1. Introduction
Environmental pollution as a result of the intensification of industrial activities is, by far, one of the most important problems of many countries in the word. Thus, the inadequate disposal of production waste, industrial effluents or gaseous emissions lead to the accumulation of dangerous pollutants in the environment (water, air, soil) causing the degradation of the ecosystems. That is why it is unanimously accepted that treating industrial emissions before they are discharged into the environment is the most effective way to reduce environmental pollution [
1,
2,
3]. This strategy has the widest applicability in the case of liquid effluents (washing water, process water, wastewater, etc.), because: (i) their transport even over short distances is expensive, (ii) their storage is difficult and requires special precautions, and (iii) they can contain a wide variety of pollutants (organic compounds and/or metal ions) in a wide range of concentrations, which can react over time. Thus, for the liquid effluents, various physical, physico-chemical and chemical methods for pollutant removal have been developed, which take into account the nature of pollutants, their concentration and the volume of effluent to be treated [
4,
5,
6]. In the case of industrial effluents containing metal ions, methods such as chemical precipitation, ion exchange, coagulation-flocculation, osmosis, etc. [
6,
7,
8,
9], have proven their applicability on a large scale. All these methods are successfully applied to reduce the content of metal ions in industrial effluents, and the main criterion for selecting a specific method is their removal efficiency [
10]. This is because, it is well known that most metal ions have a high toxic potential (even at low concentrations), are non-biodegradable (so they do not break down over time), have a strong tendency to accumulate in the environment and significantly affect the quality of ecosystems and human life [
11,
12]. Thus, numerous disorders of the nervous system, cardiovascular, endocrine, pulmonary, etc., have been proved to be determined by the presence of metal ions in drinking water or in plants [
13,
14], as a consequence of environmental pollution. Therefore, it is essential to remove metal ions from industrial effluents before they are discharged into the environment, and currently there are strict legislative regulations in this regards [
14].
But, in the current context of the circular economy, the removal efficiency of metal ions can no longer be considered the only criterion for the selection of industrial effluents treatment methods. Cost, energy consumption and the amount of secondary waste are also aspects to consider when choosing a sustainable method. Unfortunately, most of the previously mentioned methods of treating industrial effluents containing metal ions are high energy consumers, require high expenses and generate significant amounts of secondary waste, which in turn need to be treated [
15]. Therefore, finding a metal ion removal method in which these disadvantages are minimized is a challenge for the research in this field.
Compared to traditional methods, sorption is considered in the literature to be a much more ecological method that can be used to remove metal ions from aqueous media (including industrial effluents) [
16,
17,
18,
19], because: (i) it has a low cost and a simple way of operating, (ii) it can be easily adapted to treat both small and large volume of effluent, (iii) the sorbent used can be easily regenerated and the retained metal ions can be recovered, and (iv) it allows the valorisation of wide range of agricultural and industrial waste, which can be used as sorbents.
However, the applicability of large-scale sorption processes is quite limited. This is because the values of metal ions removal percent hardly reach 95-97 %, which is much lower compared to chemical precipitation, where the removal percent often exceeds 99 % [
16]. This difference is mainly due to the limited number of active centres on the surface of most sorbents, which can interact with metal ions in aqueous media. To solve this problem, many studies in the literature propose the functionalization of cheap and widely available materials with organic reagents [
20,
21,
22,
23], in order to obtain sorbents with high efficiency for the treatment of industrial effluents.
Two aspects must be taken into account in the design of such a sorbent. The first is related to the choice of the solid material to be functionalized. Such material must be available in large quantities, simple to prepare and stable over time. Biomass waste from the bio-fuels industry meets these requirements, and because they have no other uses, compared to natural materials or other agricultural waste. In addition, since such biomass wastes results from a solvent extraction step, they are already ground and sieved, therefore the preparation cost is significantly reduced. Moreover, due to the breaking of the cell walls during the extraction step [
24], their specific surface area is high (compared to the initial biomass), which is a major advantage in the subsequent functionalization step. Based on these considerations, mustard waste biomass (MWB) was selected for the experimental studies, because: (i) mustard biomass is frequently used in industry for oil extraction, due to its high content (over 39 %) [
25], (ii) the breaking of the cell walls (due to the extraction of oil) increased the specific surface area and the number of superficial functional groups [
26], which makes this biomass waste suitable for functionalization with organic reagents, and (iii) this waste has no practical uses other than incineration (due to traces of organic solvents).
The second aspect is related to the type of organic reagent used for functionalization. Such organic reagents must be easy to prepare, not required laborious synthesis procedures (which would increase the cost of functionalization), be non-toxic and have adequate chemical stability. In addition, their functional groups must be spatially available and have affinity for metal ions in aqueous solution. Many organic reagents fulfil these requirements and have been used in the literature for the functionalization [
21,
27]. However, our attention turned on METALSORB. METALSORB is a polymeric thiocarbamate that is used on an industrial scale as precipitating agent for the removal of metal ions from aqueous media. Due to its high solubility in water and the large number of functional groups with N and S donor atoms, this organic reagent allows the quantitative removal (> 99.5 %) of a large number of metal ions (Cu(II), Zn(II), Ni(II), Pb(II), Hg(II), etc.) [
28]. But the use of METASORB in the treatment of industrial effluents by precipitation has two major disadvantages, namely: (i) the excess of organic reagent added for precipitation (which does not react with metal ions) leads to the contamination of the effluents with organic compounds, and therefore to an increase in the value of chemical oxygen demand (CCO, mg O
2/L), and (ii) the recovery of metal ions from the precipitate is difficult (due to high stability of the chelated complexes), which is why the sludge obtained after removal of metal ions is stored for destruction.
In order to minimize these disadvantages, in this study, METALSORB was used for the functionalization of mustard waste biomass. The obtained material (MET-MWB) was then tested as a sorbent for the removal of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions from aqueous media. The experiments were performed in batch systems, as a function of initial metal ions concentration and contact time, both in the laboratory solutions and in real wastewater samples. A special attention was paid to the optimization of the functionalization conditions and the characterization of the obtained sorbent. The structural characteristics of MET-MWB and the detailed analysis of its sorptive performance highlight the applicative potential of this environmentally friendly sorbent in metal ions removal processes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
All chemical reagents used in this study were analytical grade and were purchased from Chemical Company (Iaşi, Romania). The stock solutions of metal ions (10-2 mol/L) were prepared by dissolving appropriate amount of metal sulphate salts (CuSO4, ZnSO4 and CoSO4) in distilled water. Volumes from the stock solutions were diluted with distilled water in order to prepare the working solutions at different concentrations. In each case the pH of the working solutions was adjusted by using HNO3 or NaOH solutions (10-2 mol/L) and measured by a pH/ion-meter (MM743 type, equipped with a combined glass electrode).
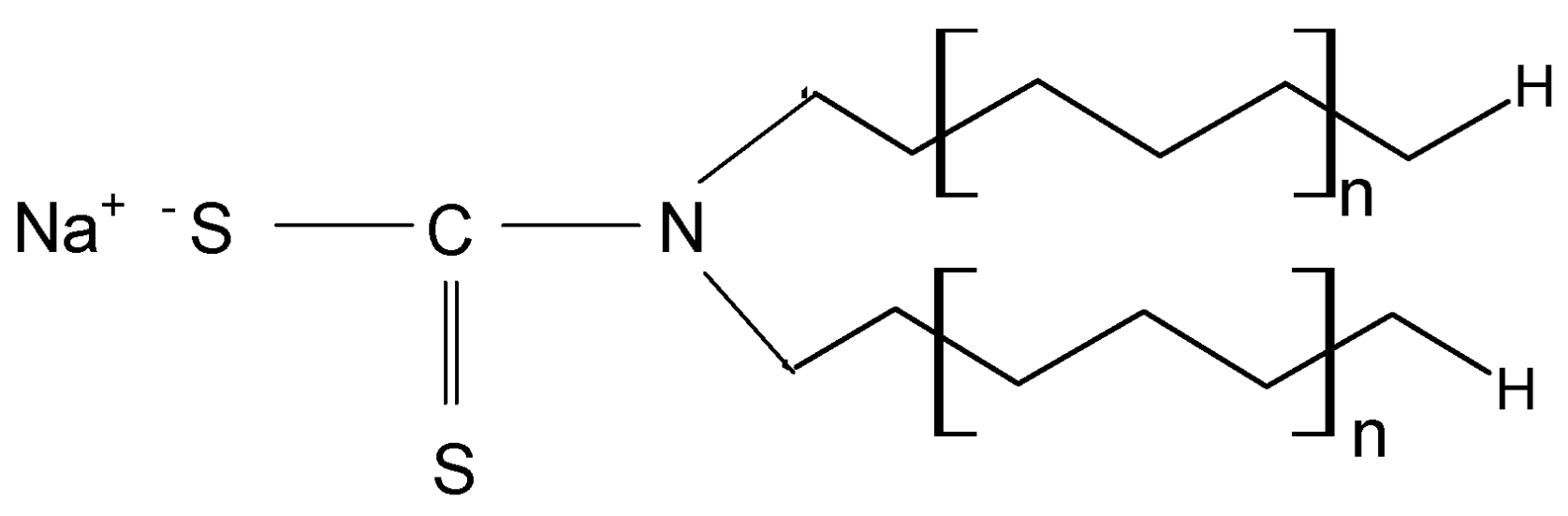
METALSORB was purchased from FLochem Industries, and was used as received. This polymeric thiocarbamate (
Figure 1) is an orange liquid, with a density of 1.1613 g/cm
3 and an average molecular weight of 5000 g/mol. Due to these characteristics, the required volumes of METALSORB were measured with a pipette.
