Submitted:
02 August 2023
Posted:
03 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
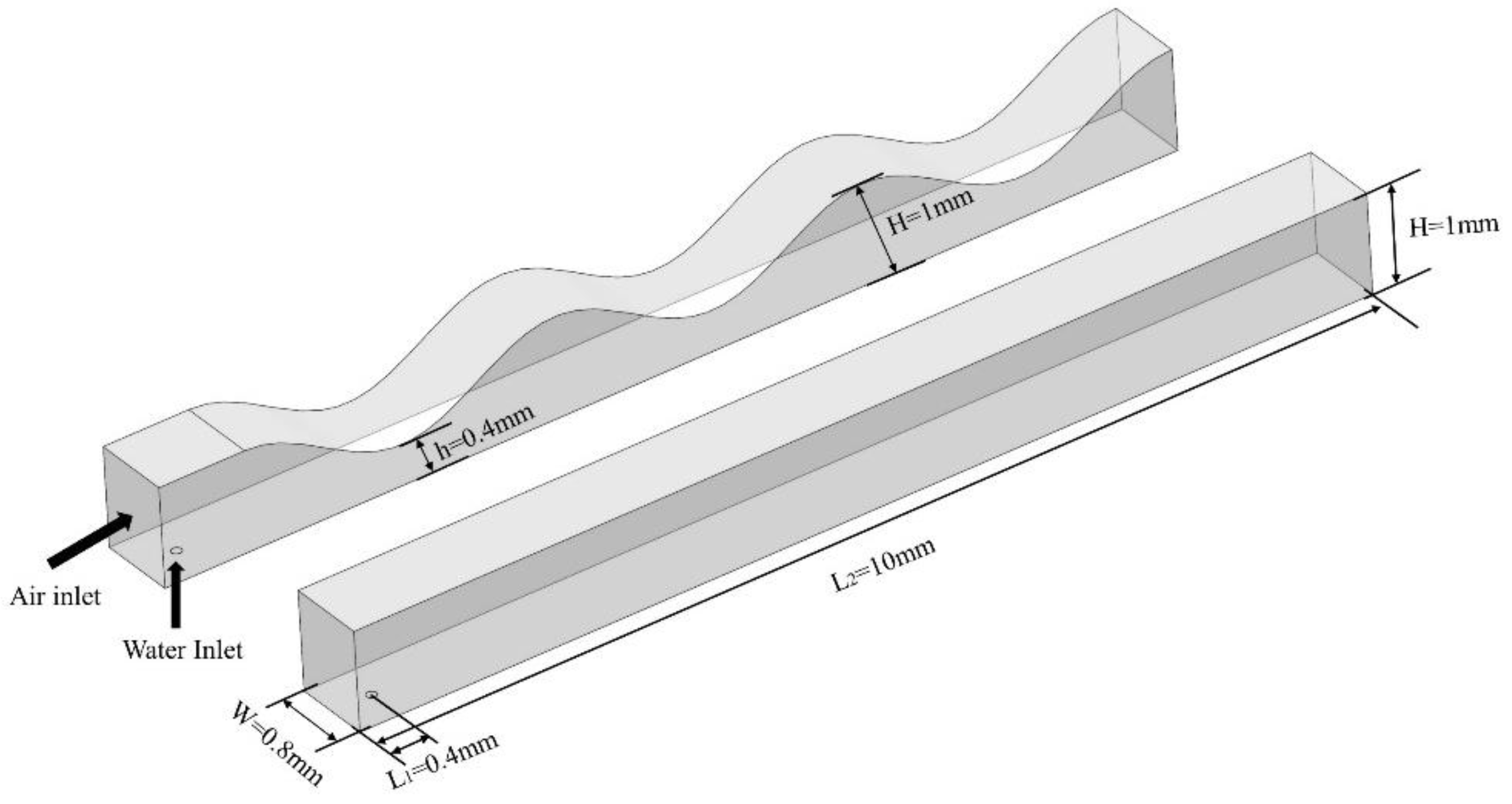
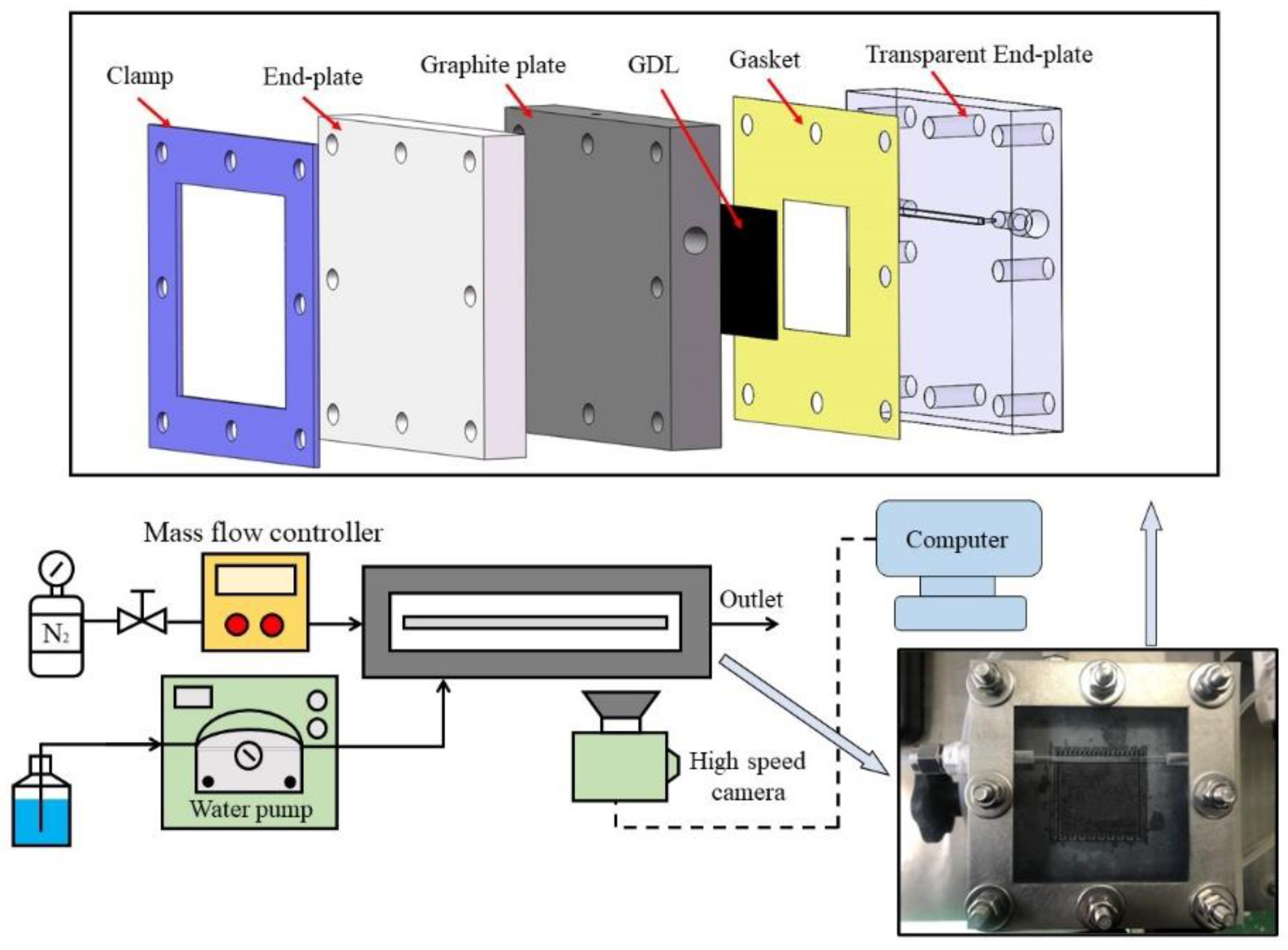
2.1. Materials
2.2. Numerical models
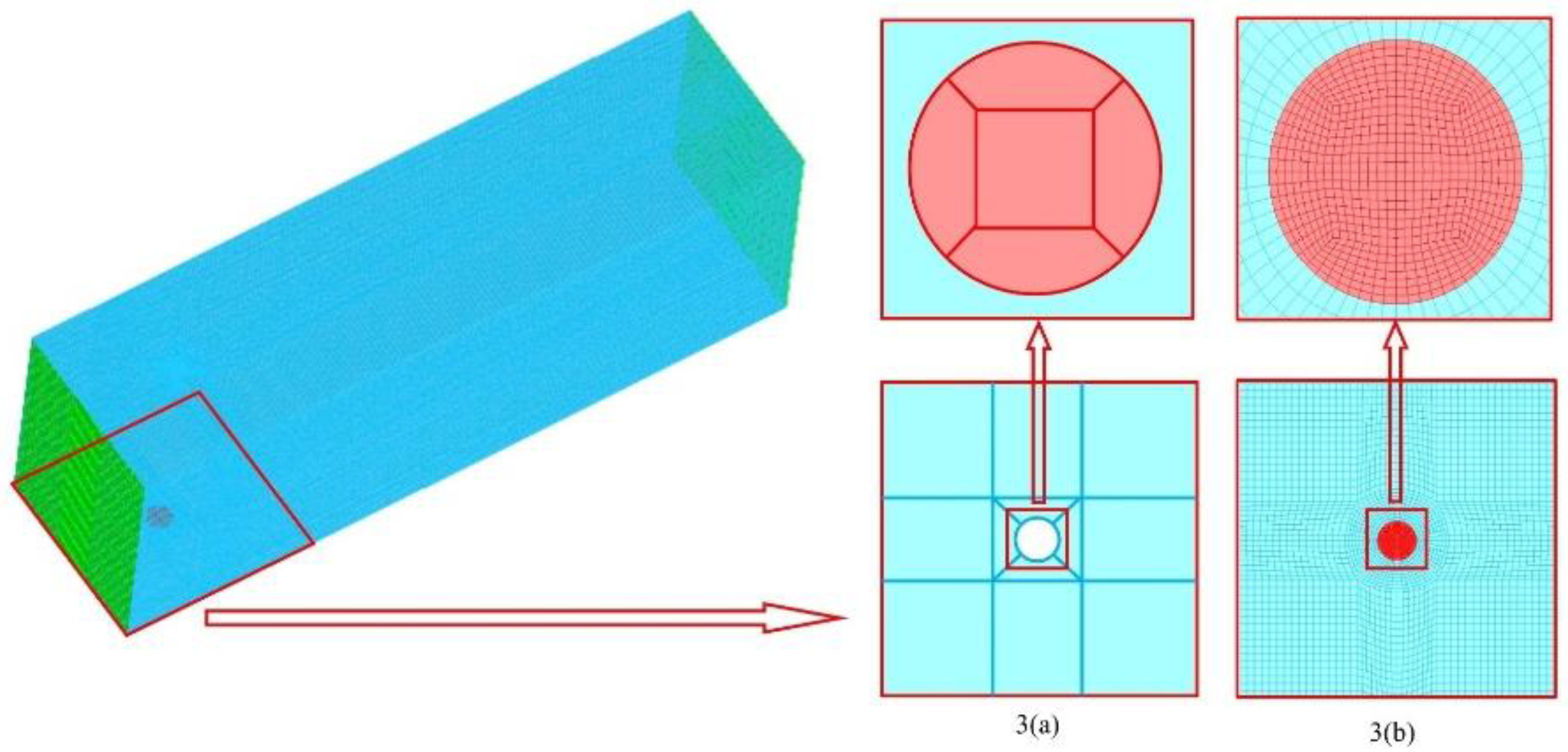
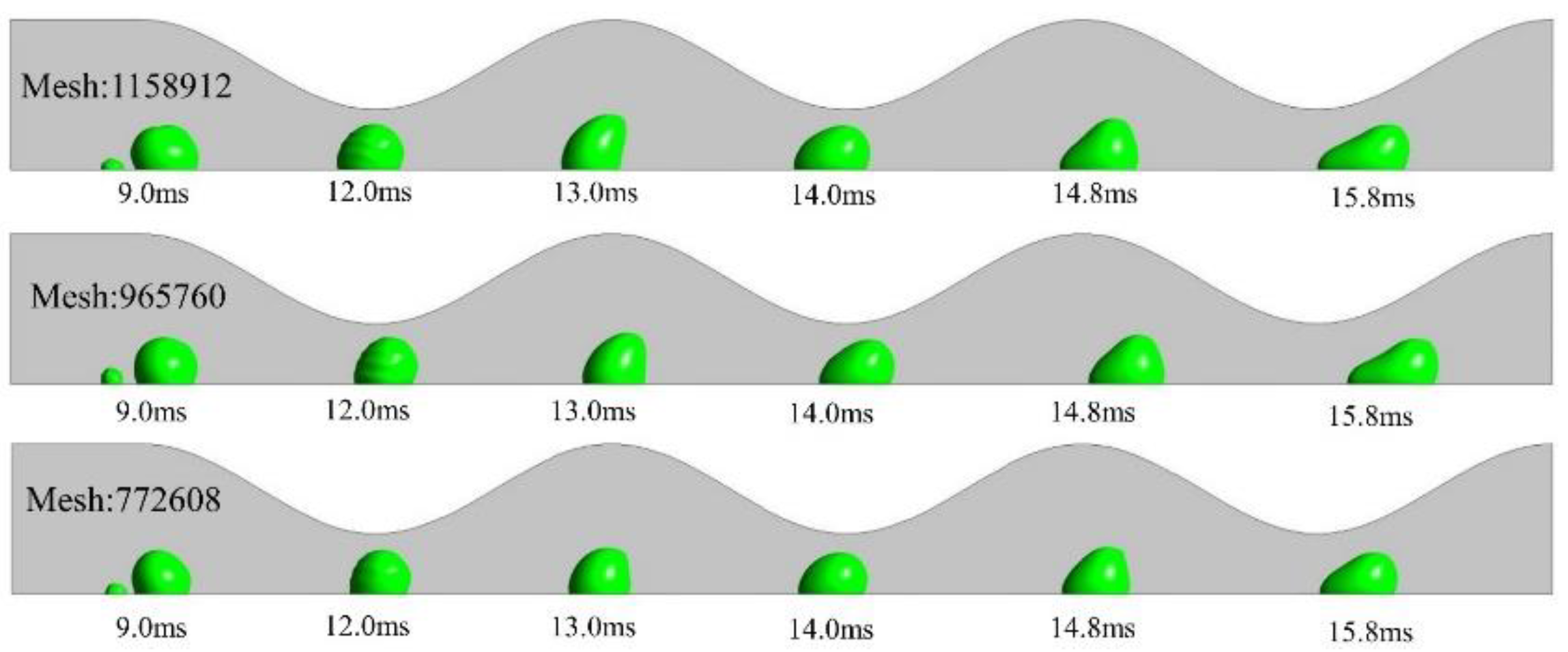
2.3. Computational domain and grid independency test
3. Results
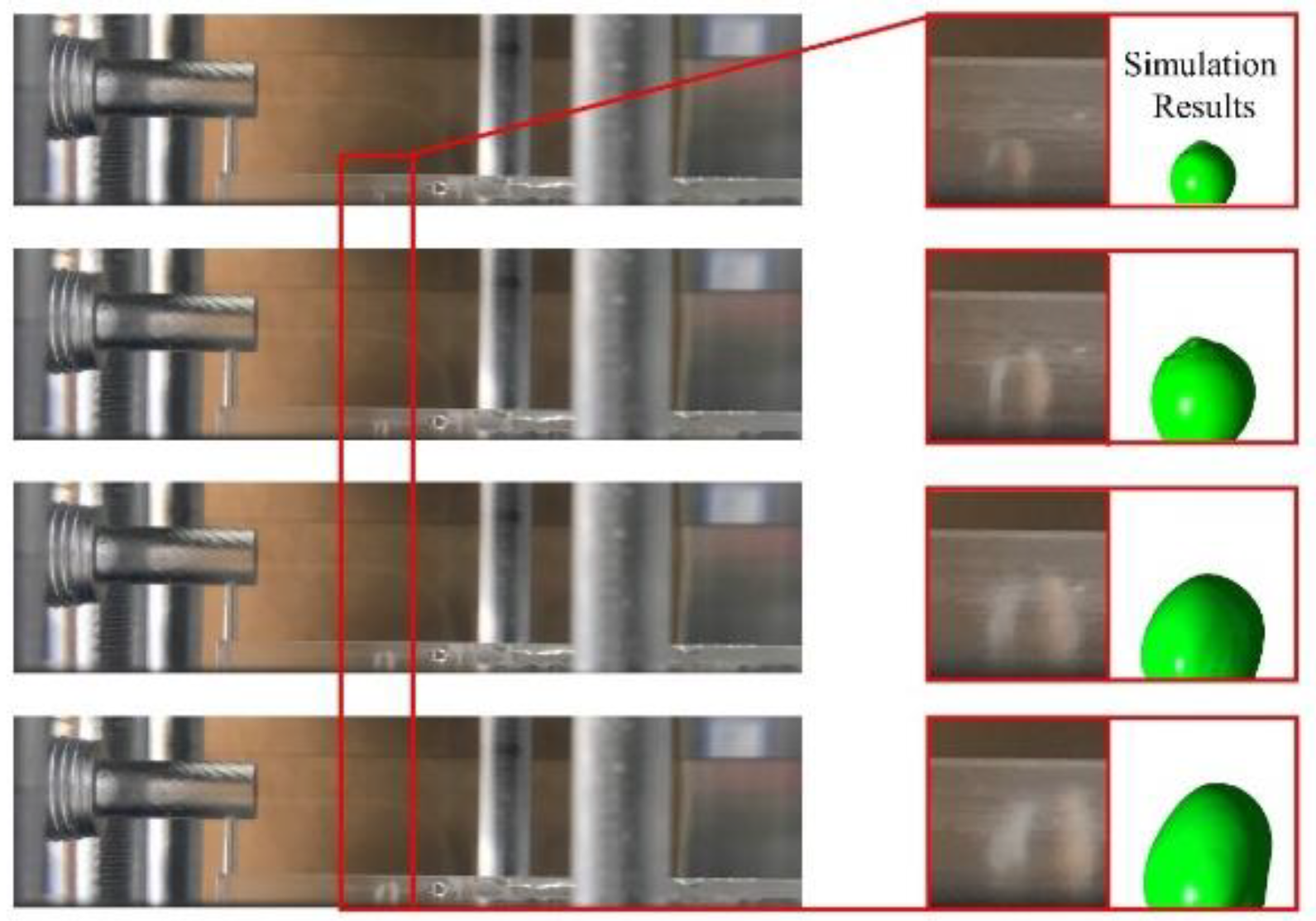
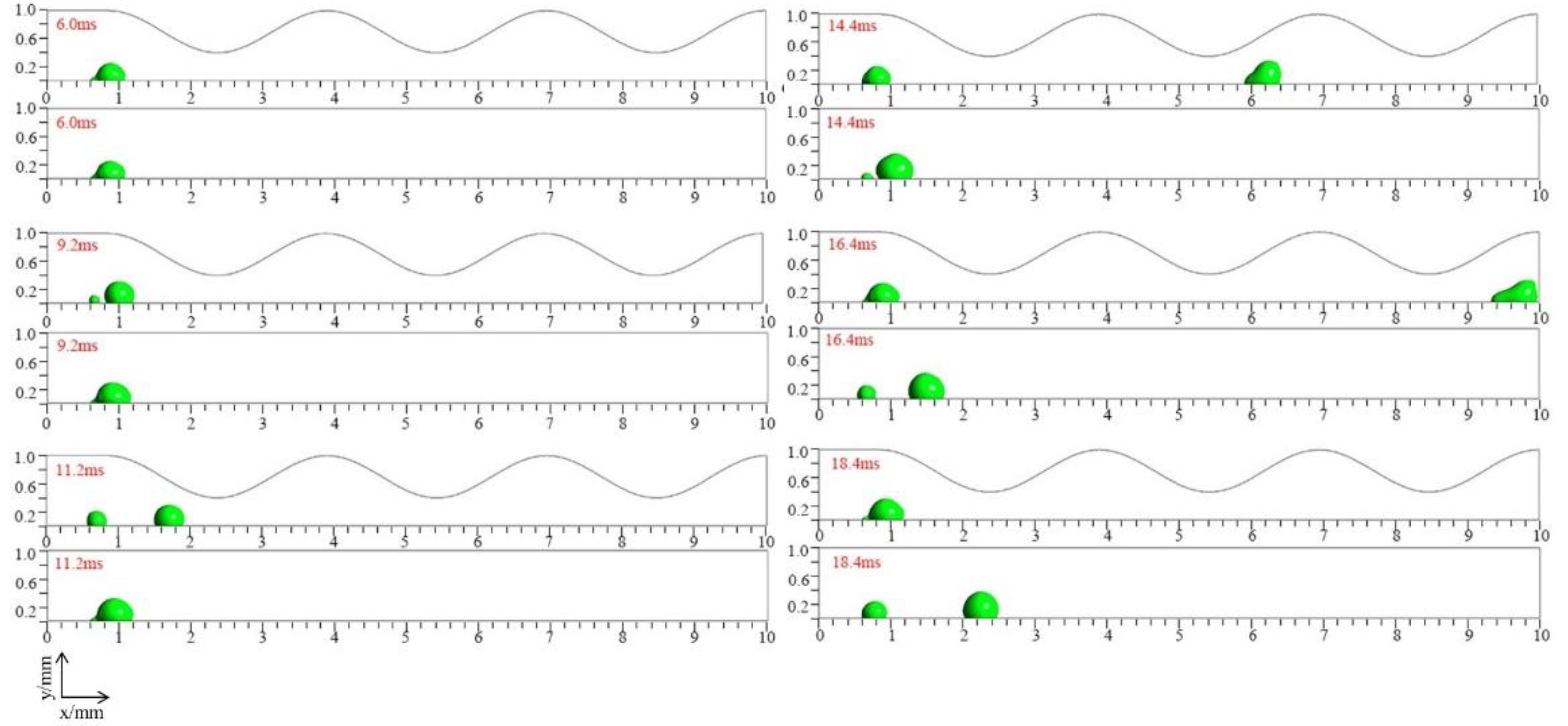
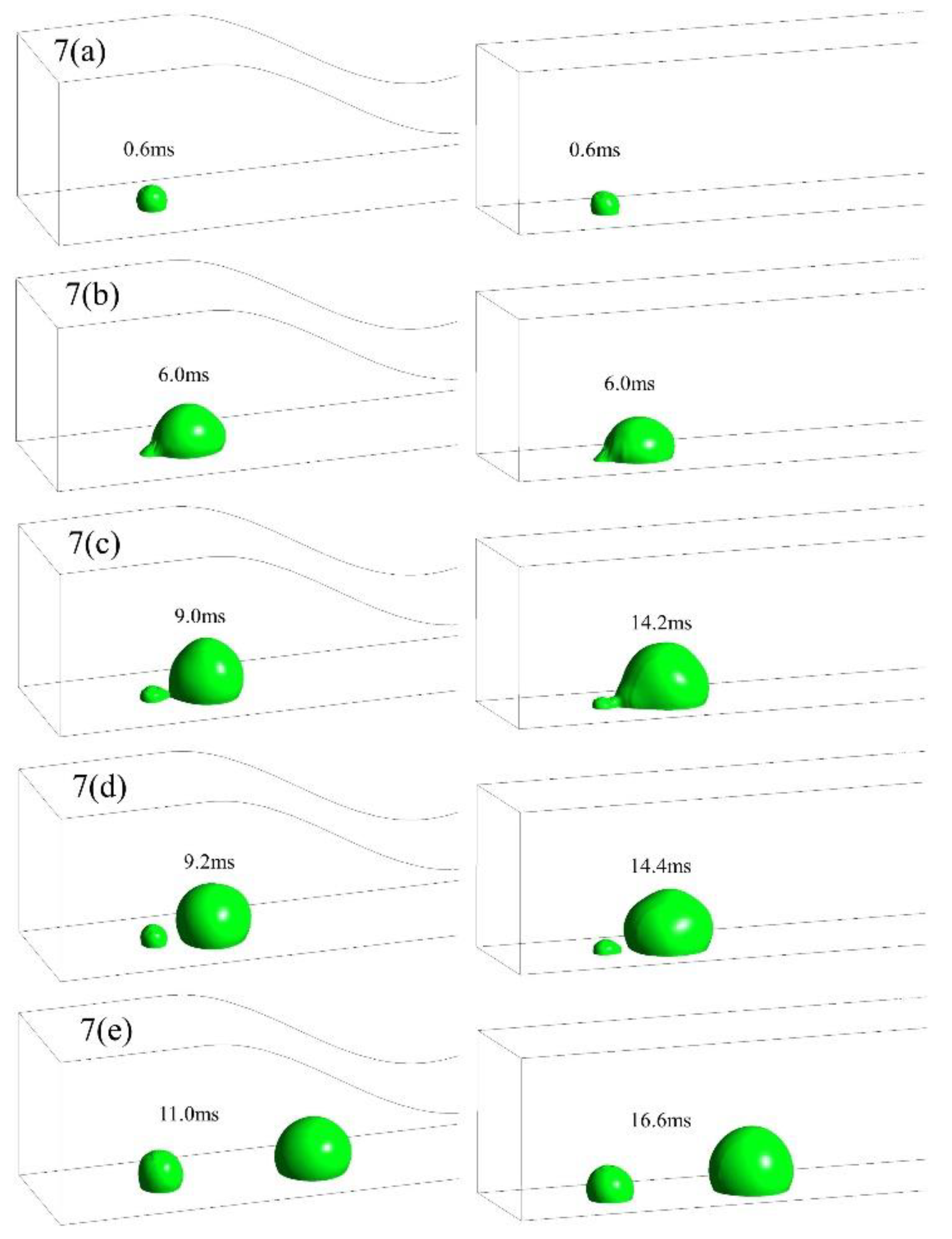
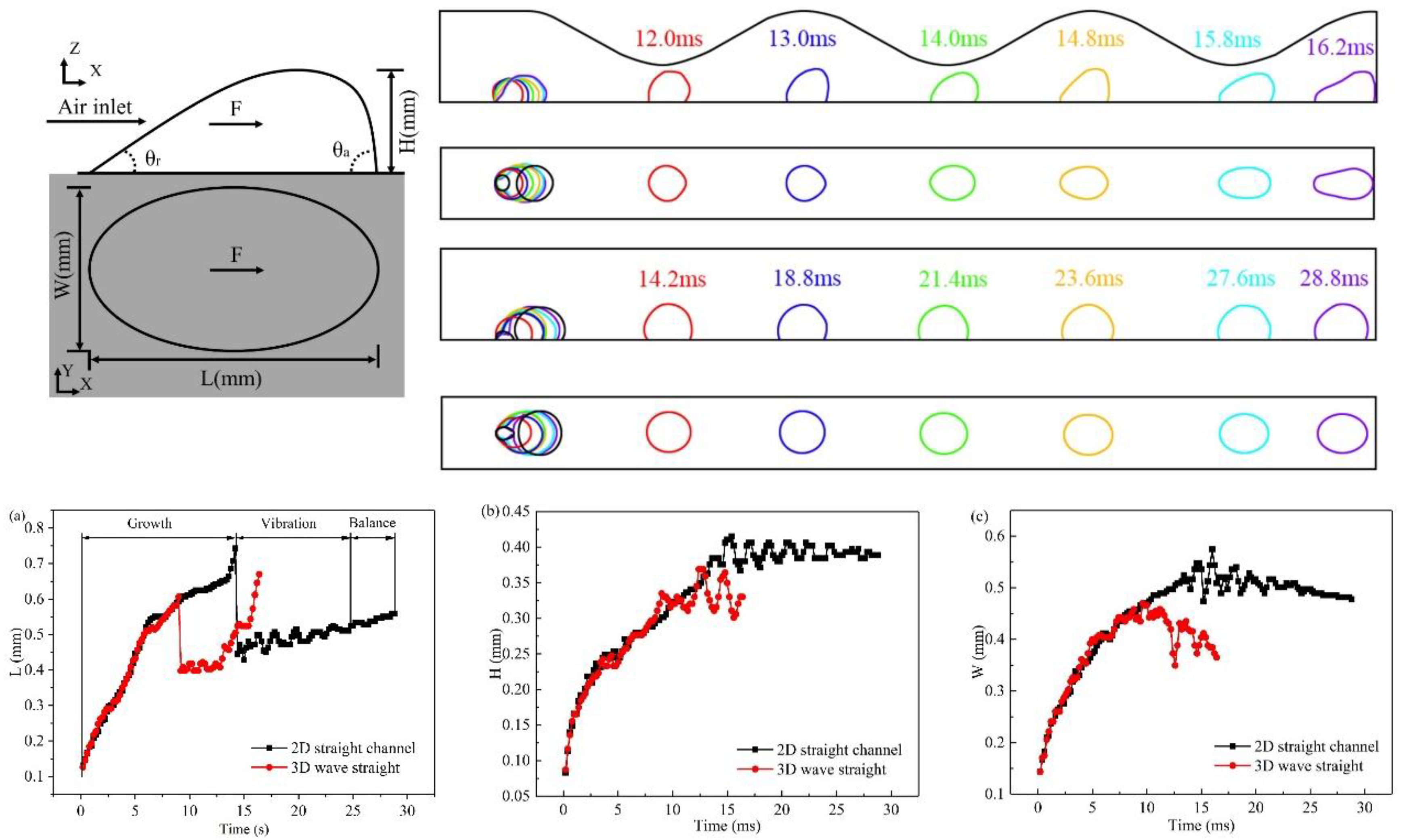
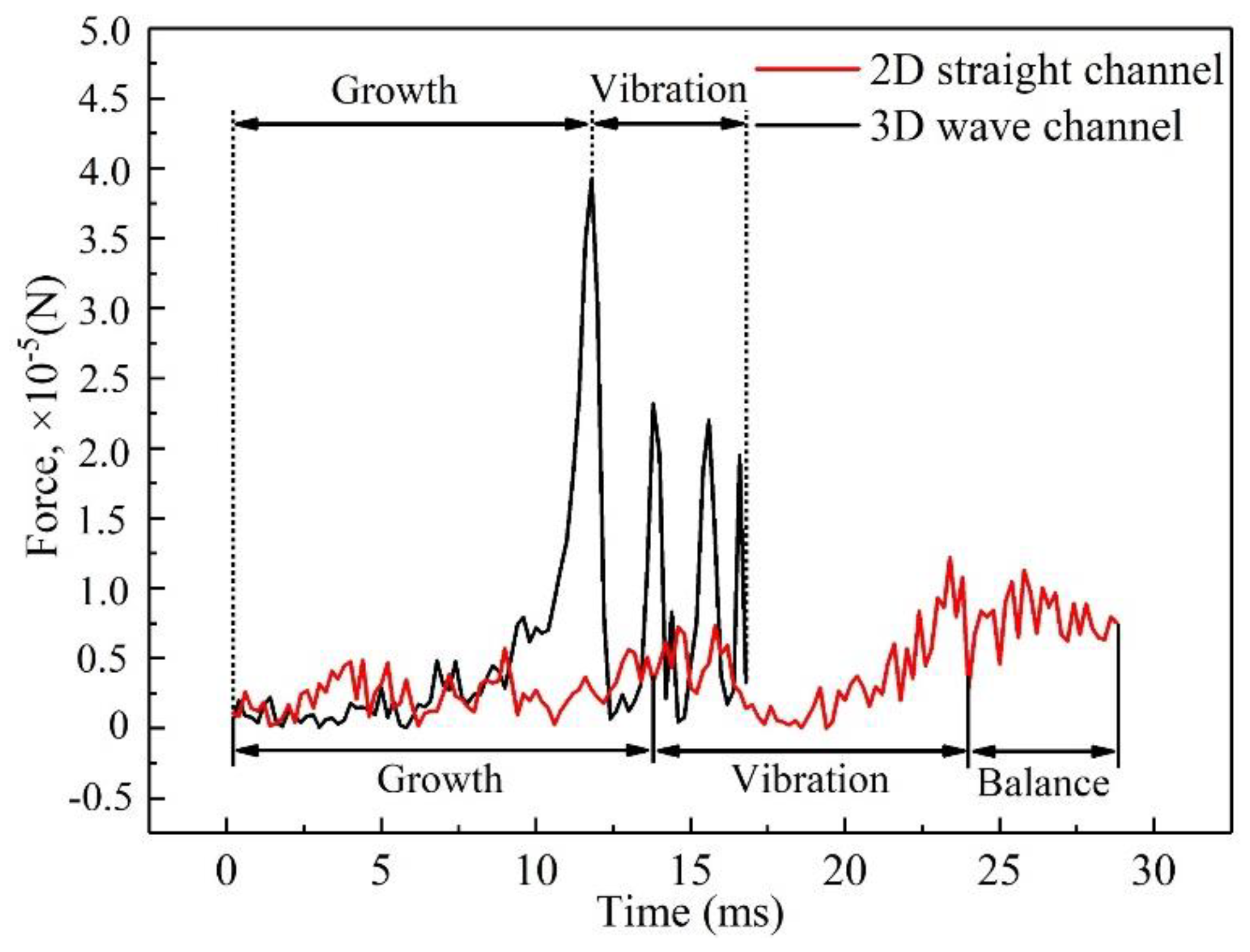
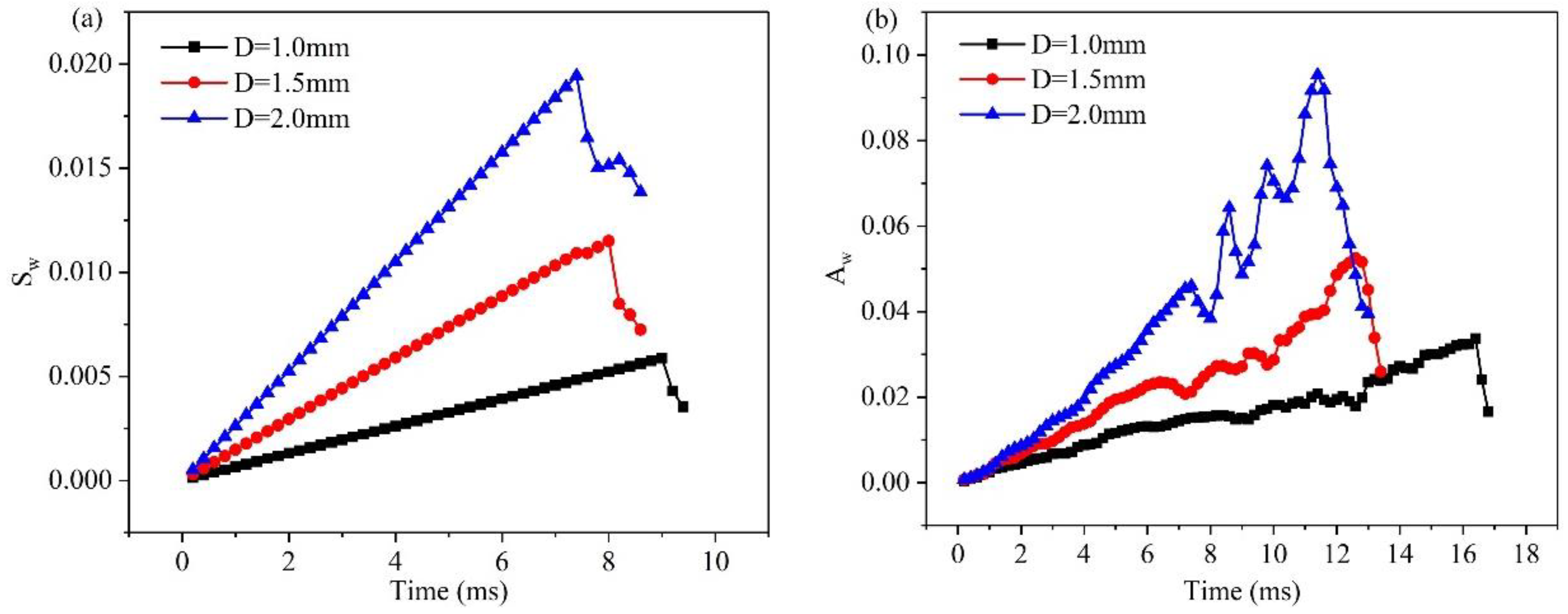
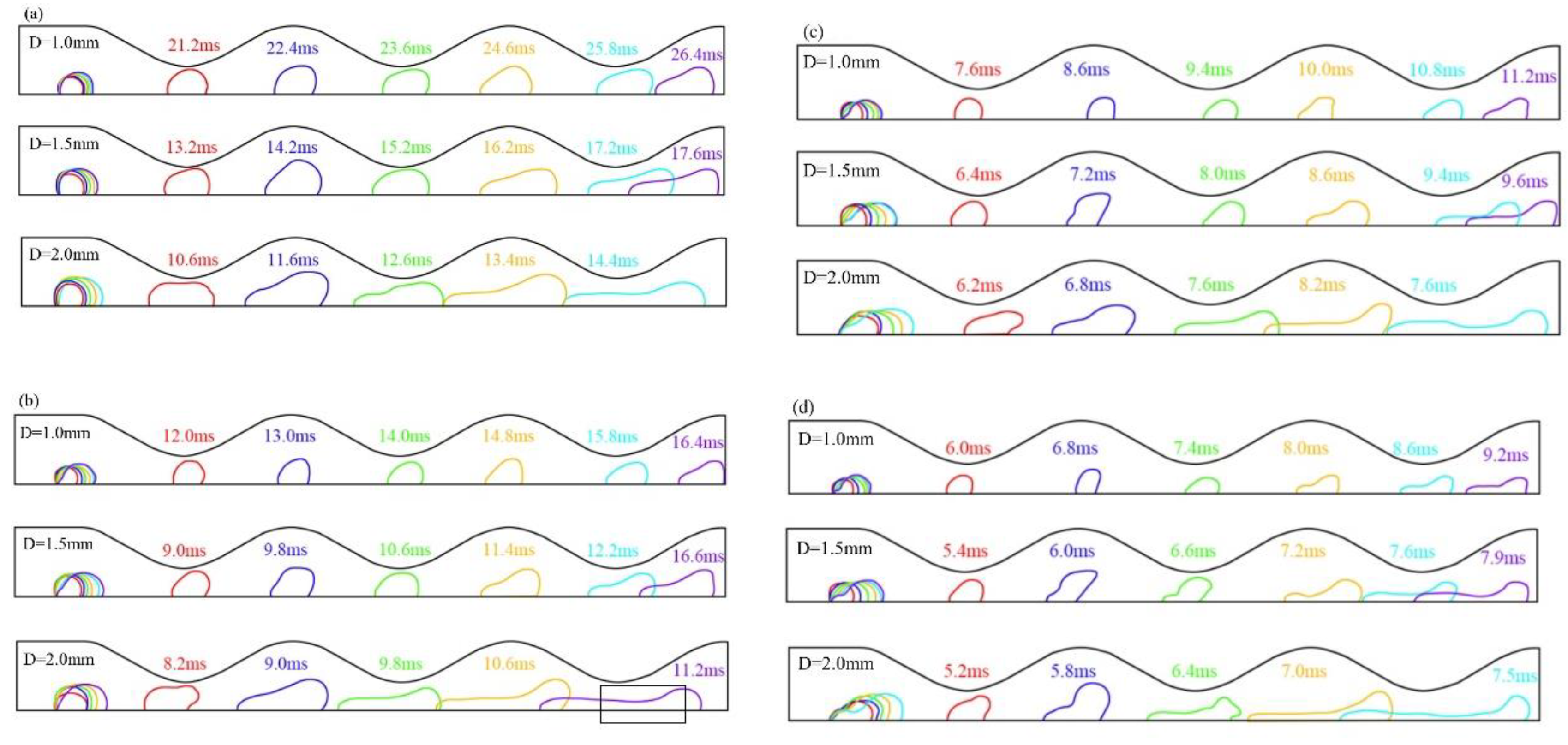
3.1. Dynamic behavior of droplets in 3D wave and 2D straight channels
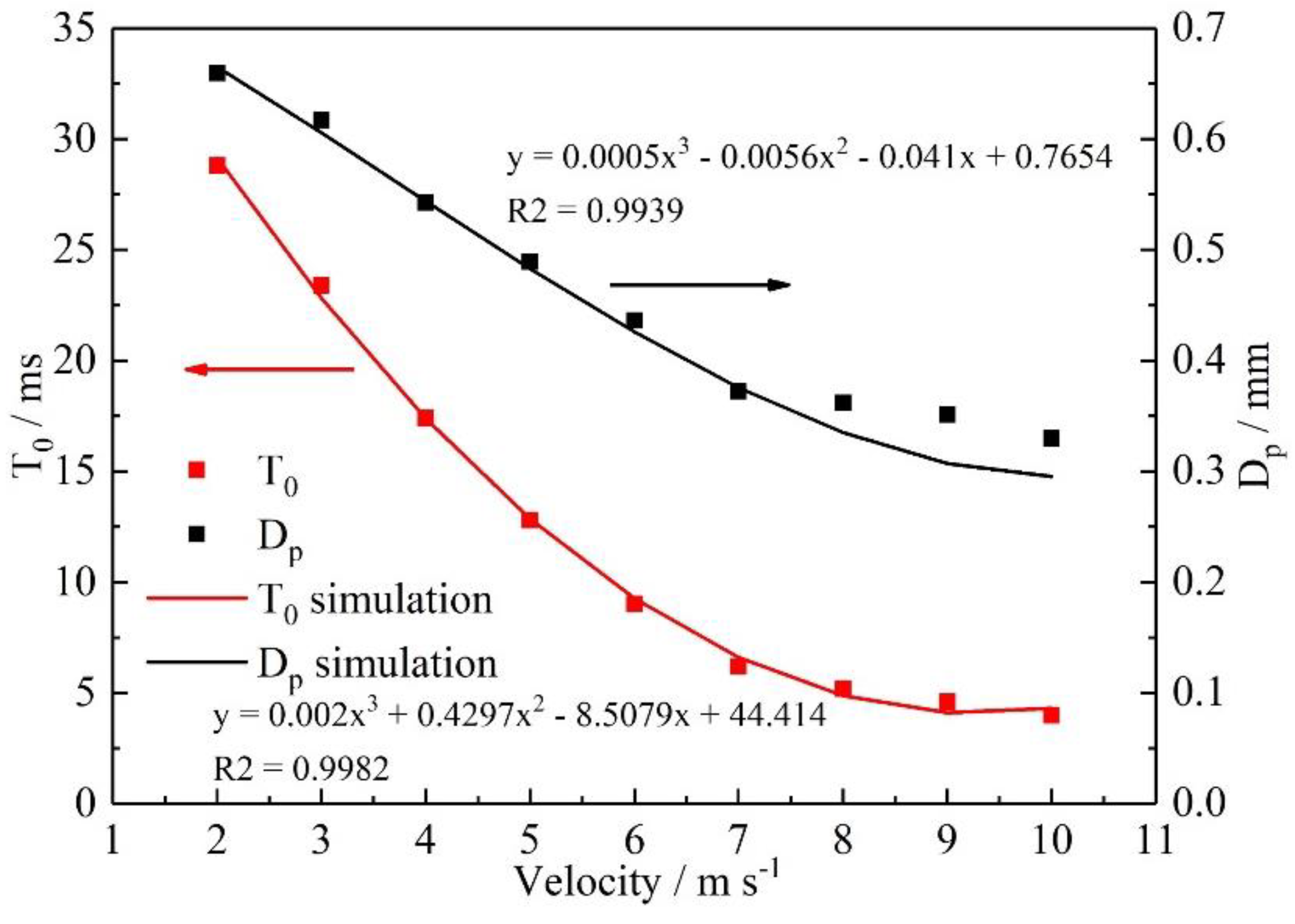
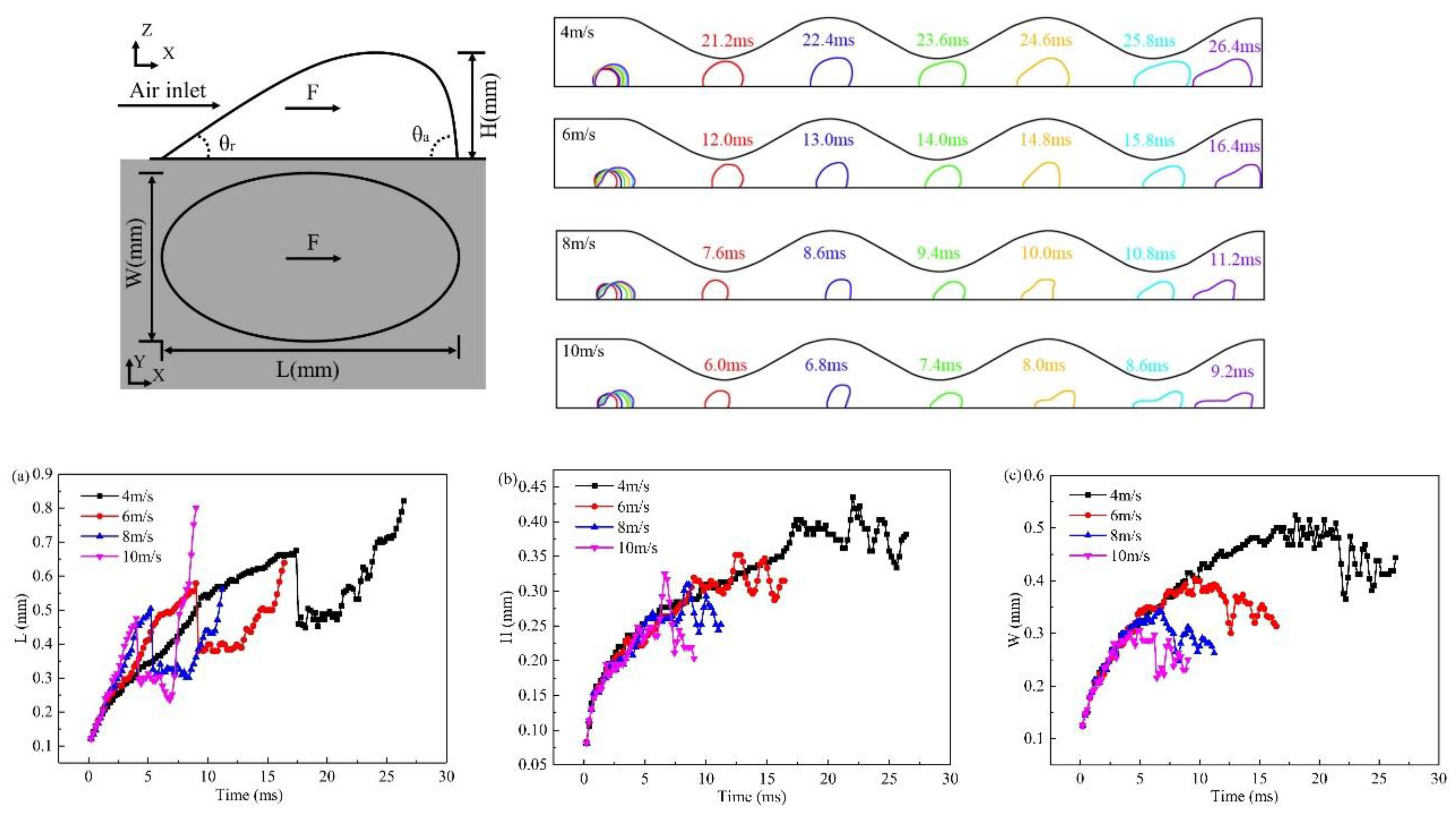
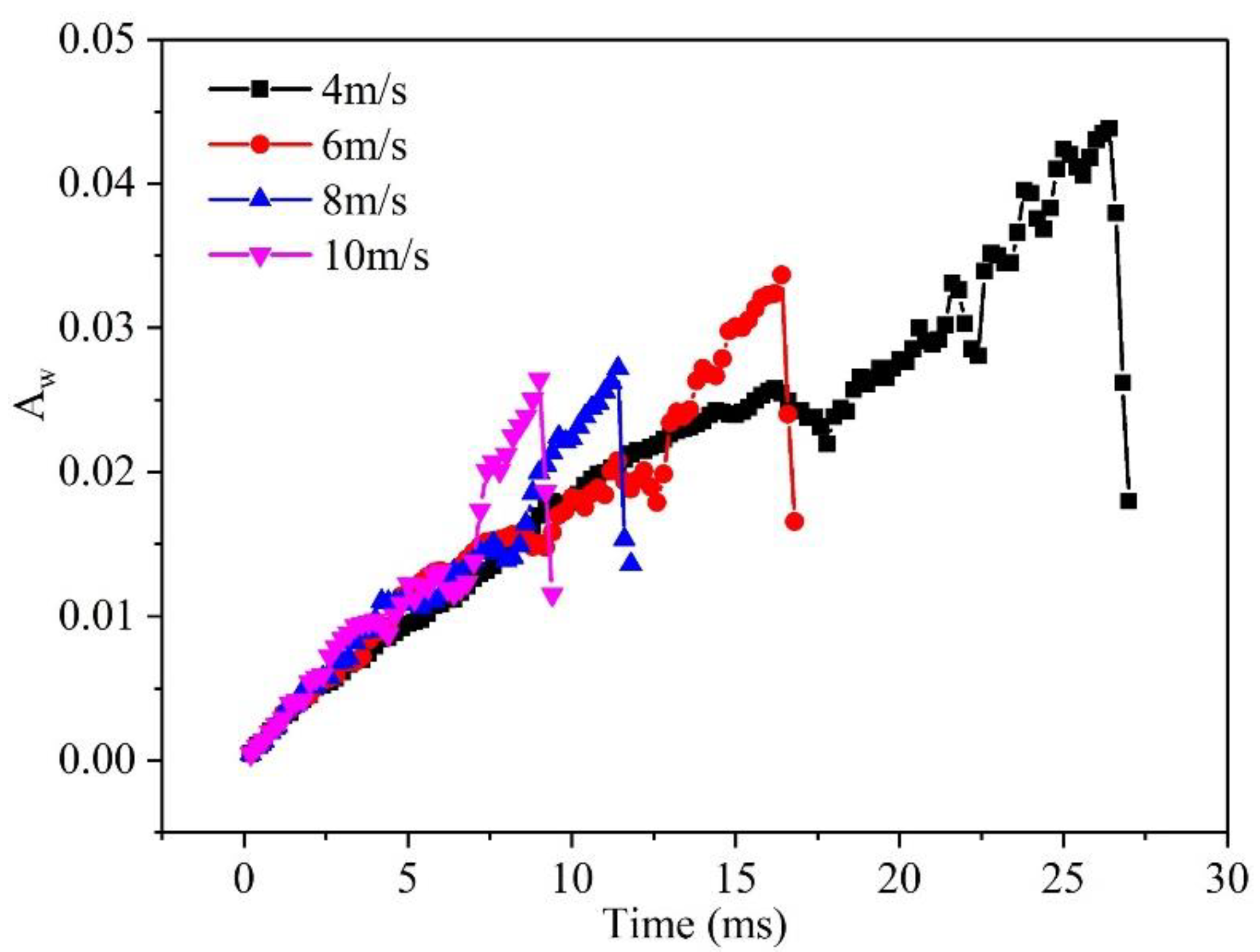
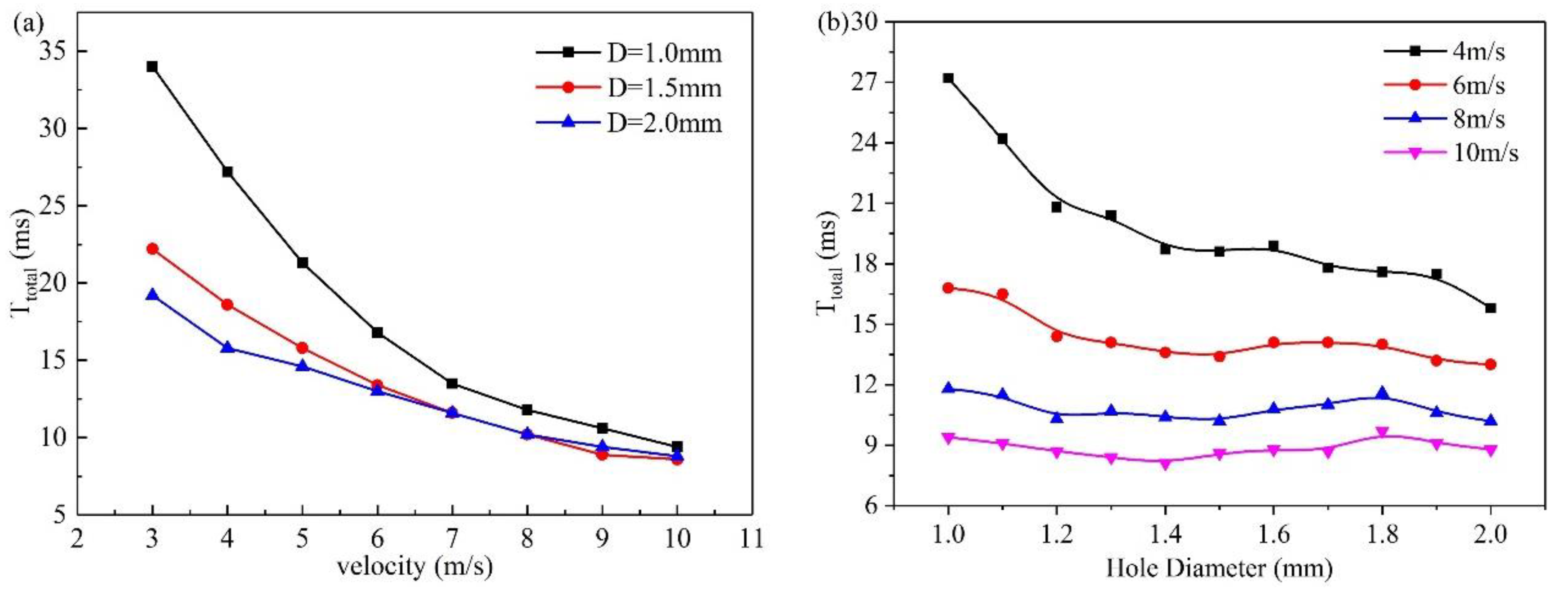
3.2. Effect of velocity on liquid water behavior in 3D channel
3.3. Effect of hole diameter of GDL on liquid water behavior in 3D channel
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Bhogilla, S.S.; Muthukumar, P. Thermal integration of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell with recuperative organic rankine cycle. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 14748–14756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasheminasab, M.; Kermani, M.J.; Nourazar, S.S.; Khodsiani, M.H. A novel experimental based statistical study for water management in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Appl. Energy 2020, 264, 114713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.W.; Zhang, W.