1. Introduction
Phytate was first discovered in vegetable seeds during the 1850s, its chemical formula (inositol hexakisphosphate, InsP6) was established in the early 1900s, and the first animal experiments assessed the effects of phytate consumption in the 1940s [
1]. These early animal experiments supplied high doses of sodium phytate to dogs and found that this led to the development of rickets [
2]. These studies led to the belief that the consumption of phytate can cause rickets and a deficiency of certain mineral elements, especially iron, calcium, and zinc. Importantly, these early studies fed dogs with very large amounts of sodium phytate. However, phytate naturally occurs in vegetables at a low level, and mainly as a calcium-magnesium salt that is insoluble in water. Therefore, the effect of consuming a moderate amount of phytate when administered in the form of this salt and with a balanced diet does not significantly affect the absorption of calcium (which is actually incorporated in phytate) or other trace elements, such as copper and zinc. However, consumption of large amounts of phytate with a very unbalanced diet, as occurs in some South Asian countries, can induce deficiencies of trace elements (1). In fact, the "Mediterranean diet”, which is rich in legumes and nuts, involves daily consumption of 1 to 2 g of phytin (calcium-magnesium phytate), and this diet clearly has beneficial health effects. By around the year 2000, researchers confirmed the important health benefits from the moderate consumption of phytate with a balanced diet [
1]. Phytate is now well-known as an antioxidant [
3], and for its ability to prevent the development of kidney stones and other pathological calcifications [
4], osteoporosis [
5], some types of cancer [
6,
7], and the formation of glycation end-products in patients with diabetes [
8,
9].
A complication in studies that evaluate the effects of InsP6 and its metabolites is determining the levels of all these substances in biological fluids and tissues [
10]. One issue is that phytate and other highly phosphorylated InsPs have a very high capacity to bind metallic elements and calcium, and these elements are present in the systems used for detection and determination. A second issue is that the less phosphorylated InsPs have many isomers, and suitable laboratory standards are often unavailable. Moreover, after an individual consumes InsP6, intestinal phytases (also from the diet) cause phytate dephosphorylation [
11,
12]. All the InsP6 hydrolysates, many of which are probably in low concentrations, cross the intestine by paracellular transport. Once in the liver or other tissues, alkaline phosphatases [
1] dephosphorylate these InsPs. Because of these many possibilities, the body contains a great diversity of InsPs, and its levels are affected by InsP6 consumption and endogenous metabolism.
Pyrophosphate is one of the first described inhibitors of calcium salt crystallization in living organisms [
13,
14]. The digestive system can hydrolyze pyrophosphate. Fleisch first described the chemical synthesis of bisphosphonates. Bisphosphonates are not hydrolyzed by digestive system, and are also absorbed at low doses via the paracellular route and are effective crystallization inhibitors, but they are now better known for their prevention of osteoporosis [
15]. In fact, all of these polyphosphates (pyrophosphate, bisphosphonates, InsP6, and InsP6 derivatives) have some activities at the intracellular and extracellular level, although these in vivo activities are complex and many are not well known.
The objective of this study is to evaluate the effect of InsP6, mixtures of InsP6 hydrolysates, and individual lower InsPs (InsP5, InsP4, InsP3, and InsP2) on the crystallization of three compounds that are fundamentally involved in pathological calcifications: calcium oxalate (CaOx), apatitic phosphate (HAP), and brushite (BRU).
2. Materials and Methods
Reagents
The synthetic urine components were obtained from PanReac (Barcelona, Spain). Myo-Inositol-1,2,3,5,6-pentaphosphate (1,2,3,5,6-InsP5), myo Inositol 2,3,5,6-tetraphosphate (2,3,5,6-InsP4), myo Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (1,4,5-InsP3), and myo Inositol 2,4-diphosphate (2,4-InsP2) isomers were purchased from SiChem (Bremen, Germany). Phytic acid sodium salt hydrate was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Schnelldorf, Germany).
Preparation of InsP6 Hydrolysates
A phytate stock solution (2 mM) was prepared from phytic acid sodium salt and adjusted to pH 2 using 0.5 M HCl. Duplicate aliquots (5 mL) were kept in a dry bath at 97 °C for 6, 9, 16, 24, 48, or 72 h to allow hydrolysis.
Crystallization Experiments
The effects of phytate and a mixture of its hydrolysis products on the crystallization of CaOx, HAP, and BRU in synthetic urine were assessed using a kinetic turbidimetric system, as previously described [
16]. This system consisted of a spectrometer equipped with a fiber-optic light-guide measuring cell (AvaSpec-ULS2048CL-EVO, Avantes, Netherlands). Crystallization was assessed at a constant temperature (37 °C) with magnetic stirring (300 rpm). Turbidity was used as an indicator of the induction time of CaOx, BRU, and HAP crystallization, and a longer time indicated greater inhibition of crystallization.
The synthetic urine solution was prepared by making a fresh mixture of equal volumes of solution A and solution B (
Table 1), followed by sonication. The pH of this solution was adjusted to 6.0 for CaOx experiments, 6.5 for BRU experiments, and 7.0 for HAP experiments.
For the CaOx experiments, 200 mL of synthetic urine at pH 6 were transferred into a crystallization flask, and 0.2 mL of InsPs stock solution or a hydrolyzed mixture was added. When the resulting solution reached a temperature of 37 °C, 2 mL of a sodium oxalate stock solution (5 g/L) was added to induce CaOx crystallization.
For the BRU and HAP experiments, 100 mL of synthetic urine solution A at pH 6.5 or 7.5 respectively, was transferred into a crystallization flask, and 0.2 mL of InsPs stock solution or a hydrolyzed mixture was added. When the resulting solution reached a temperature of 37 °C, 100 mL of synthetic urine solution B at 37 °C and pH 6.5 or 7.5 respectively was added to induce crystallization.
Scanning Electron Microscopy
The morphological and structural characteristics of the CaOx, BRU, and HAP crystals that formed in synthetic urine in the absence or presence of different InsPs were examined using a scanning electron microscopy system (SEM, Hitachi S-3400N, Tokyo, Japan) that was coupled with XR energy dispersive microanalysis (Bruker AXS XFlash Detector 4010, Berlin, Germany).
