Submitted:
28 April 2023
Posted:
03 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
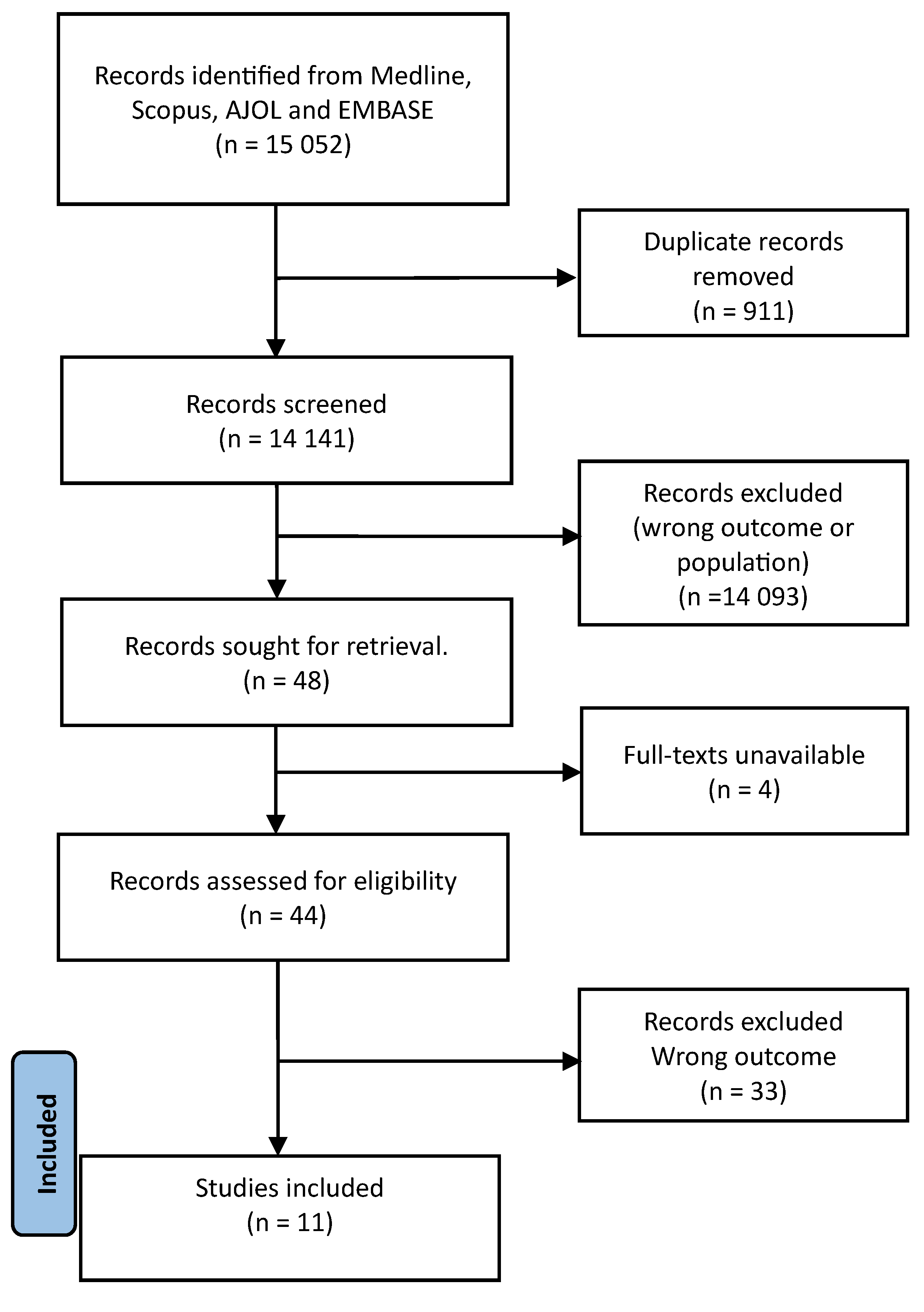
2. Methods
3. Body of the review
3.1. Incidence and prevalence of viral-attributable acute liver failure
3.2. Pathogenicity of viral-attributable acute liver failure
3.2.1. Etiologic agents
3.2.2. Pathogenesis
3.3. Features and diagnosis of viral-attributable acute liver failure
3.4. Treatment of viral-attributable acute liver failure
3.4.1. Medical treatment
3.4.2. Liver transplantation
3.4.3. Artificial and bioartificial liver support systems
3.5. Outcomes
3.6. Comorbidities
3.7. Closing remarks and outlook
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polson J, Lee WM, American Association for the Study of Liver Disease. AASLD position paper: the management of acute liver failure. Hepatol Baltim Md. 2005;41(5):1179–97. [CrossRef]
- Wlodzimirow KA, Eslami S, Abu-Hanna A, Nieuwoudt M, Chamuleau RAFM. Systematic review: acute liver failure – one disease, more than 40 definitions. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Jun;35(11):1245-56.
