1. Introduction
The Middle East North Africa (MENA) countries experienced high morbidity and mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic, with over 18 million infected and over 750,000 deaths[
1]. The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a significant burden on the health systems of MENA countries that cater to refugees and migrants, leading to inadequate diagnostic testing. This has resulted in refugees and migrants experiencing disproportionate access to COVID-19 testing[
2,
3]. Therefore, it is likely that the number of people infected and deaths due to COVID-19 were higher than reported[
4].
North-West Syria (NWS), with a population of 4.6 million, is one of the world's most politically unstable geographical areas. Nearly 2.9 million people in this area are internally displaced populations (IDPs) due to war. The population faced several challenges in accessing COVID-19 testing services due to deficiencies in the health infrastructure[
5,
6]
. There is minimal scientific evidence about the barriers to COVID-19 testing in this setting[
5]. Studies from neighbouring countries have highlighted that displaced populations face financial burdens and fear of stigma, discrimination and isolation while undergoing the COVID-19 tests[
6]. In addition, the studies indicate that the pandemic was viewed mainly by refugees as “overestimated”, and many have conspiracy beliefs that have affected COVID-19 testing in these populations[
6,
7].
Ag-RDTs are an easier and much cheaper option than molecular reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (rt-PCR) based tests[
8]. Despite being more accurate, rt-PCR tests require more resources and infrastructure [
9]. Nevertheless, Ag-RDTs can have high diagnostic utility in tackling the spread of COVID-19, especially in the first seven days of symptom onset[
10]. Thus, they can be instrumental in settings with limited access to rt-PCR testing.
In this context, the International Organization for Migration (IOM), in collaboration with Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND)[
11] implemented a pilot project for assessing the feasibility of using COVID-19 Antigen Rapid Diagnostic Tests (Ag-RDTs) in NWS. This pilot project aimed to facilitate easy access to COVID-19 testing and to understand the barriers and best practices for diagnostic testing in this displaced population setting. In NWS, the pilot project was implemented in partnership with a local non-governmental organization—Hand in Hand for Aid and Development (HiHFAD)—and involved using 25,000 Ag-RDTs at health facilities, refugee camps, informal tented settlements (ITS) and in outreach settings.
As part of this pilot project, operational research was undertaken to document the experience of implementing Ag-RDTs in NWS. The main objectives were to: a) describe the feasibility of conducting the Ag-RDTs within camps and health facilities; b) describe the uptake of Ag-RDTs from eligible persons; c) describe the yielded results of the Ag-RDTs; and d) identify the enablers and barriers for the use of the Ag RDT tests in these settings from the perspective of the health care workers who were involved in conducting these tests within NWS.
2. Materials and Methods
Study design
The study design was cross-sectional and involved secondary data analysis collected as part of the pilot project's recording, reporting, and monitoring processes.
Study population settings
As of 2023, the population of NWS is estimated to be around 4.6 million people.[
12] . The number of people needing humanitarian assistance in NWS has increased from 3.4 to 4.1 million between 2021 and 2022. Women and children make up 80% of NWS’s population.[
13]. About 2.9 million people in NWS are internally displaced persons (IDPs), and the majority are food insecure, with over 3 million unable to meet basic needs[
12,
13]. In addition, the latest health updates in NWS have stated that there is still a significant increase in daily COVID-19 cases with a limited humanitarian response as of December 2022[
14,
15].
Antigen RDT Project Settings
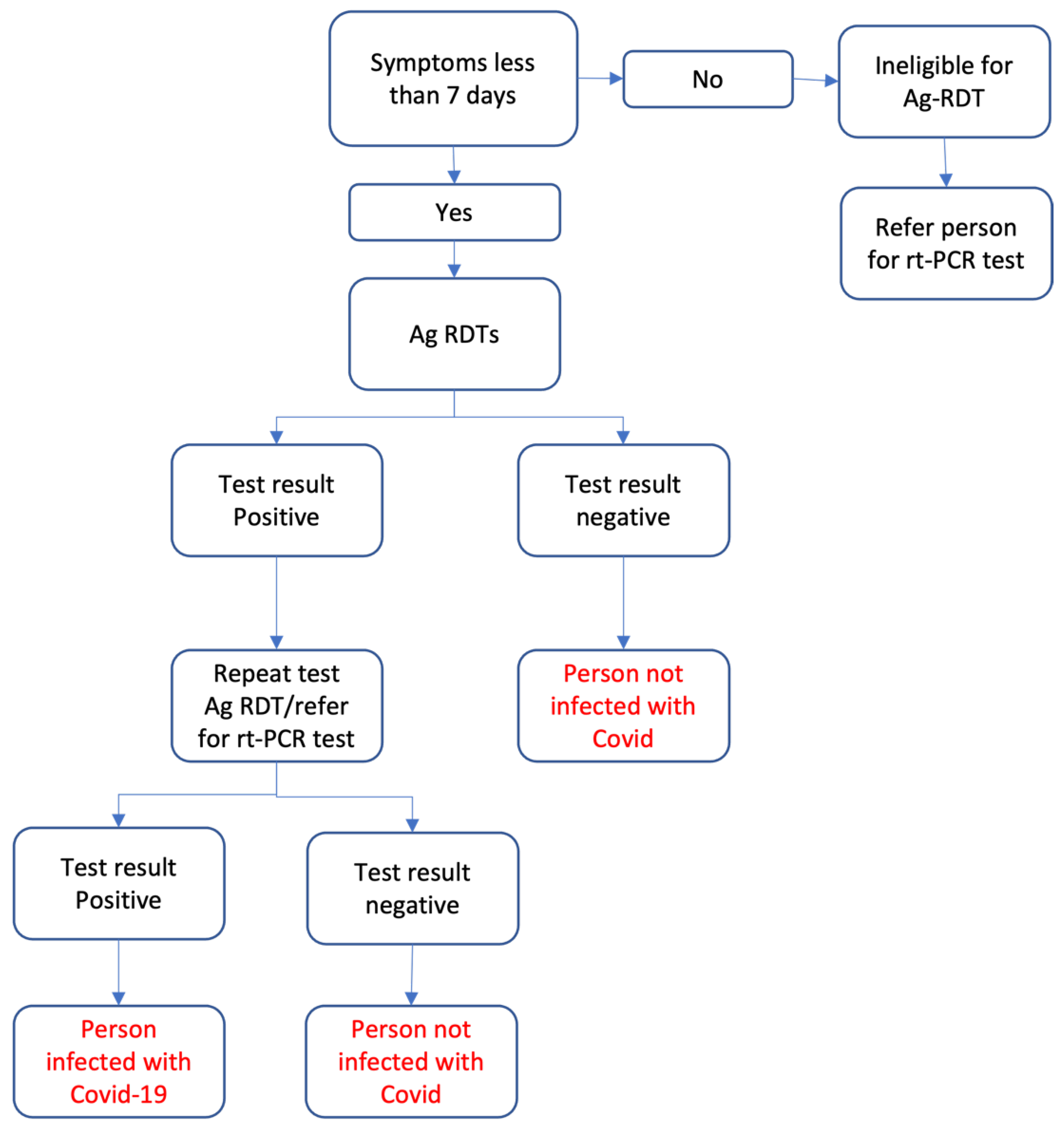
The Ag-RDT project was implemented between September and November 2022 in various camps, mobile clinics, and health facilities in three districts within NWS: Idleb, Afrin and Jarablus/Albab. An implementing partner organization, HiHFAD, was involved in implementing the Ag-RDTs within the districts of NWS. HiHFAD deployed 48 community health workers (CHWs) comprising 50% males and 50% females in 24 teams with additional 4 team leaders to oversee the implementation of 25,000 Ag-RDTs. All CHWs and team leaders underwent a two-day training on how to perform the Ag-RDTs. A context-specific algorithm consistent with WHO recommendations for low prevalence settings, as shown in
Figure 1, was used to interpret the Ag-RDTs results.
