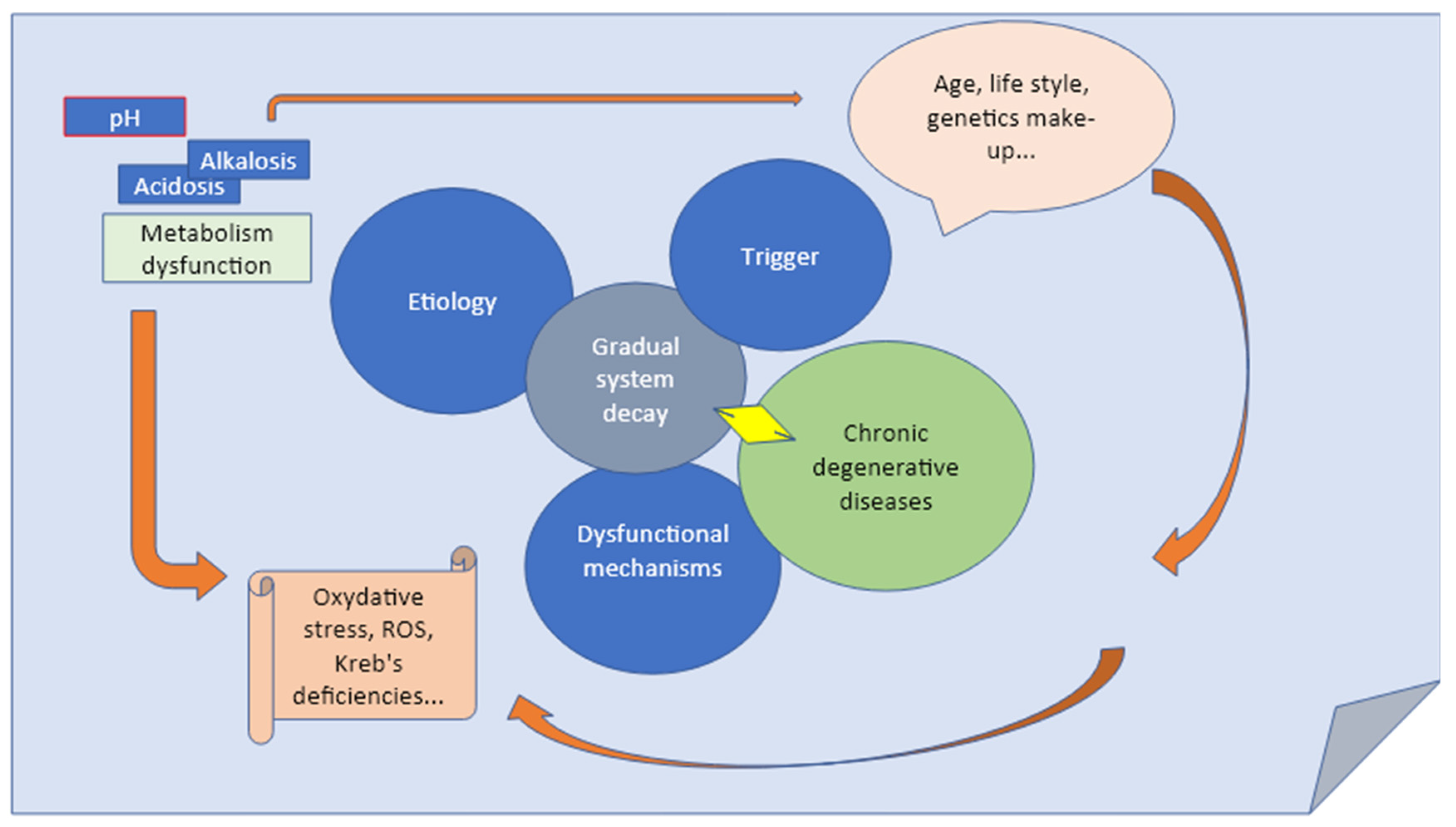
1. Introduction
Low oxygen levels and impaired alveolar gas exchange may be suggestive of disease or disorder that has nothing to do with lungs functionality. The acid-base disease ABDs indicate a wide group of diseases that are encountered in critically chronic metabolic condition such as chronic kidney disease (CKD), diabetes, chronic respiratory failure (COPD) and chronic heart failure. There are four simple ABDs generally indicated as: (1) Metabolic acidosis, (2) respiratory acidosis, (3) metabolic alkalosis, and (4) respiratory alkalosis. The use of ABG analysis in all these cases revealed to be a highly precise tool in diagnosis and prognosis including the typology of disorders evaluated as single or primary disorder or mixed ABDs [
1].
