1. Introduction
The need for sustainable urban water supplies requires that the quality of existing available water resources, as well as their watersheds, need to be under continuous monitoring. As known, chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) is the major indicator of the trophic state of waterbodies. Indeed, chlorophyll-a acts as a link between nutrient concentration, particularly phosphorus, and algal production [
1].
Phosphorus retention in sediments is a key contributor to the trophic status of water in a wide variety of ecosystems. The flow of phosphorus through the water-sediment interface, which is regulated by adsorption and desorption processes, is critical for controlling the availability of dissolved phosphorus in the water column. However, the number of factors that can affect these mechanisms and their complexity seems to make it impossible to generalize hypotheses enabling a rigorous mathematical simulation of this compartment. The release of phosphorus across the water-sediment interface is a complex process that results from the interaction of various mechanisms, which still have many unknowns, specifically when considering the retention of phosphorus in the deeper layers of sediments [
2,
3,
4,
5].
For more than four decades, remote sensing has illustrated strong capabilities to monitor and evaluate the quality of inland waters [
1,
6,
7,
8,
9]. Indeed, optically active constituents of water that interact with light and change the energy spectrum of reflected solar radiation from waterbodies can be measured using remote sensing. Nevertheless, this technique alone is not sufficiently precise and must be used in conjunction with traditional sampling methods and field surveying [
1].
The most measured qualitative parameters of water obtained using remote sensing include chlorophyll-a (Chl-a), coloured dissolved organic matters (CDOM), Secchi disk depth (SDD), turbidity, total suspended sediments (TSS), water temperature (WT), total phosphorus (TP), sea surface salinity (SSS), dissolved oxygen (DO), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) [
1]. However, most of these parameters are correlated between themselves [
1,
6,
7,
8,
9].
The parameters chlorophyll-a (Ch-a), turbidity, dissolved oxygen (DO), and total phosphorus (TP) have already been modelled with high efficiency using as explanatory variables single spectral bands, water spectral indices, and ratios from remote sensing imagery [
6]. For instance, the Sentinel-2 Multispectral Imager (MSI) imagery and the corresponding Sentinel-3 Ocean and Land Colour Instrument (OLCI) products have been used for aquatic applications to assess the parameter chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) and turbidity [
7]. Indeed, Chl-a was mapped by spatial regression using the Sentinel-2 MSI imagery [
8]. Other authors modelled a water quality index, that aggregates nine non-correlated water quality parameters, through machine learning algorithms using as explanatory variables several water spectral indices [
9].
Climate change scenarios for Portugal suggest a substantial increase in the mean air temperature, especially in summer and inland sites. Regarding precipitation, climate ate forecast uncertainty will increase shortly. However, almost all previsions anticipate reductions in mean precipitation and a decrease in the rainy season [
10]. According to the official national climate bulletins by IPMA (Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera—IPMA), having as reference the average precipitation in the period of 1971-2000, precipitation reduction is already taking place early in the 21′s century. Indeed, the last hydrological year of 2021/2022 is considered one of the driest, rising serious concerns about reservoir water quality for urban supply.
The Marateca reservoir supplies the municipality of Castelo Branco in central inland Portugal. A significant event occurred in April 2022 in this reservoir. Thus, the aims of this study were the following: (1) to explore the water quality parameters, available for the hydrological year of 2021/2022, at the monitoring points of the Marateca reservoir through the construction of spectral signatures, that may explain the event; (2) to validate the optical pollution signatures using the chemical variables measured in the selected monitoring points; and (3) to model the reservoir water characteristics regarding its deepness, trophic state, and turbidity.
The parameters total phosphorus (TP), total nitrogen (TN), and chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) were considered for the reservoir water quality characterization and to compute a trophic level index [
11]. The Sentinel-2 imagery was used to obtain the spectral signatures in the monitoring points; to compute the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI), the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), and the blue and green bands image ratio (B/G) to infer about optical water qualitative parameters; and to model the reservoir water characteristics using machine learning algorithms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study area
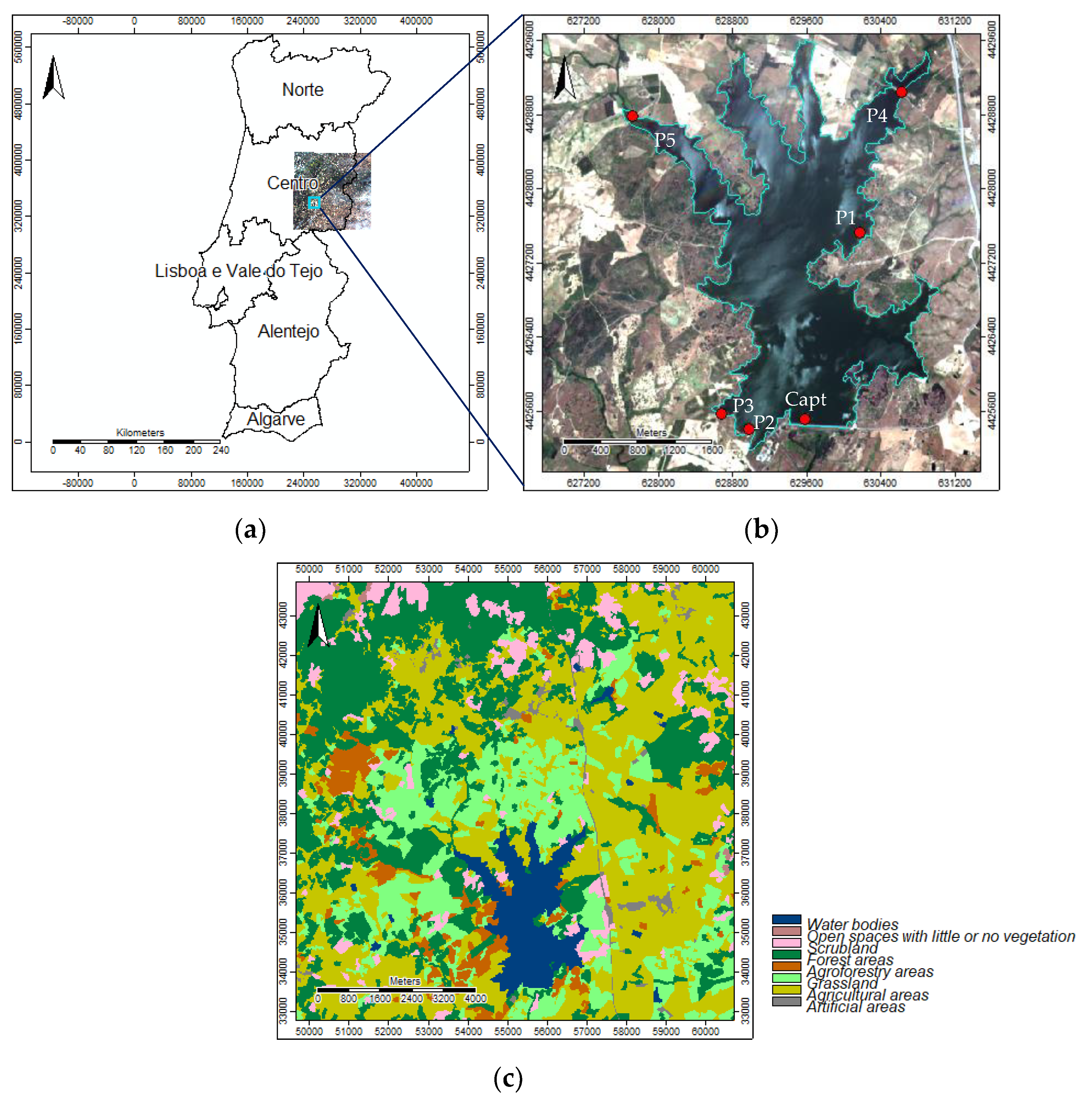
The Marateca reservoir is in the municipality of Castelo Branco, Portugal (
Figure 1a,b). This reservoir is an embankment dam that was designed in 1982 on the Ocreza river and started operating in 1991. It has a height of 25 m above the foundation (24 m above the natural terrain) and a crest length of 1054 m (width 7.6 m). The volume of the dam is 43.5 million m
3. It has a maximum discharge capacity of 15.25 m
3s
−1 on the bottom discharge plus 60 m
3s
−1 on the flood discharger. The dam’s reservoir has a floodable surface of 6.34 km
2 at the full storage level and has a total capacity of 37.2 million m
3 (useful capacity of 32.7 million m
3). The water levels in the reservoir are 385 meters at full storage level (FSL), 385.5 m at maximum flood level, and 375.5 m at minimum exploration level [
12]. According to the Portuguese Land Cover and Land Use (LCLU), 2018 thematic map (COS2018) [
13,
14], the Marateca reservoir is surrounded mainly by agricultural areas and grassland (
Figure 1c).
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Climatological data—local station
The climatological data were obtained from the nearest local climate station to the study area in Castelo Branco, which is located approximately 40 km away from the town. The monthly climatological reports were downloaded from the national official portal of Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera (IPMA) [
15].