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Sorbent
Mustard seeds purchased from a local farm (Iaşi, Romania) were washed several times with distilled water (to remove solid impurities and dust), air-dried (at room temperature), ground and sieved. The mustard biomass was subjected to an oil extraction stage (n-hexane, 36 h, Soxhlet extractor) to obtain mustard waste biomass (MWB). After air-drying (at ambient temperature), MWB was mortared (for homogenization) and mixed with METALSORB in different proportions (1 g : 0.5 mL; 1 g : 1 mL and 1 g : 2 mL) and at different temperatures (20 – 40 °C). The choice of this temperature range was made taking into account the thermal stability of METASORB specified in the technical data sheet. Each sample was stirred (at 150 rpm) in a thermostatic water bath for 3 hours. After filtration (on quantitative filter paper), the sorbents were washed three times with distilled water, dried at 50 °C for 6 hours (to remove humidity) and kept in desiccators. The selection of most efficient sorbent for the experimental studies was done by testing the sorption capacity of each material for Cu(II) ions, according with the methodology described in section 2.3.
The characterization of sorbent (MET-MWB) used in the sorption experiments was carried out by: (i) SEM microscopy (SEM/EDAX Hitachi S3000N (Tokyo, Japan), 20 kV), which allows the morphological analysis of the sorbent surface, and (ii) FTIR spectrometry (Bio-Rad Spectrometer, spectral range of 400 – 4000 cm-1, resolution of 4 cm-1, KBr pellet technique) to identify the nature of the superficial functional groups of the sorbent.
2.3. Sorption/Desorption Studies
To examine the efficiency of MET-MWB in metal ions removal processes, the sorption experiments were conducted in batch systems for each metal ion, as a function of their initial concentration and contact time. Thus, 25 mL of metal ions solution (Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II)) with an initial solution pH of 5.0 were mixed with 0.125 g MET-MWB, at room temperature (21 ± 1°C). The values of initial solution pH (5.0), sorbent dose (5 g/L) and temperature (21 °C) were established as optimal in a previous study [
29]. To study the influence of initial metal ions concentration on the sorption efficiency, experimental isotherms were recorded, where the initial concentration of metal ions ranging from 0.2 to 3.2 mmol/L. In these experiments, solution pH (5.0), sorbent dose (5 g/L), contact time (24 h) and temperature (21 °C) were kept constant. The effect of contact time was examined in the range of 5 – 180 min, for a concentration of metal ions of 0.8 mmol/L, while the other parameters were constant (as mentioned above). After phases separation (by filtration on quantitative filter paper), the metal ions concentration was determined by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS NovAA 400P Spectrometer, acetylene/air flame), and the sorption parameters were calculated using the relations:
where:
co and c are the initial and final concentration of metal ions (mmol/L);
V is volume of solution (L), and
m is the mass of sorbent used in each experiment (g).
In desorption experiments, 0.25 g of MET-MWB loaded with each metal ion was mixed with 10 mL of HNO
3 (10
-1 mol/L), and stirred for 3 hours. After filtration, the metal ions concentration was analyzed as is mentioned above. The regenerated sorbent was then washed several times with distilled water (until a neutral pH) and used in another sorption cycle. Three sorption/desorption cycles were performed for each metal ion and the regeneration efficiency (RE, %) of MET-MWB was calculated using the relation:
where: q
0 is the sorption capacity before regeneration (mmol/g) and q
r is the sorption capacity after regeneration (mmol/g).
Duplicate experiments were performed for each sorption and desorption series, and the mean value of the experimental results was used for calculations and in the graphical representations. All results were analyzed by ANOVA, and p-values less than 0.05 were considered significant.
2.4. Isotherm and Kinetic Modelling
The experimental isotherms obtained for the sorption of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) on MET-MWB were analyzed using three isotherm models, namely: Langmuir model, Freundlich model and Temkin model, whose mathematical equations [
30,
31] are:
where:
q is sorption capacity, (mmol/g);
qmax is maximum sorption capacity, (mmol/g);
KL is Langmuir constant, (L/g); c is equilibrium concentration of metal ions, (mmol/L);
KF is Freundlich constant, (L/g);
n is the heterogeneity factor; A
T is the equilibrium binding constant, (L/g); B is the constant correlated with the heat of sorption, (J/mol).
The selection of these three isotherm model was made taking into account the assumptions underlying their theoretical foundation [
31] and which allow establishing the way in which the metal ions bind on the surface of the sorbent and the nature of the interaction that take place during the sorption process.
The modelling of the experimental kinetic data was done using pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order and intra-particle diffusion kinetic models. The mathematical equations of these models [
32,
33,
34] are:
where:
qe,
qt are sorption capacity at equilibrium and at different
t values
, (mmol/g);
k1 is the rate constant of pseudo-first order model, (1/min);
k2 is the rate constant of pseudo-second order model, (g/mmol min);
kdiff is the intra-particle diffusion rate constant, (mmol/g min
1/2),
c is the concentration of metal ions, (mmol/L).
These kinetic models were chosen because they are useful in determining the rate and order of the sorption process, and thus allow the evaluation of MET-MWB performances.
The most appropriate model (isotherm and kinetic) for the description of the experimental data was evaluated based on the value of the regression coefficients (R2) calculated from the statistical analysis.
2.4. Real Industrial Effluents Tests
An industrial wastewater sample obtained from a local metal coating company was used to test the efficiency of MET-MWB biosorbent to remove Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions from real samples. Before use, the wastewater sample was filtered (on quantitative filter paper) to remove solid impurities and conditioned (24 hours) at room temperature. 100 mL of industrial wastewater was used for the sorption experiments of each metal ion using MET-MWB sorbent. The initial concentration of each metal ion was adjusted to 0.8 mmol/L and initial pH to 5.0. Each liquid phase was added over 0.5 g of sorbent, and mixed for 3 hours (at 21 °C). After filtration, the concentration of metal ions in the solution was determined as described above, while the standard methods [
35] were used to determined the other quality parameters of the effluent (before and after metal ions sorption).
3. Results and Discussion
As was already mentioned, the main disadvantage of biomass resulting from oil extraction (such as MWB) is the traces of organic solvent that remain in the biomass composition, even after several washing steps. This significantly limits the possibilities of using MWB for known applications (such as animal feed or bedding, soil compost, etc.) [
25,
29], but opens new opportunities for increasing the efficiency of this material in sorption processes, through functionalization. METALSORB was selected for the functionalization of MWB, because: (i) has a high efficiency in the removal of metal ions by precipitation, being used on an industrial scale, and (ii) the compatibility between the hydrocarbons radicals in METALSORB molecule (
Figure 1) and traces of organic solvent in MWB allows obtaining a stable functionalized sorbent over time.
Therefore, in order to highlight the efficiency of the funtionalized sorbent in the metal ions removal processed, it is necessary to take into account: (i) the establishment of the optimal functionalization conditions, (ii) the structural characterization of functionalized sorbent, and (iii) its testing in the sorption processes, both for laboratory solutions and in real samples.
3.1. Establishing the Optimal Functionalization Conditions
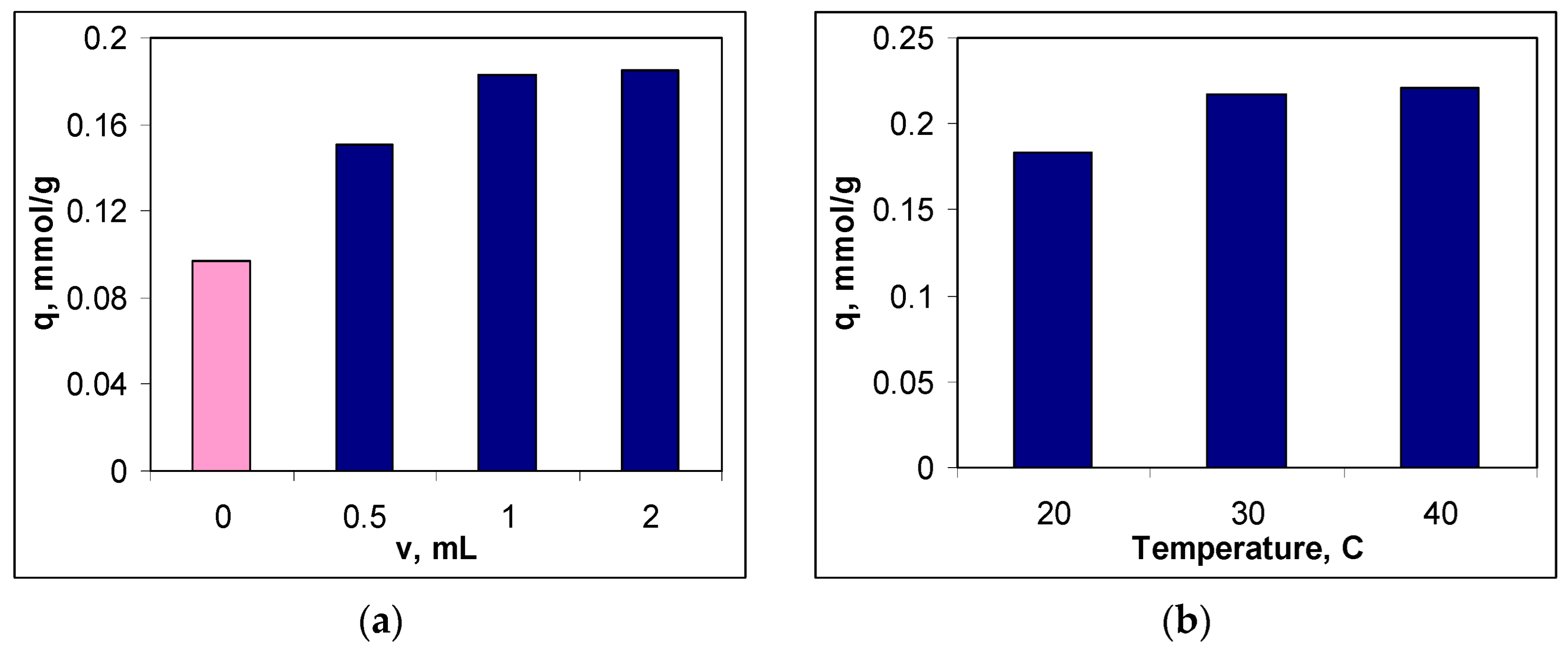
To establish the optimal functionalization conditions, two experimental parameters were considered, namely: the volume of the METALSORB solution used for functionalization and the temperature. In each case, the efficiency of the obtained sorbent was quantitatively evaluated using its sorption capacity for Cu(II) ions (see
Section 2.2), and the obtained experimental results are illustrated in
Figure 2.