The ABD may be of simple or primary type with a secondary compensatory response or may be of mixed type- occurrence of two or more independently existing primary ABDs in the same patient [
1,
2]. Nevertheless, the laboratory diagnosis should always need the comparative data from clinical details. The cause of individual acidemia or alkalaemia should be explored in each single case that allow to unveil a complete picture made of complications and co-morbidities leading to a proper condition management [
1,
2].
Complex or mixed acid-base disturbances involve more than one primary process. In these mixed disorders, values may be deceptively normal or between the normal ranges for years to the point the system can not compensate anymore [
3,
4,
5]. Thus, when evaluating acid-base disorders, it is important to determine whether changes in PCO2 and HCO3− may eventually indicate an expected compensation or it may suggestive of unnoticed, minimal fluctuation which tend accumulating over the time and deteriorating with the age building up the final disease (Fig.1) [
5]. If not, second primary process should be suspected of causing the abnormal compensation. The overall interpretation must thus consider the clinical conditions as direct consequence of disturbed compensatory mechanism (eg, chronic lung disease, in chronic renal failure, osteoporosis, osteopenia, arthritis...) [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7].
Figure 1.
Acid/base disorders are classified according to their cause, and pH change, into respiratory acidosis, metabolic acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, or metabolic alkalosis. Any deviation of the acid/base balance requires compensatory changes in an attempt to restore homeostasis. For instance, acidosis due to respiratory and metabolic failure lead to compensatory renal and skeleton changes, which lead to increased reclamation of HCO3 and Ca++.
Figure 1.
Acid/base disorders are classified according to their cause, and pH change, into respiratory acidosis, metabolic acidosis, respiratory alkalosis, or metabolic alkalosis. Any deviation of the acid/base balance requires compensatory changes in an attempt to restore homeostasis. For instance, acidosis due to respiratory and metabolic failure lead to compensatory renal and skeleton changes, which lead to increased reclamation of HCO3 and Ca++.
A steady well-balanced acid-base level is based on the assonance between all acid produced equal to all acid excreted. The renal, skeleton and lungs are key actors in the clearance of acid anions by replacing with anion base and bicarbonates; the whole process takes place on multiple level in order to reach the the systemic acid/base equilibrium, in which is reached the full reabsorption of filtered bicarbonate and the formation of a buffered urine with ammonia produced by the kidney and excreted as ammonium, with filtered phosphate and chloride. The alveolar ventilation works using a similar mechanism to reach the full carbon dioxide clearance to avoid respiratory disorders and acids overloading. Equally, though trough different mechanisms the long-term level bicarbonate concentration is constantly monitored and performed by the skeleton. In fact, the skeleton starts decaying following the persistent net acid retention and bicarbonate loss from bone mineral breakdown to keep tissues and organs acid/base in constant balance [
7,
8,
9].
The body's response to the hypoxaemic state, is characterized by an increase in minute ventilation that may drive to either an unrestrainable hypocapnia or hypercapnia (acidosis or alkalosis respectively), as the CO
2 diffuses through tissues about 20 times faster than O
2. Though the pathoanatomical and pathophysiological basis of ABG validity in assessing long-term systemic deficits still have to be fully clarify, the presence of progressive and damages remain the key point [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13].
Our team proved this in the COVID-19 pandemic during the year 2021-2022. The first period of the pandemic was very particular as a large number of patients were admitted manifesting only mild symptoms to get unexpectedly worsened only a few times later with clear signs of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Most of these patients were necessarily hospitalized, some of them deceased, all of them were affected by pre-existing metabolic diseases such as diabetes, overweight and hypertension.
Thus, the perception that acid base imbalance in metabolic disorders are only confined to metabolic acidosis was challenged by our results. In fact, the most common observed disturbances were suggestive of acid-base balance mixed disorders that were present in the almost totality of the admitted patients. The ABG parameters together with patients’ clinical history and symptoms were extremely useful in depicting the SARS-CoV-2 infection and its progression. The obtained results indicated that the majority of tested individuals (33 patients out of 46) were confirmed to be affected by COVID-19. COVID-19 affected patients revealed a quite unusual scenario made of respiratory disturbance predominantly characterized by alkalosis accompanied by hypocapnia (during the early phase of the infection) followed by hypercapnia (during the late stage of infection) and hypoxia (pH > 7.45; low PaO2 <75; low PaCO2 < 35). These patients were those who showed to be positive either to RT-PCR or thoracic CT-scan that confirmed a bilateral interstitial pneumonia characterized by ground glass opacities (46 patients out of 46) later on; whereas only a few patients suffered from respiratory acidosis, exactly those ones resulted negative to both RT-PCR and thoracic CT scan [
13,
14].
