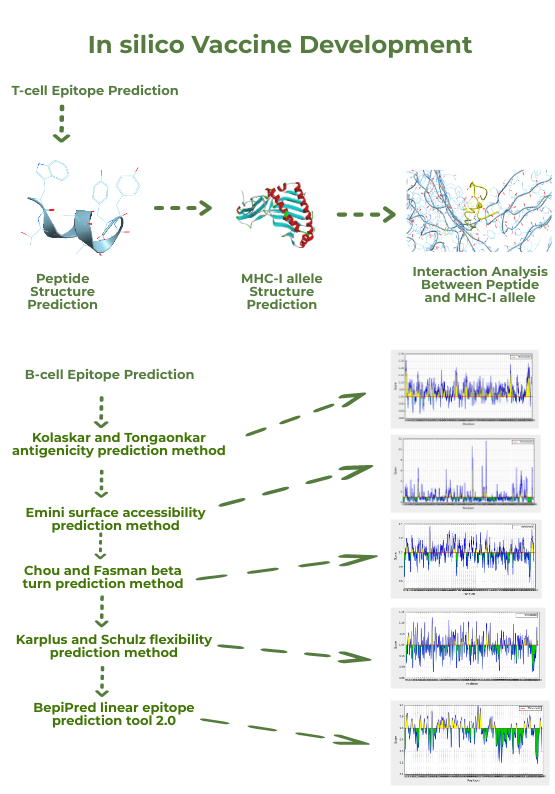
SARS-CoV-2 has been the talk of the town ever since the beginning of 2020. The pandemic has brought the complete world on a halt. Every country is trying all possible steps to combat the disease ranging from shutting the complete economy of the country to repurposing of drugs and vaccine development. The rapid data analysis and widespread tools, software and databases have made bioinformatics capable of giving new insights to the researchers to deal with the current scenario more efficiently. Vaccinomics, the new emerging field of bioinformatics uses concepts of immunogenetics and immunogenomics with in silico tools to give promising results for wet lab experiments. This approach is highly validated for the designing and development of potent vaccines. The present in-silico study was attempted to identify peptide fragments from spike surface glycoprotein that can be efficiently used for the designing and development of epitope-based vaccine designing approach. Both B-cell and T-cell epitopes are predicted using integrated computational tools. VaxiJen server was used for prediction of protective antigenicity of the protein. NetCTL was studied for analyzing most potent T cell epitopes and its subsequent MHC-I interaction through tools provided by IEDB. 3D structure prediction of peptides and MHC-I alleles (HLA-C*03:03) was further done to carry out docking studies using AutoDock4.0. Various tools from IEDB were used to predict B-cell epitopes on the basis of different essential parameters like surface accessibility, beta turns and many more. Based on results interpretation, the peptide sequence from 1138-1145 amino acid and sequence WTAGAAAYY and YDPLQPEL were obtained as a potential B-cell epitope and T-cell epitope respectively. This in-silico study will help us to identify novel epitope-based peptide vaccine target in spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Further, in-vitro and in-vivo study needed to validate the findings.