- Squires RH, Shneider BL, Bucuvalas J, Alonso E, Sokol RJ, Narkewicz MR, et al. Acute Liver Failure in Children: The First 348 Patients in The Pediatric Acute Liver Failure Study Group. J Pediatr. 2006;148(5):652–8. [CrossRef]
- Squires JE, Alonso EM, Ibrahim SH, Kasper V, Kehar M, Martinez M, et al. North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Position Paper on the Diagnosis and Management of Pediatric Acute Liver Failure. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2022;74(1):138-158. [CrossRef]
- Mudawi HMY, Yousif A. Fulminant hepatic failure in an African setting: etiology, clinical course, and predictors of mortality. Dig Dis Sci. 2007;52(11):3266-9.
- Wendon J, Cordoba J, Dhawan A, Larsen FS, Manns M, Nevens F, Samuel D, Simpson KJ, Yaron I, Bernardi M. EASL Clinical practical guidelines on the management of acute (fulminant) liver failure. J Hepatol. 2017;66:1047–1081. [CrossRef]
- Stravittz RT, Lee WM. Acute liver failure. Lancet 2019; 394: 869–81.
- Patterson J, Hussey HS, Silal S, Goddard L, Setshedi M, Spearman W, et al. Systematic review of the global epidemiology of viral-induced acute liver failure. BMJ Open. 2020;10(7):e037473. [CrossRef]
- Bihari C, Rastogi A, Saxena P, Rangegowda D, Chowdhury A, Gupta N, et al. Parvovirus B19 Associated Hepatitis. Hepat Res Treat. 2013;2013:472027. [CrossRef]
- Rabaan AA, Bakhrebah MA, Nassar MS, Natto ZS, Al Mutair A, Alhumaid S, et al. Suspected Adenovirus Causing an Emerging hepatitis among Children below 10 Years: A Review. Pathogens. 2022;11(7):712. [CrossRef]
- Jindal A, Sarin SK. Epidemiology of liver failure in Asia-Pacific region. Liver Int. 2022;42(9):2093-2109. [CrossRef]
- Diaz LA, Ayares G, Arnold J, Idalsoaga F, Corsi O, Arrese M, et al. Liver Diseases in Latin America: Current Status, Unmet Needs, and Opportunities for Improvement. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2022; 20(3): 261–278. [CrossRef]
- Lanini S, Pisapia R, Capobianchi MR, Ippolito G. Global epidemiology of viral hepatitis and national needs for complete control. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2018;16(8):625-639. [CrossRef]
- Stockdale AJ, Kreuels B, Henrion MYR, Giorgi E, Kyomuhangi I, de Martel C, et al. The global prevalence of hepatitis D virus infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2020;73(3):523-532. [CrossRef]
- Zeng D-Y, Li J-M, Lin S, Dong X, You J, Xing Q-Q, et al. Global burden of acute viral hepatitis and its association with socioeconomic development status, 1990–2019. J Hepatol. 2021;75(3):547-556. [CrossRef]
- GBD 2019 Hepatitis Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of hepatitis B, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7: 796-829.
- The Polaris Observatory HCV collaborators. Global change in hepatitis C virus prevalence and cascade of care between 2015 and 2020: a modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022; 7: 396–415.
- Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Blackmore H, Kitas GD. Writing a narrative biomedical review: considerations for authors, peer reviewers, and editors. Rheumatol Int. 2011;31(11):1409-17. [CrossRef]
- Sanders DA. How to write (and how not to write) a scientific review article. Clin Biochem. 2020;81:65-68. [CrossRef]
- United Nations Statistics Division. USA, New York. 2020 https://unstats.un.org/unsd/methodology/m49/. Accessed 23 April 2023.
- Abu-Zidan FM, Hefny AF. Clinical “case series”: a concept analysis. Afr Health Sci. 2012; 12(4): 557–562.
- Mackenjee MK, Kiepiela P, Cooper R, Coovadia HM. Clinically important immunological processes in acute and fulminant hepatitis, mainly due to hepatitis B virus. Arch Dis Child. 1982;57(4):277-82. [CrossRef]
- Coursaget P, Buisson Y, N’Gawara MN, van Cyuk-Gandre H, Roue R. Role of hepatitis E virus in sporadic cases of acute and fulminant hepatitis in an endemic area (Chad). Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1998;58(3):330-4. [CrossRef]
- Solomons RS, Rabi H, Nel E, Cotton M. An overview of Hepatitis A at Tygerberg Children’s Hospital.SA Journal of Child Health. 2008;2 (2): 43-45.