3. Results
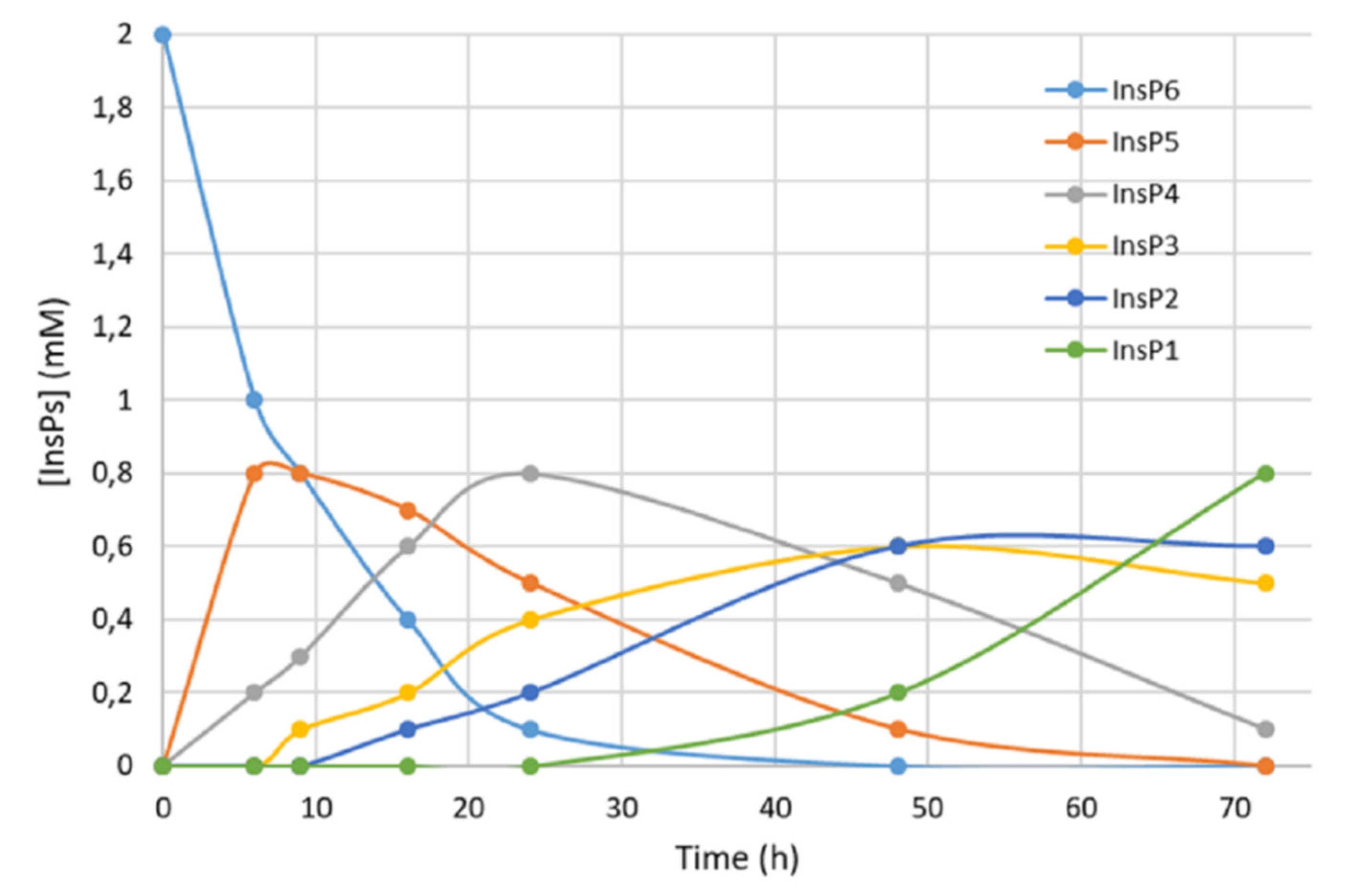
We first recorded the evolution of hydrolysates (dephosphorylation products) of InsP6 during thermal hydrolysis in a dry bath at pH 2.0 and 97 °C (
Figure 1). The InsP6 level decreased by about 50% and the InsP5 level reached its maximum at about 6 h; InsP4 reached a maximum at about 24 h; and InsP3 and InsP2 reached their maxima at about 48 h. These results coincide with those obtained in previous studies by us [
16] and other authors [
17].
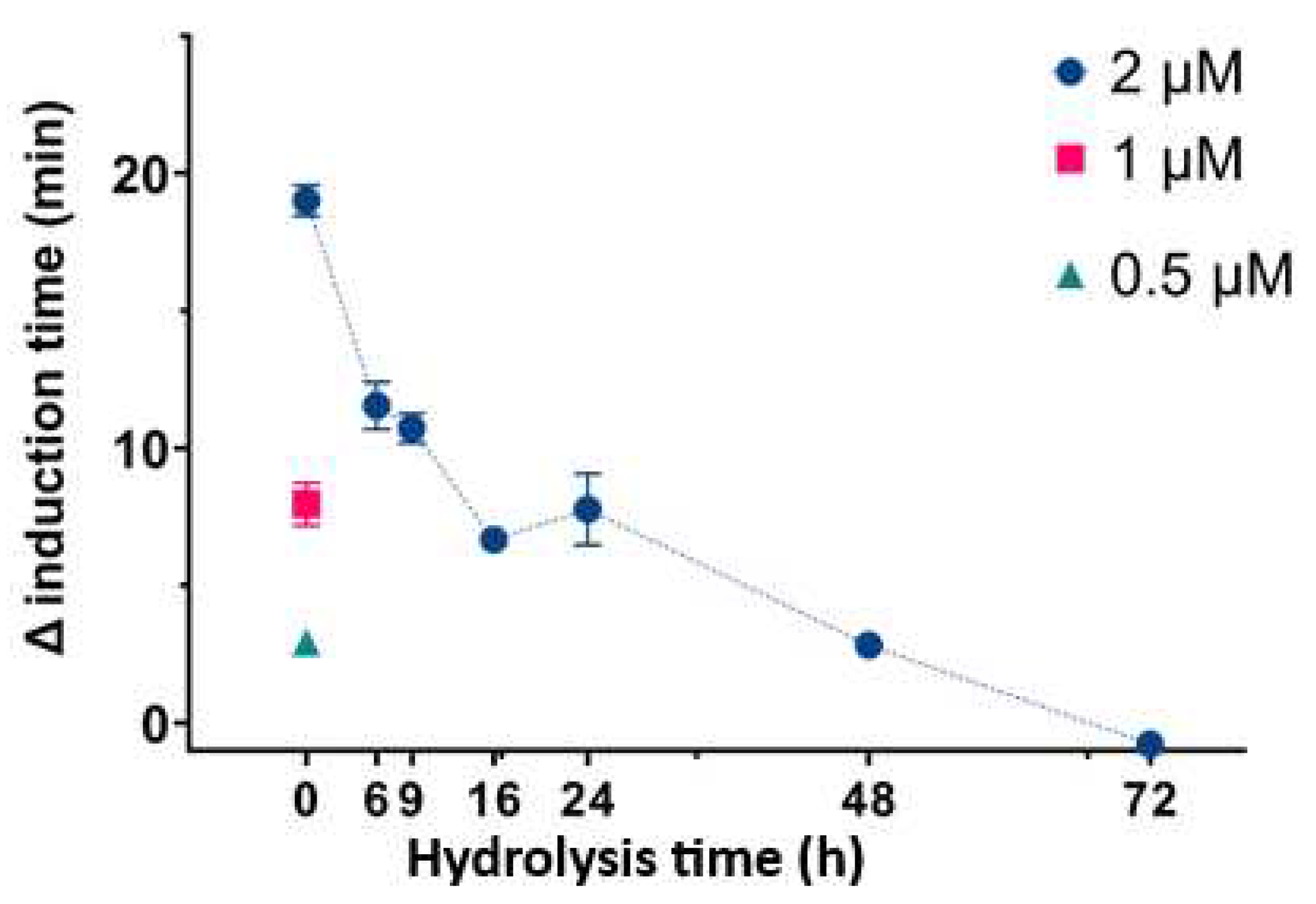
We then determined the effect of InsP6 and different mixtures of its hydrolysates on the time needed for CaOx crystallization in artificial urine at pH 6.0 and 37 °C (
Figure 2). In this experiment, InsP6 alone (0.5 µM, 1.0 µM, or 2.0 µM) or different mixtures of InsP6 hydrolysates that formed after hydrolysis of 2 µM InsP6 for 6 to 72 h were added, and the time needed for induction of CaOx crystallization was recorded. InsP6 had the strongest effect, and the hydrolysate mixtures collected from 6 h to 72 h had progressively weaker effects. These results are similar to those in previous studies under different conditions [
16]. The previous studies demonstrated that although InsP6 had the strongest inhibitory effect (it was also at the highest concentration), a mixture of InsP4 and InsP5 also had significant inhibitory effects.