Eligibility criteria
The persons from the target communities, who fulfilled any of the following conditions, were offered Ag-RDTs: a) patients presenting with COVID-19 symptoms to health facilities [primary health care centers (PHCs), hospitals and TB centers] within seven days of onset of symptoms; Symptomatic or asymptomatic persons who are: b) contacts of COVID-19 infected persons; c) internally displaced populations in dense areas; d) healthcare workers; e) other individuals who voluntarily sought COVID-19 tests. All persons who met the eligibility criteria were enrolled for Ag-RDT testing, and tests were conducted only when participants gave written consent.
Data recording and reporting
A recording and reporting system was designed to capture the demographic and clinical characteristics of the persons undergoing the Ag-RDT. The data were recorded initially in hard copies (logbooks). They were later entered into an online digital platform created in the KOBO Toolkit® to enable real-time monitoring of the project implementation.
Project supervision
To supervise and monitor the project implementation’s activities, supervisory visits were made by the four project leaders, during which they interacted with both CHWs, and participants involved in performing or undergoing the Ag-RDTs. In addition, a supervisory visit by the project coordinator to the head offices of IOM and HiHFAD in Turkey included interviewing the team leaders and the CHWs to discuss the faced progress and challenges. Detailed field visit reports were prepared and used for undertaking any corrective actions. In addition, the project coordinators also reviewed the data entered by the CHWs into the KOBO application weekly to assess gaps in the implementation, the data entered and provided feedback to address any deficiencies.
Study sample
All persons eligible for the Ag-RDTs, regardless of age, have been included. The pilot project was implemented in NWS between September and November 2022. The pilot project enrolled 27,888 eligible to be offered the Ag-RDTs test.
Data variables
For the first three objectives, the variables included the name of the health facility, date of enrolment, age, gender, presence or absence of symptoms, the reasons for Ag-RDTs testing, vaccination status, response to given consent, the results of Ag-RDTs test results and its date, presence, or absence of risk factors, and finally the results of rt-PCR testing and its date (if the person has undergone this confirmatory test). For the last objective, data gathered during the supervisory visits by the project coordinators were used to obtain information on the facilitators and barriers to the implementation and uptake of Ag-RDTs at the field level.
Data analysis and interpretation
For describing the feasibility, uptake, and results of Ag-RDTs, the data on the demographic and clinical characteristics of the persons enrolled, those who consented to undergo the tests, and those with positive and negative test results were summarized as frequencies and percentages using R and R studio statistical software. Inferences on feasibility are based on the ease with which the CHWs could conduct the tests correctly in different health facilities and geographical areas as per the designed algorithm. These assumptions were based on the verbal confirmation of CHWs and were documented in the supervisory visits. Furthermore, inferences on the uptake of Ag-RDTs have been assessed by the number and proportion of eligible persons who gave consent to undergo the tests. Finally, for identifying the enablers and barriers to Ag-RDTs testing, we provided a narrative table of the lessons learnt and challenges encountered by CHWs in implementing the project as determined by the project coordinators.
Ethical issues
This project was implemented after obtaining administrative approval from the Turkish directorates (Hatay and Gaziantep) responsible for implementing all health activities within NWS. Ethics approval was obtained from the IRB committee board of Rayak Hospital in Lebanon with a reference code: “ECO-R-35”. Confidentiality of the data taken from the pilot project’s recording system has been maintained. Consent was taken from all persons before the tests and for using their data for operational research. No names or identifying information of any person has been used in the analysis. Only aggregate data is being used to disseminate the study's results to all stakeholders.