- Goumba AI, Konamna X, Komas NP. Clinical and epidemiological aspects of a hepatitis E outbreak in Bangui, Central African Republic. BMC Infect Dis. 2011;11:93. [CrossRef]
- Rayis DA, Jumaa AM, Gasim GI, Karsany MS, Adam I. An outbreak of hepatitis E and high maternal mortality at Port Sudan, Eastern Sudan. Pathog Glob Health. 2013; 107(2): 66–68. [CrossRef]
- Bruckmann EK, Beretta M, Demepolous D, Brannigan L, Bouter C, Maher H, et al. Minding the gap-Providing quality transplant care for South African children with acute liver failure. Pediatr Transplant. 2020;24(8):e13827. [CrossRef]
- Keles E, Hassan-Kadle MA, Osman MM, Eker HH, Abuzoglu Z, Baydili KN, et al. Clinical characteristics of acute liver failure associated with hepatitis A infection in children in Mogadishu, Somalia: a hospital-based retrospective study. BMC Infect Dis. 2021;21(1):890. [CrossRef]
- Heemelaar S, Hangula AL, Chipeio ML, Josef M, Stekellenburg J, van den Hacker TH, et al. Maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancies complicated by acute hepatitis E and the impact of HIV status: A cross-sectional study in Namibia. Liver Int. 2022;42(1):50-58. [CrossRef]
- Patterson J, Cleary S, Silal SP, Hussey GD, Enoch A, Korsman S, et al. A retrospective study assessing the clinical outcomes and costs of acute hepatitis A in Cape Town, South Africa. BMC Infect Dis. 2022;22(1):45. [CrossRef]
- Walabh P, Meyer A, de Maayer T, Moshesh PN, Hassan IE, Walabh P, et al. Prognostic factors and scoring systems associated with outcome in pediatric acute liver failure. BMC Pediatr. 2022;22(1):516.
- Dong V, Nanchal R, Karvellas CJ. Pathophysiology of Acute Liver Failure. Nutr Clin Pract. 2020;35(1):24-29. [CrossRef]
- Thorgersen EB, Barratt-Due A, Haugaa H, Harboe M, Pischke SE, Nilsson PH, et al. The Role of Complement in Liver Injury, Regeneration, and Transplantation. Hepatology. 2019;70(2):725-736. [CrossRef]
- Hepatology. 2019;70(2):725-736.Chuan Y-C, Tsai K-N, Ou JHJ. Pathogenicity and virulence of Hepatitis B virus. Virulence. 2022;13(1):258-296.
- Lercher A, Popa AM, Viczenczova C, Kosack L, Klavins K, Agerer B, et al. Hepatocyte-intrinsic type I interferon signaling reprograms metabolism and reveals a novel compensatory mechanism of the tryptophan-kynurenine pathway in viral hepatitis. PLoS Pathog. 2020;16(10):e1008973. [CrossRef]
- Merle NS, Church SE, Fremaux-Bacchi V, Roumenina LT. Complement System Part I - Molecular Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Front Immunol. 2015;6:262.
- Shibabaw T, Molla MD, Teferi B, Ayelign B. Role of IFN and Complements System: Innate Immunity in SARS-CoV-2. J Inflamm Res. 2020;13:507-518.
- Michalopoulos GK, Bhushan B. Liver regeneration: biological and pathological mechanisms and implications. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 2021;18; 40–55. [CrossRef]
- McNab F, Mayer-Barber K, Sher A, Wack A, O’Garra A. Type I interferons in infectious disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015; 15(2): 87–103. [CrossRef]
- Dronina J, Samukaite-Bubniene U, Ramanavicius A. Advances and insights in the diagnosis of viral infections. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):348. [CrossRef]
- Gourd NM, Nikitas N. Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome. J Intensive Care Med. 2020;35(12):1564-1575.
- Zhao P-Y, Xia Y, Tao Z-B, Li S-Y, Mao Z, Yang X-P, et al. Global Research Status of Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome During 2001-2021: A 20-Year Bibliometric Analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:814381. [CrossRef]
- Netea MG, Balkwill F, Chondol M, Cominelli F, Donath MY, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, et al. A guiding map for inflammation. Nature Immunology. 2017; 18: 826–831. [CrossRef]
- Movafagh A, Heydary H, Mortazavi-Tabatabaei SA, Azargashb E. The Significance Application of Indigenous Phytohemagglutinin (PHA) Mitogen on Metaphase and Cell Culture Procedure. Iran J Pharm Res. 2011; 10(4): 895–903.