Why medium/severe COVID-19 patients suffered from respiratory alkalosis rather than acidosis it is something that has probably been associated with the hyperventilation mode, which evolves from hypoxemic causes, pulmonary diseases, and central diseases. In lung diseases, hypoxic stimulation usually causes hyperventilation in trying to resolve a hypoxic state at the expense of CO2 loss [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20]. Similarly in COVID-19, despite the fact that some patients did not exhibit severe external hypoxic signs, the ABG analysis was able to show a respiratory alkalosis, considered as a transient compensatory hyperventilation effort that without any prompt medical intervention often worsened in a matter of few hours.
Therefore, since respiratory alkalosis is caused mostly by hypoxia-induced hyperventilation, while respiratory acidosis is caused by hypercapnic respiratory failure, these two ABG markers were the main indicators (in the absence of RT-PCR and CT scan) of the two phases of SARS -CoV-2 infection, the early and the late phases often narrowly close to each other (table 1) [
17,
18,
19,
20].
Of note, the ABG analysis was also a life safer tool also in those cases found with COVID-19 symptoms albeit negative to RT-PCR. This variant defined later COVID-like infection, showed same clinical signs with look-like COVID-19 ABG’s parameters, accompanied by typical bilateral lung pneumoniae. Both forms, COVID-19 and COVID-like, were thus considered clinically as same respiratory disease with multi-organ involvement and unpredictable disease progression characterized by sudden worsening clinical manifestation and unexpected death [
13,
14].
Table 1.
the 118 ABG adopted procedure during COVID-19 pandemic.
Table 1.
the 118 ABG adopted procedure during COVID-19 pandemic.
2. Extracellular Acidosis and the Immunity, Clinical and Physiologic Implications
It widely accepted that metabolic acidosis works as the fertile soil of most physical, bone, nerves and mental degenerative diseases, the main traits of which are deficits in the cellular respiration mechanism. The degenerative patterns are observed with chronic inflammatory processes, and food intolerances, high toxic loading linked with active presence of opportunist micro-organism and heavy systemic dysbiosis [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18].
Metabolic acidosis is a silent progressive condition. During a long-term metabolic acidosis, the urine calcium excretion is continuously present without a compensatory phase managed by intestines via calcium absorption with a consequent net loss of bone mineral. The metabolic acidosis pathway induces bone calcium efflux initially due to biochemical dissolution and subsequently by cell-mediated mechanisms that involves a strong inhibition of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) differentiation to osteoblasts with a strong stimulation of osteoclasts in one side and and neuro cells on the other side. The inhibitory effect on MSCs differentiation process takes place only within a pH acidic environment mediated by prostaglandins (PGs). Different studies confirmed the strict correlation between calcium flux, medium PGE2 and metabolic acidosis that alters the RANKL pathway considered as the major osteoclastogenic factor which is a PGs dependent response [
18,
19,
20].
Furthermore, in metabolic acidosis, the sympathetic nervous system and corticosteroids tend to increase accompanied by an increase in leukocytes and hypercatabolic rate. The acidic pH with low bicarbonate stimulates peripheral chemosensors inducing the medullary center to generate more ventilation that leads in energy consumption by muscle, including respiratory muscles. Patients with chronic metabolic acidosis typically show, in different degrees, the Kussmaul breathing sign characterized by a deep, rapid breathing pattern, suggestive that body or organs have accumulated high level of acidic compounds. This can be read as body’s attempt to expel carbon dioxide, as acidic compound in blood, via faster and deeper breaths, in acute cases (infection, sepsis) physicians may note a clear inspiratory retraction of intercostal muscles [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12].
In chronic condition, once breathing rate is increased the trade-off will settle in due to an incomplete compensation which in turns induces the pH raise enough to maintain survival rates; the inhibition of a full compensation is necessary at this stage to preserve energy consumption whilst keeping the system active for a longer period of time. This event could be seen in both hypoventilated and hyperventilated patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in which, hypercapnic patient show less muscle energy while the emphysematous hyperventilate to keep oxygen tension (fig.2). The Henderson–Hasselbalch equation explains this mechanism: pH = pKₐ + log([A⁻]/[HA]) decreasing PaCO
2 increases the pH. Paradoxically, the acidosis tends to reflects a compensatory effect towards respiratory alkalosis which in turns affects respiration so that it rises, making the acidosis as respiratory compensation [
21].
Figure 2.
