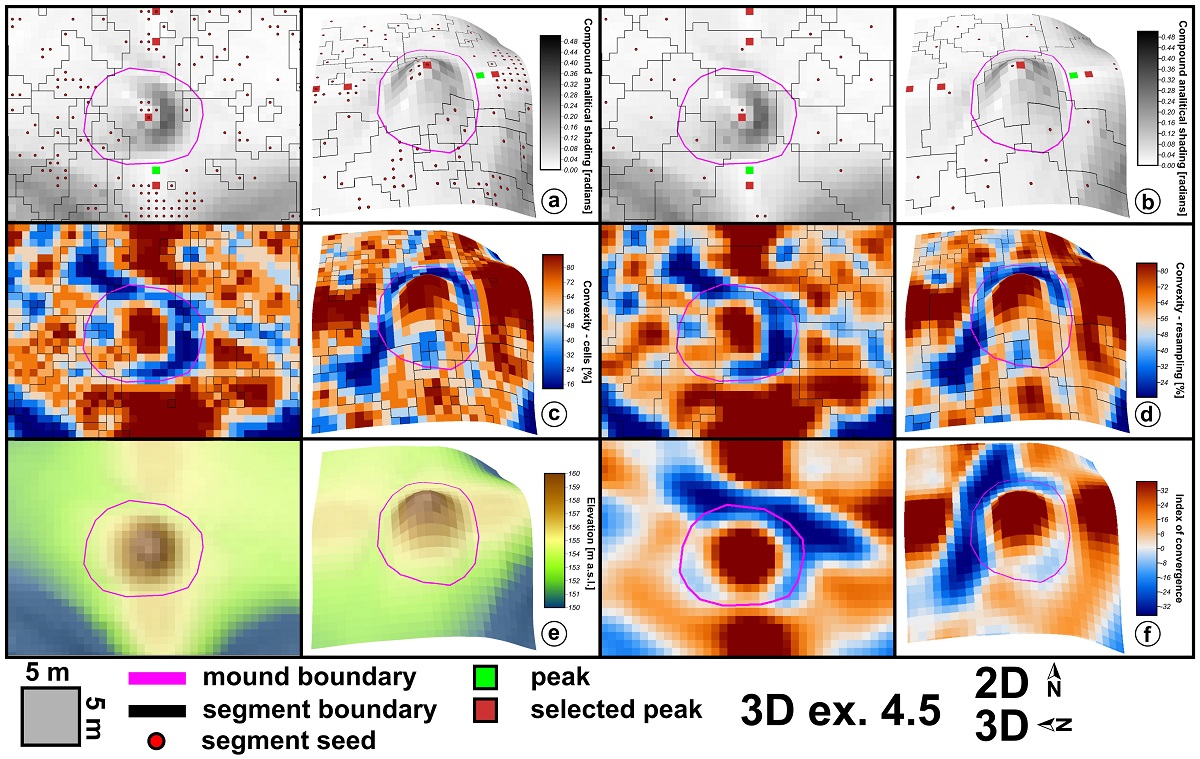
Archaeological topography identification from high-resolution DEMs is a current method that is used with high success in archaeological prospecting of wide areas. I present a methodology trough which burial mounds (tumuli) from LiDAR DEMS can be identified. This methodology uses geomorphometric and statistical methods to identify with high accuracy burial mound candidates. Peaks, defined as local elevation maxima are found as a first step. In the second step, local convexity watershed segments and their seeds are compared with positions of local peaks and the peaks that correspond or have in vicinity local convexity segments seeds are selected. The local convexity segments that correspond to these selected peaks are further feed to a Random Forest algorithm together with shape descriptors and descriptive statistics of geomorphometric variables in order to build a model for the classification. Multiple approaches to tune and selected the proper training dataset, settings and variables were tested. The validation of the model was performed on the full dataset where the training was performed and on an external dataset in order to test the usability of the method for other areas in a similar geomorphological and archaeological setting. The validation was performed against manually mapped and field checked burial mounds from two neighbor study areas of 100 km2 each. The results show that by training the Random Forest on a dataset composed of between 75% to 100% of the segments corresponding to burial mounds and ten times more non-burial mounds segments selected using latin hypercube sampling, 93% of the burial mound segments from the external dataset are identified. There are 42 false positive cases that need to be checked, and there are two burial mound segments missed. The method shows great promise to be used for burial mound detection on wider areas by delineating a certain number of tumuli mounds for model training.