- Demas GE, Zysling DA, Beechler BR, . Muehlenbein MP, French SS. Beyond phytohaemagglutinin: assessing vertebrate immune function across ecological contexts. Journal of Animal Ecology 2011, 80, 710–730.
- Purohit V, Wagner A, Yosef N, Kuchroo VK. Systems-based approaches to study immunometabolism. Cellular & Molecular Immunology. 2022;19:409–420. [CrossRef]
- Lercher A, Baazim H, Bergthaler A. Systemic Immunometabolism: Challenges and Opportunities. Immunity. 2020;53(3):496-509. [CrossRef]
- Trefts E, Gannon M, Wassermann DH. The liver. Curr Biol. 2017; 27(21): R1147–R1151.
- Shah NJ, Royer A, John S. Acute Liver Failure [Internet]. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2023 [cited 2023 Apr 19]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482374/.
- Kujovich JL. Coagulopathy in liver disease: a balancing act. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2015;2015:243-9. [CrossRef]
- Harrison MF. The Misunderstood Coagulopathy of Liver Disease: A Review for the Acute Setting. West J Emerg Med. 2018;19(5):863-871. [CrossRef]
- Trey C, Davidson CS. The management of fulminant hepatic failure. Prog Liver Dis. 1970;3:282-98.
- Sarin SK, Choudhury A, Sharma MK, Maiwall R, Al MAhtab M, Rahman S, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific association for the study of the liver (APASL): an update. Hepatol Int. 2019;13(4):353-390. [CrossRef]
- Lucey MR, Terrault N, Ojo L, Hay JE, Neuberger J, Blumberg E, et al. Long-term management of the successful adult liver transplant: 2012 practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the American Society of Transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2013;19(1):3-26. [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 2016;64(2):433-485.
- Milson C, Considine A, Cramp ME, Holt A, Hubscher S, Hutchinson J, et al. Adult liver transplantation: UK clinical guideline-part 1: pre-operation. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2020;11(5):375-384. [CrossRef]
- Milson C, Considine A, Cramp ME, Holt A, Hubscher S, Hutchinson J, et al. Adult liver transplantation: UK clinical guideline-part 2: surgery and post-operation. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2020;11(5):385-396. [CrossRef]
- Ichai P, Bouchghoul H, Laurent-Bellue A, Sacleux S-C, Boudon M, Cherqui D, et al. Urgent Liver Transplantation for Acute Liver Failure in Pregnant Women: The Optimum Timing for Delivery. Transplantation. 2023;107(1):172-180. [CrossRef]
- Germani G, Theocharidou E, Adam R, Karam V, Wendon J, O’Grady J, Burra P, et al. Liver transplantation for acute liver failure in Europe: outcomes over 20 years from the ELTR database. J Hepatol. 2012;57(2):288-96. [CrossRef]
- Tran LT, Carullo PC, Banh DPT, Vitu C, Davis PJ. Pediatric Liver Transplantation: Then and Now. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia. 2020;34: 2028-2035.
- Kumar R, Anand U, Priyadarshi RN. Liver transplantation in acute liver failure: Dilemmas and challenges. World J Transplant. 2021; 11(6): 187–202. [CrossRef]
- Tsien C, Tan H, Sharma S, Palaniyappan N, Wiyajasiri P, Leung K, et al. Long-term outcomes of liver transplant recipients followed up in non-transplant centres: Care closer to home. Clinical Medicine. 2021; 21 (1): e32–8. [CrossRef]
- Ronca V, Wootton G, Milani C, Cain O. The Immunological Basis of Liver Allograft Rejection. Front Immunol. 2020;11:2155. [CrossRef]
- Lee BT, Fiel MI, Schiano TD. Antibody-mediated rejection of the liver allograft: An update and a clinico-pathological perspective. J Hepatol. 2021;75(5):1203-1216. [CrossRef]
- Jain V, Dhawan A. Prognostic modeling in pediatric acute liver failure. Liver Transpl. 2016;22:1418–30. [CrossRef]
- Global Observatory on Donation and transplantation. International Report on Organ Donation and Transplantation Activities 2021. [Internet]. 2022. https://www.transplant-observatory.org/2021-global-report-5/. Accessed on 21 April 2023.
- Contreras AG, McCormack L, Andraus W, de Souza M Fernandes E, Latin America Liver Transplantation Group. Current status of liver transplantation in Latin America. Int J Surg. 2020;82S:14-21. [CrossRef]
- Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawwan A, Wendon J. Acute liver failure. Lancet. 2010; 376: 190-201.