Responses to acid/base imbalance is accomplished by the chemical buffers of the blood, the respiratory system, the renal system and bones. Acidosis due to either respiratory and metabolic failures lead to compensatory skeleton and renal changes, and both lead to an increased need of HCO-3 into the system. The chemical buffers resist changes in plasma pH by binding H+ ions when they are in excess and dissociating to form H+ ions when the [H+] falls. The respiratory system adjusts plasma pH by adjusting the PaCO2. During acidosis, respiration is stimulated, resulting in decreased PaCO2.
Figure 2.
Responses to acid/base imbalance is accomplished by the chemical buffers of the blood, the respiratory system, the renal system and bones. Acidosis due to either respiratory and metabolic failures lead to compensatory skeleton and renal changes, and both lead to an increased need of HCO-3 into the system. The chemical buffers resist changes in plasma pH by binding H+ ions when they are in excess and dissociating to form H+ ions when the [H+] falls. The respiratory system adjusts plasma pH by adjusting the PaCO2. During acidosis, respiration is stimulated, resulting in decreased PaCO2.
Therefore, abnormalities in systemic acid/base balance may either affect the CO
2-O
2 micro-exchange process and both in turn affect the ventilation-associated mechanism of organs and tissues generating injuries that are characterized by an increased systemic inflammation. The body's response to the hypoxaemic state either acute or chronic, is linked to an increase in minute ventilation leading to a steady increase of hypocapnia, as the CO
2 diffuses through tissues faster than O
2. Though the clinical significance of this loop still remains to clarify, the whole scenario suggests that this condition may generate a steady immune dysfunction due to a subtle inflammatory process that progress over the years almost unnoticed, typical patterns that vividly recall the the ABDs [
22,
23,
24].
Interesting, the ABDs follow a similar process of those of acute condition characterized by a steady and silent respiratory failure over the years. The presence of an unspecific inflammatory state often seen as part of progressive and diffuse tissues, veins and arteria damages with interstitial thickening and gas exchange impairments seems to be the reasonable mechanism able to clarify ABDs degenerative patterns [
24,
25].
Furthermore, evidences suggest that this atypical hypoxic/hypocapnic-hypercapnic condition enhance the formation of cholesterol oxidation products, known as oxysterols, and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE), otherwise considered the major proatherogenic components of oxidized low density hypoproteins (oxLDLs). These components significantly contribute to build up atherosclerotic plaques weakening arteria and vein walls leading to easy breakage. These oxidized lipids are active promoters of inflammatory process, oxidative stress, and tissue degeneration via unrecovered cell apoptosis. As a matter of fact, the distinctive traits of ABDs are well characterized by the release of inflammatory mediators, such tumor necrosis factor (TNF), nitric oxide (NO), macrophages and peripheral lymphocyte subset alteration that often passed without being noticed. The level of sub-set cells T-lymphocytes, macrophages (M1 and M2), and B-lymphocytes could be thus used as an independent predictor for ABDs severity and treatment efficacy [
24,
25,
26].
Studies conducted in resident macrophages or macrophage-like cell lines used acid lactic Hcl to provide a pH environment not less than 6.0 showed clear proinflammatory effects triggering nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) DNA binding or TNF synthesis. These outcomes were then confirmed in vivo in periodontal patients. Similarly, our outcomes showed a noticeable increase of macrophage polarization M1 and M2 with a significant difference between healthy individuals versus periodontal disease groups. The periodontics patients showed higher inflammatory marker expression with a significant pH difference compared to the healthy group, pH 5.5 vs pH 7. The periodontal individuals showed a lower differentiation of M2-like macrophages with a higher M1-like phenotype. The agonist/antagonist interaction was especially seen in the higher expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, like IL-1β, interferon-gamma (IFNγ), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and IL-6, linked to M1 activity and lower expression of immune-regulatory cytokines, such as the IL-10 and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) that on contrary modulate M1 by promoting the healing and regenerative mechanism driven by M2 [
27,
28,
29].
Of note, in vitro experiment showed that in the acidic conditions pH 6.5, nitric oxide (NO) release decreased in response to LPS and was again similar to pH 7.4. In pH 6.5, release of both IL-6 and IL-10 was significantly less than at pH 7.0 or 7.4. However, IL-10 release was reduced to a far greater extent than was IL-6, and thus the ratio of IL-6 to IL-10 increased significantly from 5:1 at pH 7.4 to 55:1 at pH 6.5. These findings showed that the base/acid balance and pH interpretation should analyze specific patterns in conformity with time and clinical settings. In addition, all forms of metabolic acidosis appear to be associated with prolonged length of mild metabolic condition [
30].