It can be seen that both experimental parameters influence the efficiency of the functionalization process (
Figure 2). Thus, if in the case of the volume of the METALSORB solution, the increase in its value causes an increase in the sorption capacity by more than 90 % compared to non-functionalized MWB (
Figure 2a), in the case of temperature, the variation in the sorption capacity is much smaller in the studied range (20.76 %) (
Figure 2b).
The increase in the sorption capacity for Cu(II) ions when treating MWB with METASORB shows that the functionalization process was successfully carried out. Moreover, with the increase in the volume of METASORB solution used for funtionalization, the number of superficial functional groups of sorbent also increases, which favours more effective retention of Cu(II) ions from the aqueous solution. But since the difference between the sorption capacities in the case of treating MWB with 1.0 and 2.0 mL of METALSORB is below 3 %, 1.0 mL of METASORB solution was considered sufficient for the funtionalization of 1 g of MWB, and this value was selected as optimal (
Figure 2a). Selecting this value as optimal for MWB functionalization allows both obtaining an efficient sorbent for the removal of metal ions, and keeping the cost of sorbent preparation low.
On the other hand, increasing the temperature has the effect of both increasing the thermal agitation and decreasing of the viscosity of the METALSORB solution. Consequently, the efficiency of the functionalization process increases, and this leads to an increase in the sorption capacity for Cu(II) ions (
Figure 2b). However, in the temperature range of 20 – 40 °C (imposed by the thermal stability of the METASORB solution), the sorption capacity of Cu(II) ions varies quite a bit (from 0.18 mmol/g at 20 °C to 0.22 mmol/g at 40 °C). In these conditions, the temperature of 30 °C was chosen as optimal for functionalization, because it keeps all the advantages offered by the temperature increase, without bringing unjustified additional costs (
Figure 2b).
Based on the experimental results presented in
Figure 2, the functionalization of MWB with METASORB is achieved with maximum efficiency at a mixture ratio of 1 g MWB : 1.0 mL of METASORB solution and at a temperature of 30 °C. The sorbent obtained under these experimental conditions was named MET-MWB, and this notation will be used hereafter.
To test the stability of MET-MWB in aqueous solution, 0.5 g of sorbent was mixed with 25 mL of Cu(II) ions solution (0.8 mmol/L, pH = 5.5) for 24 hours. The value of the CCO index (mg O2/L) determined for the aqueous solution before and after the sorbent separation varies insignificantly (from 38.13 mg O2/L to 37.95 mg O2/L). This shows that the METALSORB molecules are bonded to the MWB surface by strong interactions that prevent their release when in contact with the aqueous solution. Therefore the obtained sorbent is stable and can be used in the metal ions retention processes.
3.2. Characterization of MET-MWB
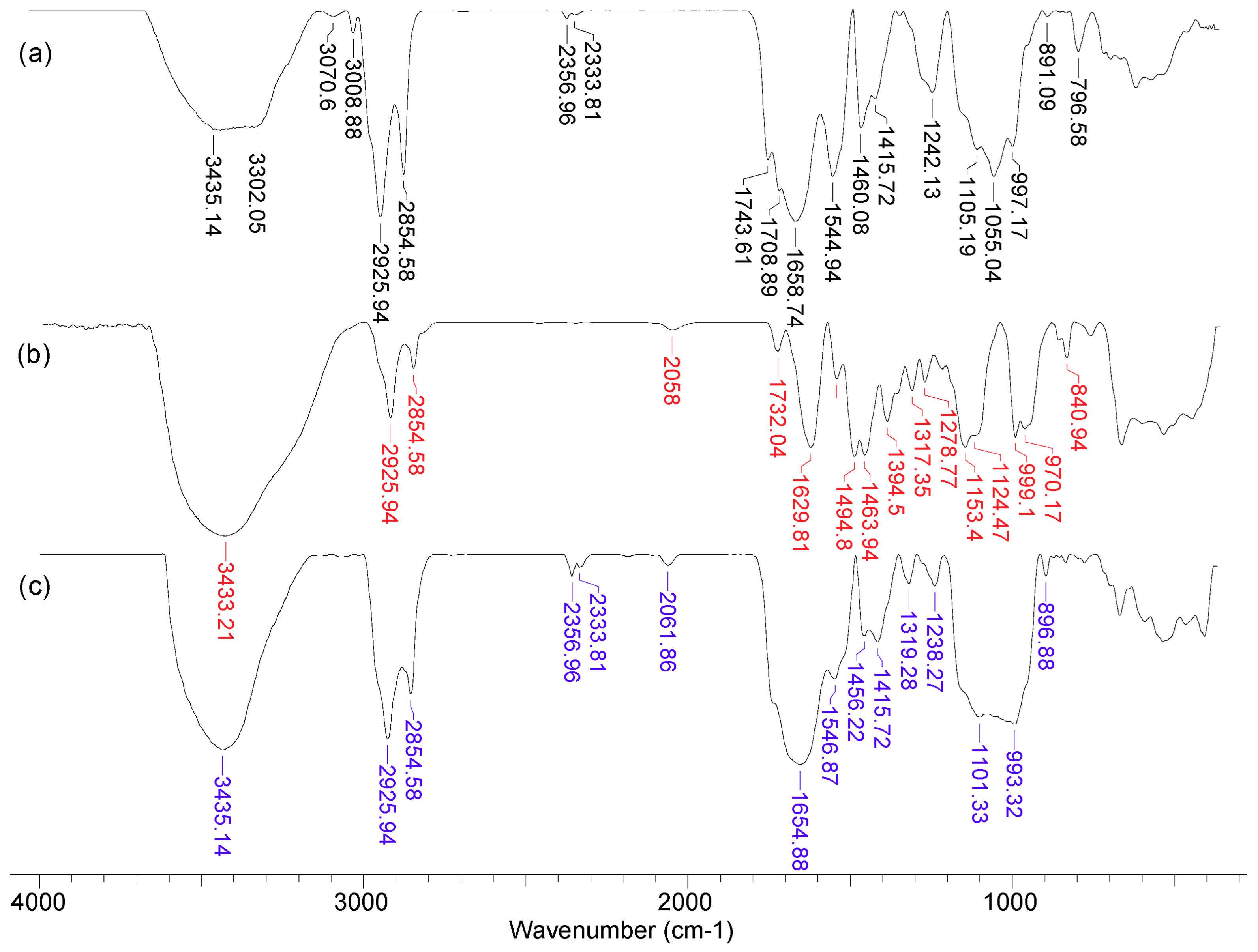
In order to highlight the structural features of MET-MWB necessary for its use as a sorbent, FTIR spectra and SEM images were recorded (Figs. 3 and 4).
As can be seen from
Figure 3, after the functionalization of MWB some significant changes can be noted. Thus, the broad band at 3300-3435 cm
-1 in MWB (spectra 1), corresponding to the stretching vibrations of O–H and N–H bonds, becomes much sharper and shows a single absorption maximum (3435 cm
-1) in MET-MWB (spectra 3), suggesting a rearrangement of –OH and –NH
2 groups. Similar changes can be observed in the case of the bands at 1544-1743 cm
-1 and 997-1105 cm
-1 (spectra 1), which correspond to stretching vibrations of C=O bonds from carbonyl and carboxyl compounds, and respectively C–O bonds from oxygenated compounds. The increase in the intensity of these bands and the reduction in the number of absorption maxima after functionalization (spectra 3) show that these groups contribute to the retention of METALSORB molecules on MWB, most likely through hydrogen bonds. On the other hand, some new bands appear in the MET-MWB spectrum (spectra 3), which are characteristic of METALSORB (spectra 2). Thus, the bands at 2061 and 1319 cm
-1 are characteristic of the stretching vibration of C–N and C=S bonds in saturated amines and thiols. In addition, the band at 1415 cm
-1 indicate the presence of N–C=S groups. Based on these observations it can be said that the functionalization of MWB was successfully achieved, and the obtained sorbent has a series of new functional groups on its surface, which can increase its efficiency in the retention of metal ions from aqueous media.