- Venick RS, Farmer DG, Soto JR, et al. One Thousand pediatric liver transplants during thirty years: Lessons learned. J Am Coll Surg 2018;226: 355–66. [CrossRef]
- Venick RS, Farmer DG, Soto JR, et al. One Thousand pediatric liver transplants during thirty years: Lessons learned. J Am Coll Surg 2018;226: 355–66. [CrossRef]
- O’Grady JG, Alexander GJ, Hayllar KM, Williams R. Early indicators of prognosis in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology. 1989;97(2):439-45. [CrossRef]
- Lewis A, Koukoura A, Tsianos GI, Gargavanis AA, Nielsen AA, Vassiliadis E. Organ donation in the US and Europe: the supply vs demand imbalance. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2021;35(2):100585. [CrossRef]
- Egawa H, Ohdan H, Saito K. Current Status of ABO-incompatible Liver Transplantation. Transplantation. 2023;107(2):313-325. [CrossRef]
- Carpentier B, Gautier A, Legallais C. Artificial and bioartificial liver devices: present and future. Gut 2009;58:1690–1702. [CrossRef]
- Tandon R, Froghi S. Artificial liver support systems. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2021; 36: 1164–1179.
- Saliba F, Banares R, Larsen FS, Wilmer A, Pares A, Mitzner S, et al. Artificial liver support in patients with liver failure: a modified DELPHI consensus of international experts. Intensive Care Med. 2022; 48:1352–1367. [CrossRef]
- Donnelli MC, Hayes PC, Simpson KJ. The Changing Face of Liver Transplantation for Acute Liver Failure: Assessment of Current Status and Implications for Future Practice. Liver Transpl. 2016;22(4):527-35. [CrossRef]
- Mahmud N. Selection for liver transplantation: indications and evaluation. Curr Hepatol Rep. 2020; 19(3): 203–212.
- Montgomery RA, Tatapudi VS, Leffel MS, Zachary AA. HLA in transplantation. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14(9):558-570.
- Bricogne C, Halliday N, Fernando R, Tsochatzis EA, Davidson BR, Harber M, et al. Donor-recipient human leukocyte antigen A mismatching is associated with hepatic artery thrombosis, sepsis, graft loss, and reduced survival after liver transplant. Liver Transpl. 2022;28(8):1306-1320.
- Downs LO, Campbell C, Yonga P, Githinji G, Ansari MA, Matthews PC, et al. A systematic review of Hepatitis B virus (HBV) prevalence and genotypes in Kenya: Data to inform clinical care and health policy. PLOS Glob Public Health. 2023; 3(1): e0001165. [CrossRef]
- Awuah WA, Ng JC, Bulut HI, Nazir A, Tenkorang PO, Yarlagadda R, et al. The unmet need of organ transplantation in Africa. Int J Surg. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Kim JH, Nelson KE, Panzner U, Kasture Y, Labrique AB, Wierzba TF. A systematic review of the epidemiology of hepatitis E virus in Africa. BMC Infectious Diseases. 2014; 14:308. [CrossRef]
- Sonderup MW, Afihene M, Ally R, Apica B, Awuku Y, Cunha L, et al. Hepatitis C in sub-Saharan Africa: the current status and recommendations for achieving elimination by 2030. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;2(12):910-919. [CrossRef]
- Spearman CW, Afihene M, Ally R, Apica B, Awuku Y, Cunha L, et al. Hepatitis B in sub-Saharan Africa: strategies to achieve the 2030 elimination targets. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;2(12):900-909. [CrossRef]
- Patterson J, Abdulahi L, Hussey GD, Muloiwa R, Kagina BM. A systematic review of the epidemiology ofhepatitis A in Africa. BMC Infectious Diseases. 2019; 19:651.
- Sonderup MP, Spearman CW. Global Disparities in Hepatitis B Elimination—A Focuson Africa. Viruses. 2022;14(1):82.
- Bigna JJ, Modiyinji AF, Nansseu JR, Amougou MA, Nola M, Kenmoe S. Burden of hepatitis E virus infection in pregnancy and maternofoetal outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020;20(1):426.
- Spearman CWN, McCulloch MI. Challenges for pediatric transplantation in Africa. Pediatr Transplant. 2014;18(7):668-74.
- Vento S, Cainelli F. Acute liver failure. Lancet. 2020;395(10240):1833.
- Loua A, Feroleto M, Sougou A, Kasilo OMJ, Nikiema JB, Fuller W, et al. A review of policies and programmes for human organ and tissue donations and transplantations, WHO African Region. Bull World Health Oragn. 2020;98(6):420-425. [CrossRef]
- Ulasi I, Ijoma C, Ifebunandu N, et al. Organ donation and transplantation in Sub-Saharan Africa: opportunities and challenges. In: Vassil Mihaylov, editor. Organ Donation and Transplantation 2021. IntechOpen. p. 35.