3. The Clinical Effectiveness of ABG Procedure in Preventing Long Term Consequences Derived from Metabolic Unbalances
Though the concept of performing prehospital ABG analysis is not yet generally accepted, and the value of this approach is still a matter of debate, several studies have already suggested the value of ABG in patients with suspected chronic multi-system decay [
31]. Clarify the effects of acid/base balance and the link with inflammatory and persistent degenerative patterns is extremely relevant to clinical and preventive medicine. The raise of an inflammatory state is always a matter of a long term silent and unnoticed loading of acid/base disorders that will eventually manifest later on in life. Most clinicians tend to ignore the effects of exogenous acidifying inducers on pH, although many tend to give a therapy for mild forms of acidemia [
1,
5,
8,
9,
10]. Therefore, an understanding of the physiologic consequences of altered pH by the use of ABG analysis would be an imperative in medical assessment (fig.3) [
30,
31,
32,
33].
For example, in patients with bone degenerative condition, renal decay and diabetes authors examined factors associated with the use of ABG and also assessed whether the measurement in patients was related to hospitalization, ICU treatment, or even death. Following this concept, prevent the extension of metabolic condition might increase the rate of survival from occasional sepsis or organ failures. Though acidosis/alkalosis has been associated with hemodynamic instability, the underlying mechanisms are not always clear [
30,
31,
32,
33].
The fact is that both metabolic acidosis/alkalosis are known to increase iNOS expression, in animals the increased of iNOS was seen inducing vasodilation and then shock. Intriguingly, both acidosis and alkalosis, even in the absence of sepsis or endotoxemia, were seen strictly linked to kidney, gut and lungs barrier dysfunction, mucosa permeability and cardiovascular condition [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36]. In addition, acidosis could be considered an important factor that drives to oxidative stress due to a steady delocalization of protein-bound iron stored in cells leading to Fenton-type biochemistry and redox stress [
35]. The latter phase is based on protonation of the peroxynitrite anion (ONOO-) acting like a potent free radical hydroxyl (OH•) which is known to irreversibly damage cells. It is well known that hyperchloremic acidosis tend to increase kidney, gut, lung and heart injuries in healthy rats [
34,
35,
36,
37].
Figure 3.
The monitoring of arterial blood gas (ABG) is an essential part of diagnosing and managing severe complications in many disease states, and often the abnormalities may be used in predicting and preventing severe life-threatening risk factor.
Figure 3.
The monitoring of arterial blood gas (ABG) is an essential part of diagnosing and managing severe complications in many disease states, and often the abnormalities may be used in predicting and preventing severe life-threatening risk factor.
Previous studies reported that it could be rather difficult to obtain arterial blood samples in prehospital patients, and the results would be no accurate due to the analytical equipment consistent failure rate. However, recent studies have demonstrated that not only the technology reached a higher standard, but emerging reports have also indicated that the capacity of targeting patient’s condition has improved [
31].
Therefore, understand the minimal variation in acid/base balance and minute ventilation over a period of time, it might be of help for physicians in highlighting important deep and unnoticed changes, correlated to the expression of specific disease patterns, for e.g., abnormal immunology profile (T and B lymphocytes, cytokines and interleukins, toll-like receptor (TLR) 4), abnormal metabolic and endocrine profile (insulin resistance, adiponectin resistance etc...) [
38,
39,
40,
41].
Any acute phase of chronic diseases tends to show common progressive patterns that drive to a general system and homeostatic breakdown that are, often if not always, confirmed by the ABG analysis irrespective of the original reason of the disease [
38,
39,
40]. Patients with chronic cardiac insufficiency, colitis, COPD, KCD and HIV both pH and hypoxemia values seem to be valuable markers. Increased oxygen consumption in absence of correct compensation and supply generates tissue hypoxia at chronically inflamed sites. Hypoxia drives an increase in HIF activity (a transcription factor known as hypoxia-inducible factor) in both resident and recruited immune cells, which in turns negatively affect immune cells functions and thus increasing the inflammatory activity [
42].
For instance, the finding of severe metabolic acidosis in these patients have confirmed to be a helpful tool for prehospital physicians to direct patients for immediate interventional procedures rather than admission to unnecessary wards. The outcomes confirmed that, not only those patients are characterized by subtle prolonged hypoventilation and hypoxia status based on their blood gas profiles but they also have been suffering of long term uncontrolled inflammatory autoimmune disorders [
31,
43,
44,
45,
46].
The ABG measured at presentation is not only a fast and inexpensive procedure but often offers significant predictions of both short and long-term outcome in dyspneic patients and has been seen as an independent data from other predictive markers, associated with mortality, either in patients with pulmonary disorders or other causes of dyspnea [
43,
44,
45]. It follows that individual’s ABG data would be essential in either to avoid unintended immunomodulation practice in clinical and laboratory settings or to explore the effectiveness of existing treatments [
38,
39,
40].