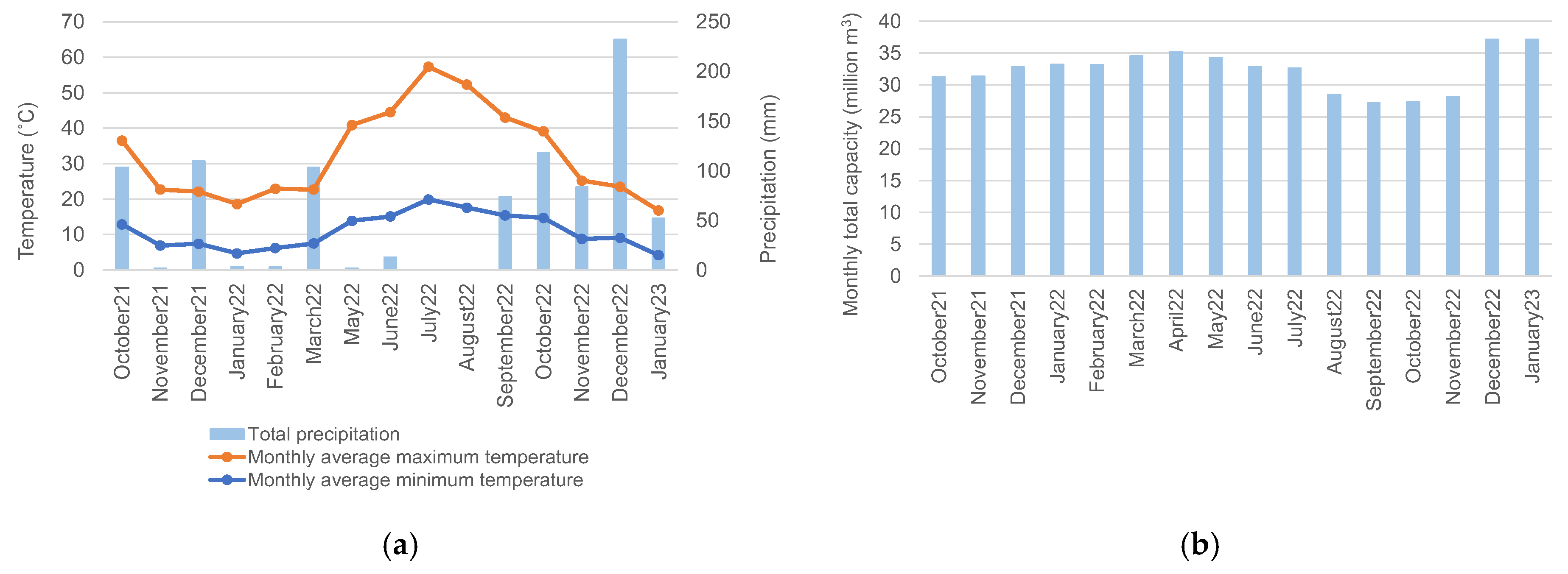
In this study, the climatological data regarding the hydrological years of 2021/2022 and 2022/2023 (from October 2021 to January 2023) were used to obtain the evolution of monthly average temperatures (minimum and maximum, °C) and of total monthly precipitation (mm) (
Figure 2). These data were used to explain the changes observed in the study area throughout the above-referenced hydrological years.
2.2.2. Sentinel2A imagery data
The Sentinel2A imagery data were downloaded from the European Union’s earth observation program called Copernicus, website (
https://sentinels.copernicus.eu/web/sentinel/missions/sentinel-2). The Sentinel-2 is one of the various missions of the Copernicus. Currently, two twin Sentinel-2 satellites (A and B) offer coverage with a high spatial resolution (up to 10 m) and temporal resolution (5 days) [
16]. The Sentinel-2 MSI imagery has 13 spectral bands covering the spectral range of 440–2180 nm, with spatial resolutions of 10, 20, and 60 m (
Table 1).
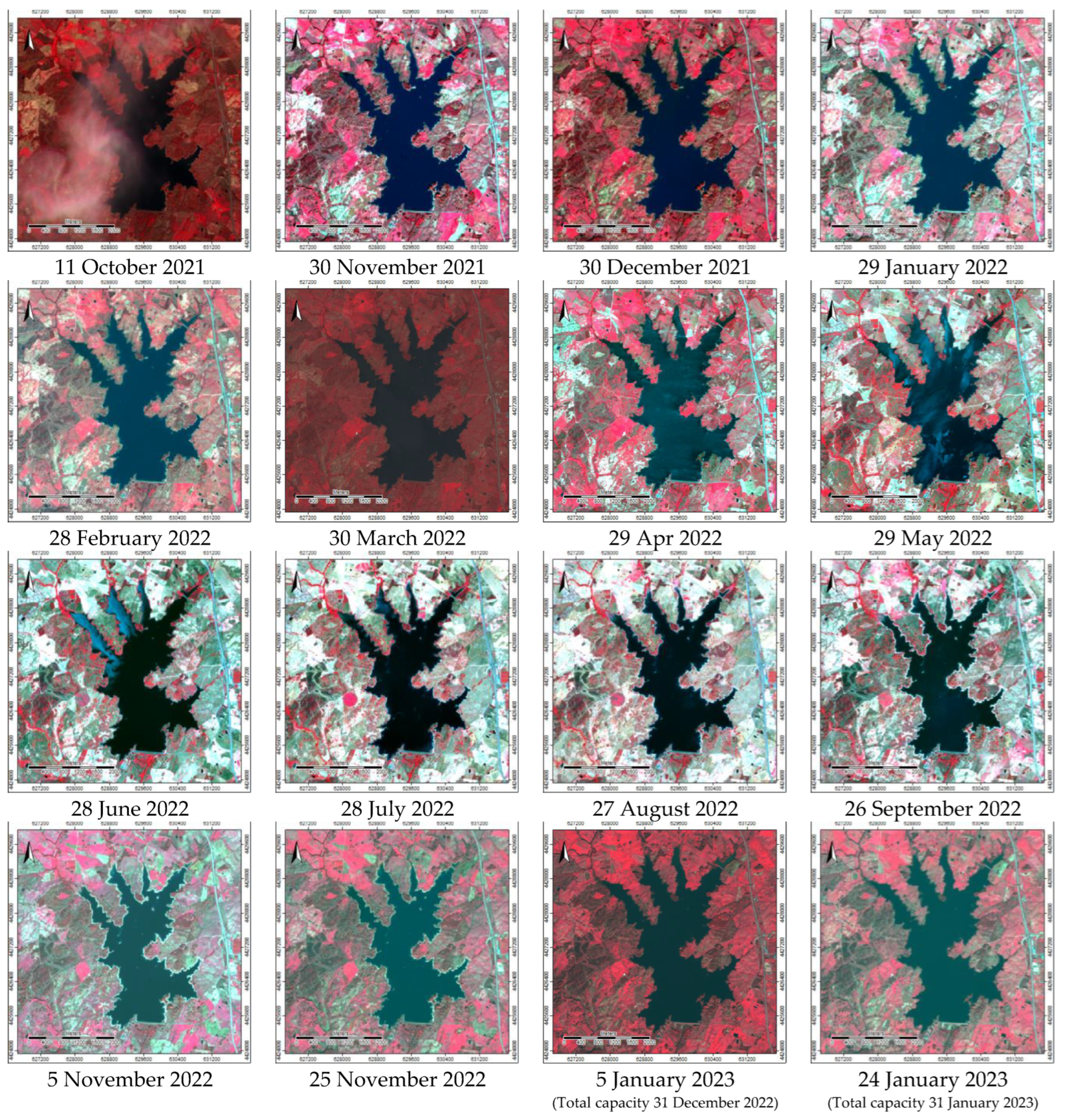
In this study, the Sentinel-2 Multispectral Instrument (MSI) imagery, level 2A (atmospherically, radiometrically, and geometrically corrected), were downloaded for 16 monthly dates of the last and current hydrological years (from October 2021 to January 2023) (
Table 2).
2.2.3. Water quality parameters—monitoring points data
This reservoir has several strategically placed monitoring points for water quality measurement (
Figure 1b). The available parameters considered were the following: total phosphorus (TP), total nitrogen (TN), chlorophyll-a (Chl-a), total suspended solids (TSS), turbidity (TUR), and dissolved oxygen (DO).
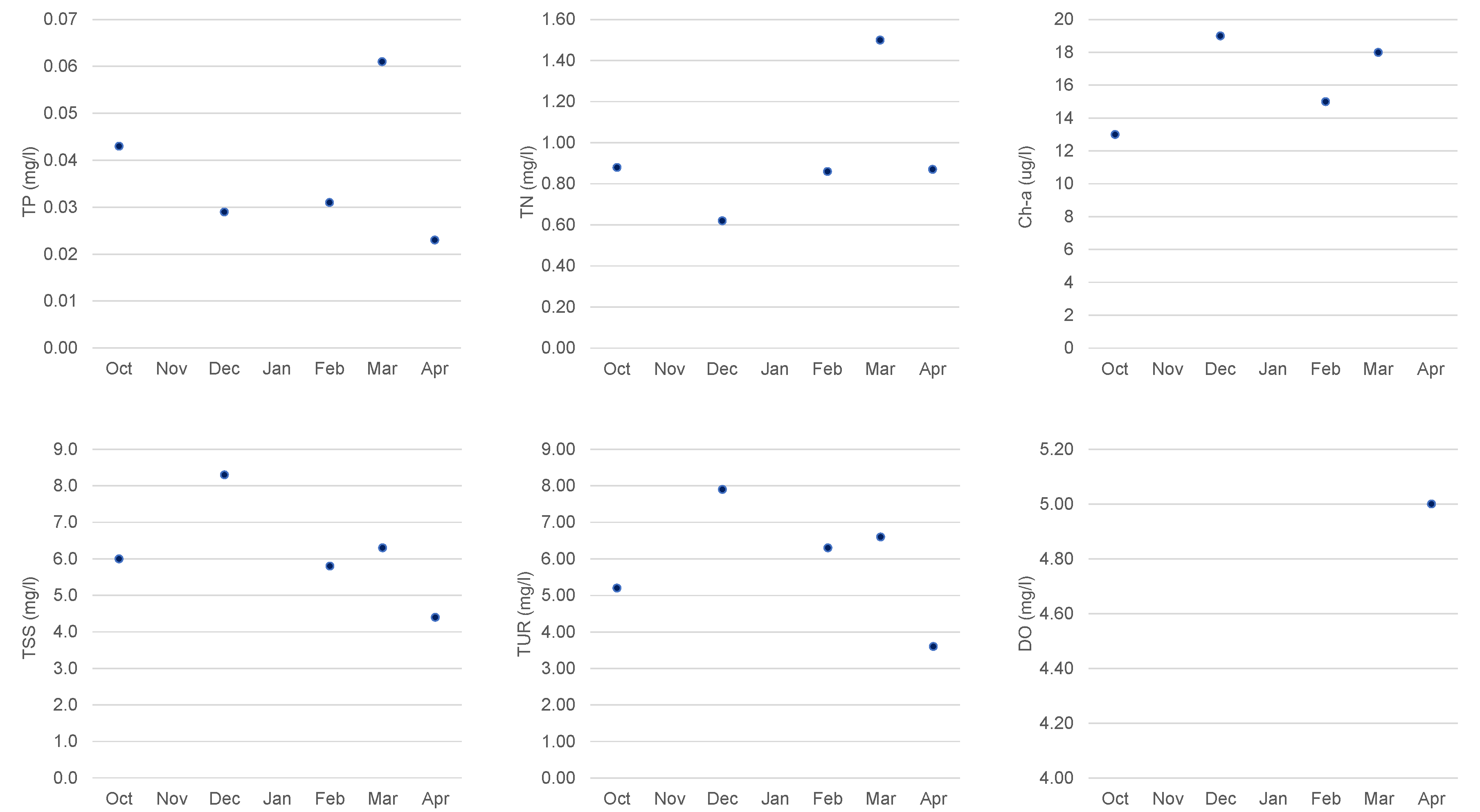
The caption point (Capt) was the only one with continuous data collection throughout the hydrological year of 2021-2022 for most of the parameters. While the date of 27 April 2022 (
Figure 3) was the one with data collection in almost all monitoring points (Capt, P1, P3, P4, and P5). The P2 point was not considered for validation as no information was available for April 27, 2022.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Composites, spectral indices, ratios imagery, and spectral signatures
A Geographical Information System (GIS) software, the free open-source software SAGA (System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses) (
https://saga-gis.sourceforge.io/en/index.html) was used to perform all the computations with the Sentinel2A imagery. The Coordinate System [EPSG 32629]: WGS84/UTM zone 29N was used.