- World Health Organization (2022). Seventy-fifth World Health Assembly. Provisional agenda item 27.2. Human organ and tissue transplantation. https://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA75/A75_41-en.pdf Accessed on 19 April 2023.
- WHO Africa. Hepatitis Scorecard for the WHO Africa Region Implementing the hepatitis elimination strategy. https://www.afro.who.int/publications/hepatitis-scorecard-who-africa-region-implementing-hepatitis-elimination-strategy. Accessed on 19 April 2023.
- Vento S, Dzudzor B, Cainelli F, Tachi K. Liver cirrhosis in sub-Saharan Africa: neglected, yet important. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6(10):e1060-e1061. [CrossRef]
- WHA57/18. Human organ and tissue transplantation. In: Fifty-seventh WorldHealth Assembly, Geneva, 17–22 May 2004. Resolutions and Decisions. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010. Available from: https://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA57/A57_R18-en.pdf [cited 21 April 2023].
- WHA63/22. Human organ and tissue transplantation. In: Sixty-thirdWorld Health Assembly, Geneva, 17–21 May 2010. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010. Available from: https://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/WHA63/A63_R22-en.pdf?ua=1 [cited 21 April 2023].
- Do HD, Mackie F, McCulloch M, Reding R, IPTA Outreach Committee. International pediatric transplant association (IPTA) guidance on developing and/or expanding pediatric solid organ transplantation programs in low- and middle-income countries. Pediatr Transplant. 2022;e14346. [CrossRef]
- Essouma M, Nkeck JR, Endomba FT, Bigna JJ, Singwe-Ngandeu M, Hachulla E. Systemic lupus erythematosus in Native sub-Saharan Africans: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Autoimmun. 2020;106:102348.
- Essouma M, Noubiap JJ, Singwe-Ngandeu M, Hachulla E. Epidemiology of Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies in Africa: A Contemporary Systematic Review. J Clin Rheumatol. 2022;28(2):e552-e562.
- Cappadona R, De Giorgi A, Di Simone E, Di Muzio M, Di Muzio F, Lamberti N, et al. Infodemiology of solid organ transplantation: relationship to the Global Observatory on Donation and Transplantation data. 2020;24(24):12630-12637. [CrossRef]
- Cappadona R, De Giorgi A, Di Simone E, Di Muzio M, Di Muzio F, Lamberti N, et al. Infodemiology of solid organ transplantation: relationship to the Global Observatory on Donation and Transplantation data. 2020;24(24):12630-12637. [CrossRef]
- Deaton AS. People In Sub-Saharan Africa Rate Their Health And Health Care Among Lowest In World. Health Aff (Millwood). 2015; 34(3): 519–527. [CrossRef]
- Oleffe A, Sako B, Paul E, Mahieu C. Formal and informal medicine retailers in Sub-Saharan Africa: a scoping review of research trends. Int J Pharm Pract. 2022;30(4):315-325. [CrossRef]
- dovor E, Czaika M, Docquier F, Moullan Y. Medical brain drain: How many, where and why? J Health Econ. 2021;76:102409. [CrossRef]
- Neupane R, Taweesedt PT, Anjum H, Surani S. Current state of medical tourism involving liver transplantation-the risk of infections and potential complications. World J Hepatol. 2021;13(7):717-722. [CrossRef]
| Query | Fields | Search term |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | All fields | “acute liver failure” OR “fulminant hepatitis” OR “fulminant hepatic failure” OR “acute hepatic failure” OR “ALF” |
| #2 | All fields | “hepatitis” OR “viral hepatitis” OR “hepatitis A” OR “HAV” OR “hepatitis B” OR “HBV” OR “hepatitis C” OR “HCV” OR “hepatitis D” OR “HDV” OR “hepatitis E” OR “HEV” OR “herpes simplex virus” OR “HSV” OR “Epstein-Barr virus” OR (“herpesvirus 4, human”[MeSH Terms] OR “human herpesvirus 4” OR “ebv” OR “CMV” OR (“cytomegalovirus”[MeSH Terms] OR “cytomegalovirus” OR “cytomegaloviruses” OR (“adenoviridae”[MeSH Terms] OR “adenoviridae” OR “adenovirus” |