3. Results
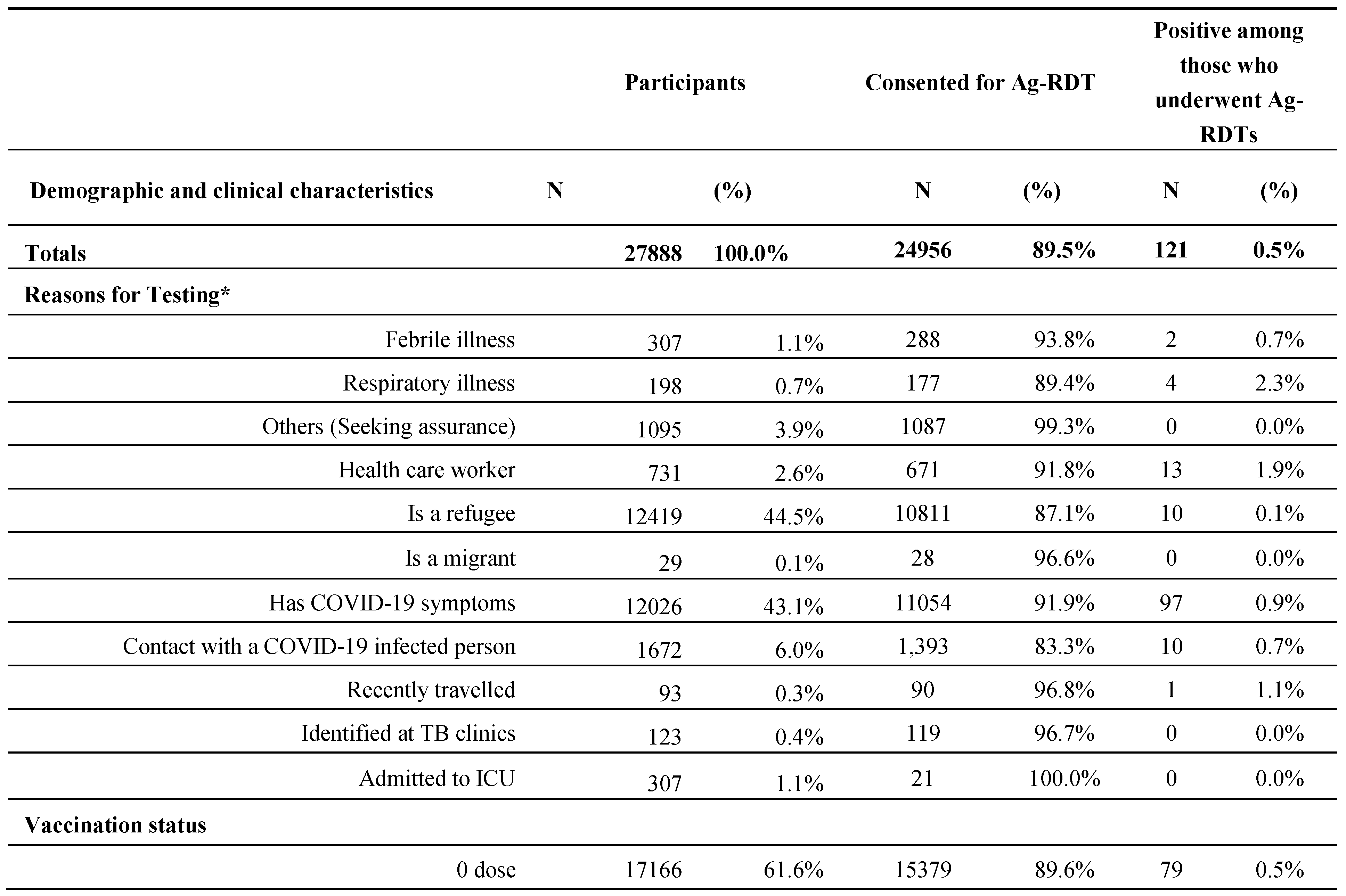
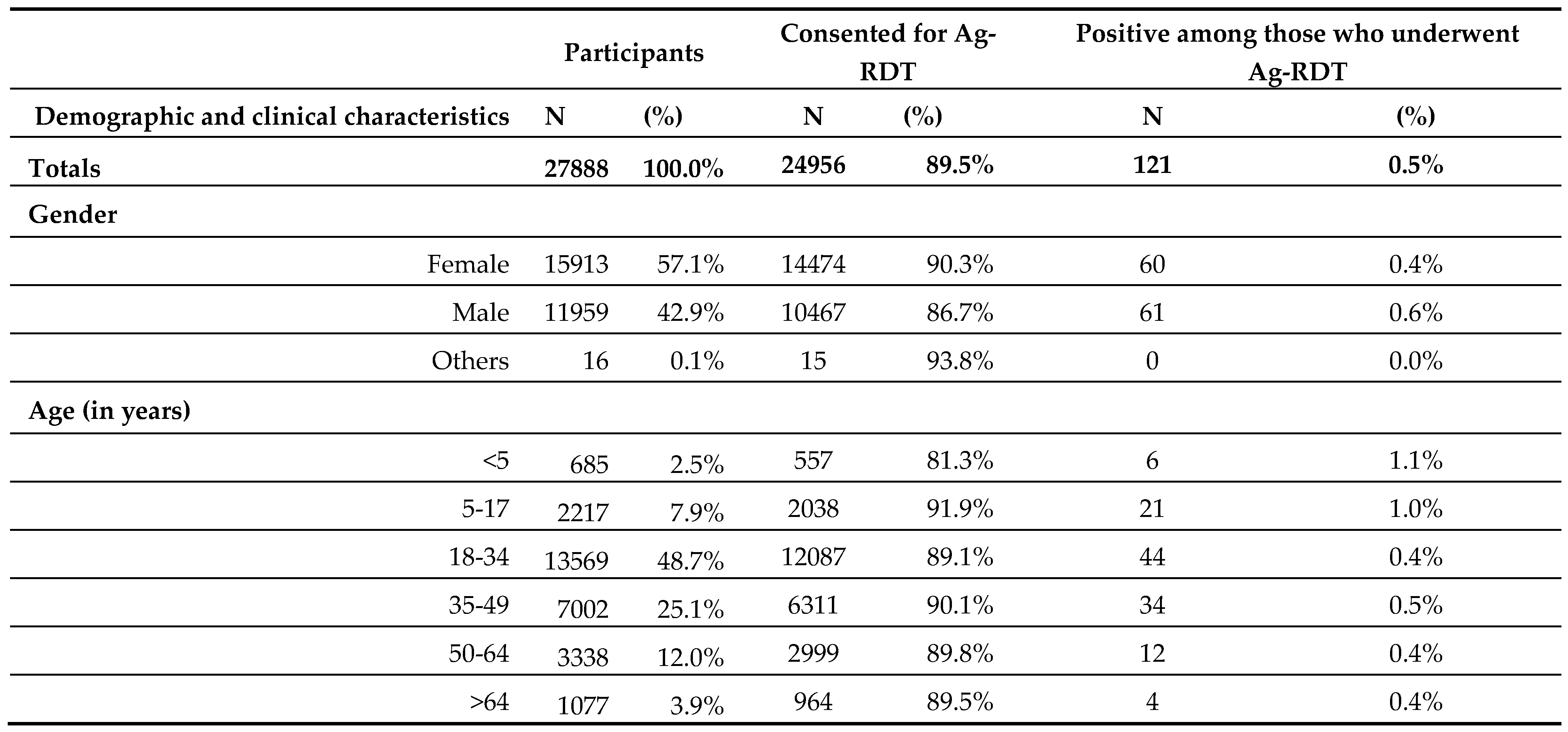
Between September and early November 2022, 27,888 persons were found eligible to enrol on the project and were offered Ag-RDTs. The demographic and clinical characteristics of all enrolled participants, those who consented, and their Ag-RDTs’ positivity rates are represented and were segregated by Gender and Age Group (
Table 1), Reason for Testing, Vaccination Status, Duration, and Severity of Symptoms (
Table 2), and by Testing Facility (
Table 3).
Overall, 24956 (89.5%) people have consented to undergo the test from the total 27,888 enrolled including 121 (0.5%) positive Ag-RDTs results.