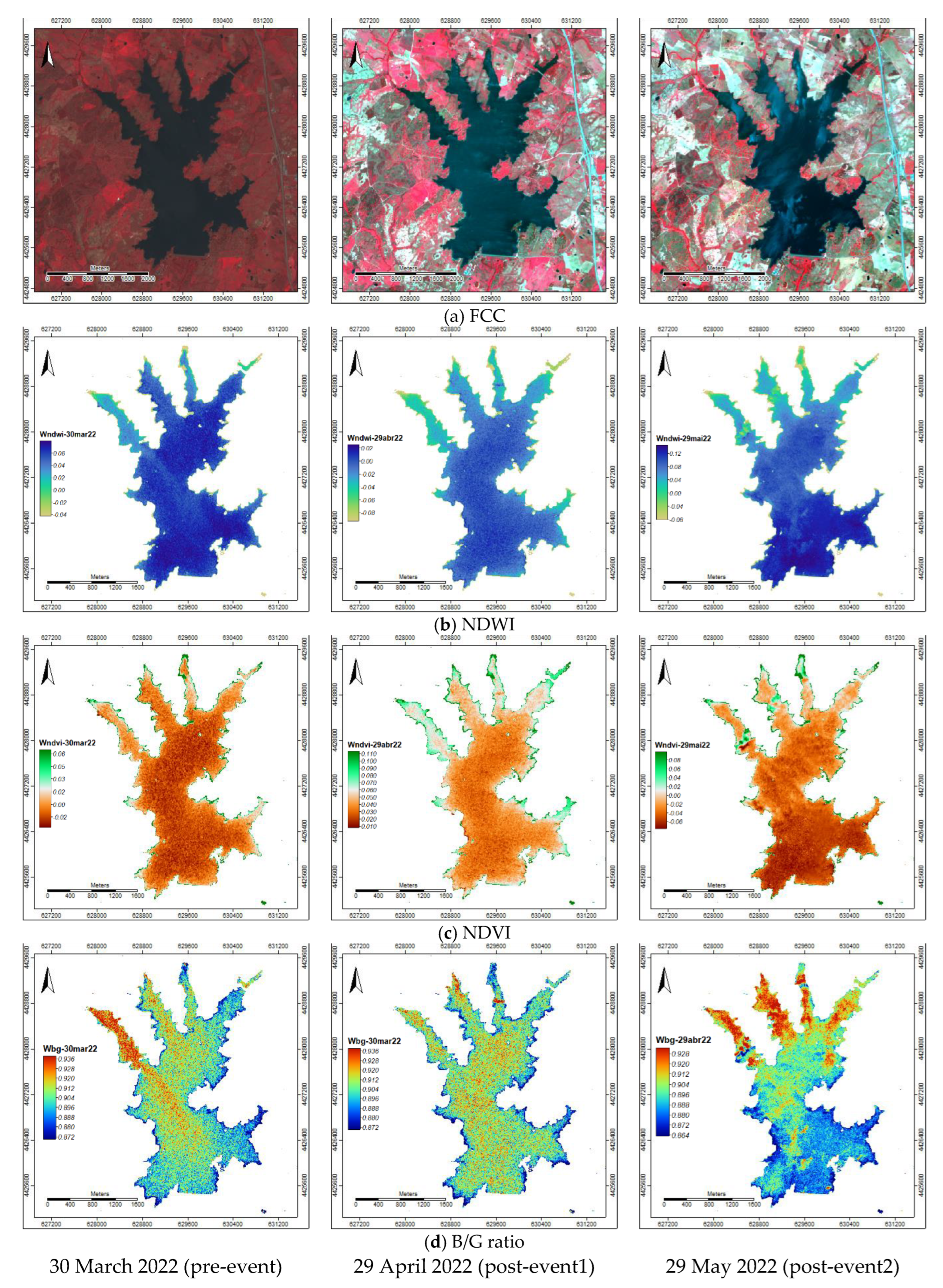
The false colour composition (FCC;
Figure A1), the spectral indices Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), and the spectral blue and green bands image ratio (B/G) were computed for the 16 dates using the spatial resolution of 10 m imagery (
Table 3).
As it is known, the NDWI values range from -1 to 1, where water surfaces usually fall within 0.2 to 1; flooding, humidity within 0 to 0.2; moderate drought, non-aqueous surfaces within -0.3 to 0; and drought, non-aqueous surfaces within -0.1 to -0.3 [
18].
Regarding the NDVI values they also range from -1 to 1, where water surfaces, manmade structures, rocks, clouds, and snow correspond to negative values; bare soil usually falls within the 0.1–0.2 range and plants will always have positive values between 0.2 and 1. Particularly, a healthy, dense vegetation canopy should be above 0.5, and sparse vegetation will most likely fall within the 0.2 to 0.5 range [
19].
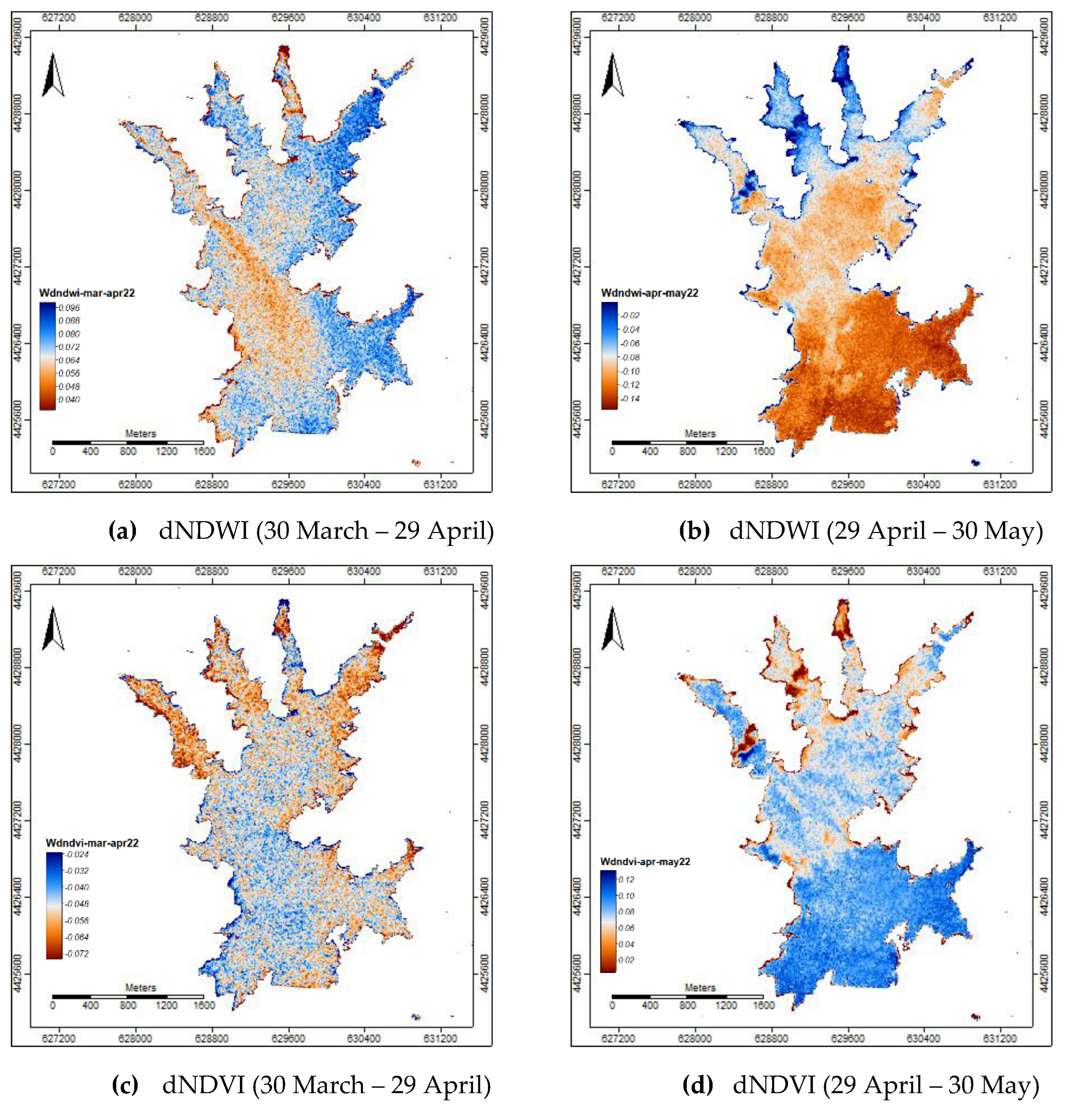
The monthly difference indices dNDWI and dNDVI were also computed to highlight the changes observed from October 2021 to January 2023 in Marateca reservoir, particularly the ones between the 30 March 2022 (pre-event), 29 April 2022 (post-event1), and 29 May 2022 (post-event2).
