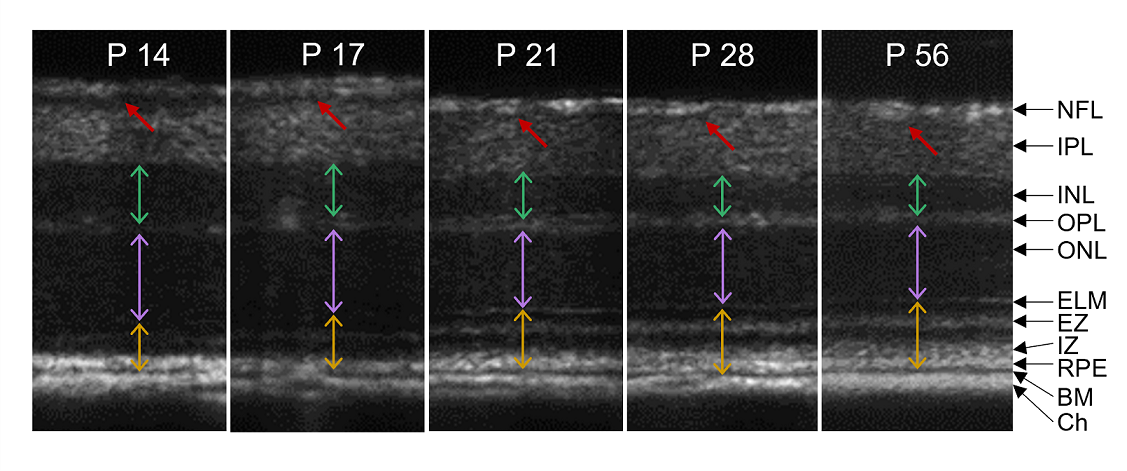
A better study of the postnatal retinal development is not only essential for the in-depth understanding of the nature of the vision system but also may provide insights for treatment developments of eye conditions, such as retinopathy of premature (ROP). To date, quantitative analysis of postnatal retinal development is primarily limited to endpoint histological examination. This study is to validate in vivo optical coherence tomography (OCT) for longitudinal monitoring of postnatal retinal development in developing mouse eyes. Three-dimensional (3D) frame registration and super averaging were adopted to investigate the fine structure of the retina. Interestingly, a hyporeflective layer (HRL) between the nerve fiber layer (NFL) and inner plexiform layer (IPL) was observed in developing eyes and gradually disappeared with aging. To interpret the observed retinal layer kinetics, a model based on eyeball expansion, cell apoptosis, and retinal structural modification was proposed.