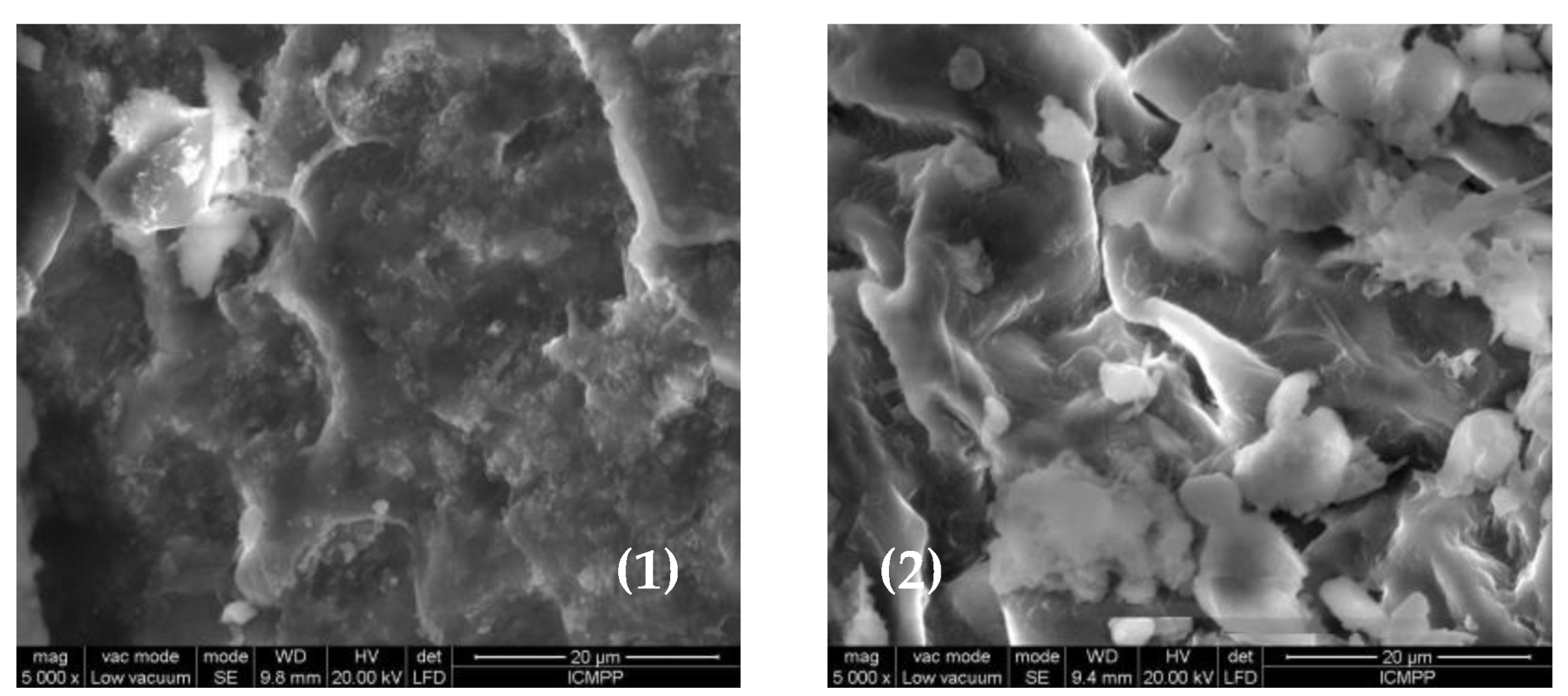
The differences observed in the FTIR spectra of MWB before and after functionalization (
Figure 3) are also supported by the changes in the surface morphology of the two materials, recorded by the SEM images (
Figure 4). Thus, it can be observed that after functionalization, new non-uniform formations appear on the MET-MWB surface (
Figure 4(2)).
These formations are most likely due to METALSORB macromolecules that form local conglomerates, and their presence leads to an increase in the roughness of the new sorbent, thus to an increase in its specific surface area. These structural features significantly influence the sorption process [
36], and therefore it is expected that the removal of metal ions will be more efficient when using the functionalized sorbent.
3.3. Testing the Sorptive Performances of MET-MWB
To test the performance of MET-MWB sorbent, three metal ions (Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II)) were selected based on their physico-chemical characteristics and their importance for industrial activities. Batch sorption experiments were performed in optimal experimental conditions (initial solution pH = 5.0, sorbent dose = 5.0 g/L; temperature = 21 °C), established in a previous study [
29].
3.3.1. Influence of Initial Metal Ions Concentration and Isotherms Modelling
One of the most important parameters influencing the performance of a sorbent is the initial concentration of metal ions. This is because the study of the variation of the sorption efficiency as a function of initial metal ions concentration allows obtaining essential information for establishing: (i) the concentration range of metal ions in which the sorbent allows their quantitative removal, and (ii) the maximum concentration of metal ions where the sorbent saturation occurs [
20]. These aspects are important in designing such a system for large-scale applications.
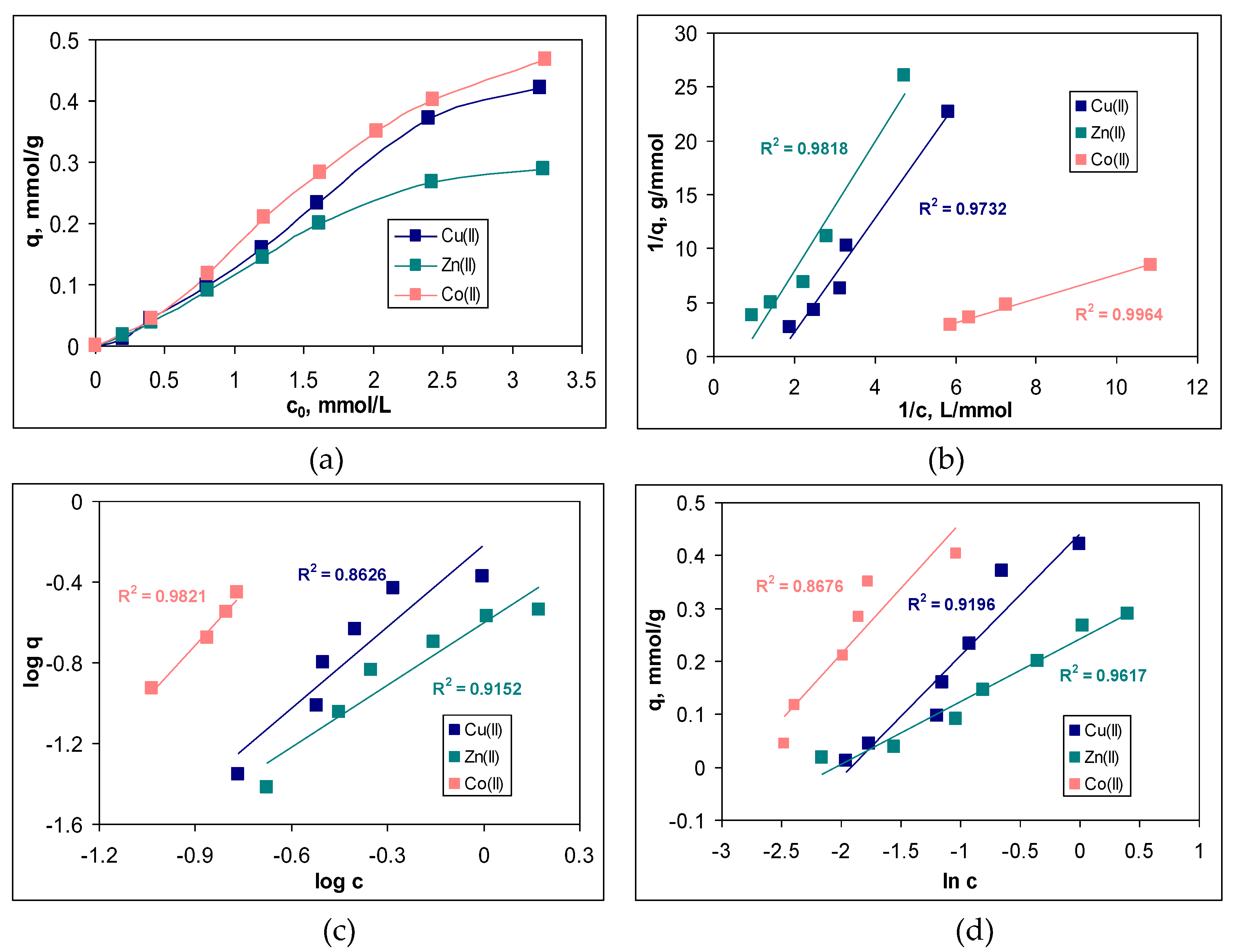
In this study, the initial concentration of metal ions was varied in a range between 0.2 and 3.2 mmol/L, and the variation of the sorption capacity (q, mmol/g) and the removal percent (R, %) for each metal ion is presented in
Figure 5a.