The study population consisted of more females (57.1%) than males (42.9%), and approximately 74% were between the ages of 18 and 49. The consent to testing was relatively lower (86.7%) among males.
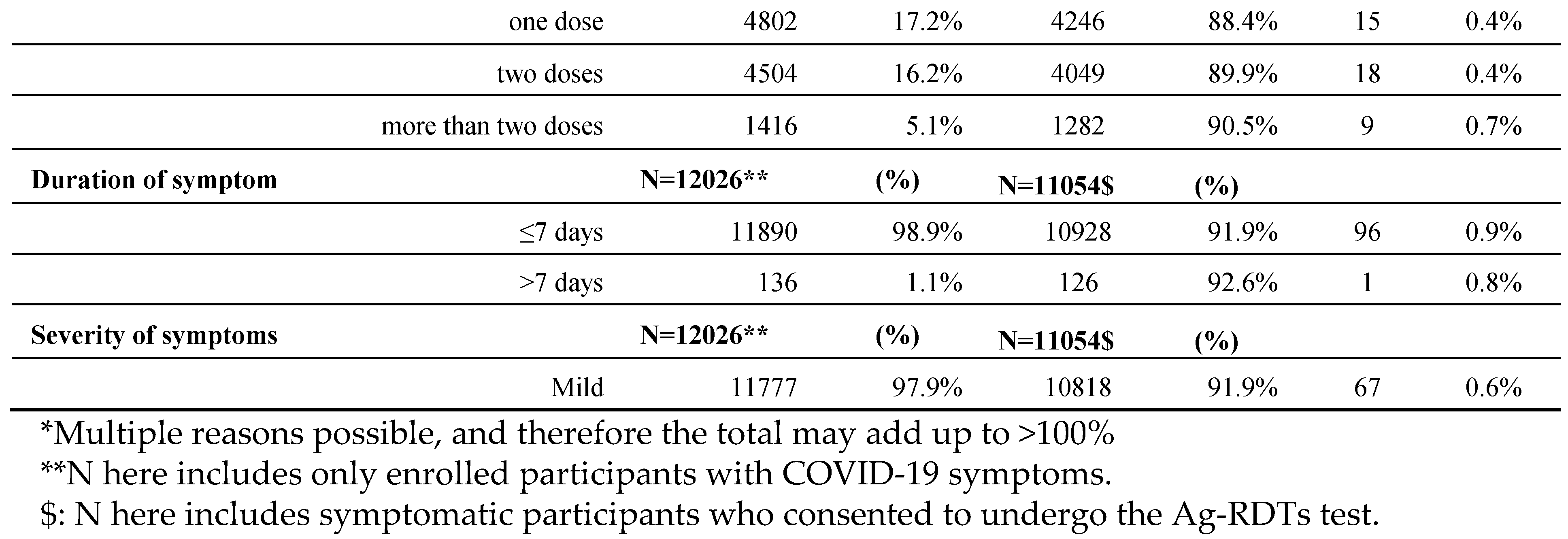
Table 2.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of people enrolled, consented for Ag-RDTs, and their positivity rates in a pilot project in NWS, segregated by Reasons for Testing, vaccination status, Duration and Severity of Symptoms.
Table 2.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of people enrolled, consented for Ag-RDTs, and their positivity rates in a pilot project in NWS, segregated by Reasons for Testing, vaccination status, Duration and Severity of Symptoms.
The main reasons for testing at the enrolment stage were being a refugee (44.5%) living within a high population dense area followed by having COVID-19 symptoms (43%). The highest positivity in those consented to test was observed among those with severe COVID-19 symptoms (12.7%), those with respiratory illnesses (2.5%), followed by healthcare workers (1.9%).
Among those who reported COVID-19 symptoms (N=12026), 98.9% reported the onset of symptoms within seven days or less, with 97.9% having mild symptoms.
About 61.6% of participants had not received a single dose of any COVID-19 vaccine.
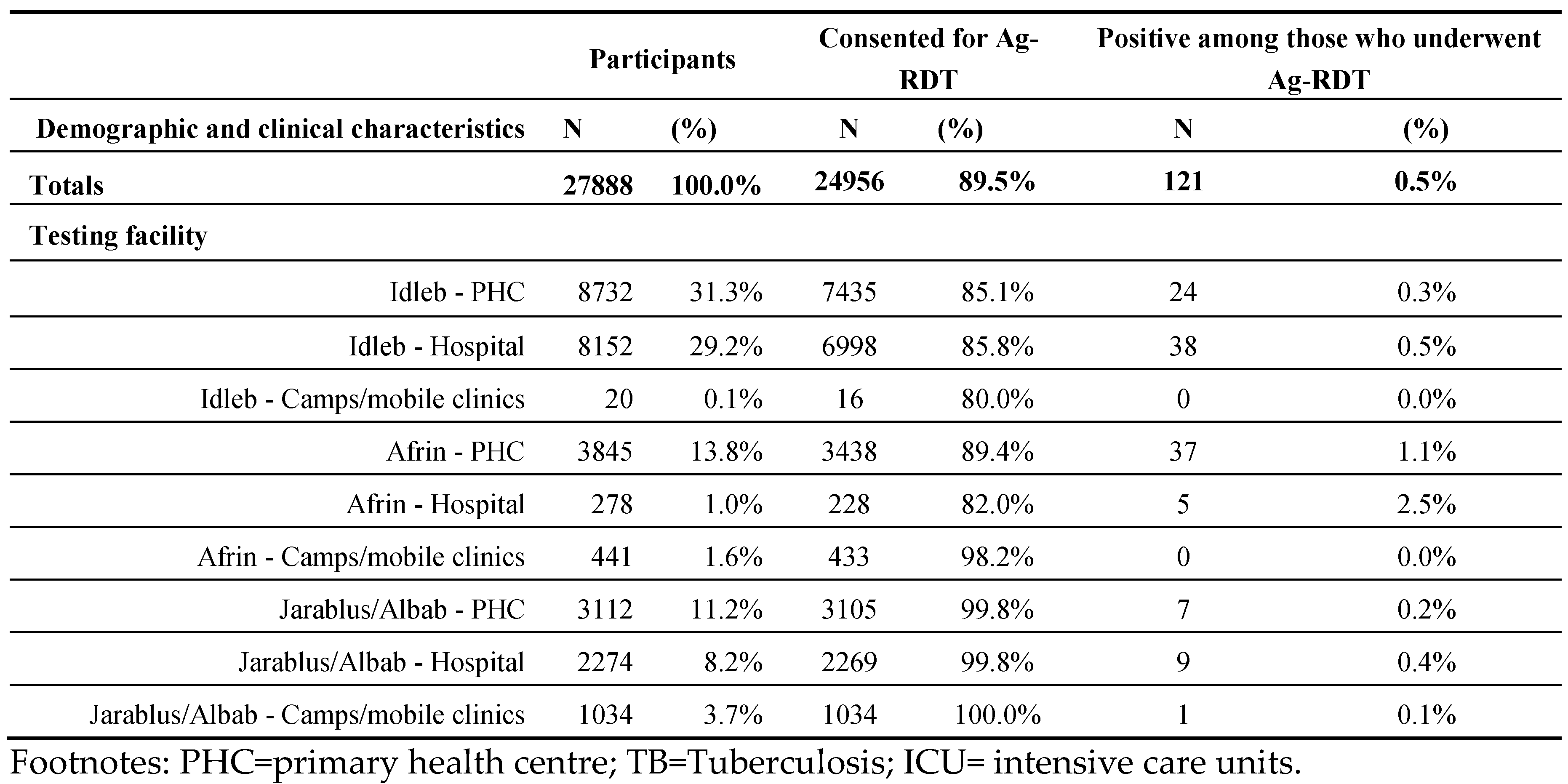
Table 3.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of people enrolled, consented for Ag-RDTs, and their positivity rates in a pilot project in NWS, segregated by Testing Facility.
