±3.49 | 24.60±2.50 | ||
| ------- | 0.498 | 0.002 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||
|
500 mg/kg p-value |
49.60±2.07 | 44.00±2.91 | 44.20±5.63 | 44.40±2.96 | 40.20±1.09 | 39.20±2.48 | ||
| ------ | 0.085 | 0.037 | 0.278 | 0.005 | 0.003 | |||
| MNPCEs /1000 PCEs | ||||||||
| Controls | SW | 3.20 ± 1.48 | 4.00 ±1.00 | 3.40 ±1.51 | 3.00 ±1.22 | 2.80 ± 1.09 | 4.20 ± 0.44 | |
| p-value | ----- | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| CP | 5.00±0.81 | 5.50 ±1.73 | 6.75 ± 1.70 | 6.000 ±2.58 | 10.75± 2.21 | 18.50 ±4.35 | ||
| p-value | ---- | 1.00 | 0.446 | 1.00 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | ||
| Leaf of C. oxyacantha | Aqueous Ext. | 2000 mg/kg | 2.60±0.89 | 3.40±0.89 | 4.40±1.67 | 5.20±1.48 | 5.00±2.12 | 3.60±1.34 |
| p-value | ----- | 1.00 | 0.202 | 0.002 | 0.025 | 1.00 | ||
| 1000 mg/kg | 3.00±1.22 | 4.20±1.64 | 4.80±1.92 | 3.60±0.54 | 5.00±2.34 | 4.20±2.16 | ||
| p-value | ----- | 0.567 | 0.202 | 1.00 | 0.111 | 1.00 | ||
| 500 mg/kg | 2.80±1.09 | 3.00±0.70 | 3.80±1.30 | 4.40±0.89 | 2.40±1.14 | 1.40±0.54 | ||
| p-value | ----- | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.155 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Hydroalcoholic Ext. |
2000 mg/kg P value |
2.40±0.54 ----- |
2.20±1.30 1.00 |
3.00±1.00 1.00 |
4.60±0.89 0.011 |
3.60±0.54 1.00 |
3.00±1.22 1.00 |
|
|
1000 mg/kg p-value |
4.00±0.70 ---- |
3.60±1.34 1.00 |
2..80±0.83 1.00 |
3.20±1.30 1.00 |
2.40±0.89 0.433 |
2.80±1.30 1.00 |
||
|
500 mg/kg p-value |
2.60±1.14 ----- |
2.20±0.44 1.00 |
2.60±0.89 1.00 |
3.20±1.30 1.00 |
4.00±1.22 0.806 |
3.20±1.30 1.00 |
||
| Number of newborns | PCEs/1000 TEs | MNPCEs /1000 PCEs | MNEs /10000 TEs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls | Negative control (SW) |
30 | 678.56 ±72.57 | 4.87±1.35 | 7.00±2.01 |
| Positive control (CP) | 30 | 500±93.23 | 27.07±10.63 | 13.33±5.33 | |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| Aqueous Ext of leaf | 2000 mg/kg | 30 | 532.66±84.48 | 8.30±1.98 | 8.17±1.70 |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.384 | ||
| 1000 mg/kg | 30 | 618.70±78.05 | 6.03±1.92 | 6.73±1.63 | |
| p-value | 0.083 | 0.208 | 1.000 | ||
| 500 mg/kg | 30 | 658.30±95.59 | 5.50±1.30 | 7.43±1.87 | |
| Valor de p | 1.00 | 0.835 | 1.000 | ||
| Hydroalcoholic Ext. of leaf | 2000 mg/kg p-value |
30 | 636.70±98.84 | 4.40±1.07 | 5.40±1.65 |
| 0.813 | 0.977 | 0.038 | |||
| 1000 mg/kg p-value |
30 | 652.73±80.84 | 4.50±1.35 | 5.27±1.66 | |
| 0.995 | 1.000 | 0.017 | |||
| 500 mg/kg p-value |
30 | 661.06±107.06 | 3.23±0.93 | 4.23±1.38 | |
| 1.00 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