| #3 | All fields | “sub-saharan africa” OR “Sub-saharan african” OR “SSA” OR “subsaharan africa” OR “subsaharan african” OR “africa*” OR “Eastern Africa” OR “east african” OR “east africa” OR “Eastern african” OR “British indian ocean territory” OR “burund*” OR (“comoros”[MeSH Terms] OR “comoros” OR “comoro”[All Fields]) OR “djibout*” OR “eritrea*” OR “ethiopia*”[All Fields] OR “French southern territories” OR “kenya* “ OR “madagasca*”OR “malaw*” OR “mauriti*” OR (“comoros”[MeSH Terms] OR “comoros” OR “mayotte”[All Fields]) OR “mozambi*” OR (“reunion”[MeSH Terms] OR “reunion” OR “reunions” OR “rwanda*” OR (“seychelles”[MeSH Terms] OR “seychelles” OR “somalia*” OR “south sudan” OR “south sudanese”OR “uganda*” OR “tanzania*” OR “zambia*” OR “zimbabw*” OR “middle africa” OR “Middle african” OR “angola*” OR “cameroon*” OR “Central african republic” OR (“chad”[MeSH Terms] OR “chad”) OR “congo*” OR “equatorial guinea” OR (“gabon”[MeSH Terms] OR “gabon” OR “sao tome and principe” OR “southern africa” OR “southern african” OR “bostwana” OR (“eswatini”[MeSH Terms] OR “eswatini” OR (“lesotho”[MeSH Terms] OR “lesotho” OR “namibia*” OR “south africa” OR “south african” OR “west african” OR “west africa” OR “western africa” OR “western african” OR (“benin”[MeSH Terms] OR “benin” OR “benin s” OR (“burkina faso”[MeSH Terms] OR (“burkina” AND “faso”OR “burkina faso” OR “cabo verde” OR (“cote d ivoire”[MeSH Terms] OR (“cote” AND “d ivoire” OR “cote d ivoire” OR “ghana*”[All Fields] OR “guinea*” OR (“guinea bissau”[MeSH Terms] OR “guinea bissau” OR (“guinea” AND “bissau” OR “guinea bissau” OR “liberia*” OR “mali*” OR “mauritania*” OR “niger*” OR “Saint helena” OR “senegal*” OR “sierra Leone” OR “togo*” |
| #4 | N/A | #1 AND #2 AND #3 |
| Author, year of publication | Country | Study design | Study period | Timing of data collection | Sampling method | ALF classification criteria | Type of population | Sample size | ALF cases | % Males among ALF cases | Mean/Median age (age range) of ALF cases, years | Viral-attributable ALF (% of ALF cases) |
Causal virus | CFR among subjects with ALF/viral-attributable ALF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mackenjee, 1982 [22] | South Africa | Case-Control | NR | Retrospective | Non-probabilistic | -Jaundice -Encephalopathy -No previous liver disease -Illness of < 8-weeks’ duration |
Pediatric subjects with acute hepatitis and ALF | 46 | 12 | Unclear | NR (3-11) | 8 (66.7) | HBV (n=8) | Unclear/100 |
| Coursaget, 1998 [23] | Chad | Case-Control | 1/1993-12/1993 | Retrospective | Non-probabilistic | -SGOT > 100 U/L - Encephalopathy |
Pediatric subjects, adults, and pregnant women with acute hepatitis and ALF | 127 | 14 | 57 | 29.3 (16-64) | 12 (85.7) | -HEV (n=8) -HBV (n=2) -HCV (n=2) -HBV and HEV (n=1) |
NR |
| Mudawi, 2007 [5] | North Sudan | Cross-sectional | 7/2003-10/2004 | prospective | Non-probabilistic | -Jaundice -Encephalopathy -Encephalopathy occurrence within 12 weeks of the onset of jaundice |
-Adults And pregnant women with ALF |
37 | 37 | 57 | 38 (19-75) | 10 (27) | HBV (n=8) HEV (n=2) |
84/NR |
| Solomons, 2008 [24] | South Africa | Cross-sectional | 1/2001- 8/2004 | Retrospective | Non-probabilistic | -INR >2 non-responsive to vitamin K -Encephalopathy -No previous liver disease -Clinical liver disease of < 8-weeks’ duration |
Pediatric subjects with positive hepatitis A virus IgM serology | 184 | 2 | NR | NR (< 13) | 2 (100) | HAV (n=2) | 100/100 |
| Goumba, 2011 [25] | Central African Republic | Cross-sectional | 6/2004- 9/2005 | prospective | Non-probabilistic | NR* | Pediatric and adult subjects presenting to healthcare facilities in Bangui with gastrointestinal features and fever after the exclusion of malaria, during the 2004 outbreak of hepatitis E | 411 | 5 | NR | NR | 5 (100) | HEV (n=5) | NR/NR |