Table 3.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of people enrolled, consented for Ag-RDTs, and their positivity rates in a pilot project in NWS, segregated by Testing Facility.
The majority (86.0%) of enrolments occurred at health facilities. The positivity rate among those consented to testing was highest at Afrin Hospitals (2.5%).
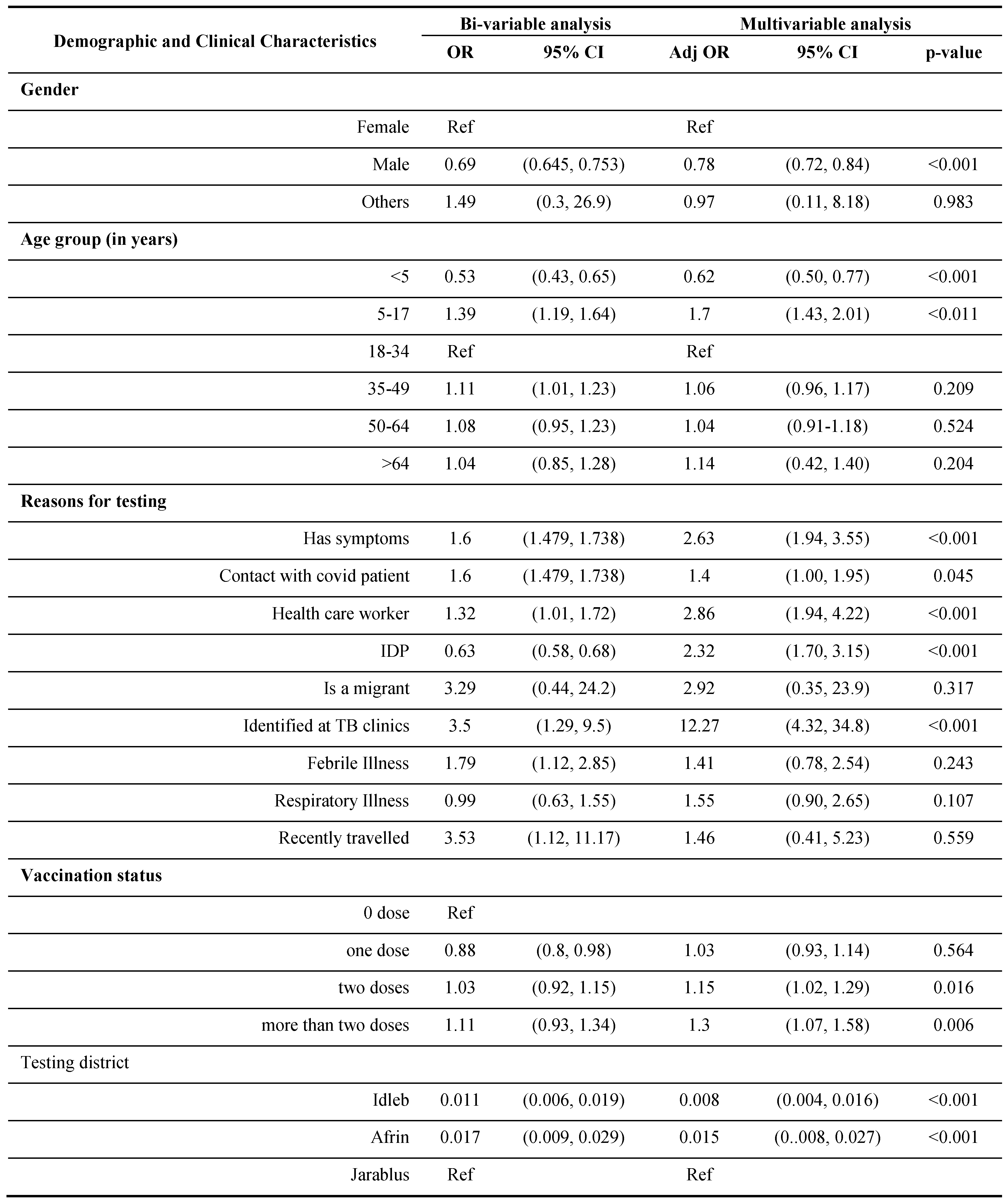
The demographic and clinical characteristics associated with those who consented to undergo the Ag-RDT tests are given in
Table 4. In the bivariate analysis, males were less likely than females to consent to undergo Ag-RDT. Participants aged 5 to 17 were 1.35 times more likely to consent to the Ag-RDT than those aged 18 to 34. Most participants with a reason for testing, such as COVID-19-like symptoms, contacts with a confirmed covid patient, or recent travel, were more likely to agree to undergo RDTs than those without reason. However, participants’ willingness to take the Ag-RDTs was significantly lower for IDPs in Northwest Syria than non-IDPs. Participants with severe COVID-19-like symptoms were 1.6 times more likely to agree to use Ag-RDTs than those with mild symptoms. Consent rates were highest at Jarablus facilities, while participants from Idlib and Afrin health facilities and PHCs were less likely to consent to Ag-RDTs than at Jarablus.