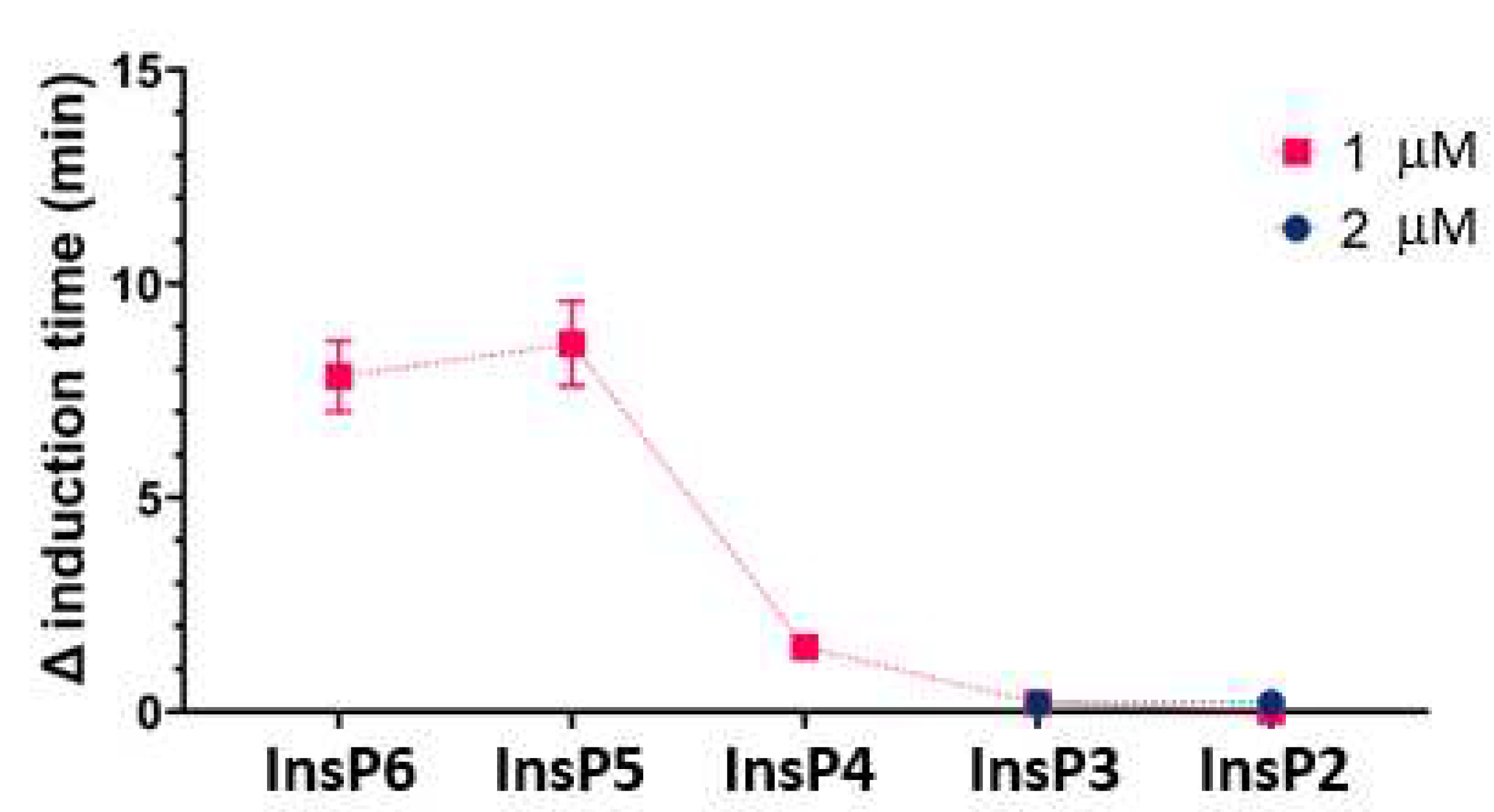
We then compared the effects of different specific InsPs on the time needed for CaOx crystallization (
Figure 3). The results showed that InsP6 and 1,2,3,5,6-InsP5 had similar inhibitory effects, and this effect was greater than that of 2,3,5,6-InsP4, 1,4,5-InsP3, and 2,4-InsP2.
We also compared the effect of four different bisphosphonates (2 µM) on the time needed for induction of CaOx crystals (
Table 2, top left). Under the conditions studied, these bisphosphonates had much weaker inhibitory effects (0.6 to 1 min) than InsP6 and its hydrolysates (up to 18 min).