| Rayis, 2013 [26] | Eastern Sudan | Cross-sectional | 11/2010-3/2011 | Retrospective | Non-probabilistic | NR | Pregnant women with clinical features suggestive of viral hepatitis during an hepatitis E outbreak | 39 | 11 | 0 | NR | 11 (100) | HEV (N=11) | 100/100 |
| Bruckmann, 2020 [27] | South Africa | Cross-sectional | 11/2005-9/2019 | Retrospective | Non-probabilistic | PALFSG criteria | Pediatric subjects undergoing LT for ALF | 27 | 27 | 51.8 | 3.7 (unclear) | 16 (59.3%) | -HAV (n=11) -Enterovirus (n=2) -Adenovirus (n=1) -Parvovirus (n=1) -Epstein Barr Virus (n=1) |
18.5/NR |
| Keles, 2021 [28] | Somalia | Cross-sectional | 6/2019-12/2019 | Retrospective | Non-probabilistic | PALFSG criteria | Pediatric subjects tested for HAV | 219 | 25 | 64 | 6.7 (NR) | 25 (100) | HAV (n=25) | NR/NR |
| Heemelaar, 2021 [29] | Namibia | Cross-sectional | 10/2017-5/2019 | Retrospective | Non-probabilistic | -Acute elevation of serum transaminases -Encephalopathy of any grade -INR>1.5 |
Pregnant women and women within 42 days of the post-partum period, with acute hepatitis E in the context of an outbreak | 70 | 28 | 0 | NR | 28 (100) | HEV (n=28) | 46.4/46.4 |
| Patterson, 2022 [30] | South Africa | Cross-sectional | 1/2008- 3/2018 | Retrospective | Non-probabilistic | 2005 AASLD criteria [1] | Pediatric and adult subjects with hepatitis A | 451 | 5 | NR | NR | 5 (100) | HAV (n=5) | 20/20 |
| Walabh, 2022 [31] | South Africa | Cross-sectional | 1/2015-10/2020 | Retrospective | Non-probabilistic | PALFSG criteria | Pediatric subjects with ALF | 45 | 45 | 53.3 | 3.3 (NR) | 30 (66.7) | -HAV (n=19) -Adenovirus (n=5) -HSV (n=3) -Enterovirus (n=2) -EBV (n=1) |
42/NR |
| Variable | Acute liver failure | Chronic hepatic and non-hepatic conditions | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion of LT procedures | ~10% | ~90% | [55,56,61] | |
| Before surgery | Indication | Virtually all patients * | ESLD§ | [54,55,56,60] |
| Prognostic scoring systems | No consensus for both adults and pediatric subjects: KCC, CV criteria... | -Adult: MELD/MELD-Na, UKELD, -Pediatric subject: PELD |
[6,7,54,55,56,65] | |
| Aim | Lifesaving | Life-prolonging | [56,61] | |
| Recipients’ demographic characteristics | -Adult: typically young females -Pediatric subject: unspecified |
-Adult: no age or gender predilection -Pediatric subject: NR |
[59] | |
| Living donors’ demographic characteristics | Gender: -Females: 52% -Males: 48% |
[66] | ||
| Mean age: 41±16 years in in Europe | Mean age: unspecified | [59] | ||
| Standard type of donor liver | Adults: -Western world: whole cadaveric donor -Global South: whole living donor |
[11,54,55,56,67] | ||
| Pediatric subjects: living split liver transplant (left lateral segment) globally | ||||
| During surgery | Surgical stages | All age groups: -Pre-hepatic: recipient hepatectomy -Anhepatic: implantation of the donor liver -Neohepatic: revascularization |
[60] | |
| After surgery | Standard immunosuppressive drug regimens | Induction -Corticosteroids: Methylprednisolone, Prednisone/prednisolone -T-cell depleting antibody: alemtuzumab, -Anti-interleukin 2 receptor antibody: basiliximab, daclizumab -Rabbit Anti-thymocyte globulin |
[54,55,56,60] |
|
| Maintenance drugs: -Corticosteroids: Methylprednisolone, Prednisone, prednisolone -calcineurin inhibitor: tacrolimus, ciclosporine -Antimetabolites: azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil -mTOR inhibitors: sirolimus, everolimus | ||||
| Specific physiological populations: -Pediatric recipients of ABO-incompatible LT: plasmapheresis, intravenous immunoglobulins, rituximab -Post-partum: TAC, corticosteroids | ||||
| 1-year survival | Adult -Recipient (all-cause LT): > 80%-100% -ALF recipients in Europe: 74% -Graft (all-cause LT): >80%-96% -Graft for ALF recipients in Europe: 63% |
[59,60,68,69,70] | ||
| Pediatric subject: -Recipient (all-cause LT): 86-95% -Graft (all-cause): 73% | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