In the multivariate analysis, gender remained a significant predictor of consenting to the Ag-RDTs after considering potential confounders [OR= 0.69, 95% CI (0.645, 0.753)]. After controlling for confounders, we observed that younger ages (below 18 years old) are significantly associated with more chance to consent for taking Ag-RDTs compared to those aged 18-34 years. Health workers, refugees, and symptomatic individuals are more likely to agree to Ag-RDTs than others. A significant predictor of giving Ag-RDTs consent is the severity of symptoms, as they were 2.3 times more likely to consent for Ag-RDTs than people with mild symptoms.
Of those who underwent the Ag-RDTs, a non-random sample of 239 persons also underwent rt-PCR tests (
Table 5). This included 72 of the 121 persons (59.5%) with positive Ag-RDT test results and 166 (6.7%) of the 24,811 persons with negative Ag-RDT test results.
Of those who underwent the confirmatory rt-PCR test (n=239), the project team could not collect/receive information about the rt-PCR test results of 3 persons. Therefore, excluding these persons, a total of 236 persons had both Ag-RDTs and rt-PCR test results, as shown in
Table 5. From this data of 236 persons, the observed sensitivity of Ag-RDTs was 80.0% [(95% CI: (71.2% to 88.7%)] (64/80), specificity was 96.1% [95% CI (93%-99%)] (149/155), positive predictive value was 91.4% [95% CI (84.8%-97.9%)] (64/70) and negative predictive value was 90.3% [95%CI (85.7%- 94.8%)] (149/165).
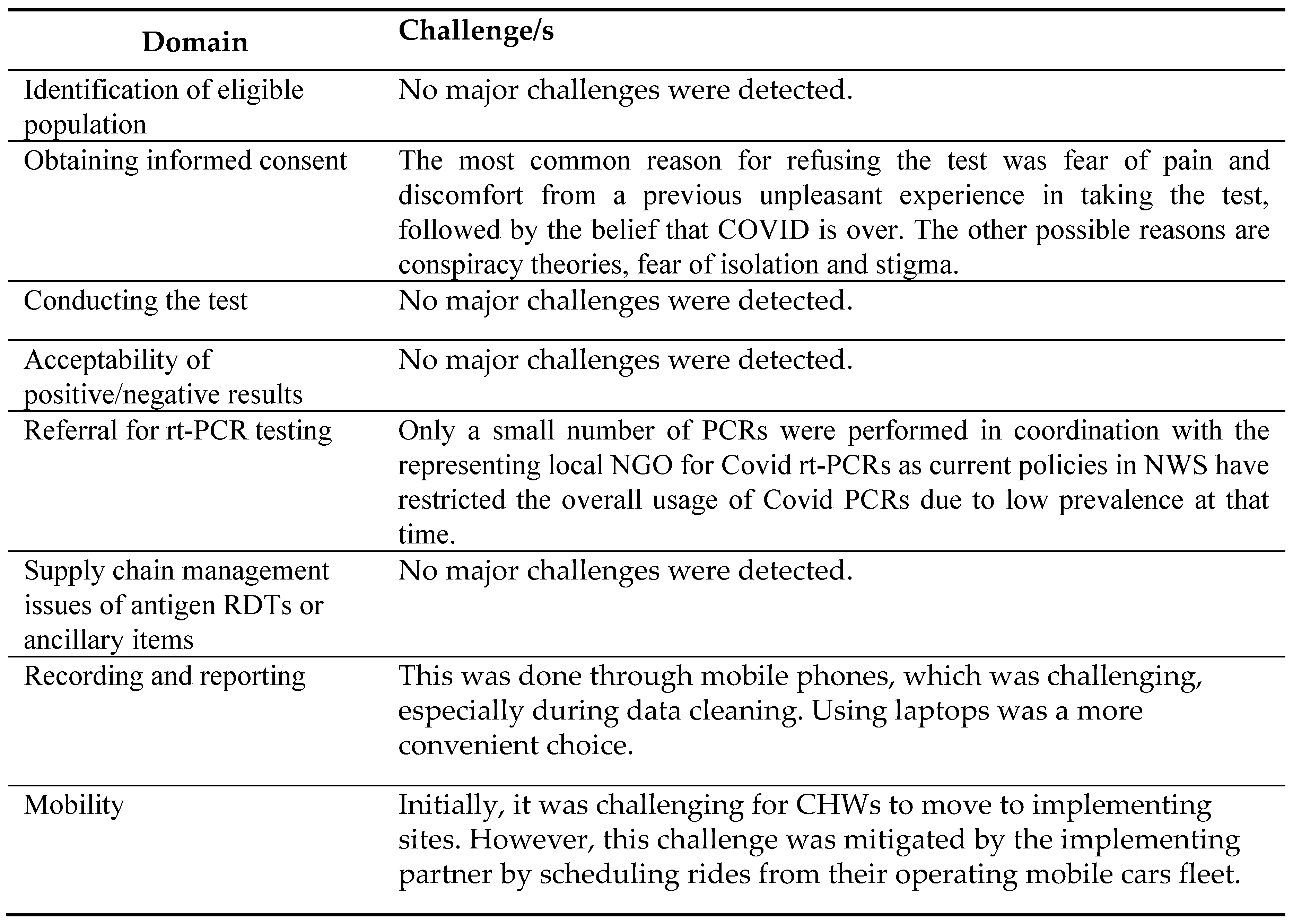
The reported challenges and facilitators encountered during project implementation are listed in
Table 6 and
Table 7. The key challenges were obtaining informed consent, referral for confirmatory rt-PCR testing and recording and reporting the data under the project.
4. Discussion
This is one of the first studies from NWS describing the use of COVID-19 Ag-RDTs in a piloting project. The study showed the following.
First, people eligible for Ag-RDTs testing were reached out to fulfil the project’s Ag-RDTs targeted quota within a very short 2-month implementation period. The wide variations seen in the numbers enrolled at the nine different sites are due to the differences in the population distribution in these geographical areas. The enrollment at PHCs and hospitals was higher than at the camps/mobile clinics since all health facilities and hospitals in NWS are distributed inside the camps. As reported by the implementing partner, only a few camps lack these facilities. All the selected nine facilities had successfully deployed all their Ag-RDTs, indicating good feasibility of using these tests at all sites within NWS through CHWs. Also, interviewing the CHWs during supervisory visits did not reveal any major challenges in performing/deploying these tests, adding to the global evidence on the feasibility of rapid deployment of Ag-RDTs to inform necessary control and care measures in all settings[
16,
17]
Second, the uptake of Ag-RDTs was nearly 90%. This was mainly due to the positive communication by the CHWs about the advantages and need for undergoing Ag-RDTs to ensure there is no break in COVID-19 surveillance. This communication enabled positive perceptions about the Ag-RDTs and facilitated their uptake. The uptake was relatively higher among those with COVID-19 symptoms, healthcare workers, refugees, those who had received more than two or more doses of vaccination, and those identified at TB clinics. Previous studies show good overall uptake of Ag-RDTs from different populations, especially among symptomatic[
18,
19]. The reasons for the lower uptake of Ag-RDTs among those aged less than 18 years and among those identified at Idleb and Afrin districts could not be identified through CHWs interviews in the supervisory visits. This is an area that needs further investigation through qualitative research methods.