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.X.; Ma, G.J. A systematic review for structure optimization and clamping load design of large proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack. J. Power Sources 2020, 476, 228724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Ou, M.; Xie, M.; Shao, H.; Yang, D.; Li, B.; Ming, P.; Zhang, C. Performance degradation and process engineering of the 10 kW proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack. Energy 2021, 219, 119623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, M.G.; Larsen, M.J.; Andersen, S.M. Andersen Improved durability of proton exchange membrane fuel cells by introducing Sn (IV) oxide into electrodes using an ion exchange method. J. Power Sources 2017, 343, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjari, M.; Khemili, F.; Ben Nasrallah, S. The effects of the cathode flooding on the transient responses of a PEM fuel cell. Renew. Energy 2008, 33, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nara, H.; Momma, T.; Osaka, T. Impedance analysis of the effect of flooding in the cathode catalyst layer of the polymer electrolyte fuel cell. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 113, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endoh, E.; Honmura, S.; Terazono, S.; Widjaja, H.; Takimoto, Y. Degradation study of MEA for PEMFCs under low humidity conditions. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2004, 7, A209–A211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, J.; Hayden, C.; Xie, T.; et al. Aspects of the chemical degradation of PFSA ionomers used in PEM fuel cells. Fuel Cell 2005, 5, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knights, S.D.; Colbow, K.M.; St-Pierre, J.; et al. Aging mechanisms and lifetime of PEFC and DMFC. J. Power Sources 2004, 127, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasheminasab, M.; Kermani, M.J.; Nourazar, S.S.; Khodsiani, M.H. A novel experimental based statistical study for water management in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Appl. Energy 2020, 264, 114713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.P.; Zhang, H.M.; Hu, J.; Cai, Y.H.; Yi, B.L. Diagnostic tool to detect liquid water removal in the cathode channels of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, H.; Ye, F.; Ma, C.F. Flow dynamic characteristics in flow field of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 1040–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bi, H.T.; Wilkinson, D.P.; Stumper, J.; Wang, H. Gas–liquid two-phase flow patterns in parallel channels for fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2008, 183, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Kandlikar, S.G.; Rath, C.; Grimm, M.; Domigan, W.; White, A.D.; Hardbarger, M.; Owejan, J.P.; Trabold, T.A. Water management studies in PEM fuel cells, Part II: Ex situ investigation of flow maldistribution, pressure drop and two-phase flow pattern in gas channels. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 3445–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-I.; Nam, J.H.; Shin, D.; Chung, T.-Y.; Kim, Y.