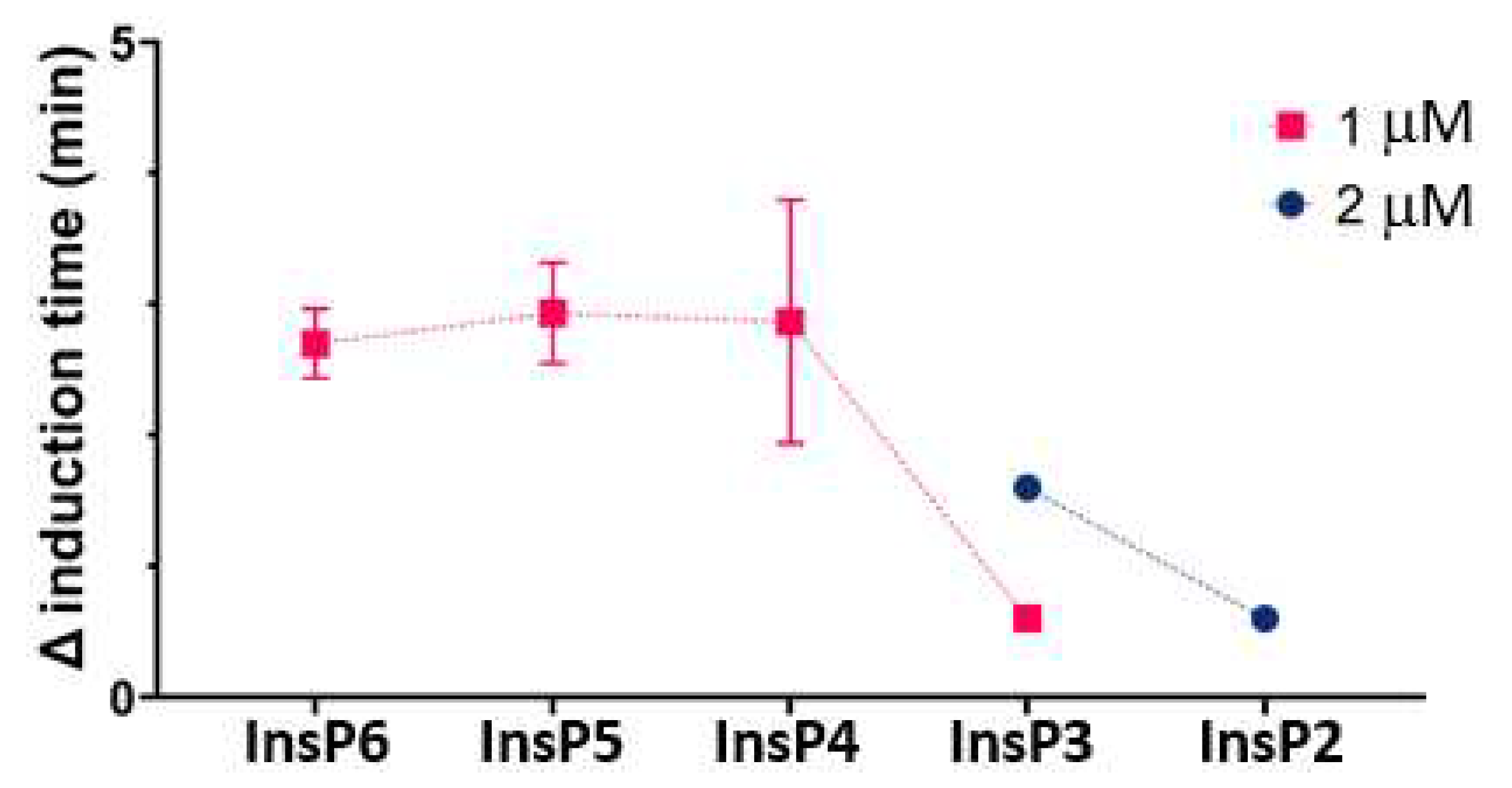
We used the same basic procedures to determine the effect of different InsPs on the formation of BRU crystals in artificial urine at pH 6.5 and 37 °C. The results showed that the InsP6 hydrolysates collected at 16 h and 24 h (which were abundant in InsP4 and Insp5) had much stronger inhibitory effects than InsP6 alone (
Figure 4). However, examination of individual InsPs showed that Insp6, 1,2,3,5,6-InsP5, and 2,3,5,6-InsP4 each had about the same inhibitory effects, and 1,4,5-InsP3 and 2,4-InsP2 had weaker effects (
Figure 5).
We then examined the effects of four different bisphosphonates (2 µM) on the inhibition of BRU crystallization relative to 2 µM phytate alone (
Figure 6). Alendronate had the greatest inhibition, and pamidronate, etidronate, and ibandronate had weaker effects. The effect of ibandronate was similar to that of phytate.
We also determined the effects of four different bisphosphonates and InsP6 and its hydrolysates on the induction of HAP crystallization (
Table 2, right). These results showed that ibandronate had a remarkable inhibitory effect, followed by alendronate and pamidronate. Moreover, InsP6 and its hydrolysates had very weak inhibitory effects under the tested conditions, and the most effective hydrolysates were those collected at 16 h and 48 h (predominantly the lower InsPs).
We performed electron microscopy to confirm the inhibitory effects of the different treatments. The results showed that calcium oxalate crystallized as a CaOx trihydrate in the absence of inhibitors (control), and as a CaOx monohydrate-dihydrate mixture in the presence of InsP5, InsP6, and InsP6 hydrolysates that were collected at 6 h (
Figure 7). The InsP6 hydrolysates that were collected at 16 h and 24 h, InsP5 alone, and InsP4 alone inhibited the formation of BRU crystals, and also altered the morphology and size of these crystals (
Figure 8).
4. Discussion
The present study extended our previous findings [
16] by examining the effect of InsP6 alone, hydrolysates of InsP6, and individual InsPs on the crystallization of CaOx, Bru, and HAP. Our results indicated that the lower InsPs (InsP3 and InsP2) and bisphosphonates had weak effects on CaOx crystallization. However, it must be considered that this inhibition depends on InsP concentration. As shown in previous studies [
10,
18], these lower InsPs are the most abundant InsPs in blood and urine. Because of their higher concentrations, these lower InsPs could have major inhibitory effects in vivo. Our examination of InsP6 hydrolysates suggested that InsP4 inhibited CaOx crystallization, but the effect of the pure 2,3,5,6-InsP4 isomer was less than expected. This might be because 2,3,5,6-InsP4 is a weaker inhibitor than the InsP4 isomers that are present in the hydrolysate mixture. Alternatively, it is possible that there are synergistic effects in the mixture of InsP hydrolysates. As noted above, the plasma and urinary levels of InsP4, InsP3, and InsP2 are also much higher than those of InsP6 and InsP5 [
10,
18], and the inhibition of crystallization is related to concentration.
Our examination of BRU crystallization showed that the 16 h and 24 h hydrolysates (which were enriched with InsP5 and InsP4) had the strongest effects. Nevertheless, our examination of individual InsPs showed that InsP6, InsP5, and InsP4 had similar effects. As above, these results can be explained by synergistic effects of the multiple InsPs or different InsPs isomers in the hydrolysate.
Interestingly, we found that InsP6 and its hydrolysates had little effect on the crystallization of HAP, and that bisphosphonates (except ibandronate) also had little effect. In contrast, studies with experimental animals and humans showed that the intake of InsP6 significantly reduced HAP calcification [
19,
20,
21]. This may be because the mechanism responsible for formation of HAP deposits is completely different from the mechanism responsible for the formation of CaOx and BRU crystals. In particular, the formation a HAP crystal begins with the formation of discrete ion clusters consisting of about 10 to 15 calcium and phosphate ions. These clusters are grouped into larger units (nanoparticles) that form HAP deposits in the presence of appropriate substrates [
22,
23,
24]. For example, calciproteins seem to play an important role in the development of cardiovascular calcifications [
25,
26]. More precisely, inorganic pyrophosphate (an analogue of bisphosphonates) hinders the nucleation and crystallization of amorphous calcium phosphate and inhibits the growth and maturation of HAP crystals [
27]. Therefore, pyrophosphate and polyphosphates affect the evolution of calciprotein particles in vivo, in that they can prevent or inhibit calcification. Obviously, because the formation of HAP crystals is strongly dependent on the presence of other compounds, the inhibitory effects we observed in vitro are likely to be very different from those in vivo.