4. Conclusion
We are aware that there are numerous ways to fall into erroneous conclusions or oxygen saturation discrepancies may lead to misleading ABG interpretations. Nevertheless, recognizing spurious and apparent “volatile” values will help improve precise patients evaluation and predictive conclusions, by avoiding improper therapies and possible harm arising from a wrong diagnosis. Therefore, with this study we proposed and discussed the possible advantages of using prehospital ABG measurement as additional screening procedure that may eventually improve both predictive and diagnostic accuracy of the advancements of metabolic diseases, it is a fast and inexpensive procedure. ABG parameters may fluctuate with minimal changes during a period of many years and therefore are often unrecognized by physicians. Commonest acid base disorders start early in life and slowly progress showing minimal audible fluctuations that will become a consolidate disease later in life. For example, cardiac failure, liver failure, renal failure, ventilated patients, severely and unwell patients from any cause. We therefore suggested that the ABG analysis may enable the prehospital physicians to make the correct diagnosis in a timely manner, thus allowing the appropriate treatment to be initiated before disease outbreak.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.G.I. and N.C.D.K.; investigation, C.G.I. and M.G.B., P.D., R.L.; figures, C.G.I. and N.C.D.K,; data curation, L.S., A.M., V.H.P., T.C.T. and S.K.A.; writing, review and editing, C.G.I., L.S., S.K.A., A.M.K., R.D.P. and M.G.B.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted did not involving humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gutowski, L.; Gutowska, K.; Brożek, A.; Nowicki, M.; Formanowicz, D. ABG Assistant—Towards an Understanding of Complex Acid-Base Disorders. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1516. [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Shabsigh, M.; Morimatsu, H. Traditional approach versus Stewart approach for Acid-Base disorders: Inconsistent evidence. SAGE Open Med. 2018, 6, 6. [CrossRef]
- Berend, K.; Duits, A.J. The role of the clinical laboratory in diagnosing acid-base disorders. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2019, 56, 147–169. [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, P.; Ahluwalia, M.; Vaibhav, K.; Mondal, A.; Sahajpal, N.; Islam, S.; Fulzele, S.; Kota, V.; Dhandapani, K.; Baban, B.; et al. Infections of the lung: A predictive, preventive and personalized perspective through the lens of evolution, the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 and its pathogenesis. EPMA J. 2020, 11, 581–601. [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, A. Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron. Clin. practice. 2012, 120, 179–184. [CrossRef]
- Polivka, J.; Pesta, M.; Rohan, V.; Celedova, L.; Mahajani, S.; Topolcan, O.; Golubnitschaja, O. Risks associated with the stroke predisposition at young age: Facts and hypotheses in light of individualized predictive and preventive approach. EPMA J. 2019, 10, 81–99. [CrossRef]
- Abuzinadah, A.R.; Almalki, A.K.; Almuteeri, R.Z.; Althalabi, R.H.; Sahli, H.A.; Hayash, F.A.; Alrayiqi, R.H.; Makkawi, S.; Maglan, A.; Alamoudi, L.O.; Alamri, N.M.; Alsaati, M.H.; Alshareef, A.A.; Aljereish, S.S.; Bamaga, A.K.; Alhejaili, F.; Abulaban, A.A.; Alanazy, M.H. Utility of Initial Arterial Blood Gas in Neuromuscular versus Non-Neuromuscular Acute Respiratory Failure in Intensive Care Unit Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4926. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Hur, J.; Lee, T.W.; Ju, S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, K.J.; Cho, Y.J.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Lee, J.D.; Kim, H. C. Myasthenia gravis presenting initially as acute respiratory failure. breath. Care 2015, 60, e14–e16. [CrossRef]
- Kalita, J.; Kumar, M.; Misra, U.K. Serial single breath count is a reliable tool for monitoring respiratory functions in Guillain-Barré Syndrome. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 72, 50–56. [CrossRef]
- Rabinstein, A.A.; Wijdicks, E.F. Warning signs of imminent respiratory failure in neurological patients. sowing Neurol. 2003, 23, 97–104. [CrossRef]
- Champigneulle, B.; Reinhard, L.; Mademilov, M.; Marillier, M.; Ulrich, T.; Carta, A.F.; Scheiwiller, P.; Shabykeeva, S.B.; Sheraliev, U.U.; Abdraeva, A.K.; Magdieva, K.M.; Mirzalieva, G .; Taalaibekova, A.T.; Ozonova, A.K.; Erkinbaeva, A.O.; Shakiev, N.U.; Azizbekov, S.A.; Ainslie, P.N.; Soononbaev, T.M .; Ulrich, S.; Bloch, K.E.; Verges, S.; Furian, M. Validation of Noninvasive Assessment of Pulmonary Gas Exchange in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease during Initial Exposure to High Altitude. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 795. [CrossRef]
- Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease(2022 Report). Available online: https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/GOLD-REPORT-2022-v1.1-22Nov2021_WMV.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2023).