The increase in the initial concentration of metal ions (c
0, mmol/L) causes an increase in the values of sorption capacity (q, mmol/g), for the entire studied concentration range and for all metal ions (
Figure 5a). Such a variation is characteristic of sorption processes [
20,
21], and is due to the fact that with the increase of the initial concentration, more and more metal ions reach the surface of the sorbent, where they interact with the superficial functional groups and are retained. Thus, according to the experimental data presented in
Figure 5a, increasing the initial metal ions concentration from 0.2 to 3.2 mmol/L leads to an increase in the sorption capacity from 0.01 to 0.42 mmol/g in the case of Cu(II), from 0.02 to 0.29 mmol/g in the case of Zn(II), and from 0.04 to 0.47 mmol/g in the case of Co(II). In this concentration range, the removal percents varied between 29 – 78 % for Cu(II), 42 – 65 % for Zn(II) and 54-91 % for Co(II) (data not shown).
Although the increase in sorption capacity is significant in the studied concentration range, from a practical point of view two aspects attract attention. The first is related to the fact the sorbent saturation in reached at high initial concentration of metal ions. As can be seen from
Figure 5a, the increase in the sorption capacity is slower only at concentration higher than 2.4 mmol M(II)/L, although the appearance of a plateau is not obvious. This suggests that MET-MWB allows the treatment of large volumes of effluents in which the metal ion content can vary within fairly wide limits, without the need to replace it (due to exhaustion).
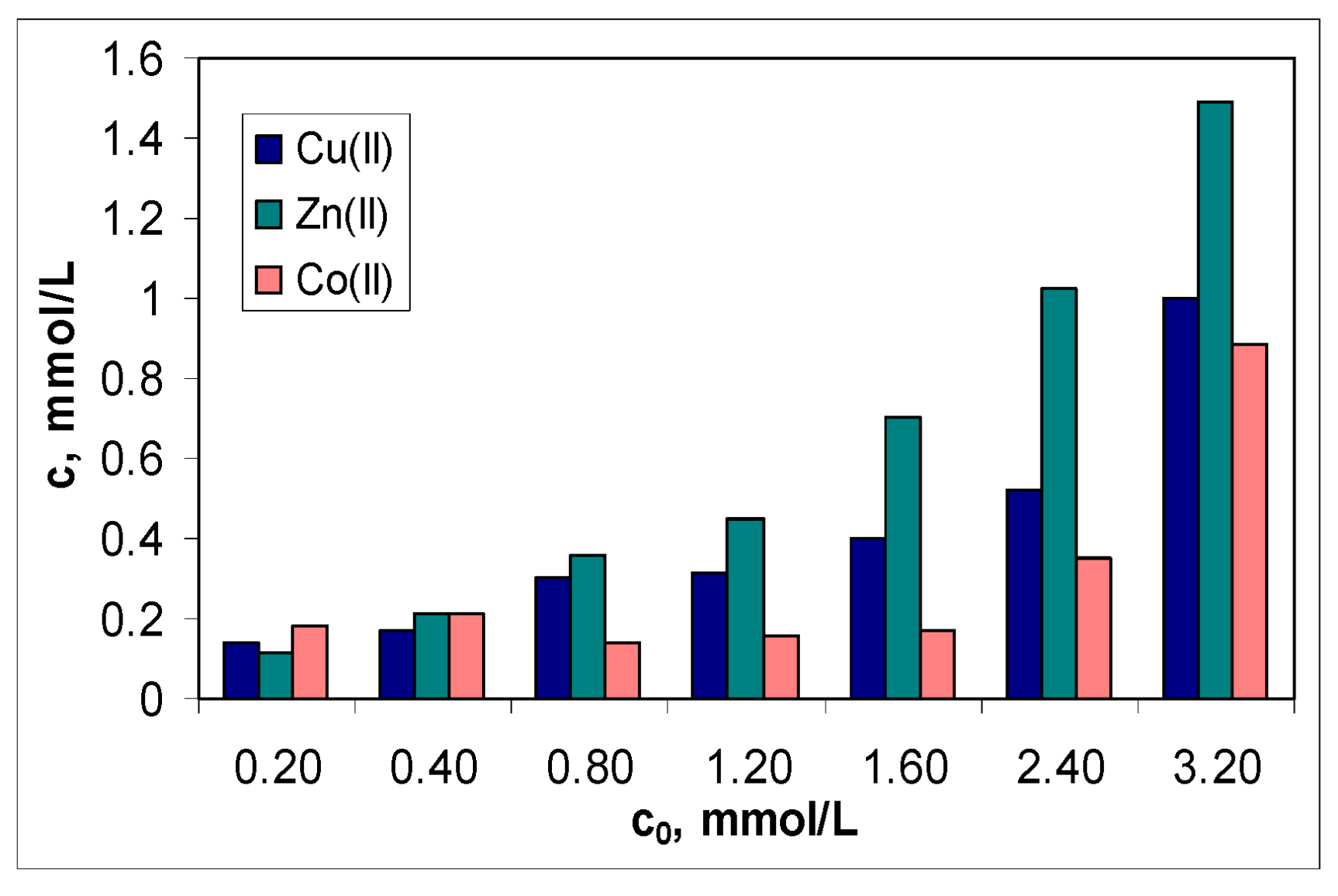
The second aspect is related to the efficiency of this sorbent in the treatment of effluents. Although the values of the sorption capacity increase in the order: Co(II) > Cu(II) > Zn(II) (
Figure 5a), the graphical representation of the metal ions concentration before (c
0, mmol/L) and after (c, mmol/L) the sorption process (
Figure 6) indicates a moderate efficiency of MET-MWB.
The regression analysis of the dependencies illustrated in
Figure 6 shows that for the treated effluent to meet the conditions required by NTPA [
37], the initial concentration of metal ions must not be higher than 10 mg M(II)/L. This is not viable from a practical point of view. Therefore it is recommended that MET-MWB be used to reduce the content of metal ions in industrial effluents, and then the treated effluents be subject to either a new sorption step (with clean MET-MWB) or another advanced treatment method.
Quantitative evaluation of the sorption of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions on MET-MWB was performed by mathematical analysis of the equilibrium data using Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin models. The linear representations of these models (according with the equations (4)-(6)) are illustrated in
Figure 5b–d, and the isotherm parameters calculated for each metal ion are summarized in
Table 1.
Comparing the regression coefficients (R
2) obtained for the three isotherm models (
Figure 5b–d), it can be seen that the experimental data are best described by the Langmuir model. This means that the retention of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions on MET-MWB is a monolayer sorption process, which takes place on a heterogeneous surface (as demonstrated by the high values of R
2 in the case of the other two models). The maximum sorption capacities (q
max, mmol/g) (
Table 1), calculated from the Langmuir model, have values close to the experimental ones, which explains the flattening of the experimental isotherms at high initial concentration of metals ions (
Figure 5a). In addition, such behaviour shows that the retention of metal ions is achieved through the interactions occurring at the surface of the MET-MWB. These interactions are predominantly electrostatic (according with the values of B parameter of Temkin model) and involve superficial active sites, which makes the sorption process a favourable event at high metal ions concentrations (values of n in the Freundlich model are greater than unity). In addition, the variation of the maximum sorption capacity, which increases in the order: Co(II) > Cu(II) > Zn(II) is mainly determined by the physico-chemical characteristics of the metal ions. Thus, the greater the ratio between electronegativity and ionic radius (0.0149 for Co(II), 0.0141 for Cu(II) and 0.0135 for Zn(II)), the more effectively the metal ions interact with the functional groups of the sorbent, and the values of the sorption capacity is greater.
The values of the maximum sorption capacity obtained for the retention of Cu(II), Zn(II) şi Co(II) ions on MET-MWB are comparable to the values reported in the literature when using different natural of functionalized materials as sorbents, in similar experimental conditions [
38,
39,
40]. However, much more important is the fact that after functionalization with METALSORB, the maximum sorption capacity of the obtained sorbent (MET-MWB) increases significantly compared to the non-functionalized biomass (MWB). Thus in the case of Cu(II) this increase is 58.59 % (from 0.26 to 0.42 mmol/g), in the case of Zn(II) of 18.86 % (from 0.24 to 0.29 mmol/g), and in the case of Co(II) of 69.35 % (from 0.27 to 0.47 mmol/g) (data not shown). All these observations show that MET-MWB has potential and can be practically used as a sorbent in the decontamination of industrial effluents.