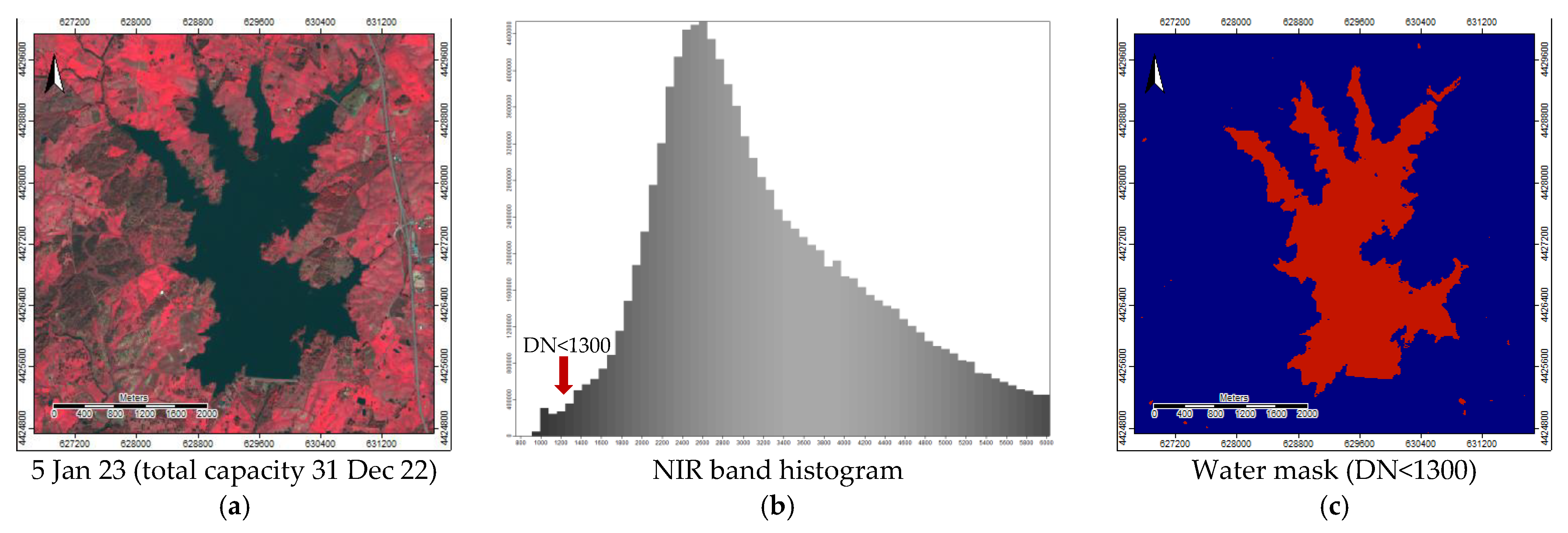
To extract the Marateca reservoir a single-band threshold approach based on the NIR band histogram (digital number DN<1300) at the total capacity date (e.g., 5 Jan 2023—37.2 million m
3;
Figure 2b) was used to obtain a water mask (Boolean) (
Figure 3).
Then, this water mask grid was converted to shape format (polygons) and used to extract the Marateca reservoir from the imagery previously computed with the spatial resolution of 10 m (NDWI, NDVI, B/G ratio, dNDWI, and dNDVI).
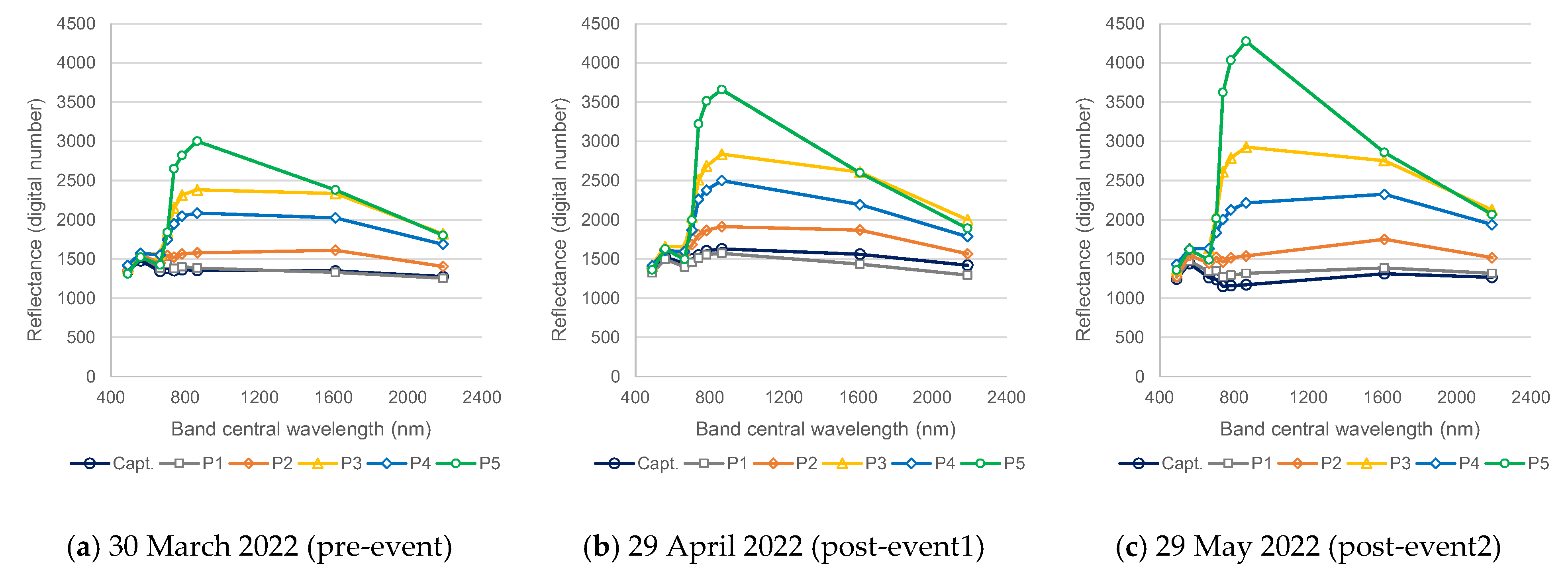
The nine spectral bands (e.g., B, G, R, R-edge 1, R-edge 1, R-edge 1, NIR narrow, SWIR 1, and SWIR2) of 20 m spatial resolution were used to obtain the spectral signatures at the monitoring points for the dates of 30 March 2022 (pre-event), 29 April 2022 (post-event1) and 29 May 2022 (post-event2).
2.3.2. Water quality parameters—monitoring and validation data
The monitoring date of 27 April 2022 was chosen for validation because some days before a significant number of dead fish were found in the reservoir, an event reported by the local news on 10 April 2022.
The selected parameters for the water quality characterization were TP, TN, and Chl-a* estimated values based on TP, using the equation proposed by [
11] (Equation (1)).
Trophic classifications for lakes are an important issue concerning lake ecosystem function for aquatic scientists [
20,
21,
22,
23]. General functional features exist among the lakes in each of the main categories of trophic status. Conceptually it is universal to consider three main groups: oligotrophic lakes, corresponding to low nutrients, low algal biomass, high clarity, and deep photic zones; eutrophic lakes where it is frequent blooms of cyanobacteria with high total nutrients and the mesotrophic level corresponding to intermediate characteristics (Dodds et al., 1998). Additionally, a reservoir trophic level index (RTLI − (TP)), based on TP values, was calculated according to Lamparelli [
11] (Equation (2)), as follows:
Lamparelli [
11] considers six different levels of the Trophic status: Ultraoligotrophic (IET-(TP) <= 47), oligotrophic (47 < IET-(TP) <= 52), mesotrophic (52 < IET-(TP) <= 59); eutrophic (59 < IET-(TP) <= 63); super-eutrophic (63 < IET-(TP) <= 67) and hypereutrophic (IET-(TP) > 67). Where the first level corresponds to clean water and the following levels to increasing eutrophication.
The water quality chemical parameters TP, TN, estimated Chl-a*, and the reservoir trophic level index (RTLI –(TP)) were used to validate the spectral signatures on 29 April 2022, using the closest monitoring day, 27 April 2022.
2.3.3. Water characteristics modelling
The spectral bands, the spectral indices, and the bands’ ratios allowed for obtaining information about some water quality parameters with optical active constituents, namely: DO, TP, TSS, TUR, and Chl-a (
Table 4).