Our results suggest that the effects of InsP6 on experimental animals and humans on crystallization are a consequence of the mixture of the different InsPs. These mixtures of hydrolysates can form in the intestine prior to paracellular absorption (despite the absence of phytases in the human intestine) because certain foods contain phytases. Once in the blood, phytases/phosphatases produced by humans and experimental animals can give rise to lower InsPs. Obviously, we did not demonstrate whether the in vivo effects are due to the presence of certain isomers, differences in the concentrations of different InsPs, or interactions among different InsPs. To answer these questions, it is necessary to use analytical methods that can determine all these different InsP isomers in biological fluids and appropriate InsPs standards must be available. At present, most of these standards are not available, and currently available analytical methods do not allow the precise determination of different InsPs isomers.
Finally, it is necessary to consider that in addition to the direct interference of crystallization by the different InsPs examined here, many other in vivo molecules and interactions can also affect crystallization. For example, previous research reported that InsPs can inhibit osteoclastogenesis and mineralization of osteoblasts [
28]. Another recent study showed that the intake of InsP6 by menopausal women with hypercalciuria significantly decreased the elimination of urinary calcium [
29]. In this later case, phytate reduces calcium elimination and thereby decreases the concentration of free calcium salts in the urine, in addition to functioning as a crystallization inhibitor.
The major limitations of this study are that we did not determine the specific InsPs isomers that formed during the thermal hydrolysis of InsP6, and we did not test the effect of these different isomers. This is simply because these isomers are not readily available or are extremely expensive.
5. Conclusions
Although the lower InsPs appear responsible for inhibition of the crystallization of calcium salts in vivo, our in vitro studies showed that the higher InsPs (InsP6 and InsP5) were most effective in inhibiting CaOx crystallization and InsP5 and InsP4 were most effective in inhibiting BRU crystallization. For the specific in vitro experimental conditions of the present study, the InsPs had very weak effects on HAP crystallization. HAP deposits seem to form by a mechanism totally different to the formation of well-defined crystals, and depends on the conditions of each case. The in vitro conditions that we examined do not correspond exactly to the in vivo conditions in which HAP deposits are usually formed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C.-B. and F.G.; methodology, A.C.-B. and F.G.; formal analysis, P.C.; investigation, P.C.; writing—original draft preparation, P.C., A.C.-B. and F.G.; writing—review and editing, A.C.-B. and F.G.; supervision, A.C.-B. and F.G.; funding acquisition, A.C.-B. and F.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.”
Funding
Grant PID2019-104331RB-I00 funded by the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Agencia Estatal de Investigación, MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033. P. Calvó is grateful to the Conselleria d'Educació, Universitat i Recerca of the Government of the Balearic Islands for a fellowship (FPI_003_2020).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Schlemmer, U.; Frølich, W.; Prieto, R.M.; Grases, F. Phytate in Foods and Significance for Humans: Food Sources, Intake, Processing, Bioavailability, Protective Role and Analysis. Mol Nutr Food Res 2009, 53, S330–S375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellanby, E. The Rickets-producing and Anti-calcifying Action of Phytate. J Physiol 1949, 109, 488–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, E.; Empson, K.L.; Eaton, J.W. Phytic Acid. A Natural Antioxidant. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1987, 262, 11647–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grases, F.; Costa-Bauza, A. Key Aspects of Myo-Inositol Hexaphosphate (Phytate) and Pathological Calcifications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-González, Á.A.; Grases, F.; Monroy, N.; Marí, B.; Vicente-Herrero, M.T.; Tur, F.; Perelló, J. Protective Effect of Myo-Inositol Hexaphosphate (Phytate) on Bone Mass Loss in Postmenopausal Women. Eur J Nutr 2013, 52, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucenik, I.; Shamsuddin, A.M. Protection against Cancer by Dietary IP6 and Inositol. Nutr Cancer 2006, 55, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsuddin, A.M. Inositol Phosphates Have Novel Anticancer Function. Journal of Nutrition 1995, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, H.J.; Chun, H.K.; Cho, S.Y.; Cho, S.M.; Lillehoj, H.S. Dietary Phytic Acid Lowers the Blood Glucose Level in Diabetic KK Mice. Nutrition Research 2006, 26, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis, P.; Rivera, R.; Berga, F.; Fortuny, R.; Adrover, M.; Costa-Bauza, A.; Grases, F.; Masmiquel, L. Phytate Decreases Formation of Advanced Glycation End-Products in Patients with Type II Diabetes: Randomized Crossover Trial. Sci Rep 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Riemer, E.; Schneider, R.; Cabuzu, D.; Bonny, O.; Wagner, C.A.; Qiu, D.; Saiardi, A.; Strauss, A.; Lahaye, T.; et al. The Phytase RipBL1 Enables the Assignment of a Specific Inositol Phosphate Isomer as a Structural Component of Human Kidney Stones. RSC Chem Biol 2023. [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, A.S.; Andersson, H. Effect of Dietary Phytase on the Digestion of Phytate in the Stomach and Small Intestine of Humans. Journal of Nutrition 1988, 118, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapp, C.; Lantzsch, H.J.; Drochner, W. Drochner, W. Hydrolysis of Phytic Acid by Intrinsic Plant and Supplemented Microbial Phytase (Aspergillus Niger) in the Stomach and Small Intestine of Minipigs Fitted with Re-Entrant Cannulas 3. Hydrolysis of Phytic Acid (IP6) and Occurrence of Hydrolysis Products (IP5, IP4, IP3 and IP2). J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 2001, 85, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleisch, H.; Russell, R.G.G.; Straumann, F. Effect of Pyrophosphate on Hydroxyapatite and Its Implications in Calcium Homeostasis. Nature 1966, 212, 901–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.G.; Fleisch, H. Inorganic Pyrophosphate and Pyrophosphatases in Calcification and Calcium Homeostasis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1970, 69, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleisch, H.; Russell, R.G.G. A Review of the Physiological and Pharmacological Effects of Pyrophosphate and Diphosphonates on Bones and Teeth. J Dent Res 1972, 51, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grases, F.; Costa-Bauzá, A.; Calvó, P.; Julià, F.; Dietrich, J.; Gomila, R.M.; Martorell, G.; Sanchis, P. Phytate Dephosphorylation Products Also Act as Potent Inhibitors of Calcium Oxalate Crystallization. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrfeld, J. HPLC Separation and Quantitation of Phytic Acid and Some Inositol Phosphates in Foods: Problems and Solutions. J Agric Food Chem 1994, 42, 2726–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grases, F.; Costa-Bauzá, A.; Berga, F.; Gomila, R.M.; Martorell, G.; Martínez-Cignoni, M.R. Intake of Myo-Inositol Hexaphosphate and Urinary Excretion of Inositol Phosphates in Wistar Rats: Gavage vs. Oral Administration with Sugar. PLoS One 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.C.; Tilden, M.T. Inhibition of Mineralization by Hydrolysates of Phytic Acid. Johns Hopkins Medical Journal 1972, 131, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Grases, F.; Perelló, J.; Prieto, R.M.; Simonet, B.M.; Torres, J.J. Dietary Myo-Inositol Hexaphosphate Prevents Dystrophic Calcifications in Soft Tissues: A Pilot Study in Wistar Rats. Life Sci 2004, 75, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grases, F.; Sanchis, P.; Perello, J.; Isern, B.; Prieto, R.M.; Fernandez-Palomeque, C.; Fiol, M.; Bonnin, O.; Torres, J.J. Phytate (Myo-Inositol Hexakisphosphate) Inhibits Cardiovascular Calcifications in Rats. Frontiers in Bioscience 2006, 11, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onuma, K.; Ito, A. Cluster Growth Model for Hydroxyapatite. Chemistry of Materials 1998, 10, 3346–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, S.H.; Lee, J. Do; Tanaka, J. Nucleation of Hydroxyapatite Crystal through Chemical Interaction with Collagen. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 2000, 83, 2890–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grases, F.; Zelenková, M.; Söhnel, O. Structure and Formation Mechanism of Calcium Phosphate Concretions Formed in Simulated Body Fluid. Urolithiasis 2014, 42, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiss, A.; Eckert, T.; Aretz, A.; Richtering, W.; Van Dorp, W.; Schäfer, C.; Jahnen-Dechent, W. Hierarchical Role of Fetuin-A and Acidic Serum Proteins in the Formation and Stabilization of Calcium Phosphate Particles. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2008, 283, 14815–14825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostom, A.; Pasch, A.; Madsen, T.; Roberts, M.B.; Franceschini, N.; Steubl, D.; Garimella, P.S.; Ix, J.H.; Tuttle, K.R.; Ivanova, A.; et al. Serum Calcification Propensity and Fetuin-A: Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Am J Nephrol 2018, 48, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäck, M.; Aranyi, T.; Cancela, M.L.; Carracedo, M.; Conceição, N.; Leftheriotis, G.; Macrae, V.; Martin, L.; Nitschke, Y.; Pasch, A.; et al. Endogenous Calcification Inhibitors in the Prevention of Vascular Calcification: A Consensus Statement From the COST Action EuroSoftCalcNet. Front Cardiovasc Med 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Mar Arriero, M.; Ramis, J.M.; Perelló, J.; Monjo, M. Inositol Hexakisphosphate Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis on RAW 264.7 Cells and Human Primary Osteoclasts. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimerà, J.; Martínez, A.; Bauza, J.L.; Sanchís, P.; Pieras, E.; Grases, F. Effect of Phytate on Hypercalciuria Secondary to Bone Resorption in Patients with Urinary Stones: Pilot Study. Urolithiasis 2022, 50, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Kinetics of InsP6 hydrolysis in a dry bath at pH 2.0 and 97 °C. Concentrations were estimated from MS/MS measurements and the concentration of inorganic phosphorus [
16], and agree with previously published data [
17].
Figure 1.
Kinetics of InsP6 hydrolysis in a dry bath at pH 2.0 and 97 °C. Concentrations were estimated from MS/MS measurements and the concentration of inorganic phosphorus [
16], and agree with previously published data [
17].
Figure 2.
Effect of InsP6 concentration (hydrolysis time: 0 h) and different mixtures of InsP6 hydrolysates (hydrolysis time of 2 µM InsP6: 6 h to 72 h) on the time for induction of CaOx crystallization. Values are the means and SDs of three experiments.
Figure 2.
Effect of InsP6 concentration (hydrolysis time: 0 h) and different mixtures of InsP6 hydrolysates (hydrolysis time of 2 µM InsP6: 6 h to 72 h) on the time for induction of CaOx crystallization. Values are the means and SDs of three experiments.
Figure 3.
Effect of individual InsPs (InsP6, 1,2,3,5,6-InsP5, 2,3,5,6-InsP4, 1,4,5-InsP3, and 2,4-InsP2 at 1 or 2 µM) on the time for induction of CaOx crystallization. Values are the means and SDs of three experiments.
Figure 3.
Effect of individual InsPs (InsP6, 1,2,3,5,6-InsP5, 2,3,5,6-InsP4, 1,4,5-InsP3, and 2,4-InsP2 at 1 or 2 µM) on the time for induction of CaOx crystallization. Values are the means and SDs of three experiments.
Figure 4.
Effect of InsP6 concentration (hydrolysis time: 0 h) and different mixtures of InsP6 hydrolysates (hydrolysis time of 2 µM InsP6: 6 h to 72 h) on the time for induction of BRU crystallization. Values are the means and SDs of three experiments.
Figure 4.
Effect of InsP6 concentration (hydrolysis time: 0 h) and different mixtures of InsP6 hydrolysates (hydrolysis time of 2 µM InsP6: 6 h to 72 h) on the time for induction of BRU crystallization. Values are the means and SDs of three experiments.
Figure 5.
Effect of individual InsPs (InsP6, 1,2,3,5,6-InsP5, 2,3,5,6-InsP4, 1,4,5-InsP3, and 2,4-InsP2 at 1 or 2 µM) on the time for induction of BRU crystallization. Values the means and SDs of three experiments.
Figure 5.
Effect of individual InsPs (InsP6, 1,2,3,5,6-InsP5, 2,3,5,6-InsP4, 1,4,5-InsP3, and 2,4-InsP2 at 1 or 2 µM) on the time for induction of BRU crystallization. Values the means and SDs of three experiments.