Third, the overall positivity rate within our sample was very low (0.5%), indicating low infection prevalence levels at the community level. The highest positivity was observed among those with severe COVID-19 symptoms (12.7%), those with respiratory illnesses (2.5%), and participants enrolled at Afrin Hospitals (2.5%), followed by healthcare workers (1.9%). These findings, on the one hand, indicate the high-risk groups who should be targeted for COVID-19 testing in these low prevalence/transmission settings. On the other hand, these findings also suggest that some geographical regions/pockets with persisting COVID-19 infection can flare up COVID-19 transmission if there is a new mutant of the virus. Therefore, continuous surveillance will be needed. The data on positivity rates among different participants’ characteristics can play an essential role in surveillance activities, especially to screen-in and diagnose COVID-19 infection in these high-risk groups.
Fourth, a formal assessment of the sensitivity and specificity of the Ag-RDTs at the field level could not be done due to challenges in identifying an academic partner in this setting. Nevertheless, we could estimate sensitivity and specificity in a non-random sample of persons undergoing Ag-RDTs and rt-PCR tests. The observed sensitivity of 80.0% (95% CI: 71.2% to 88.7%)], specificity of 96.1% [95% CI (93%-99%)], the positive predictive value of 91.4% [95% CI (84.8%-97.9%)] (64/70) and negative predictive value of 90.3% [95%CI (85.7%- 94.8%)] (149/165) observed in this study were in line with other studies reviewing the accuracy of the same Ag-RDTs type as used in our pilot project[
20,
21]. The relatively less observed sensitivity and negative predictive values in this pilot project than the manufacturer-reported values could be due to the quality of the nasopharyngeal samples collected and the appropriate processing of collected samples and reagents in the test kits [
22,
23,
24,
25,
26].
Such deficiencies must be identified and rectified through training and supportive supervision in future projects. In addition, considering the high specificity (96.1%) and good negative predictive value (90.3%), screening-out persons as free of COVID-19 based on the Ag-RDTs results would be a reasonable approach in this setting whether a confirmatory PCR test followed it or not.
Fifth, Confirmatory rt-PCR tests could be conducted (per the algorithm) in only 60% of those with positive Ag-RDT tests. This indicates operational challenges in following the complete algorithm needed for optimal deployment of Ag-RDTs. This observation was similarly observed in other related studies evaluating Ag-RDTs implementation [
27,
28]. Therefore, there is a need to enhance both the capacity and accessibility of rt-PCR within the health system catering to these populations. If not, the clinical and public health actions on COVID-19 infection/transmission will have to be based on Ag-RDTs alone.
Finally, 61.6% of our sample have reported they did not receive a single COVID-19 vaccine dose. The reported percentage of people in NWS who have not received a single COVID-19 vaccine dose during our implementation period as per the WHO was 86.4%[
29] showing significant global inequities in vaccination coverage in these populations.
Strengths and limitations
The major strength of this study is that it was done using data from the pilot project implemented under routine programmatic conditions using the existing health service delivery mechanisms. Therefore, the study findings on feasibility, uptake, Ag-RDT performance and positivity rates likely reflect ground-level realities. The study's major limitations are: First, the project was conducted in a low prevalence/transmission setting. Therefore, the results may not be replicable if there is a flare in the COVID-19 prevalence. Second, the implementation challenges and facilitators' data were collected during routine supervision visits. As a result, the information provided by CHWs may be biased if they have failed or were uncomfortable reporting any critical issues to their supervisors. Third, due to challenges/restrictions in meeting the community members, their perspectives about the feasibility and acceptability of Ag-RDTs could not be fully captured. This is an area for future research.
5. Conclusions
This pilot project in NWS demonstrated that using Ag-RDTs as a screening/diagnostic tool through CHWs for COVID-19 infections is feasible. The data on uptake and positivity rates indicates that Ag-RDTs can be targeted to health facilities, people with respiratory, febrile, or COVID-19 symptoms, contacts of COVID-19 patients and health workers. The project also highlights the need for a thorough strategy to independently use Ag-RDTs results in screening in/out of COVID-19 infections among refugees and IDP settings. Finally, continuous surveillance and enhancement of COVID-19 vaccination coverage are needed.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Document S1: Written Consent Form – English (Arabic Translation is Available).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Nevin Wilson, Sanjay Sarin, Kekeletso Kao; Methodology, Nevin Wilson, Srinath Satyanarayana, Laila Tomeh, Hassan Ghawji, Hussam Alkhellov and Sali Hasan; Data Curation, Hassan Ghawji, Mohamad Nihad Alyousfi; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, Hassan Ghawji, Mohamad Nihad Alyousfi and Srinath Satyanarayana; Writing – Review & Editing, Hassan Ghawji, Srinath Satyanarayana, Mohammad Nihad, Alyousfi, Laila Tomeh, Hussam Alkhellov, Sali Hasan, Sanjay Sarin, Kekeletso Kao and Nevin Wilson; Supervision, Nevin Wilson, Hassan, Ghawji, Srinath Satyanarayana Hussam Alkhellov and Sali Hasan; Funding Acquisition, Sanjay Sarin and Kekeletso Kao.
Funding
This project was funded by the Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND) to IOM with an agreement and IOM number ID: [JO10P0520/MP.0308]. Article processing charges are also funded by [FIND].
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Rayak Hospital – Institutional Review Board in Lebanon (Ref.: ECO-R-35) on 13 March 2023.
Informed Consent Statement
All subjects gave their written informed consent for inclusion in the Ag-RDTs project.
Data Availability Statement
The clean set of raw data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author in MS Excel. The data are not publicly available due to data protection and privacy policies following the UN Migration Agency (IOM) standards.
Acknowledgments
Grace Javier and Noor ABZADOUGH, project administration, Christopher TOGARA, procurement and supply management, Nick BANKS, Information Technology, FIND, HiHFAD and All CHWs.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Bank. MENA-Crisis-Tracker-2-7-2022. Office of the Chief Economist. 2022. Available: chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://thedocs.worldbank.org/en/doc/a32a611d09ad47947f154d81c635b658-0280032022/original/MENA-Crisis-Tracker-2-7-2022.
