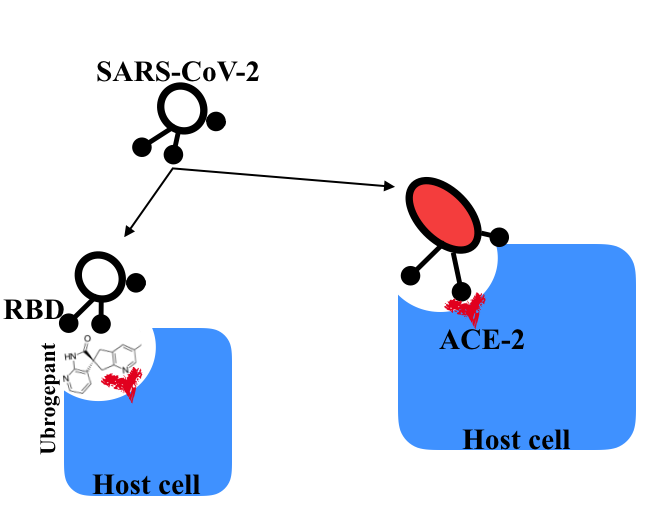
Background: COVID-19, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a global pandemic affecting approximately 490,000 people and accounting for more than 22,000 deaths and has no generally acceptable cure. Here, the recently resolved 3D structure of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD) in complex with its receptor-the angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2) have provided the basis for screening chemical database for novel entry inhibitors. Methods: Molecular docking protocols have been used to rapidly screen FDA database for high affinity interaction at the SARS-CoV-2-RBD/ACE-2 interface. One of the top candidates, ubrogepant has been selected and further studied using atomistic molecular dynamics simulation method. Results: Molecular docking result showed that ubrogepant (UBR) and darunavir have binding energies of -10.4 kcal/mol. MMPBSA free energy analyses of UBR bound to RBD, ACE-2 and RBD/ACE-2 revealed RBD/ACE-2 > ACE-2 > RBD preference. Network analysis showed that interaction captured in the crystal structure were disrupted in UBR-bound state, hydration of the interface and increased atomic fluctuation within the RBD oligomerization interface and ACE-2 zinc binding site. Conclusions: The ability of ubrogepant to rupture the interaction at the RBD/ACE-2 interface residues of SARS-CoV-2 RBD/ACE-2 complex may result in loss of protein function with direct implication on oligomerization formation in RBD and loss of function in ACE-2 thus, making binding, cellular receptor recognition impossible. General Significance: Ubrogepant represents a new therapeutic candidate in the fight against COVID-19, as it binds with relatively high affinity with free RBD, ACE-2 receptor and SARS-CoV-2 RBD/ACE-2 complex based on binding affinity calculations.