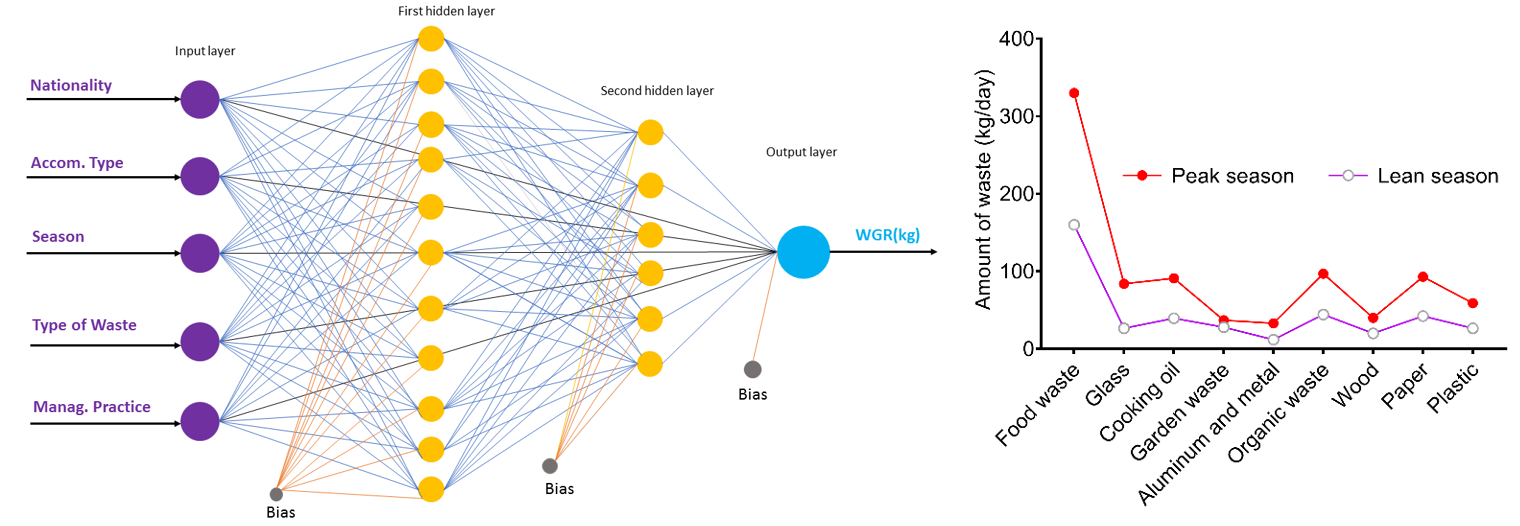
This study was undertaken to forecast waste generation rates of accommodation sector of North Cyprus as a case. Three predictor models including multiple linear regression (MLR), artificial neural networks (ANNs) and central composite design (CCD) were applied to predict the waste generation rate during the lean and peak seasons. ANN showed highest prediction performance, specifically, lowest values of the standard error of prediction (SEP = 2.153), mean absolute error (MAE=1.378) and highest R2 value (0.998) confirmed the accuracy of the model. The analysed wastes were categorised into recyclable, general waste and food residues. The authors estimated the total waste generated during the lean season as 2010.5 kg/day, in which large-sized hotel accounted for largest fraction (66.7%), followed by the medium hotels (19.4%) and guesthouse accounted for smallest part (2.6%). During the peak season, about 49.6% increases in the waste generation rates were obtained. Interestingly, 45% of the wastes were generated by the British tourists while the least waste was generated by African tourists (7.5%). The ANN predicted that the small and large hotels would produce 5.45 and 22.24 tons of waste by the year 2020, respectively. The findings herein are promising and useful in establishing a sustainable waste management system.