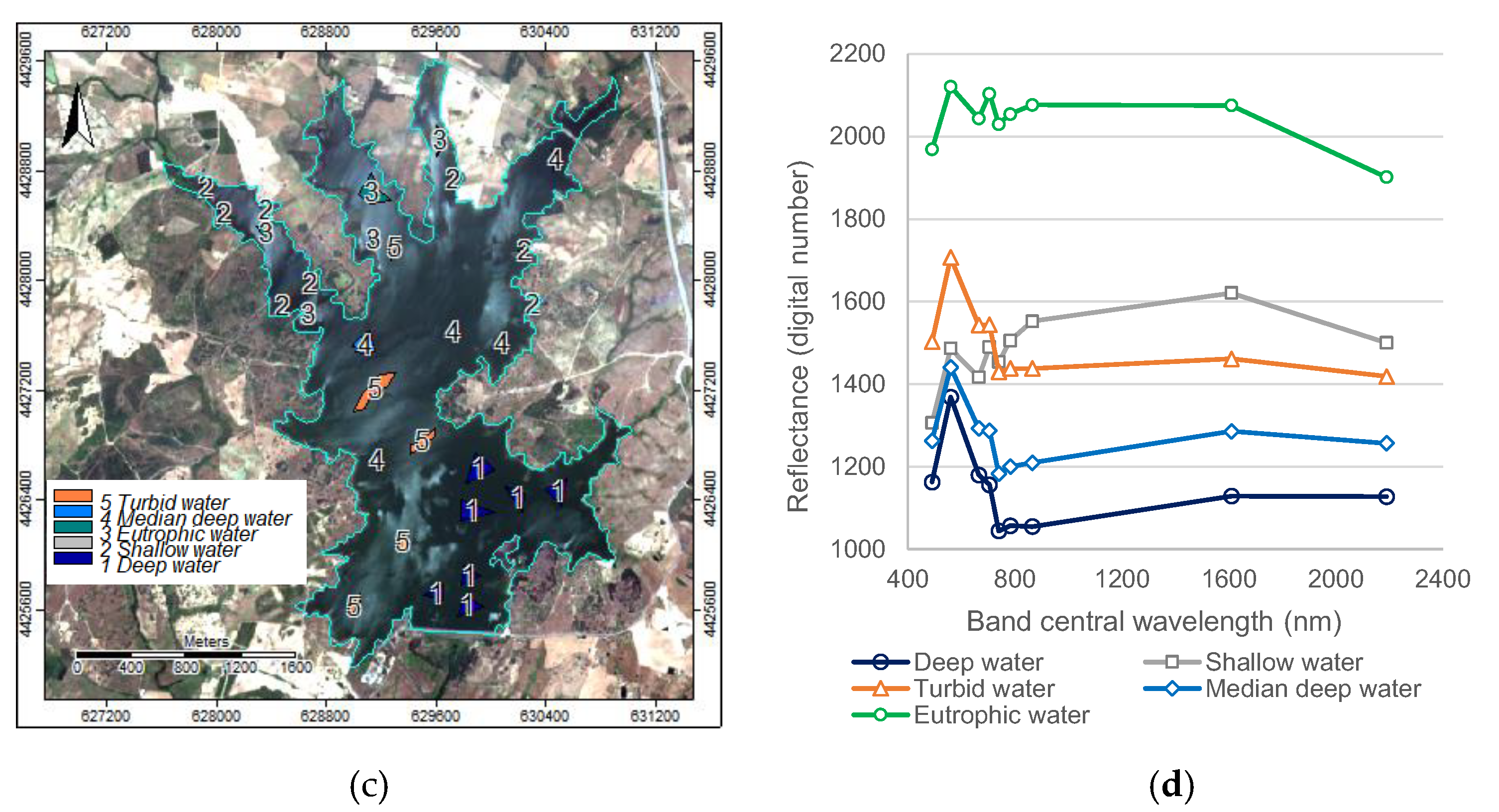
Additionally, the 13 optical water types for inland waters, from hyperspectral water reflectance measurements, by Spyrakos et al. [
24] were used as a reference to support the analysis of the spectral bands’ image ratio (B/G) (
Figure 4).
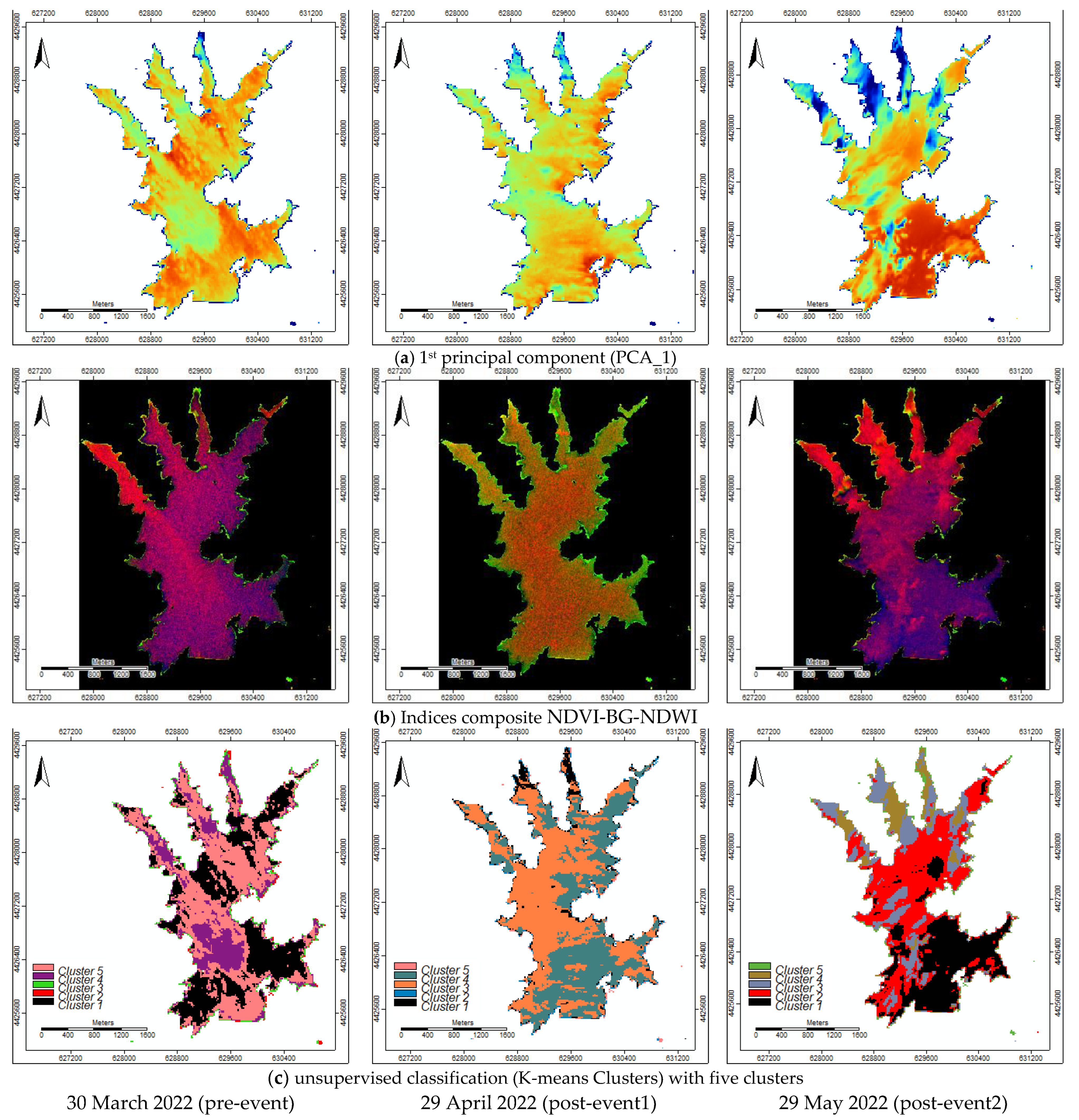
Based on the analysis of the spectral indices performed from October 2021 to January 2023 (NDWI, NDVI, and B/G) the date of 29 May 2022 was then selected as one presenting the highest variability, to define the spectral signatures for the water characteristics classes considered: 1—Deepwater; 2—Shallow water; 3—Eutrophic water; 4—Median deep water; and 5—Turbid water.
The nine spectral bands of the spatial resolution of 20 m imagery (e.g., B, G, R, R-edge 1, R-edge 1, R-edge 1, NIR narrow, SWIR1, and SWIR2;
Table 1) for the date of 29 May 2022 were used to support the classification and modelling procedures for water characteristics. The FCC, NDWI, NDVI, and B/G ratios were computed with the spatial resolution of 20 m imagery. Afterward, the water mask grid was used to extract the Marateca reservoir from the nine bands and the computed imagery.
A principal components analysis was performed to highlight the nine bands’ variability (e.g., the first principal component image explains about 95% or more of the data’s variance). A false colour composite was obtained with the B/G ratio, NDVI, and NDWI imagery. An unsupervised procedure (e.g., K-means cluster analysis for grids) was used to determine the natural spectral classes in the imagery. In this case, four, five, and 10 clusters were essayed.
Furthermore, a supervised classification was performed based on this first exploratory analysis and ground-truth knowledge supported by the Marateca reservoir monitoring points water quality parameters data. The first step of a supervised classification is to set the training areas that will be used as a reference to generate class signatures using the nine spectral bands. The water quality classes considered were as follows: 1—Deepwater; 2—Shallow water; 3—Eutrophic water; 4—Median deep water; and 5—Turbid water. The second step is the classification by using classifiers algorithms (e.g., the maximum likelihood—MaxLike) that will classify the entire image into the set of spectral classes previously identified.
Random Forest algorithm (ML-RF) was used as a machine learning procedure and performed for the dates of 30 March 2022 (pre-event), 29 April 2022 (post-event), and 29 May 2022 (post-event) using the training areas digitalized for the date 29 May 2022.
The error matrix was computed to assess the training areas’ quality and to compare the imagery classification and simulation by the different approaches essayed. The error matrix is obtained by comparing the land cover category found in the training sub-set (ground-truth) to that which was obtained in the classification phase for the same location. It shows the distribution of the percentage of pixels classified correctly and in an erroneous way. The statistical accuracy assessment, derived from the error matrix, that was considered were: the overall accuracy that allowed evaluating the overall thematic classification of the map produced; and Cohen’s Kappa coefficient. This last statistic allows quantifying the model accuracy concerning the expected accuracy using a random assignment of pixels to categories. The Kappa statistics considers all elements of the confusion matrix in its evaluation (i.e., also includes the elements off the main diagonal, which represent disagreements in classification) as opposed to the overall accuracy which uses only the diagonal elements (real agreement) [
25].
3. Results
3.1. Composites, spectral indices, ratios imagery, and spectral signatures
The FCC, NDWI, NDVI, and B/G ratio imagery (10 m spatial resolution) for the dates of 30 March 2022 (pre-event), 29 April 2022 (post-event1), and 29 May 2022 (post-event2) showed that in March land cover had high humidity due to the high precipitation occurred in that month (
Figure 2a and
Figure 5a). A plume entering point P5 was observed both in the DNWI and B/G ratio images (
Figure 5b,d).
The monthly difference indices dNDWI and dNDVI between the dates of 30 March 2022 (pre-event), 29 April 2022 (post-event1), and 29 May 2022 (post-event2) also highlighted the changes that occurred (
Figure 6): intense precipitation in March followed by almost no precipitation in April and May (
Figure 2a) making the impact of any contamination less diluted.