- Balzanelli, G.M.; Distratis, P.; Aityan, K.S.; Gargiulo-Isacco, C et al. Clinical Features in Predicting COVID-19. Biomedical J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2020; 29(5): 22921-22926. [CrossRef]
- Balzanelli, M.G.; Distratis, P.; Dipalma, G. and Gargiulo-Isacco, C. Immunity Profiling of COVID-19 Infection, Dynamic Variations of Lymphocyte Subsets, a Comparative Analysis on Four Different Groups. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2036. [CrossRef]
- Alfano, G.; Fontana, F.; Mori, G. et al. Acid base disorders in patients with COVID-19. Int Urol Nephrol. 2022;54: 405–410.
- Longhitano, Y.; Zanza, C.; Romenskaya, T.; Saviano, A.; Persian, T.; Leo, M.; Piccioni, A.; Betti, M.; Maconi, A.; Pindinello, I.; Boverio, R.; Rello, J.; Franceschi, F.; Racca, F. Single-Breath Counting Test Predicts Non-Invasive Respiratory Support Requirements in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 179. [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Taniguchi, L.U.; Noritomi, D.T.; Libório, A.B.; Maciel, A.T.; Cruz-Neto, L.M. Clinical utility of standard base excess in the diagnosis and interpretation of metabolic acidosis in critically ill patients. Braz. J. Med. Biol. 2008, 41, 241–249. [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, P.; Ahluwalia, M.; Vaibhav, K.; Mondal, A.; Sahajpal, N.; Islam, S.; Fulzele, S.; Kota, V.; Dhandapani, K.; Baban, B.; et al. Infections of the lung: A predictive, preventive and personalized perspective through the lens of evolution, the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 and its pathogenesis. EPMA J. 2020, 11, 581–601. [CrossRef]
- Carnauba, R.A.; Baptistella, A.B.; Paschoal, V.; Hübscher, G.H. Diet-Induced Low-Grade Metabolic Acidosis and Clinical Outcomes: A Review. Nutrients 2017, 9, 538. [CrossRef]
- Jajoo, R.; Song, L.; Rasmussen, H.; Harris, S.S.; Dawson-Hughes, B. Dietary acid-base balance, bone resorption, and calcium excretion. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2006, 25, 224–230. [CrossRef]
- Ortegon-Reyna, D.; Garcías-Morales, C.; Padilla-Martínez, I.; García-Báez, E.; Aríza-Castolo, A.; Peraza-Campos, A.; Martínez-Martínez, F. NMR Structural Study of the Prototropic Equilibrium in Solution of Schiff Bases as Model Compounds. Molecules 2014, 19, 459-481. [CrossRef]
- Gaynullina, D.K.; Tarasova, O.S.; Shvetsova, AA; Borzykh, A.A.; Schubert, R. The Effects of Acidosis on eNOS in the Systemic Vasculature: A Focus on Early Postnatal Ontogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5987. [CrossRef]
- Slobod, D.; Damia, A.; Loyal, M.; Spinelli, E.; Mauri, T. Pathophysiology and Clinical Meaning of Ventilation-Perfusion Mismatch in the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Biology 2023, 12, 67. [CrossRef]
- Boedtkjer, E. Acid/base regulation and sensing: Accelerators and brakes in metabolic regulation of cerebrovascular tone. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2018, 38, 588–602. [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Vogel, P.; Lassen, N.A.; Mulvany, M.J.; Andreasen, F.; Aalkjær, C. Role of extracellular and intracellular acidosis for hypercapnia-induced inhibition of tension of isolated rat cerebral arteries. Circ. 1995, 76, 269–275. [CrossRef]
- Lordan, S.; Mackrill, J.J.; O'Brien, N.M. Oxysterols and mechanisms of apoptotic signaling: Implications in the pathology of degenerative diseases. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2009, 20, 321–336. [CrossRef]
- Shibata, N.; Glass, C.K. Macrophages, oxysterols and atherosclerosis. Circ. J. 2010, 74, 2045–2051. [CrossRef]
- Lasola, J.J.M.; Cottingham, A.L.; Scotland, B.L.; Truong, N.; Hong, C.C.; Shapiro, P.; Pearson, R.M. Immunomodulatory Nanoparticles Mitigate Macrophage Inflammation via Inhibition of PAMP Interactions and Lactate-Mediated Functional Reprogramming of NF-κB and p38 MAPK. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1841. [CrossRef]