3.3.2. Influence of Contact Time and Kinetic Modelling
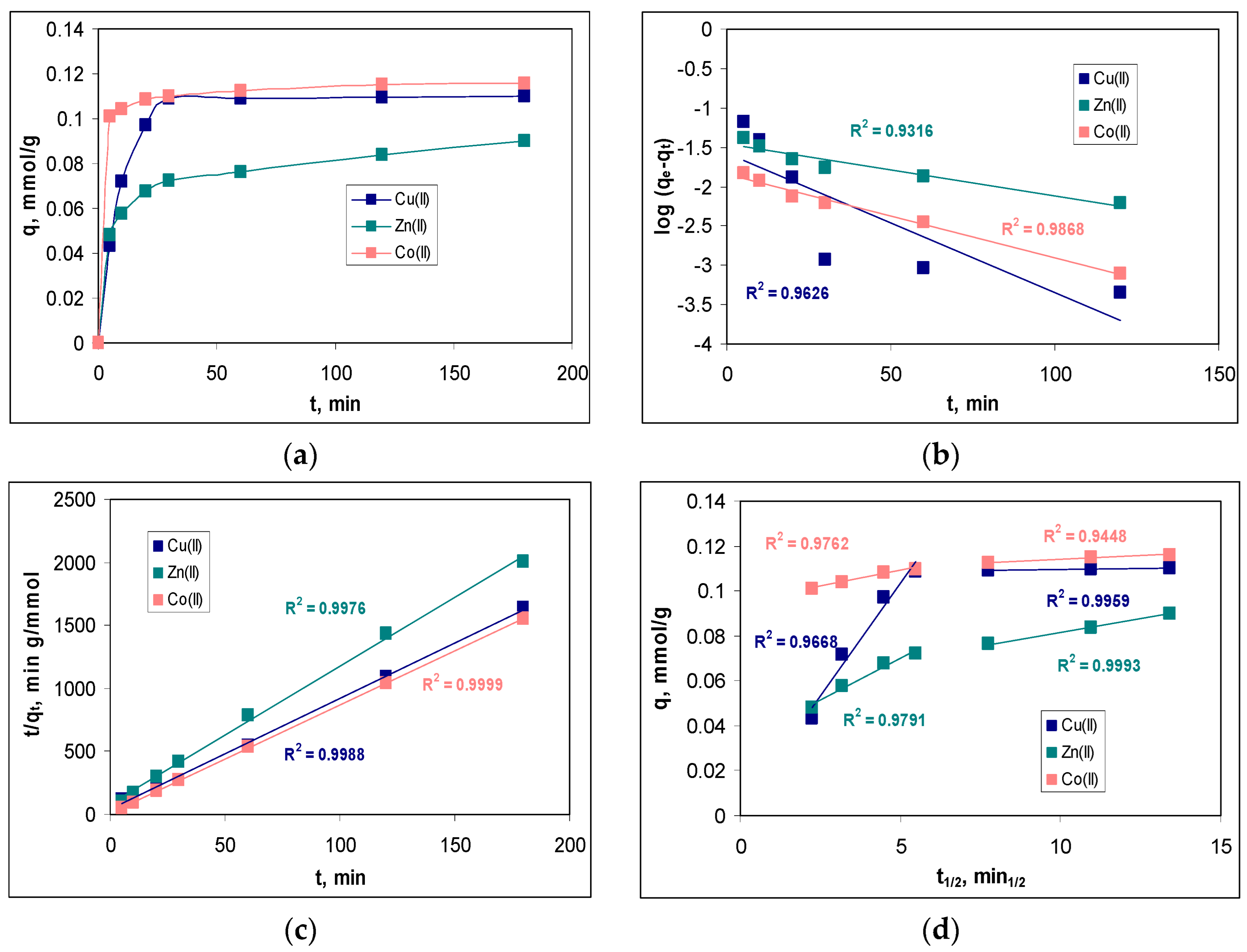
In order to determine the minimum contact time required to reach equilibrium, the variation of the sorption capacity at different contact time values (between 5 and 180 min) was examined.
Figure 7a illustrates the influence of contact time on the sorption efficiency of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions on MET-MWB.
The variation of the sorption capacity over the entire studied contact time interval (
Figure 7a) shows a significant increase of this parameter in the interval 0-30 min. At higher contact time values, the increase in sorption capacity of MET-MWB is much slower, indicating that the sorption processes have reached equilibrium. At a contact time of 30 min, the retention of metal ions is quantitative (68.18 % for Cu(II), 46.51 % for Zn(II) and 73.84 % for Co(II)). The subsequent increase in the contact time (up to 180 min), does not significantly change the values of the retention percent of metal ions (4.39 % for Cu(II), 8.51 % for Zn(II) and 2.75 % for Co(II)). Therefore, a contact time of at least 30 min ensures that the equilibrium state is reached in the studied sorption processes, and this value once again underlines the practical potential of using MET-MWB in decontamination processes of industrial effluents.
Modelling of the experimental kinetic data was performed using pseudo-first order model, pseudo-second order model and intra-particle diffusion model (eqs. 7-9), and the best-fitting model was selected based on the regression coefficient (R
2). The linear representations of these three kinetic models are illustrated in
Figure 7b–d, while the values of the kinetics parameters are summarized in
Table 2.
As can be seen from
Figure 7b–d, all the kinetic models describe the experimental data very well, as the values of R
2 are greater than 0.9, in all cases. However, in the case of the pseudo-second order kinetic model, the calculated values of the sorption capacity (q
ecalc, mmol/g) are closer to the experimental ones (q
eexp, mmol/g) than in the case of the pseudo-first order model. This allows us to say that the pseudo-second order model is the most suitable for the analysis of the experimental data. Consequently, the retention of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions on MET-MWB is done by electrostatic interactions that require two binding centers, with favorable geometric orientation, located on the surface of the sorbent. The rate constants of the pseudo-second order kinetic model (k
2, g/mmol min) follow the order: Co(II) > Cu(II) > Zn(II), which is similar to the ratio between electronegativity and ionic radius (0.0149 for Co(II), 0.0141 for Cu(II) and 0.0135 for Zn(II)). This variation in rate constants indicates that Co(II) ions have higher affinity for the superficial functional groups of MET-MWB, compared with Cu(II) and Zn(II) ions, and this difference can be easily observed in
Figure 7a.
However, the following two aspects should be also mentioned. The first is that the pseudo-first order kinetic model fits the experimental data very well at low values of the contact time, for all metal ions (
Figure 7b). This indicates that in the initial moments of the sorption processes, when a large number of metal ions reach the surface of the sorbent, their binding is done through a single active centre. Only after that, the superficial complex is stabilized by removing one more water molecule and forming a new bond with another superficial functional group of the sorbent. This behaviour shows that the functional groups on the sorbent have a high affinity for the metal ions in the aqueous solution, and explains the good correlation between the experimental data and the Freundlich isotherm model (see section 3.3.1). The second aspect is related to the importance of elementary diffusion processes. As can be seen from
Figure 7d, none of the linear representations of the intra-particle diffusion model pass through the origin. This means that elementary diffusion processes are not the rate-controlling step in the retention of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions on MET-MWB. Analyzing the values of the kinetic parameters of the intra-particle diffusion model (
Table 2), it can be seen that the concentrations of metal ions in the diffusion layer (c
1, mmol/L) are close to the values of their concentration in the bulk of solution (c
2, mmol/L), while between the rate constants there are significant differences (k
1 >>k
2). These observations show that as soon as the metal ions reach the surface of the sorbent, they find functional groups available for their binding and, consequently, the elementary diffusion steps occur with high rates.
3.4. Sorbent Regeneration and Desorption of Metal Ions
To evaluate the regeneration and reuse potential of the sorbent, samples of 0.25 g of MET-MWB loaded with each metal ion were treated for 3 h with 10 mL of HNO3 solution (10-1 mol/L). After washing (until a neutral pH), the same amount of sorbent was used for another sorption cycle.
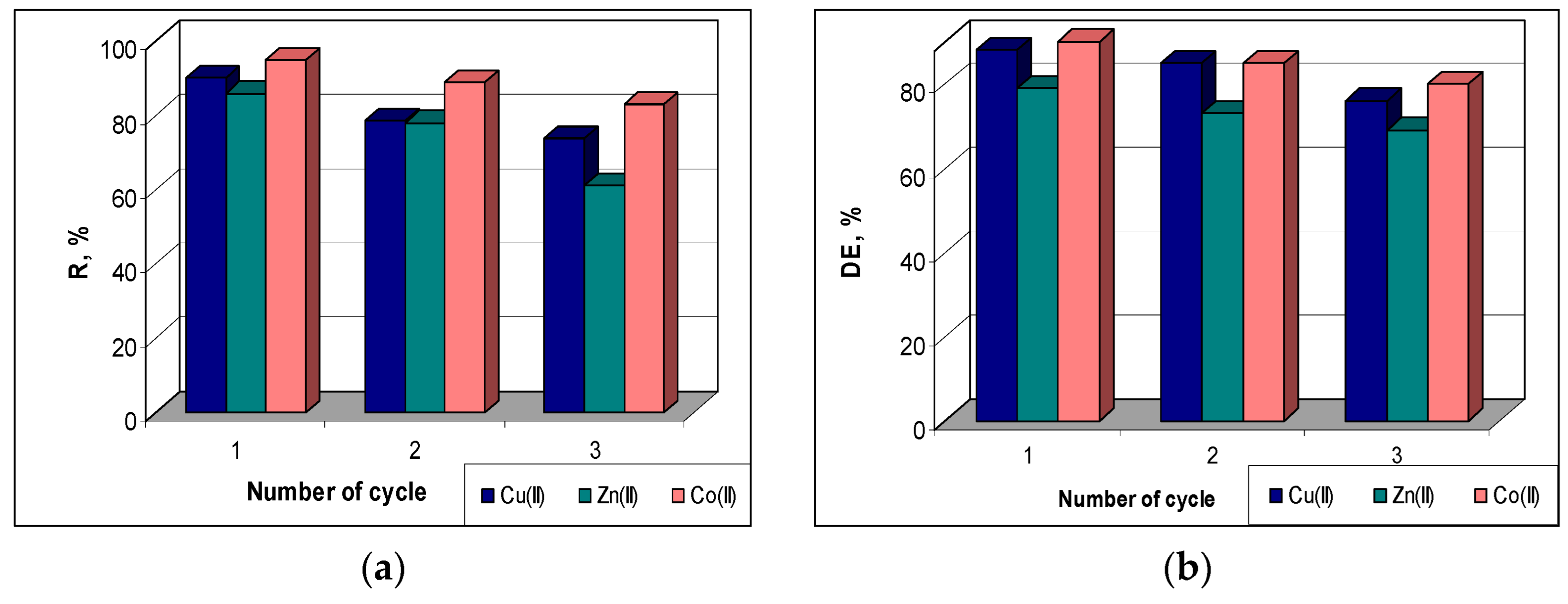
The sorption efficiency (R, %) was found to decrease quite a bit in higher cycles compared to the initial value (
Figure 8a). Thus, from the first to the third cycle, the R values decrease by 12 % in the case of Co(II) ions (from 95 % to 83%), by 16 % in the case of Cu(II) ions (from 90 % to 74 %) and by 25 % in the case of Zn(II) ions (from 86 % to 61 %). A similar behaviour can be observed in the case of desorption of metal ions retained on MET-MWB sorbent. The desorption efficiency (DE, %) decreases by 10 % for Co(II) and Zn(II) ions and by 12 % for Cu(II) ions with the increasing of number of sorption/desorption cycles (
Figure 8b). This decrease in sorption/desorption efficiency in subsequent cycles is most likely determined by the changes occurring at the sorbent surface (ex. inactivation/loss of superficial functional groups) during the regeneration and washing steps. However, the maintenance of good values of metal ion removal percents (R %) up to three cycles, and the high efficiency of metal ion recovery after each cycle show that MET-MWB is a reusable material that can be used in decontamination processes of industrial effluents.