Overall, between pre-event and post-event1 the dNDWI showed positive values, but a noticeable plume was observed from the entry point P5 (
Figure 6a). Between post-event1 and post-event2 negative values were observed (
Figure 6b). Conversely, the dNDVI showed negative values between pre-event and post-event1 (
Figure 6c) and positive values between post-event1 and post-event2 (
Figure 6d).
Thus, indicates firstly an increase in moisture content, particularly at the east side of the reservoir (
Figure 6a), with a decrease in eutrophication also at the east side and mostly at the reservoir water entries (
Figure 6c), due to high precipitation in March (
Figure 2a). After occurred a decrease in moisture content (
Figure 6b) and an increase in eutrophication, mostly at the entry point P5 (
Figure 6).
The spectral signatures at the monitoring points for the dates of 30 March 2022 (pre-event), 29 April 2022 (post-event1), and 29 May 2022 (post-event2) showed a general trend of increasing differentiation between the monitoring points (
Figure 7).
3.2. Water quality parameters—monitoring and validation data
The Capt monitoring point was the only point with consistent continuous data collection from October to April 2022. On 8 March 2022 (pre-event) the Capt point revealed very high values for the parameters TP, TN, and Chl-a and moderate values for TSS and TUR (
Figure 8). On 10 April 2022, a significant number of dead fish in the reservoir was observed.
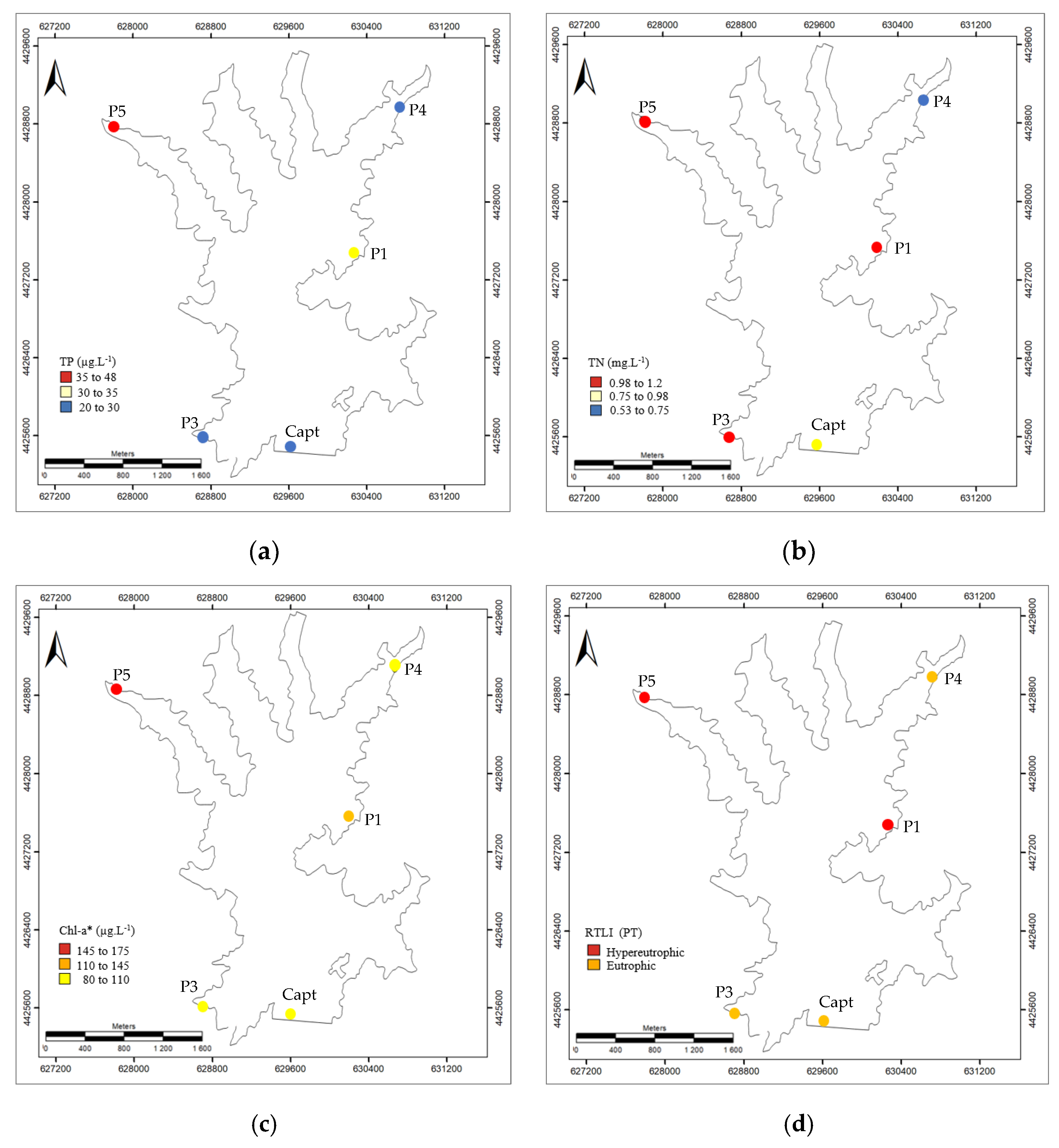
On 27 April 2022 (post-event1) the water quality parameters for TP and TN were available for almost all monitoring points (Capt, P1, P3, P4, and P5) and thus they were the focus of this study analysis, for validation purposes (
Figure 9).
The evaluation of the obtained values for the five monitoring points (Capt, P1, P3, P4, and P5) regarding the TP maximum admissible value of 35 μgL
−1 (DL nº152/2017, 7th of December)[
26] resulted in high values in point P5, intermediate value in point P1, and low values in points Capt, P3, and P4 (
Figure 9a).
Considering as reference for TN the maximum admissible value of 1,5 mgL
−1 (DL nº152/2017, 7th of December)[
26], high values were observed in points P1, P3, and P5, intermediate values in point Capt, and a lower value in point P4. It is worth noticing, that point P5 had the highest values for both TP and TN and above the recommended maximum admissible values (
Figure 9b).
Concerning the estimated values of Chl-a* and assuming the recommended value of 20 μgL−1 for reservoirs by APA (Portuguese Environmental Agency) it is possible to observe that the distribution is as expected concordant with the one for the TP and exceeds the recommended value in all the monitoring points.
The reservoir trophic level index (RTLI –(TP)) showed two levels [
11]: Hypereutrophic level in points P1, and P5; and Eutrophic level in points Capt, P3, and P4. Therefore, revealing a reservoir requires corrective action (
Figure 9c).
The spectral signatures for the monitoring points on 29 April 2022 (
Figure 7b) were consistent with the water quality chemical parameters TP, TN, and Chl-a* estimated and the reservoir trophic level index (RTLI –(TP)) for the date of 27 April 2022 (
Figure 8). For point P5 the spectral signature pattern was close to the Hypereutrophic water-type curve (
Figure 4).
3.3. Water characteristics modelling
The imagery for the date of 29 May 2022 (
Figure 5) showed to have the highest variability in water characteristics throughout this reservoir when compared to the dates of 30 March and 29 April 2022. The spectral signatures at the monitoring points also showed to have less spectral confusion on 29 May 2022 (
Figure 7c). This variability was also highlighted by the first principal component image and the false colour composite image from the B/G ratio, NDVI, and NDWI imagery (
Figure 10a,b).
The nine spectral bands (e.g., B, G, R, R-edge 1, R-edge 1, R-edge 1, NIR narrow, SWIR1, and SWIR2) natural clustering with four, five, and 10 clusters obtained by the unsupervised procedure (e.g., K-means cluster analysis for grids) also emphasized the variability previously observed and highlighted possible training areas with no spectral confusion (
Figure 10c).
Based on the unsupervised clustering image and the ground-truth knowledge, supported by the Marateca reservoir monitoring points water quality chemical parameters data, the digitalized training areas (polygons) for five water characteristics classes considered (e.g., 1—Deepwater; 2—Shallow water; 3—Eutrophic water; 4—Median deep water; and 5—Turbid water) revealed again that its spectral signatures had no spectral confusion (
Figure 11).
The error matrix computed to validate the training areas (
Figure 11a) against the classified image by the classifier of the maximum likelihood (MaxLike) delivered an overall accuracy and a Cohen’s Kappa coefficient of 99%. The error matrix between the Maxlike image and the Cluster 5 image (
Figure 10c) delivered an overall accuracy of 72% and a Cohen’s Kappa coefficient of 45%.
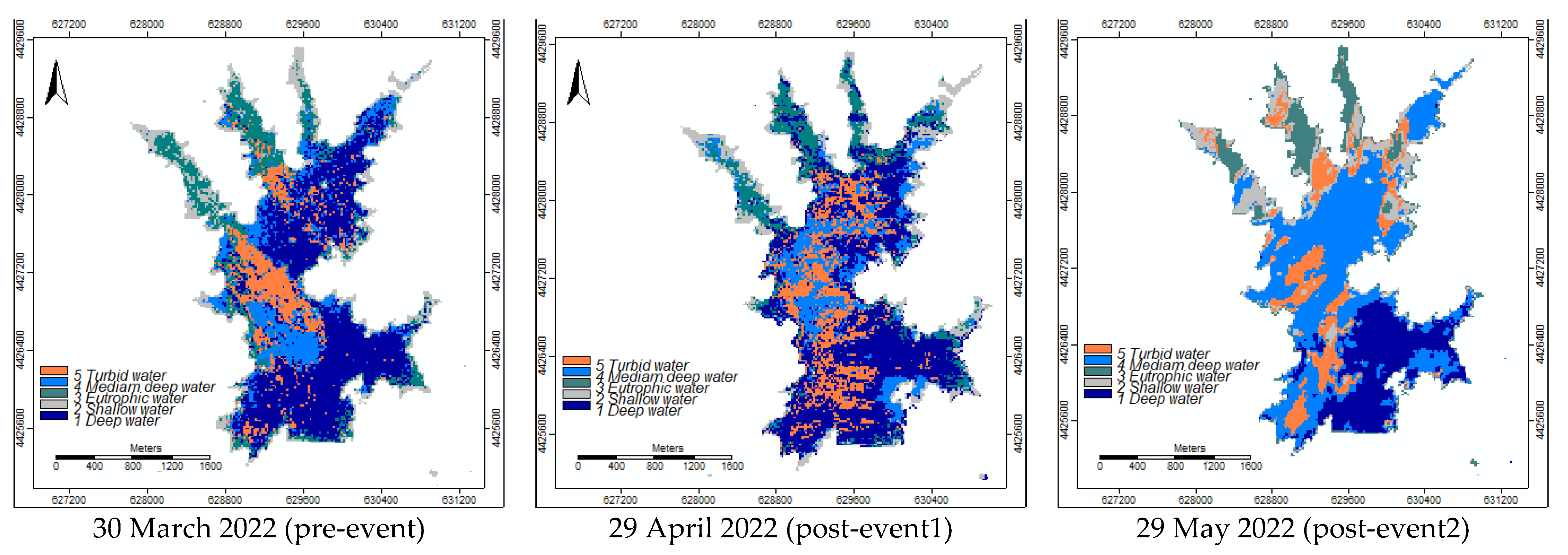
The error matrix between the ML-RF simulated image (
Figure 12b), modelled using the training areas (Figur2 11a), and the Cluster 5 image (
Figure 10c) delivered an overall accuracy of 76% and a Cohen’s Kappa coefficient of 53%. The ML-RF simulated images for the dates of 30 March 2022, 29 April 2022, and 30 May (
Figure 12), using the training areas digitalized on 29 May 2022 (
Figure 11a), clearly identified the natural clusters (
Figure 10c), particularly the plume at the entry point P5 and the eutrophication zones (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6).