-G. A numerical study on liquid water exhaust capabilities of flow channels in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Curr Appl Phys 2010, 10, S91–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvay, A.; French, J.; Wang, J.-C.; Peng, X.-H.; Kannan, A.M. Nature inspired flow field designs for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 3717–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, H.; Ma, C. Water flooding and two-phase flow in cathode channels of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2006, 156, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazylak, A.; Sinton, D.; Liu, Z.-S.; Djilali, N. Effect of compression on liquid water transport and microstructure of PEMFC gas diffusion layers. J. Power Sources 2007, 163, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasheminasab, M.; Kermani, M.J.; Nourazar, S.S.; Khodsiani, M.H. A novel experimental based statistical study for water management in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Appl. Energy 2020, 264, 114713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, M.J.; Kevrekidis, I.G.; Benziger, J.B. Water Slug Formation and Motion in Gas Flow Channels: The Effects of Geometry, Surface Wettability, And Gravity. Langmuir 2013, 29, 9918–9934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Pei, P.; Zha, H.; Xu, H. Water management of proton exchange membrane fuel cell based on control of hydrogen pressure drop. J. Power Sources 2014, 267, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Kim, H.-S.; Min, K. Transient response of a unit proton-exchange membrane fuel cell under various operating conditions. J. Power Sources 2008, 185, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Min, K. Experimental investigation of dynamic responses of a transparent PEM fuel cell to step changes in cell current density with operating temperature. J. Mech Sci Technol 2008, 22, 2274–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussaini, I.S.; Wang, C.-Y. Visualization and quantification of cathode channel flooding in PEM fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2009, 187, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, K.; Nakata, M.; Yodo, T.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Yamauchi, M.; Itoh, Y. Evaluation of a cathode gas channel with a water absorption layer/waste channel in a PEFC by using visualization technique. J. Power Sources 2005, 145, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. Experimental study on the two phase flow behavior in PEM fuel cell parallel channels with porous media inserts. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Yang, C.; Chen, Y.; Jin, C.; Ding, Y.; Li, W.; Wan, Z. Performance investigation on a novel 3D wave flow channel design for PEMFC. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 11127–11139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, N.; Mizuno, S.; Nakaji, H. Development of Compact and High-Performance Fuel Cell Stack. SAE Int. J. Alt. Power. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonobe, Y. Development of the Fuel Cell Vehicle Mirai. IEEJ Trans 2017, 12, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Sui, P.C.; Djilali, N. Dynamic behaviour of liquid water emerging from a GDL pore into a PEMFC gas flow channel. J. Power Sources 2007, 172, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Sui, P.C.; Djilali, N. Three-dimensional numerical simulations of water droplet dynamics in a PEMFC gas channel. J. Power Sources 2008, 181, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.D.; Zhou, B. Fundamental understanding of liquid water effects on the performance of a PEMFC with serpentine-parallel channels. Electrochim Acta 2009, 54, 2137–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manso, A.P.; Marzo, F.F.; Barranco, J.; Garikano, X.; Mujika, M.G. Influence of geometric parameters of the flow fields on the performance of a PEM fuel cell. A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 15256–15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Luo, G.; Wang, C.-Y. Modeling two-phase flow in three-dimensional complex flow-fields of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 365, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarian, A.; Kermani, M.J. Enhancement of PEM fuel cell performance by flow channel indentation. Energ Convers Manage 2016, 110, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Yan, X.; Shen, S.; Xia, G.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, J. Experimental and numerical analysis of a three-dimensional flow field for PEMFCs. Appl. Energy 2017, 195, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perng, S.-W.; Wu, H.