3.5. Sorption Mechanism
The retention of metal ions on the surface of solid materials can be achieved by three distinct mechanisms: ion exchange, superficial complexation and superficial precipitation [
16]. The identification of the predominant mechanism is important because it allows establishing the limits of the use of the sorption process (efficiency in metal ions removal, selectivity, desorption conditions, etc.), in large-scale practical applications.
In the case of using MET-MWB for the retention of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions, the experimental working conditions (pH = 5.0, 5 g sorbent/L), practically exclude the possibility of metal ions precipitation on the sorbent surface. Therefore, ion exchange and superficial complexation remain the only viable options.
The modelling of the kinetic and equilibrium data, presented in the previous sections, revealed that: (i) metal ions are retained on the sorbent surface until a monolayer coverage is formed (according with Langmuir model assumptions), (ii) the maximum sorption capacity depends on the ratio between the electronegativity and the ionic radius of the metal ions, (iii) the sorption energies have relative low values, (iv) the retention of metal ions requires the existence of two binding centres located in favourable geometric positions (according with pseudo-second order kinetic model assumptions), and (v) desorption of metal ions is quantitative in strong acid media.
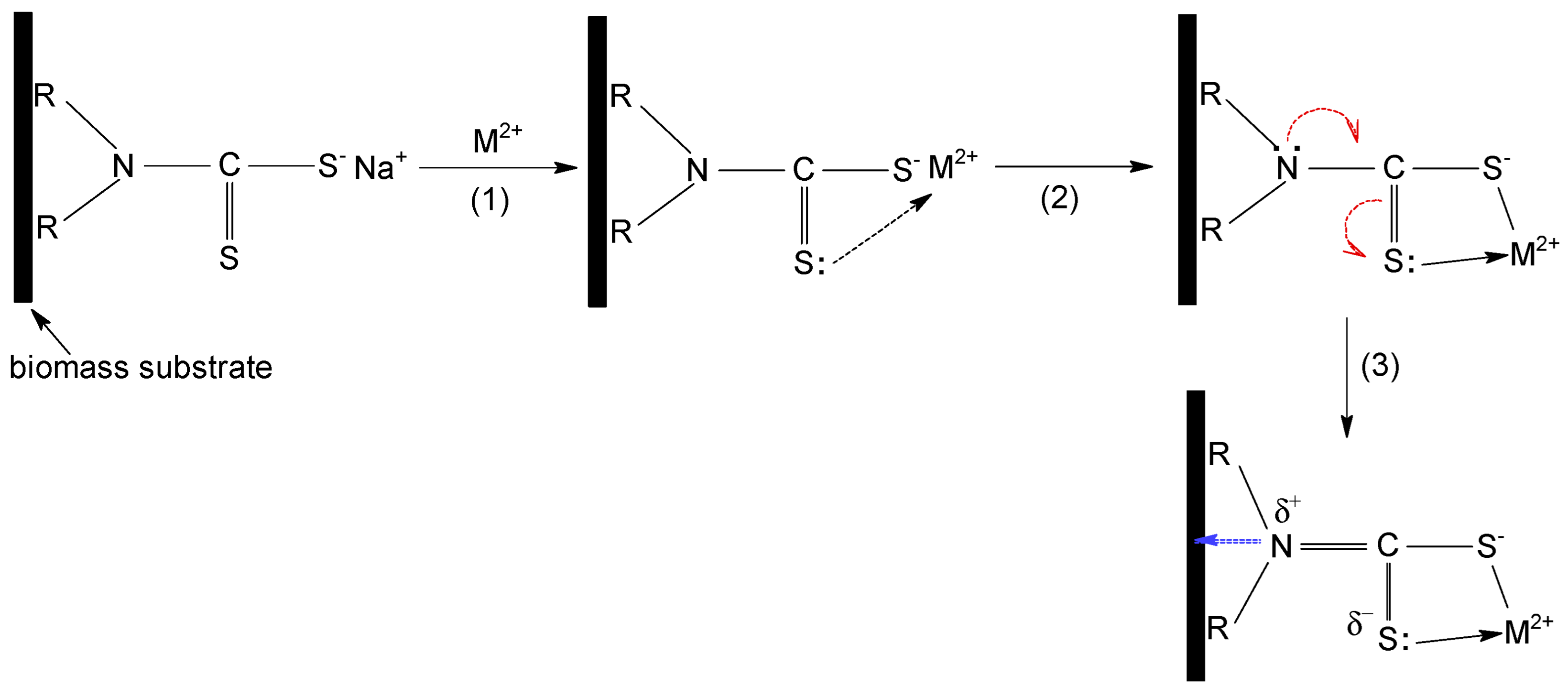
All these observations indicate that the sorption of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions on MET-MWB is governed by a complex mechanism, involving both electrostatic and donor-acceptor interactions. A schematic representation of the sorption mechanism of metal ions on MET-MWB is illustrated in
Figure 9.
The metal ions (positively charged) are attracted to the surface of the sorbent by the negatively charges of the ionized thiol groups (step 1). These electrostatic interactions most likely represent the first stage of the sorption mechanism, since their realization involves low binding energies, thus high rates. After the neutralization of the first positive charge of the metal ion, the intermediate complex is stabilized by the formation of a donor-acceptor bond between the metal ion (still positively charged) and the lone pair of electrons of the doubly bonded sulphur atom to carbon (step 2). These donor-acceptor interactions take a little longer to achieve, because the metal ion must find the C=S bond that has a favourable geometric position. Most likely, both electrostatic and donor-acceptor interactions involve the participation of the same METALSORB molecule, but the experimental data do not exclude the possibility of the participation of two molecules of the functionalization agent. The involvement of the non-participating electrons of the S atom (C=S bond) in donor-acceptor interactions with metal ion, causes a displacement of electrons in METALSORB molecule, due to electronic effects. Consequently, the electron density on the N atom decreases, and this is essential for the functionalization of MWB, as it allows the stabilization of METASORB molecules on the biomass surface trough electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonds (step 3).
All these observations are supported by FTIR spectra and SEM images recorded for MET-MWB before and after metal ions retention. For example,
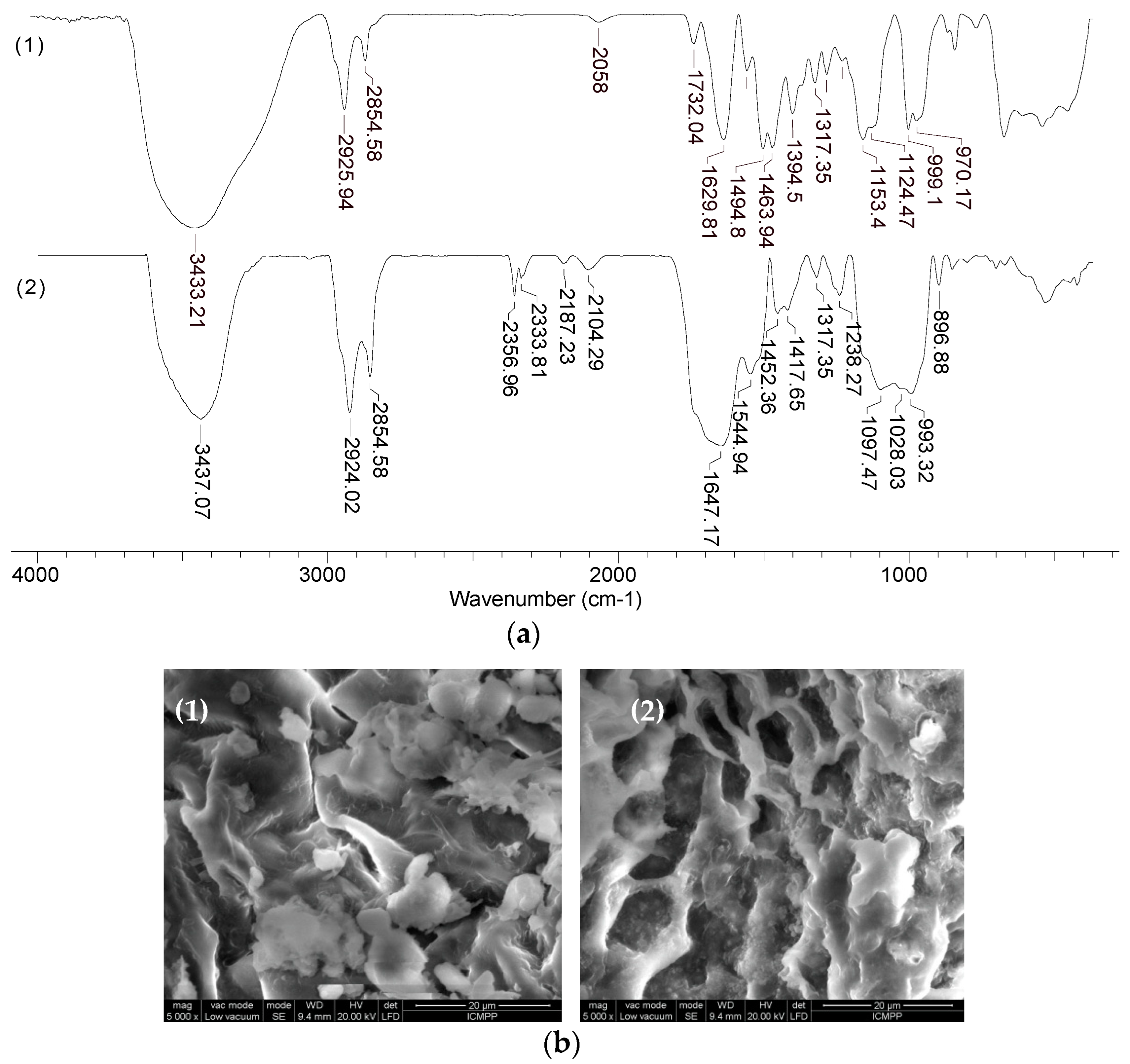
Figure 10 shows the FTIR spectra and SEM images before and after the sorption of Co(II) ions (which are retained most efficiently on MET-MWB), but similar results were also obtained for Cu(II) and Zn(II) ions.