4. Discussion
This study results revealed that on 8 March 2023, the water quality parameters TP, TN, and Chl-a showed high values in the Capt point. After, on 10 April 2022 a significant number of dead fish in the reservoir was observed. On 27 April 2022 the TP, TN, and estimated Chl-a* values were above the recommended values (e.g., 35 μgL
−1, 1,5 mgL
−1, and 20 μgL
−1, respectively) in several monitoring points (e.g., P1, P2, P3, and P5). The reservoir trophic level index (RTLI –(TP)) [
11] showed two levels: The hypereutrophic level (points P1, P2, and P5) and the Eutrophic level (points Capt, P3, and P4). Thus, confirming it as one of the most problematic, entry point P5. The spectral information is concordant with these results allowing us to validate the nominal spectral signatures, namely, for TP, TN, and Chl-a*.
Indeed, the principal sources of nutrients in lakes and reservoirs are land runoff and atmospheric inputs. Relatively small internal reservoirs, such as Marateca, are highly sensitive to seasonal intakes. Runoff and atmospheric inputs may vary significantly in the concentration and ratio of TP and TN, and, therefore, in the proportion of organic and inorganic forms of these nutrients [
27,
28].
Considering the Marateca reservoir characteristics, two reasons may explain the elevated levels of TP, TN, and estimated Chl-a. One possibility is eutrophication due to agricultural fertilizers. In this scenario, a high TP value and a lower TN value would be expected. The second possibility is soil erosion with the transport of large amounts of nutrients into the reservoir, especially phosphorus which tends to adhere to soil particles, while nitrogen more soluble can be washed away more easily [
29].
Furthermore, the identified Hypereutrophic and Eutrophic levels refer to excessive growth of algae and other aquatic plants in the water body. This growth is often caused by an excess of nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen in the water. When these nutrients are available in abundance, algae, and other plants can grow very quickly, leading to the water body becoming overgrown and appearing green or brown in colour. This excess growth of plants can also lead to a depletion of oxygen in the water, which can harm fish and other aquatic life, and are often the result of human activities such as agriculture, urbanization, and industrialization.
The spectral signatures for the monitoring points on 29 April 2022 also confirmed that the spectral signature pattern in point P5 is close to the Hypereutrophic water-type reflectance curve. From March to May 2022 a general trend of increasing differentiation between the monitoring points was observed.
Due to the high precipitation in March an increase in moisture content, particularly at the east side of the reservoir was observed, along with a decrease in eutrophication also at the east side and mostly at the reservoir water entries. During the following two months, there was no significant precipitation, consequently, a decrease in moisture content and an increase in eutrophication occurred, mostly at the entry point P5.
In this study, five water characteristics classes were differentiated in the Marateca reservoir (e.g., 1—Deepwater; 2—Shallow water; 3—Eutrophic water; 4—Median deep water; and 5—Turbid water) using the spectral signatures created with the 29 May 2022 imagery. The ML-RF simulated image, modelled using these training areas, delivered an overall accuracy of 76% and a Cohen’s Kappa coefficient of 53% when compared to the Cluster 5 image (natural clustering) proving to be robust. Thus, these training areas allowed modelling of Marateca reservoir water characteristics for the period under analysis (March, April, and May 202) forecasting the problematic zones either due to drought and/or contamination.
Indeed, the Sentine2A imagery proved to be of value to monitor and evaluate reservoir water quality in conjunction with traditional sampling methods and field surveying [
1,
6,
7,
8,
9].
The methodological approach developed in this study can be easily applied to other reservoirs and is a key support tool for decision-makers. Nevertheless, continuous monitoring with consistent data collection over time is mandatory. Furthermore, the water sample’s location should be improved to provide a better distribution of water quality parameters throughout the entire reservoir for effective variability monitoring.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.A.; data curation, C.A., and T.A.; methodology, C.A., and T.A.; formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, C.A., and T.A.; writing—review and editing, C.A. and T.A. The author has read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by CERNAS-IPCB [UIDB/00681/2020] funding from the Foundation for Science and Technology (Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia—FCT)]; and by ICT [UIDB/04683/2020] also funding from FCT.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
Figure A1.
Study area—Marateca reservoir: FCC imagery (October 2021 to January 2023).
Figure A1.
Study area—Marateca reservoir: FCC imagery (October 2021 to January 2023).
References
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. A comprehensive review of water quality parameters estimation using remote sensing techniques. Sensors (Switzerland) 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgakov, N.G.; Levich, A.P. The nitrogen: phosphorus ratio as a factor regulating phytoplankton community structure. Arch. für Hydrobiol. 1999, 146, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammeorg, O.; Nürnberg, G.K.; Tõnno, I.; Kisand, A.; Tuvikene, L.; Nõges, T.; Nõges, P. Sediment phosphorus mobility in Võrtsjärv, a large shallow lake: Insights from phosphorus sorption experiments and long-term monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.; Li, D.; Xu, C.; Sun, P. Using sediment resuspension to immobilize sedimentary phosphorus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1837–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorasani, H.; Zhu, Z. Phosphorus retention in lakes: A critical reassessment of hypotheses and static models. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-alzate, D.F.; Garcés, Y.A.; Henao-cespedes, V. LANDSAT -7 ETM + based remote sensing as a tool for assessing lakes water quality characteristics. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University 2021, 56(1), 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.A.; Simis, S.G.H.; Selmes, N. Complementary water quality observations from high and medium resolution Sentinel sensors by aligning chlorophyll-a and turbidity algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 265, 112651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.J.; He, Y.C.; Chusnah, W.N.; Jaelani, L.M.; Chang, C.H. Multi-reservoir water quality mapping from remote sensing using spatial regression. Sustain. 2021, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ding, J.; Ilyas, N. Machine learning method for quick identification of water quality index (WQI) based on Sentinel-2 MSI data: Ebinur Lake case study. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2021, 21, 1291–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, P.M.A.; Coelho, F.E.S.; Tomé, A.R.; Valente, M.A.; Carvalho, A.; Pires, C.; Pires, H.O.; Pires, V.C.; Ramalho, C. (2002). 20th-century Portuguese climate and climate scenarios. In Climate Change in Portugal: Scenarios, Impacts and Adaptation Measures (SIAM Project); Santos, F.D., Forbes, K., Moita, R., Eds; Gradiva: Lisbon, Portugal; 2002; pp.23-38.
- Lamparelli, M. Graus de trofia em corpos d’agua do Estado de Sao Paulo: Avaliacao dos métodos de monitoramento. 2004, 238. [CrossRef]
- APA Barragem da Marateca. Comissão Nacional Portuguesa das Grandes Barragens. Agência Portuguesa do Ambiente. Available online: https://cnpgb.apambiente.pt/gr_barragens/gbportugal/FICHAS/Maratecaficha.htm (accessed on March 29, 2023).
- DGT. Especificações técnicas da carta de uso e ocupação do solo de Portugal Continental para 1995, 2007, 2010 e 2015. Relatório técnico; Direção-Geral do Território: Lisboa, Portugal, 2018; Available online: http://www.dgterritorio.pt/cartografia_e_geodesia/cartografia/cartografia_tematica/cartografia_de_uso_e_ocupacao_do_solo__cos_clc_e_copernicus_/(accessed on March 29, 2023).
- DGT. Carta de uso e ocupação do solo. Registo nacional de dados geográficos. SNIG. Direção-Geral do Território. Lisboa. Portugal. Available online: https://snig.dgterritorio.gov.pt/rndg/srv/por/catalog.search#/search?anysnig=COS&fast=index (accessed on March 29, 2023).
- IPMA. Boletins Climatológicos de Portugal Continental. Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera. Available online: https://www.ipma.pt/pt/publicacoes/boletins.jsp?cmbDep=cli&cmbTema=pcl&idDep=cli&idTema=pcl&curAno=-1 (accessed on March 29, 2023).
- Navarro, G.; Caballero, I.; Silva, G.; Parra, P.-C.; Vázquez, Á.; Caldeira, R. Evaluation of forest fire on Madeira Island using Sentinel-2A MSI imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, R.; Sobrino, J.A.; Fernández, C.; Fernández-Alonso, J.M.; Vega, J.A. A methodology to estimate forest fires burned areas and burn severity degrees using Sentinel-2 data. Application to the October 2017 fires in the Iberian Peninsula. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 95, 102243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulácsi, A.; Kovács, F. Drought Monitoring With Spectral Indices Calculated From Modis Satellite Images In Hungary. J. Environ. Geogr. 2015, 8, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EOS NDVI FAQ: All You Need To Know About Index. Available online: https://eos.com/blog/ndvi-faq-all-you-need-to-know-about-ndvi/ (accessed on March 29, 2023).