-W. Heat transfer in a PEMFC flow channel. Appl Therm Eng 2009, 29, 3579–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, M.; Bosomoiu, M.; Tsotridis, G. Gas flow field with obstacles for PEM fuel cells at different operating conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 2303–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.K.; Yen, T.S.; Chen, C.K. Improvement of performance of gas flow channel in PEM fuel cells. Energ Convers Manage 2008, 49, 2776–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.-K.; Yen, T.-S.; Chen, C.-K. Three-dimensional numerical analysis of PEM fuel cells with straight and wave-like gas flow fields channels. J. Power Sources 2008, 177, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perng, S.-W.; Wu, H.-W. A three-dimensional numerical investigation of trapezoid baffles effect on non-isothermal reactant transport and cell net power in a PEMFC. Appl. Energy 2015, 143, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarian, A.; Kermani, M.J. Enhancement of PEM fuel cell performance by flow channel indentation. Energ Convers Manage 2016, 110, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, W.; Pan, F.; Wu, S.; Zhang, G.; Park, J.W.; Xie, B.; Yin, Y.; Jiao, K. A dot matrix and sloping baffle cathode flow field of proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2019, 434, 226741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, H.; Ye, F.; Ma, C.F. Baffle shape effects on mass transfer and power loss of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with different baffled flow channels. Int. J Energe Res 2019, 43, 2737–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Zhu, T.; Fan, Z.; Xie, X. Droplet dynamics in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell flow field design with 3D geometry. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 16693–16707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Yao, S.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Zhu, T.; Xie, X. Experimental and numerical study on improvement performance by wave parallel flow field in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 45, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-kharouf, A.; Mason, T.J.; Brett, D.J.L.; Pollet, B.G. Ex-situ characterisation of gas diffusion layers for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2012, 218, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenyuk, I.V.; Parkinson, D.Y.; Connolly, L.G.; Weber, A.Z. Gas-diffusion-layer structural properties under compression via X-ray tomography. J. Power Sources 2016, 328, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ous, T.; Arcoumanis, C. Visualisation of water droplets during the operation of PEM fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2007, 173, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ma, X.; Fei, L.; Zhang, X.; Luo, K.H.; Shuai, S. Effects of hysteresis window on contact angle hysteresis behaviour at large Bond number. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 566, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Fan, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, T.; Xie, X. Laser-perforated gas diffusion layer for promoting liquid water transport in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 29995–30003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