The changes in the wave numbers corresponding to the absorption bands in the region 970-1155 cm
-1 and 1317-1732 cm
-1 (
Figure 10a, spectrum 1) show that the functional groups of alcohol and carbonyl type (from MWB) and thiol groups (characteristic of METALSORB) are involved in the retention of metal ions. In addition, the appearance of absorption bands in the 2104-2356 cm
-1 region (
Figure 10a, spectrum 2), which are determined by the stretching vibrations of the C-N bond in tertiary amine salts, supports the hypothesis of METASORB stabilization on the biomass surface through direct interactions between the N atom and the biomass functional groups. This hypothesis is also supported by the SEM images (
Figure 10b), in which an ordering of the METASORB molecules can be observed after the retention of metal ions.
All these observations once again demonstrate that the use of METASORB for MWB functionalization allows obtaining a sorbent (MET-MWB) with superior performances in the removal of metal ions (as demonstrated in the previous sections), which has potential to be used in large-scale decontamination processes.
3.6. Removal of Metal Ions in Wastewater
To test the potential of MET-MWB in the treatment of industrial effluents, the sorption of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions was performed in a single component systems, using wastewater samples (purchased from local metal coating company). In each wastewater sample, the initial concentration of metal ions was adjusted at 0.8 mmol/L (~ 50 mg/L), and the sorption experiments were performed in the following conditions: initial pH of 5.0, 0.5 g of MET-MWB, contact time of 3 hours and temperature of 21 °C. The concentration of each metal ion, as well as the values of some quality parameters used for the evaluation of wastewater [
37], before and after sorption on MET-MWB, are presented in
Table 3.
More than 95 % of metal ions content (97.54 % for Cu(II), 96.80 % for Zn(II) and 95.68 % for Co(II)) is removed from wastewater samples using MET-MWB. Although the sorption capacities obtained in wastewater samples are lower than those obtained in laboratory solutions (± 10-15 %), and the concentration of metal ions remaining after sorption are higher than the maximum permissible values (see
Table 3), MET-MWB could effectively remove metal ions from industrial effluents. In addition, the values of the other quality parameters (CCO, water hardness, turbidity, electrical conductibility) do not change significantly (
Table 3), indicating that MET-MWB is a chemical stable material that behaves similar to an ion exchanger.
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of METALSORB (n is the number of ethylene groups from aliphatic chain).
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of METALSORB (n is the number of ethylene groups from aliphatic chain).
Figure 2.
Influence of the volume of METALSORB solution (20 °C) (a) and the temperature (1.0 mL of METASORB) (b) on sorption capacity of Cu(II) ions on functionalized sorbent (pH = 5.5; 5.0 g sorbent/L; c0 = 0.8 mmol/L, 3 hours, 20 °C).
Figure 2.
Influence of the volume of METALSORB solution (20 °C) (a) and the temperature (1.0 mL of METASORB) (b) on sorption capacity of Cu(II) ions on functionalized sorbent (pH = 5.5; 5.0 g sorbent/L; c0 = 0.8 mmol/L, 3 hours, 20 °C).
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of MWB (1), METALSORB (2) and MET-MWB (3).
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of MWB (1), METALSORB (2) and MET-MWB (3).
Figure 4.
SEM images of MWB (1) and MET-MWB (2) at 5000X magnitude order.
Figure 4.
SEM images of MWB (1) and MET-MWB (2) at 5000X magnitude order.
Figure 5.
Variation of the sorption capacity as a function on initial concentration of metal ions (a), and linear representations of Langmuir (b), Freundlich (c) and Temkin (d) models for the sorption of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) on MET-MWB.
Figure 5.
Variation of the sorption capacity as a function on initial concentration of metal ions (a), and linear representations of Langmuir (b), Freundlich (c) and Temkin (d) models for the sorption of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) on MET-MWB.
Figure 6.
c vs.c0 for the sorption of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions on MET-MWB.
Figure 6.
c vs.c0 for the sorption of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions on MET-MWB.
Figure 7.
Effect of contact time (a), and linear representations of pseudo-first order model (b), pseudo-second order model (c) and intra-particle diffusion model (d) for the sorption of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) on MET-MWB.
Figure 7.
Effect of contact time (a), and linear representations of pseudo-first order model (b), pseudo-second order model (c) and intra-particle diffusion model (d) for the sorption of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) on MET-MWB.
Figure 8.
Sorption efficiency (R, %) (a) and desorption efficiency (DE, %) (b) of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions on MET-MWB.
Figure 8.
Sorption efficiency (R, %) (a) and desorption efficiency (DE, %) (b) of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions on MET-MWB.
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of the sorption mechanism of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions on MET-MWB.
Figure 9.
Schematic representation of the sorption mechanism of Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions on MET-MWB.
Figure 10.
FTIR spectra (a) and SEM images (b) of MET-MWB before (1) and after (2) Co(II) ions sorption.
Figure 10.
FTIR spectra (a) and SEM images (b) of MET-MWB before (1) and after (2) Co(II) ions sorption.
Table 1.
Isotherm parameters for Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions sorption on MET-MWB.
Table 1.
Isotherm parameters for Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions sorption on MET-MWB.
| Isotherm parameter |
Cu(II) |
Zn(II) |
Co(II) |
| Langmuir model |
qmax, mmol/g
KL, L/mmol |
0.4106
1.5867 |
0.2399
0.6904 |
0.4282
3.1635 |
| Freundlich model |
n
KF, L1/n/g·mmol1/(n-1)
|
2.62
0.6076 |
1.98
0.2477 |
3.58
2.2979 |
| Temkin model |
AT, L/g
B, kJ/mol |
6.7715
22.96 |
5.7959
11.80 |
8.2599
24.83 |
Table 2.
Kinetic parameters for Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions sorption on MET-MWB.
Table 2.
Kinetic parameters for Cu(II), Zn(II) and Co(II) ions sorption on MET-MWB.
| Kinetic parameter |
Cu(II) |
Zn(II) |
Co(II) |
| qeexp, mmol/g |
0.1102 |
0.0898 |
0.1159 |
| Pseudo-first order model |
qecalc, mmol/g
k1, 1/min |
0.0265
0.0177 |
0.0347
0.0066 |
0.0144
0.0106 |
| Pseudo-second order model |
qecalc, mmol/g
k2, g/mmol min |
0.1136
1.9952 |
0.0916
1.4588 |
0.1166
5.8479 |
| Intra-particle diffusion model |
c1, mmol/L
kdiff1, mmol/g min1/2
|
0.0933
0.0201 |
0.0327
0.0057 |
0.0951
0.0028 |
| c2, mmol/L |
0.1081 |
0.0578 |
0.1077 |
| kdiff2, mmol/g min1/2
|
0.0002 |
0.0024 |
0.0006 |
Table 3.
Quality parameters of wastewater before and after treatment with MET-MWB.
Table 3.
Quality parameters of wastewater before and after treatment with MET-MWB.
| Parameter |
Initial wastewater |
Treated wastewater |
Maximum permissible value [37] |
| Cu(II), mg/L |
50.83 |
1.25 |
0.2 |
| Zn(II), mg/L |
52.31 |
1.67 |
1.0 |
| Co(II), mg/L |
47.14 |
0.61 |
1.0 |
| pH* |
5.0 |
6.12 |
6.5 – 8.5 |
| CCO, mg O2/L* |
318.43 |
275.14 |
500 |
| Water hardness, ° Ge* |
13.45 |
13.79 |
- |
| Turbidity, NTU* |
11.02 |
7.13 |
- |
| Electrical conductibility, μS/cm* |
1327 |
1219 |
- |