- Karamouzian M, Madani N. COVID-19 response in the Middle East and north Africa: challenges and paths forward. Lancet Glob Health 2020, 8, e886–e887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores G, Abbasi A, Korachais C, Lavado R. Unaffordability of COVID-19 tests: assessing age-related inequalities in 83 countries. Int J Equity Health 2022, 21, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 4. Esposito A, Palmisano A, Scotti GM, Morelli MJ, Vignale D, Cobelli F de, et al. Why is chest CT important for early diagnosis of COVID-19? Prevalence matters. medRxiv. 2004. [CrossRef]
- Ly TDA, Nguyen NN, Hoang VT, Goumballa N, Louni M, Canard N, et al. Screening of SARS-CoV-2 among homeless people, asylum-seekers and other people living in precarious conditions in Marseille, France, March-April 2020. Int J Infect Dis 2021, 105, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Kheirallah KA, Ababneh BF, Bendak H, Alsuwaidi AR, Elbarazi I. Exploring the Mental, Social, and Lifestyle Effects of a Positive COVID-19 Infection on Syrian Refugees in Jordan: A Qualitative Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19, 12588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marc Lynch. (PDF) COVID-19: Lebanon’s Experience and Response. In: POMEPS Studies [Internet]. 2020 [cited 7 Jan 2023]. Available: https://www.researchgate. 3408.
- Peeling RW, Heymann DL. Innovations in COVID-19 testing: the road from pandemic response to control. Lancet Infect Dis 2021, 21, 1334–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeling RW, Heymann DL, Teo YY, Garcia PJ. Diagnostics for COVID-19: moving from pandemic response to control. The Lancet 2022, 399, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brümmer LE, Katzenschlager S, Gaeddert M, Erdmann C, Schmitz S, Bota M, et al. Accuracy of novel antigen rapid diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2: A living systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Medicine. Public Library of Science; 2021. [CrossRef]
- Foundation of Innovative New Diagnostics. FIND | Diagnosis for all. 2023 [cited 23 Jan 2023]. Available: https://www.finddx.
- UNOCHA. North-west Syria | Situation Reports. 2023 [cited 23 Jan 2023]. Available: https://reports.unocha.org/en/country/syria/.
- ARCS. Statement on the Continuation of UN-Led Cross-Border Humanitarian Assistance in Northwest Syria | American Relief Coalition for Syria. 2023 [cited 23 Jan 2023]. Available: https://arcsyria.org/article/statement-continuation-un-led-cross-border-humanitarian-assistancenorthwest-syria.
- Alanba A-K. ارتفاع يومي بإصابات الكوليرا وكورونا شمال. 23 Dec 2022. Available: https://www.alanba.com.kw/1160966. Accessed 7 Jan 2023.
- OCHA. COVID-19 Monthly Update Northwest Syria (As of ) - Syrian Arab Republic | ReliefWeb. 2022 [cited 13 Apr 2023]. Available: https://reliefweb.int/report/syrian-arab-republic/covid-19-monthly-update-northwest-syria-31-december-2022. 31 December 2022.
- Lindner AK, Nikolai O, Rohardt C, Kausch F, Wintel M, Gertler M, et al. Diagnostic accuracy and feasibility of patient self-testing with a SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid test. Journal of Clinical Virology 2021, 141, 104874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Use of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detection rapid diagnostic tests for COVID-19 self-testing. 2022.
- Vink M, Iglói Z, Fanoy EB, van Beek J, Boelsums T, de Graaf M, et al. Community-based SARS-CoV-2 testing in low-income neighbourhoods in Rotterdam: Results from a pilot study. J Glob Health 2022, 12, 05042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finch LS, Harris A, Lester C, Veal D, Jones K, Fulton J, et al. Implementation study of SARS-CoV-2 antigen lateral flow tests in men’s professional (Premiership) rugby union sports squads in England during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Infection 2022, 84, e3–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger LJ, Lindner AK, Gaeddert M, Tobian F, Klein J, Steinke S, et al. A Multicenter Clinical Diagnostic Accuracy Study of SureStatus, an Affordable, WHO Emergency Use-Listed, Rapid, Point-Of-Care Antigen-Detecting Diagnostic Test for SARS-CoV-2. [cited 13 Mar 2023]. [CrossRef]
- Cubas Atienzar AI, Byrne RL, Aljayyoussi G, Kontogianni K, Clerkin K, McIntyre M, et al. Head-to head comparison of anterior nares and nasopharyngeal swabs for SARS-CoV-2 1 antigen detection in a community drive-through test centre in the UK Running title: Anterior nares or NP swabs for SARS-CoV-2 RDTs. [cited 13 Mar 2023]. [CrossRef]
- Baro B, Rodo P, Ouchi D, Bordoy AE, Saya Amaro EN, Salsench S v. , et al. Performance characteristics of five antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic test (Ag-RDT) for SARS-CoV-2 asymptomatic infection: a head-to-ead benchmark comparison. Journal of Infection 2021, 82, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- la Scola B, le Bideau M, Andreani J, Hoang VT, Grimaldier C, Colson P, et al. Viral RNA load as determined by cell culture as a management tool for discharge of SARS-CoV-2 patients from infectious disease wards. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 2020, 39, 1059–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wölfel R, Corman VM, Guggemos W, Seilmaier M, Zange S, Müller MA, et al. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 2020, 581, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 25. Quicke K, Gallichotte E, Sexton N, Young M, Janich A, Gahm G, et al. Longitudinal Surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 RNA Among Asymptomatic Staff in Five Colorado Skilled Nursing Facilities: Epidemiologic, Virologic and Sequence Analysis. medRxiv. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Mina MJ, Parker R, Larremore DB. Rethinking Covid-19 Test Sensitivity — A Strategy for Containment. New England Journal of Medicine 2020, 383, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachinger J, Olaru ID, Horner S, Schnitzler P, Heeg K, Denkinger CM. The potential of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detection tests in the screening of asymptomatic persons. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2021, 27, e1–e1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagna AS, Seydi AG, Gueye MM, Fall MTA, Mansuy JM. Contribution of COVID Antigenic RDT to the Management Strategy of COVID-19 Pandemic in a Senegalese Company. J Occup Environ Med 2022, 64, e257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Monthly COVID-19 Bulletin October 2022. 2022. Available: https://www.emro.who.int/pandemic-epidemic-.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).