- Ballini, A.; Dipalma, G.; Isaac, C.G.; Boccellino, M.; Di Domenico, M.; Santacroce, L.; Nguyễn, K.C.D.; Scacco, S.; Calvani, M.; Boddi, A.; Corcioli, F.; Quagliolo, L.; Cantor, S .; Martelli, F.S.; Inchingolo, F. Oral Microbiota and Immune System Crosstalk: A Translational Research. Biology 2020, 9, 131. [CrossRef]
- Fubini, P.E.; Suppan, L. Prehospital Diagnosis of Shortness of Breath Caused by Profound Metformin-Associated Metabolic Acidosis. Healthcare 2021, 9, 74. [CrossRef]
- Zwisler, S.T.; Zincuk, Y.; Bering, C.B. et al. Diagnostic value of prehospital arterial blood gas measurements – a randomized controlled trial. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2019; 27(32). [CrossRef]
- Jaber, S.; Paugam, C.; Futier, E.; Lefrant, J.Y.; Lasocki, S.; Lescot, T.; Pottecher, J.; Demoule, A.; Ferrandiere, M.; Asehnoune, K.; et al. Sodium bicarbonate therapy for patients with severe metabolic acidaemia in the intensive care unit (BICAR-ICU): A multicentre, open-label, randomized controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 31. [CrossRef]
- Seidowsky, A.; Nseir, S.; Houdret, N.; Fourrier, F. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis: A prognostic and therapeutic study. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 2191–2196. [CrossRef]
- LeBaron, T.W.; Sharpe, R.; Ohno, K. Electrolyzed–Reduced Water: Review I. Molecular Hydrogen Is the Exclusive Agent Responsible for the Therapeutic Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14750. [CrossRef]
- Varum, F.; Hatton, G.; Basit, A. Food, physiology and drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 446–460. [CrossRef]
- Castro, D.; Patil, SM.; Keenaghan, M. Arterial Blood Gas. [Updated 2022 Sep 12]. In: Stat Pearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536919/.
- Koyama, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Saihara, Y.; Ando, D.; Goto, Y.; Katayama, A. Effect of hydrogen saturated alkaline electrolyzed water on urinary oxidative stress markers after an acute exercise: A randomized controlled trial. Anti-aging Med 2008, 4, 117–122.
- Borrelli, C.; Buckley, C.T. Synergistic Effects of Acidic pH and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α for Cell-Based Intervertebral Disc Regeneration. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 9009. [CrossRef]
- Hadjipavlou, A.G.; Tzermiadianos, M.N.; Bogduk, N.; Zindrick, M.R. The pathophysiology of disc degeneration: A critical review. J.Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2008, 90, 1261–1270. [CrossRef]
- Phillips, K.L.; Cullen, K.; Chiverton, N.; Michael, A.L.; Cole, A.A.; Breakwell, L.M.; Haddock, G.; Bunning, R.A.; Cross, A.K.; Le Maitre, C.L. Potential roles of cytokines and chemokines in human intervertebral disc degeneration: Interleukin-1 is a master regulator of catabolic processes. Osteoarthritis. Cartil. 2015, 23, 1165–1177. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Hajage, D.; Lebreton, G.; Monsel, A.; Voiriot, G.; Levy, D.; Baron, E.; Beurton, A.; Chommeloux, J.; Meng, P.; et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Breath. Med. 2020, 8, 1121–1131. [CrossRef]
- Eoin, P.C.; Cormac, T.T. Hypoxia and inflammation. 2017. Biochemical Society. Inflammation (University College Dublin, Ireland).
- Weiss, S.L.; Alexander, J.; Agus, M.S. Extreme stress hyperglycemia during acute illness in a pediatric emergency department. Pediatrics Emerg. Care 2010, 26, 626–632. [CrossRef]
- Reyes, A.; Duarte, L.F.; Farías, M.A.; Tognarelli, E.; Kalergis, A.M.; Bueno, S.M.; González, P.A. Impact of Hypoxia over Human Viral Infections and Key Cellular Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7954. [CrossRef]
- Cassavaugh, J.; Lounsbury, K.M. Hypoxia-mediated biological control. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 735–744. [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Feng, X.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Sun, L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in autoimmune diseases. Cell Immunol. 2016; 303:7-15. Epub 2016 Apr 7. PMID: 27071377. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).