- Ha, N.; Dzung, D.; Hang, H.; Huy, T.; Tu, N. Water Quality Assessment and Eutrophic Classification of Hanoi Lakes Using Different Indices. Vietnam J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojavan, A.F.; Kreakie, B.J.; Hollister, J.W.; Qian, S.S. Rethinking the lake trophic state index. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.-L.; Jiao, Y. Trophic Classification for Lakes☆. In; Fath, B.B.T.-E. of E. (Second E., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, 2019; pp. 487–494. ISBN 978-0-444-64130-4.
- Dodds, W.K.; Jones, J.R.; Welch, E.B. Suggested classification of stream trophic state: distributions of temperate stream types by chlorophyll, total nitrogen, and phosphorus. Water Res. 1998, 32, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrakos, E.; O’Donnell, R.; Hunter, P.D.; Miller, C.; Scott, M.; Simis, S.G.H.; Neil, C.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Binding, C.E.; Bradt, S.; et al. Optical types of inland and coastal waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 846–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DR Decreto-Lei no152/2017 de 7 de dezembro. Diário da República, I Série-no 235/2017 de 7 de dezembro. Available online: https://dre.pt/dre/detalhe/decreto-lei/152-2017-114315242.
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, D.; Song, X. Empirical estimation of total nitrogen and total phosphorus concentration of urban water bodies in china using high resolution IKONOS multispectral imagery. Water (Switzerland) 2015, 7, 6551–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guildford, S.J.; Hecky, R.E. Total nitrogen, total phosphorus, and nutrient limitation in lakes and oceans: Is there a common relationship? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Gao, J. Key factors affecting discharge, soil erosion, nitrogen and phosphorus exports from agricultural polder. Ecol. Modell. 2021, 452, 109586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Study area: (a) Portugal and the Sentinel2A imagery tile (29 May 2022); (b) Marateca reservoir’s limit from the LCLU (COS 2018), and the monitoring points (Capt, P1, P2, P3, P4, and P5); and (c) LCLU (COS 2018) around the Marateca reservoir.
Figure 1.
Study area: (a) Portugal and the Sentinel2A imagery tile (29 May 2022); (b) Marateca reservoir’s limit from the LCLU (COS 2018), and the monitoring points (Capt, P1, P2, P3, P4, and P5); and (c) LCLU (COS 2018) around the Marateca reservoir.
Figure 2.
Study area: (
a) Castelo Branco climatological station (October 2021–January 2023) data—monthly, average, minimum, and maximum temperatures and total monthly precipitation [
15]; and (
b) Marateca reservoir‘s, monthly total capacity (million m
3) (
https://snirh.apambiente.pt/index.php?idMain=2&idItem=3).
Figure 2.
Study area: (
a) Castelo Branco climatological station (October 2021–January 2023) data—monthly, average, minimum, and maximum temperatures and total monthly precipitation [
15]; and (
b) Marateca reservoir‘s, monthly total capacity (million m
3) (
https://snirh.apambiente.pt/index.php?idMain=2&idItem=3).
Figure 3.
Study area—Marateca reservoir: (a) FCC at total capacity (e.g., 5 Jan 2023—37.2 million m3); (b) Near-infrared band (NIR) histogram and threshold for the water mask; and (c) Water mask (Boolean).
Figure 3.
Study area—Marateca reservoir: (a) FCC at total capacity (e.g., 5 Jan 2023—37.2 million m3); (b) Near-infrared band (NIR) histogram and threshold for the water mask; and (c) Water mask (Boolean).
Figure 4.
Optical water types by Spyrakos et al. (2018).
Figure 4.
Optical water types by Spyrakos et al. (2018).
Figure 5.
Study area—Marateca reservoir imagery (10 m spatial resolution) for the dates of 30 March 2022, 29 April 2022, and 29 May 2022: (a) FCC; (b) NDWI; (c) NDVI; and (d) B/G ratio.
Figure 5.
Study area—Marateca reservoir imagery (10 m spatial resolution) for the dates of 30 March 2022, 29 April 2022, and 29 May 2022: (a) FCC; (b) NDWI; (c) NDVI; and (d) B/G ratio.
Figure 6.
Study area—Marateca indices change: (a) dNDWI (30 March–29 April); (b) dNDWI (29 April–30 May); (c) dNDVI (30 March–29 April); and (d) dNDVI (29 April–30 May).
Figure 6.
Study area—Marateca indices change: (a) dNDWI (30 March–29 April); (b) dNDWI (29 April–30 May); (c) dNDVI (30 March–29 April); and (d) dNDVI (29 April–30 May).
Figure 7.
Study area—Marateca reflectance curves for the monitoring points (Capt, P1, P2, P3, P4, and P5): (a) 30 March 2022 (pre-event); (b) 29 April 2022 (post-event); and (c) 29 May 2022 (post-event).
Figure 7.
Study area—Marateca reflectance curves for the monitoring points (Capt, P1, P2, P3, P4, and P5): (a) 30 March 2022 (pre-event); (b) 29 April 2022 (post-event); and (c) 29 May 2022 (post-event).
Figure 8.
Study area—Marateca’s water quality parameters at the monitoring sampling point Capt from October 2021 to April 2022: TP—total phosphorus, Chl-a—chlorophyll, TSS—total suspended solids, TUR—turbidity, and DO—dissolved oxygen.
Figure 8.
Study area—Marateca’s water quality parameters at the monitoring sampling point Capt from October 2021 to April 2022: TP—total phosphorus, Chl-a—chlorophyll, TSS—total suspended solids, TUR—turbidity, and DO—dissolved oxygen.
Figure 9.
Values at monitoring points (Capt, P1, P3, P4, and P5) on 27 April 2022 (post-event) for: (a) TP—total phosphorus; (
b) TN—total nitrogen, (
c) Chl-a*—estimated chlorophyll-a; and (
d) RTLI (TP)—reservoir trophic level index [
11].
Figure 9.
Values at monitoring points (Capt, P1, P3, P4, and P5) on 27 April 2022 (post-event) for: (a) TP—total phosphorus; (
b) TN—total nitrogen, (
c) Chl-a*—estimated chlorophyll-a; and (
d) RTLI (TP)—reservoir trophic level index [
11].
Figure 10.
Study area—Marateca reservoir imagery (20 m spatial resolution) for the dates of 30 March 2022, 29 April 2022, and 29 May 2022: (a) 1st principal component (PCA_1); (b) indices composite NDVI-BG-NDWI; and (c) unsupervised classification (K-means Clusters) with five clusters.
Figure 10.
Study area—Marateca reservoir imagery (20 m spatial resolution) for the dates of 30 March 2022, 29 April 2022, and 29 May 2022: (a) 1st principal component (PCA_1); (b) indices composite NDVI-BG-NDWI; and (c) unsupervised classification (K-means Clusters) with five clusters.
Figure 11.
Study area—Marateca reservoir reflectance curves on 29 May 2022 imagery of 20 m spatial resolution: (a) training areas (polygons); and (b) reflectance curves for the considered five water classes (e.g., 1—Deepwater; 2—Shallow water; 3—Eutrophic water; 4—Median deep water; and 5—Turbid water).
Figure 11.
Study area—Marateca reservoir reflectance curves on 29 May 2022 imagery of 20 m spatial resolution: (a) training areas (polygons); and (b) reflectance curves for the considered five water classes (e.g., 1—Deepwater; 2—Shallow water; 3—Eutrophic water; 4—Median deep water; and 5—Turbid water).
Figure 12.
Study area—Marateca reservoir imagery modelling by ML-RF for (a) 30 March 2022; (b) 29 April 2022; and (c) 29 May 2022.
Figure 12.
Study area—Marateca reservoir imagery modelling by ML-RF for (a) 30 March 2022; (b) 29 April 2022; and (c) 29 May 2022.
Table 1.
Sentinel-2 MSI—spectral bands and spatial resolution [
17].
Table 1.
Sentinel-2 MSI—spectral bands and spatial resolution [
17].
| Band |
Name |
Central wavelength (nm) |
Spatial resolution (m) |
| 1 |
Coastal aerosol |
443 |
60 |
| 2 |
Blue |
490 |
10 and 20 |
| 3 |
Green |
560 |
10 and 20 |
| 4 |
Red |
665 |
10 and 20 |
| 5 |
Red-edge 1 |
705 |
20 |
| 6 |
Red-edge 2 |
740 |
20 |
| 7 |
Red-edge 3 |
783 |
20 |
| 8 |
NIR |
842 |
10 |
| 8a |
NIR narrow |
865 |
20 |
| 9 |
Water vapour |
945 |
60 |
| 10 |
Cirrus |
1375 |
60 |
| 11 |
SWIR 1 |
1610 |
20 |
| 12 |
SWIR 2 |
2190 |
20 |
Table 2.
Sentinel-2A MSI imagery—dates of acquisition.
Table 2.
Sentinel-2A MSI imagery—dates of acquisition.
| Year |
Date of acquisition |
| |
Jan |
Feb |
Mar |
Apr |
May |
Jun |
Jul |
Aug |
Sep |
Oct |
Nov |
Dec |
| 2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11 |
30 |
30 |
| 2022 |
29 |
28 |
30 |
29 |
29 |
28 |
28 |
27 |
26 |
|
5 and 25 |
|
| 2023 |
4 and 24 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 3.
Spectral indices and ratios (spatial resolution 10 m).
Table 3.
Spectral indices and ratios (spatial resolution 10 m).
| Acronym |
Spectral bands |
Formula |
Equation |
| NDWI |
G—green band
NIR—near infrared band |
|
|
| NDVI |
R—red band
NIR—near infrared band |
|
|
| B/G |
B—blue band
G—green band |
|
|
Table 4.
Water quality parameters with optical active constituents measured by remote sensing [
1,
6,
7,
8,
9].
Table 4.
Water quality parameters with optical active constituents measured by remote sensing [
1,
6,
7,
8,
9].
| Acronym |
TP |
Chl-a |
TSS |
TUR |
DO |
| NDVI |
|
x |
|
|
|
| B/G |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).