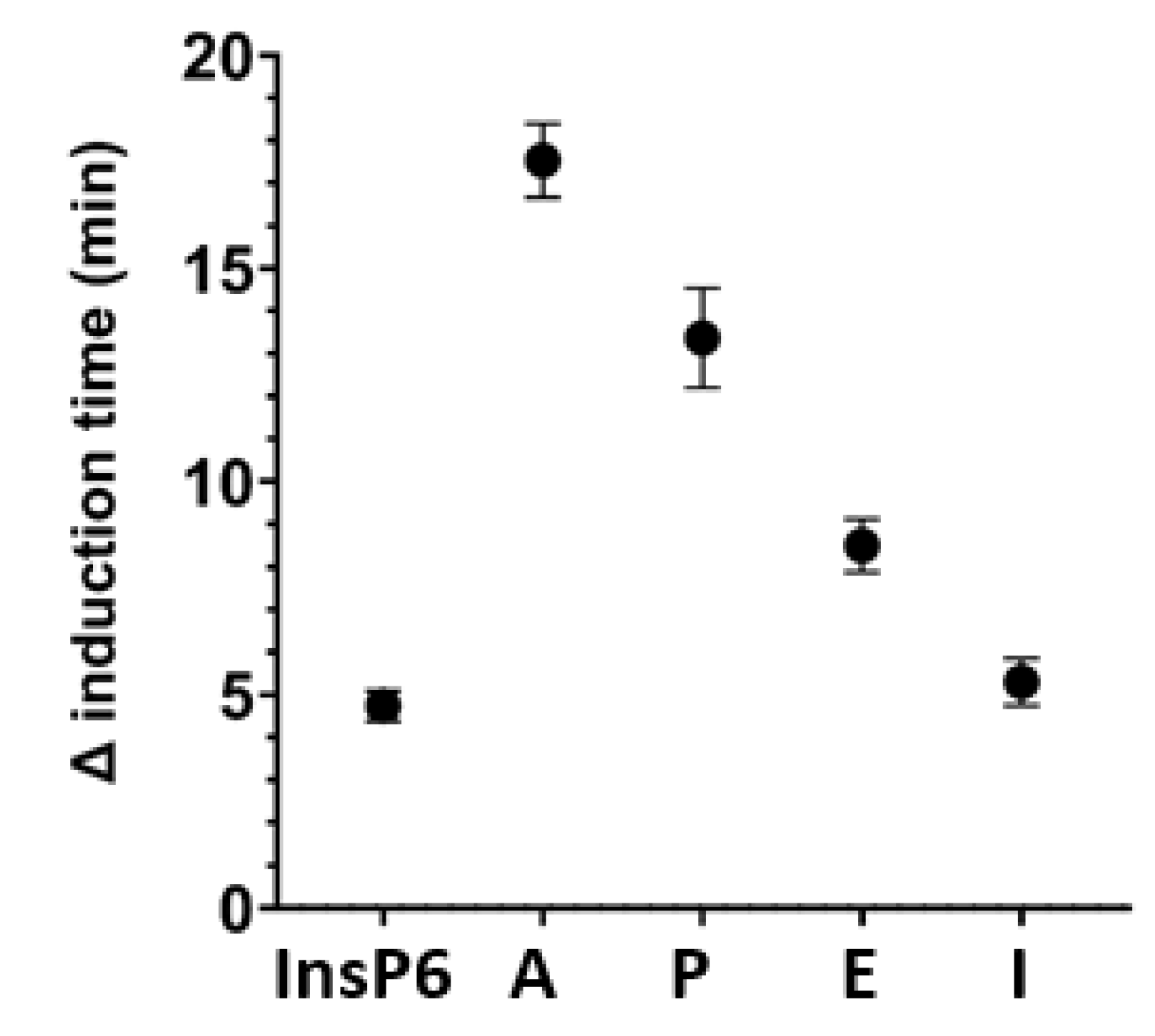
Figure 6.
Effect of InsP6 and different bisphosphonates at a concentration of 2 µM on the time for induction of BRU crystallization. A: Alendronate; P: Pamidronate; E: Etidronate; I: Ibandronate. Values are the means and SDs of three experiments.
Figure 6.
Effect of InsP6 and different bisphosphonates at a concentration of 2 µM on the time for induction of BRU crystallization. A: Alendronate; P: Pamidronate; E: Etidronate; I: Ibandronate. Values are the means and SDs of three experiments.
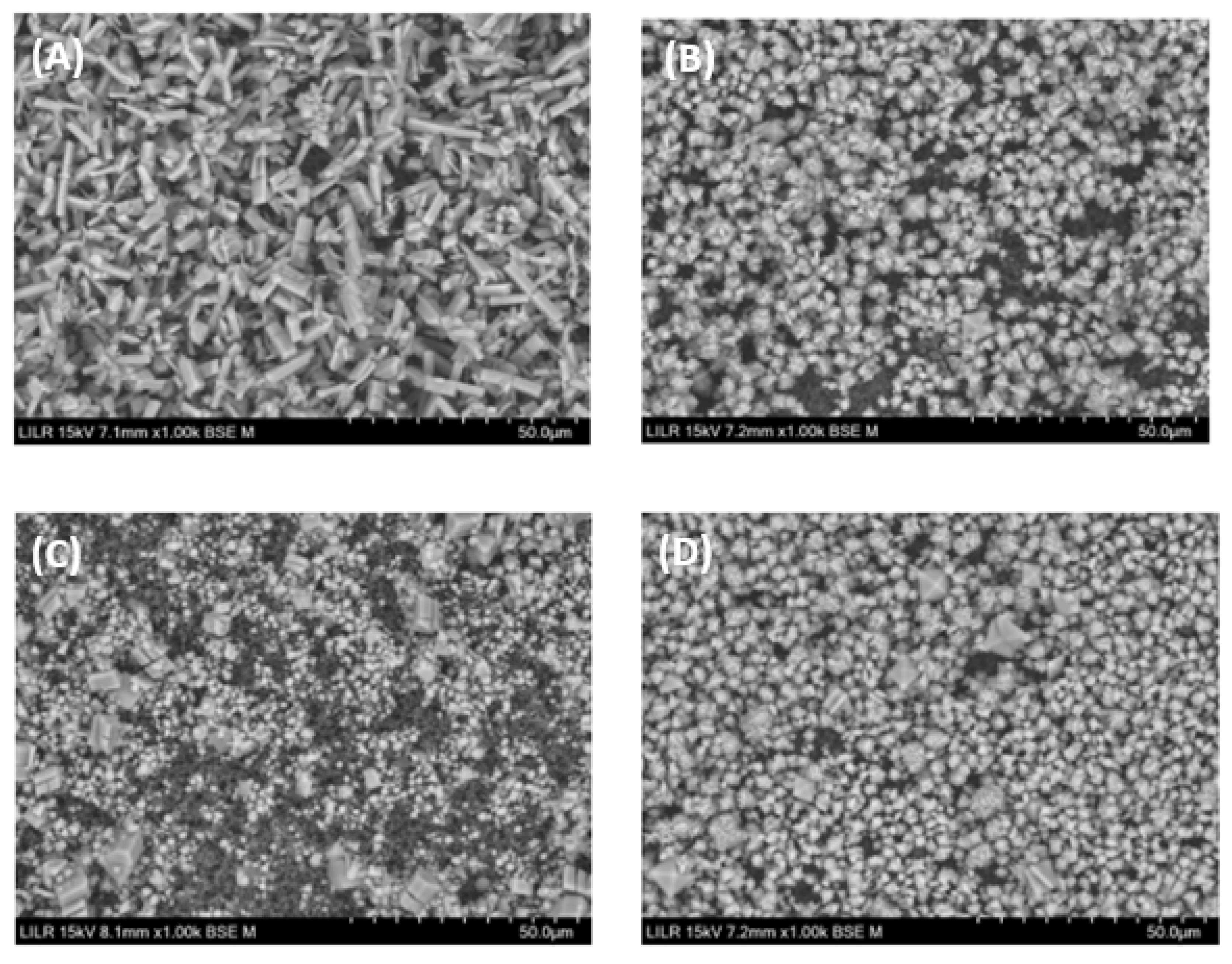
Figure 7.
Scanning electron microscopy of calcium oxalate crystals obtained after completion of the turbidimetric assay with (A) no phytate (control), (B) 2 µM InsP6, (C) 1 µM 1,2,3,5,6-InsP5, or (D) InsP6 (2 µM) hydrolysate after 6 h.
Figure 7.
Scanning electron microscopy of calcium oxalate crystals obtained after completion of the turbidimetric assay with (A) no phytate (control), (B) 2 µM InsP6, (C) 1 µM 1,2,3,5,6-InsP5, or (D) InsP6 (2 µM) hydrolysate after 6 h.
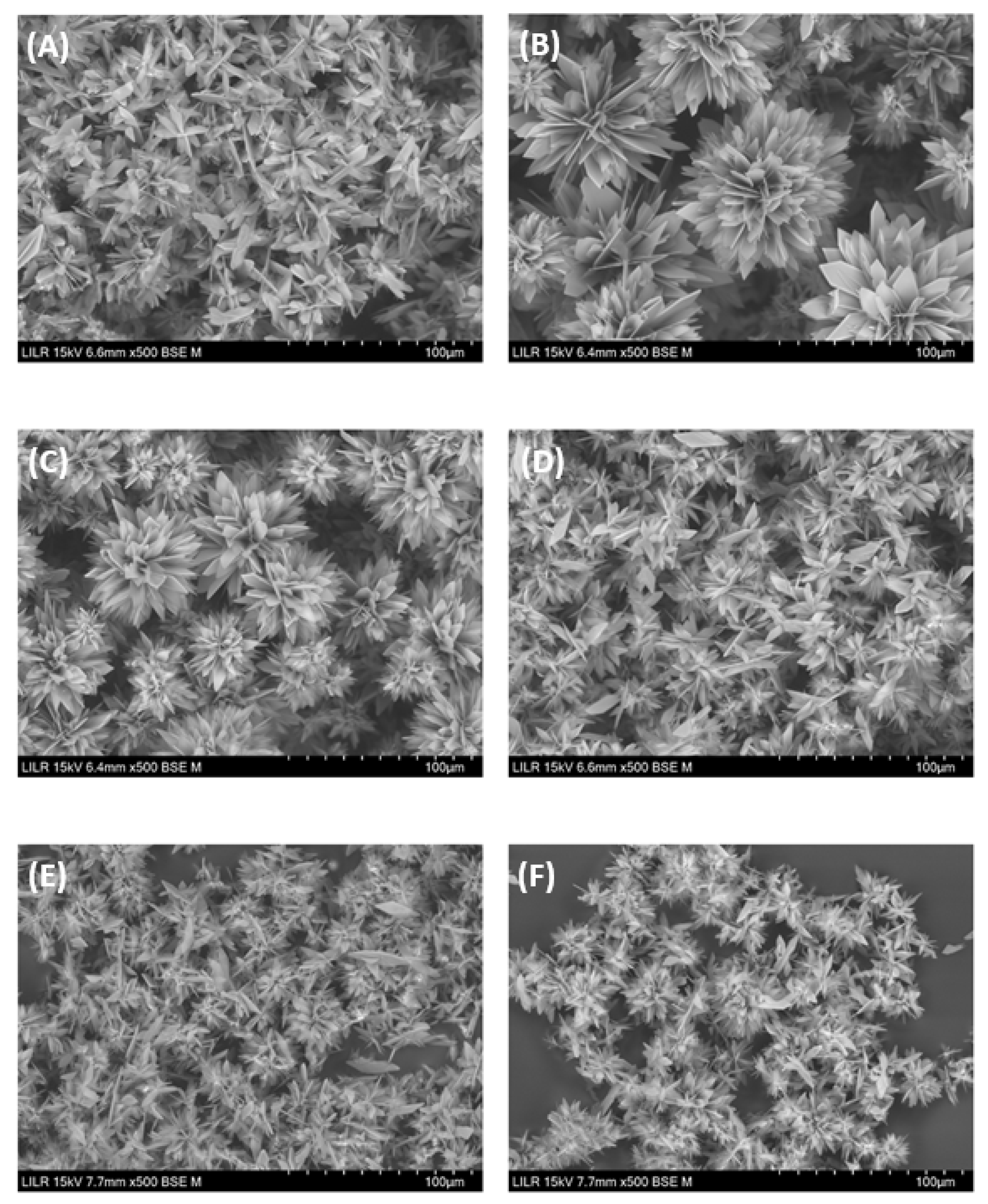
Figure 8.
Scanning electron microscopy of brushite crystals obtained after completion of the turbidimetric assay (A) with no phytate (control), (B) InsP6 (2 µM) hydrolysate after 16 h, (C) InsP6 (2 µM) hydrolysate after 24 h, (D) 2 µM InsP6, (E) 1 µM 1,2,3,5,6-InsP5, or (F) 1 µM 2,3,5,6-InsP4.
Figure 8.
Scanning electron microscopy of brushite crystals obtained after completion of the turbidimetric assay (A) with no phytate (control), (B) InsP6 (2 µM) hydrolysate after 16 h, (C) InsP6 (2 µM) hydrolysate after 24 h, (D) 2 µM InsP6, (E) 1 µM 1,2,3,5,6-InsP5, or (F) 1 µM 2,3,5,6-InsP4.
Table 1.
Composition of synthetic urine.
Table 1.
Composition of synthetic urine.
| Solution A |
|
Solution B |
|
| Na2SO4.10H2O |
6.23 g/L |
NaH2PO4.2H2O |
2.41 g/L for CaOx and HAP 4.06 g/L for BRU |
| MgSO4.7H2O |
1.46 g/L |
Na2HPO4.12H2O |
5.6 g/L for CaOx and HAP
9.31 g/L for BRU |
| NH4Cl |
4.64 g/L |
NaCl |
13.05 g/L |
| KCl |
12.13 g/L |
|
|
| CaCl2
|
5 mM for CaOx
4.25 mM for BRU
3 mM for HAP |
|
|
Table 2.
Effect of different bisphosphonates (top) and of phytate and phytate hydrolysis products (bottom) on the time needed for CaOx crystallization and HAP crystallization. All values are the means of three experiments.
Table 2.
Effect of different bisphosphonates (top) and of phytate and phytate hydrolysis products (bottom) on the time needed for CaOx crystallization and HAP crystallization. All values are the means of three experiments.
| |
Δti (min) |
| |
CaOx |
HAP |
| BISPHOSPHONATES |
| Alendronate (2 µM) |
1 |
6.95 |
| Pamidronate (2 µM) |
1 |
4.10 |
| Ibandronate (2 µM) |
1 |
13.67 |
| Etidronate (2 µM) |
0.6 |
|
| PHYTATE AND HYDROLYSIS PRODUCTS |
| Phytate (2 µM), nonhydrolyzed |
|
0 |
| Phytate (2 µM), 6 h hydrolysis |
|
0 |
| Phytate (2 µM), 9 h hydrolysis |
|
0.7 |
| Phytate (2 µM), 16 h hydrolysis |
|
1.28 |
| Phytate (2 µM), 24 h hydrolysis |
|
1.9 |
| Phytate (2 µM), 48 h hydrolysis |
|
1.88 |
| Phytate (2 µM), 72 h hydrolysis |
|
0.1 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).